Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2nd 9 Weeks Week 3
2nd 9 Weeks Week 3
Uploaded by
api-3497802040 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views2 pagesNatural selection is the mechanism of evolution where organisms with favorable traits that help them survive and reproduce pass those traits to offspring. Selective breeding is when humans breed other organisms like plants and animals for specific desirable traits. Adaptations are physical or behavioral characteristics that help organisms survive in their environment, like internal adaptations like hollow bones or gills, behavioral adaptations like migration or hibernation, and physiological adaptations like a camel's ability to concentrate urine.
Original Description:
Original Title
2nd 9 weeks week 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNatural selection is the mechanism of evolution where organisms with favorable traits that help them survive and reproduce pass those traits to offspring. Selective breeding is when humans breed other organisms like plants and animals for specific desirable traits. Adaptations are physical or behavioral characteristics that help organisms survive in their environment, like internal adaptations like hollow bones or gills, behavioral adaptations like migration or hibernation, and physiological adaptations like a camel's ability to concentrate urine.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views2 pages2nd 9 Weeks Week 3
2nd 9 Weeks Week 3
Uploaded by
api-349780204Natural selection is the mechanism of evolution where organisms with favorable traits that help them survive and reproduce pass those traits to offspring. Selective breeding is when humans breed other organisms like plants and animals for specific desirable traits. Adaptations are physical or behavioral characteristics that help organisms survive in their environment, like internal adaptations like hollow bones or gills, behavioral adaptations like migration or hibernation, and physiological adaptations like a camel's ability to concentrate urine.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
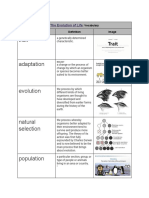
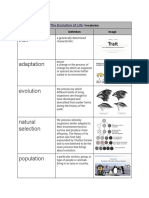
Natural selection Mechanism for change in populations;
occurs when organisms with favorable
variations survive, reproduce, and pass
their variations to the next generation.
Selective Breeding Selective breeding (also called artificial
selection) is the process by which
humans breed other animals and plants
for particular traits.
Internal Structure existing or situated within the limits or
surface of something: such asa (1) :
situated near the inside of the body
Adaptation An adaptation is something an organism
HAS or DOES to help it survive.
Internal Adaptation Internal Adaptions are adaptions that are
in the inside of a living organism. Ex.
Birds have hollow bones, Fish contain
Gills Xylem Supporting plant tissues that
help transport water and nutrients from
a plant's roots to its leaves
Behavioral Adaptation Evolution of a behavior that enables an
organism to respond to environmental
factors and live to produce offspring. Ex.
Migration and Hibernation
Physiology The study of internal and external
functions of living systems
Physiological Adaptation A metabolic or physiologic adjustment
within the cell, or tissues, of an organism
in response to an environmental
stimulus resulting in the improved ability
of that organism to cope with its
changing environment. For example, the
adaptation of horses' teeth to the
grinding of grass, or their ability to run
fast and escape predators. The camels
produce concentrated urine compared to
other mammals as it has to reduce the
water loss, this is a kind of physiological
adaptation as the kidney of camels are
designed in a such a way that the
wastage of water is minimum.
External adaptation An external adaptation is an adaptation
that is outside of your body. For example
Dark fur to blend into trees. An adaption
is what you adapt to so you live longer.
Migration Movement to a different geographical or
climate region where food is more
available
Hibernation A slowed physiological state of an
organism to survive long periods of cold
temperature or reduced food supplies
Variation A distinct feature, behavior or physiology
of the organism that occurs to
individuals within a population or species
Traits A characteristic that an organism can
pass on to its offspring through its
genes.
Species A group of organisms capable of
interbreeding and producing fertile
offspring.
Gills The paired respiratory organ of fishes
and some amphibians, by which oxygen
is extracted from water flowing over
surfaces within or attached to the walls
of the pharynx.
Bulb A short, modified, underground stem
surrounded by usually fleshy modified
leaves that contain stored food for the
shoot within: an onion bulb; a tulip bulb.
Asexual form of reproduction
Xylem Transports water from the roots
throughout the plant
Phloem Moves food from where it is made to
other parts of the plant
Hollow Having a hole or empty space inside
Surface Area The total area outside part or uppermost
layer of something
You might also like
- Reproductive - Systems - in - Vertebrates ss2Document12 pagesReproductive - Systems - in - Vertebrates ss2Ezeh Princess100% (1)
- Basic Science Lesson Notes 8 PDFDocument46 pagesBasic Science Lesson Notes 8 PDFRavineel KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Living AnimalDocument43 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Living AnimalLouella Artates67% (3)
- Spiral Dynamics Integral 1Document3 pagesSpiral Dynamics Integral 1Wangshosan100% (2)
- Chapter 1 Signal and SystemsDocument30 pagesChapter 1 Signal and SystemsJex DeyNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of LifeDocument19 pagesCharacteristics of LifeCrestfallen KunNo ratings yet
- Biology Key WordsDocument1 pageBiology Key WordsJun QiangNo ratings yet
- Adaptation IDocument37 pagesAdaptation IJeny StivaniNo ratings yet
- (Week 8) - AdaptationDocument5 pages(Week 8) - AdaptationNaiza AlamanNo ratings yet
- List of Biology - Zoology Terms and Definitions Flashcards - Easy NotecardsDocument42 pagesList of Biology - Zoology Terms and Definitions Flashcards - Easy NotecardsMubashir AmjadNo ratings yet
- Adaptation: Survival of The FittestDocument29 pagesAdaptation: Survival of The FittestDanielle ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Evolutionary AdaptationsDocument30 pagesEvolutionary Adaptationsapi-264004571100% (2)
- Q2 Lesson 2Document45 pagesQ2 Lesson 2mrfwbsttr9No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiologyDuaa GillaniNo ratings yet
- The Living World FullDocument20 pagesThe Living World Fullparul kaushalNo ratings yet
- Evolution Changes Over Time QuestionsDocument2 pagesEvolution Changes Over Time QuestionskanepatrickgNo ratings yet
- Adaptations: MammalsDocument2 pagesAdaptations: Mammalsdj9890935No ratings yet
- 20.ecology, Ecosystem and Functions of EcosystemDocument9 pages20.ecology, Ecosystem and Functions of Ecosystemsalihundamravikumar100No ratings yet
- Adaptive Value of Behavior: Teacher Notes and AnswersDocument4 pagesAdaptive Value of Behavior: Teacher Notes and AnswersFaiza FauziNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Processes of Animals and Plants: Biology IiDocument3 pagesMetabolic Processes of Animals and Plants: Biology IiKristal Pearl SindacNo ratings yet
- 7AP AdaptationsDocument20 pages7AP AdaptationsAnhar ElayyanNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Evolution GZ 2018 ChsDocument56 pagesGenetics and Evolution GZ 2018 ChsSayali PatilNo ratings yet
- Continuity of An Organism's LifeDocument31 pagesContinuity of An Organism's LifeNadia TaradhitaNo ratings yet
- Evolution Knowledge Organiser - 1Document2 pagesEvolution Knowledge Organiser - 1fiyanu9No ratings yet
- Group Project PresenatationDocument12 pagesGroup Project Presenatationdf7r5kmvjvNo ratings yet
- Pagbabasaat PagsusuriDocument3 pagesPagbabasaat PagsusuriRina EsquierraNo ratings yet
- Instructional Project 6 Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesInstructional Project 6 Lesson Planapi-322596215No ratings yet
- Adaptational TheoryDocument15 pagesAdaptational TheoryKrhyss John NotoNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument3 pagesScienceEdelyn UnayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 THEMES OF BIOLOGYDocument3 pagesLesson 5 THEMES OF BIOLOGYPocholo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Unifying Themes of Life ScienceDocument96 pagesUnifying Themes of Life ScienceWycleaf Geffin GalulaNo ratings yet
- Animal AdaptationDocument3 pagesAnimal AdaptationRaymond AguilarNo ratings yet
- Rction PperDocument2 pagesRction PperjayNo ratings yet
- Evolution and EcologyDocument6 pagesEvolution and EcologyJoenetha Ann ApariciNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Zoology As Part of BiologyDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Zoology As Part of Biologygel cayunaNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Ecology Lecture ActivityDocument8 pagesEvolution and Ecology Lecture ActivitychristeldutosmeNo ratings yet
- KS3 Biology KeyDocument8 pagesKS3 Biology KeyFIKRIYE ONDEROLNo ratings yet
- Adaptations and SpeciationDocument47 pagesAdaptations and SpeciationAndre AzevedoNo ratings yet
- Understanding RepDocument1 pageUnderstanding RepCyra BantilloNo ratings yet
- Animal Adaptations 1Document9 pagesAnimal Adaptations 1samson aslamNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Yr7Document3 pagesBiology Notes Yr7kevinNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Processes of Animals and Plants: Biology IiDocument3 pagesMetabolic Processes of Animals and Plants: Biology IiKristal Pearl SindacNo ratings yet
- Brandon de Arcos - The Evolution of Life VocabularyDocument2 pagesBrandon de Arcos - The Evolution of Life Vocabularyapi-451865174No ratings yet
- Brandon de Arcos - The Evolution of Life VocabularyDocument2 pagesBrandon de Arcos - The Evolution of Life Vocabularyapi-451865174No ratings yet
- 13 Ecosystem1Document9 pages13 Ecosystem1salihundamravikumar100No ratings yet
- Basic Biology: 1. Cellular StructureDocument3 pagesBasic Biology: 1. Cellular StructureAbhay VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Evolution - Review Concepts - PPTDocument22 pagesEvolution - Review Concepts - PPTayaandatoo89No ratings yet
- WEEK2 ModuleLec (BIO101)Document9 pagesWEEK2 ModuleLec (BIO101)Maricris GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Part 2Document3 pagesTheory of Evolution by Natural Selection Part 2tileshadowNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument90 pagesCharacteristics of Living Thingsaisah isnaeniNo ratings yet
- Vision of Al Nahda National School Everyone Engages, Everyone Learns, Everyone ReflectsDocument29 pagesVision of Al Nahda National School Everyone Engages, Everyone Learns, Everyone ReflectsSalma DAGAMSEHNo ratings yet
- Niche and AdaptationsDocument10 pagesNiche and AdaptationsKumaran JothiramNo ratings yet
- Science Notebook CharOfLifeMSDocument1 pageScience Notebook CharOfLifeMSMuhammad Amin SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Adaptation and Evolution PowerpointDocument64 pagesAdaptation and Evolution Powerpointapi-263357086No ratings yet
- Week 3 Evolution BiodiversityDocument24 pagesWeek 3 Evolution BiodiversityKassandra Cassiopeia MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Life ScienceDocument16 pagesLife ScienceJNo ratings yet
- ExcerptDocument10 pagesExcerptAlifah RizkaNo ratings yet
- Living WorldDocument24 pagesLiving Worldsaifali986254No ratings yet
- 12 Biology Notes ch13 Organisms and Populations PDFDocument10 pages12 Biology Notes ch13 Organisms and Populations PDFYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- 6 Life Processes NotesDocument7 pages6 Life Processes NotesBurhaan MalikNo ratings yet
- Animal Adaptations IDocument8 pagesAnimal Adaptations IPheby Alfimay Natysya PutriNo ratings yet
- ReviwerDocument1 pageReviwerBitancor JemimaNo ratings yet
- Aqualisa Quartz Simply A Better ShowerDocument12 pagesAqualisa Quartz Simply A Better ShowerPranjal SinghNo ratings yet
- OTC-24958 MEIDP Owen Fracture Zone CrossingDocument16 pagesOTC-24958 MEIDP Owen Fracture Zone CrossingFrds123No ratings yet
- MSDS Diamond Paste (Metprep)Document3 pagesMSDS Diamond Paste (Metprep)Claudia MmsNo ratings yet
- Stokes Second Problem by Laplace TransformDocument19 pagesStokes Second Problem by Laplace TransformSidra AfzalNo ratings yet
- Changes From Rev AK To Rev AL Skyview Installation GuideDocument608 pagesChanges From Rev AK To Rev AL Skyview Installation GuideF BakımNo ratings yet
- What Is Pure Substance?: Pure Substances Are Substances That Are Made Up of Only One Kind ofDocument3 pagesWhat Is Pure Substance?: Pure Substances Are Substances That Are Made Up of Only One Kind ofNi Made FebrianiNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Salt (Worksheet)Document11 pagesPreparation of Salt (Worksheet)terencechen1225No ratings yet
- Material History Record: Ogsp Cutter Process Solutions India Private LimitedDocument5 pagesMaterial History Record: Ogsp Cutter Process Solutions India Private LimitedSumit SinghNo ratings yet
- Talent Level 3 IGCSE Keys and ScriptsDocument2 pagesTalent Level 3 IGCSE Keys and ScriptsLUISA CASTRO CUNEONo ratings yet
- Analyser Shelter ATEC Italy - WWW - AtecsrlDocument3 pagesAnalyser Shelter ATEC Italy - WWW - AtecsrlMalyshAVNo ratings yet
- Medibuddy-EnrolPolicyConditions 22Document23 pagesMedibuddy-EnrolPolicyConditions 22Vadivelan BaskarNo ratings yet
- Lesley Nair Thematic Summary of All You ZombiesDocument3 pagesLesley Nair Thematic Summary of All You Zombiesnair1904No ratings yet
- Preventing Misuse of Medicines DR - Marwa Salih Al-NaimiDocument12 pagesPreventing Misuse of Medicines DR - Marwa Salih Al-NaimiMustafa MuayedNo ratings yet
- Medicines Control Authority of ZimbabweDocument38 pagesMedicines Control Authority of ZimbabweBK RegulatoryNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.ieltsDocument11 pagesUnit 2.ieltsKarina HrishkovskaNo ratings yet
- Greenboro Polychem PVT LTDDocument57 pagesGreenboro Polychem PVT LTDMehdi MadaniNo ratings yet
- TP-Link WiFi 6E AXE5400 PCIe WiFi Card - User GuideDocument23 pagesTP-Link WiFi 6E AXE5400 PCIe WiFi Card - User GuidehelpfulNo ratings yet
- The Tangents Drawn at The Ends ofDocument6 pagesThe Tangents Drawn at The Ends ofpjojibabu100% (2)
- Important Intial McqsDocument34 pagesImportant Intial Mcqslover boyNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning EbookDocument63 pagesMachine Learning EbookGhost Rider100% (1)
- BO0008 - Kixx LUBO 150BS - EngDocument9 pagesBO0008 - Kixx LUBO 150BS - EngkokoNo ratings yet
- Daily ReportDocument3 pagesDaily ReportJoseph AbousafiNo ratings yet
- 011CMEDDocument13 pages011CMEDphilip xeroNo ratings yet
- A Survey of One of The Most Important Pressure Pipe CodesDocument3 pagesA Survey of One of The Most Important Pressure Pipe CodesnerioalfonsoNo ratings yet
- Arduino Earthquake CodeDocument3 pagesArduino Earthquake Codekimchen edenelleNo ratings yet
- Control Electrical Appliances Using PCDocument46 pagesControl Electrical Appliances Using PCsumit gandhi100% (1)
- Smudge Cells:: What Technologists Need To KnowDocument5 pagesSmudge Cells:: What Technologists Need To KnowdewaNo ratings yet