Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2: Matter: Temperature, C
Chapter 2: Matter: Temperature, C
Uploaded by
teoh6234Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2: Matter: Temperature, C
Chapter 2: Matter: Temperature, C
Uploaded by
teoh6234Copyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 2: MATTER
1. To determine melting point
Heating Cooling
Water bath to ensure uniform heating
Plot graph y axis (Start at 50 o C).
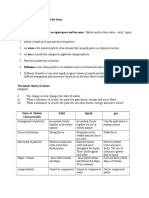
2. The kinetic theory of matter (solid, solid liquid, liquid, liquid-gas, gas)
Matter is made up of tiny and discrete particles (atoms, ions or molecules), there is space between these
particles.
a) arrangement of particles-pack closely together, orderly arrangement, far apart from each other
b) Movement of particles-vibrates, rotate, slowly, rapidly, vigorously, randomly.
c) kinetic energy content-
d) change in energy content-
e) force of attraction-strong, weak, weaker
Temperature,oC
Boiling point
Time, s
to t1 t2 t3
Example:
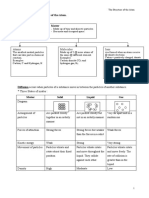
Graph shows the heating curve of element X.
Describe the graph in terms of states of matter, particle arrangements and changes in energy.
Sample answer:
Stage State of matter Particles arrangement Changes in energy
to t1 Liquid The particles are close to each other. The kinetic energy increases
The particles arrangement is not orderly.
t1 - t 2 Liquid Some of particles are close to each other The kinetic energy is constant
gaseous and some far apart.
The particles arrangement is not orderly.
t2 t3 Gaseous The particles are far away from each other. The kinetic energy increases
The particles arrangement is not orderly.
3. Diffusion the movement of particles (atom/ions/molecule) of substance in between the particles of
another substance / from highly concentrated area to less concentrated area. Gas > liquid > solid
4. Isotope are atoms of the same element (same number of proton) with different number of
neutrons/nucleon number.
You might also like
- StatisticalPhysics Part1 HandoutDocument27 pagesStatisticalPhysics Part1 HandoutMauro LaraNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The AtomDocument57 pagesThe Structure of The AtomGranville RegalarioNo ratings yet
- Matter Unit NotesDocument7 pagesMatter Unit NotesAnonpcNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science1Document6 pagesReviewer in Science1Cailin Loraine VibarNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument57 pagesStructure of Atomnurulakmal mohd kamalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Structure of The Atom.: Atoms Molecules IonsDocument9 pagesChapter 2: The Structure of The Atom.: Atoms Molecules Ionschiet pingNo ratings yet
- KMT Notes and WSDocument7 pagesKMT Notes and WSangie432meNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry 2017: AnswersDocument4 pagesSPM Chemistry 2017: AnswersLam Kah Lam KahNo ratings yet
- Lect 1Document43 pagesLect 1Prateek DasNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Thermal Physics CIEDocument27 pagesUnit 2 Thermal Physics CIEShrirang ChandankhedeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 A NotesDocument67 pagesChemistry Form 4 A NotesJia En TanNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science Chapter 5 NotesDocument7 pagesGrade 7 Science Chapter 5 NotesTajiriMollelNo ratings yet
- Notes Chem Enely 1Document11 pagesNotes Chem Enely 1rickyNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 2 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMDocument11 pagesCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 2 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMJay Bee83% (29)
- Chapter 4: Matter and SubstanceDocument8 pagesChapter 4: Matter and SubstanceAzrina Mat JaliNo ratings yet
- Structure of MatterDocument54 pagesStructure of MatterMustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasDocument5 pagesKinetic Theory of Gasbenazeerbeevi9No ratings yet
- 2.1 Matter: 1 Chapter 2: The Structure of The AtomDocument6 pages2.1 Matter: 1 Chapter 2: The Structure of The AtomThaatchayani MuralleNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2 Structure of AtomDocument23 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2 Structure of AtomTan YLunNo ratings yet
- 2A The Structure of The Atom-AnswerDocument6 pages2A The Structure of The Atom-AnswerjohnyeapNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chap 1 To 10 ReviewDocument4 pagesChemistry Chap 1 To 10 Reviewlev_445777659No ratings yet
- IB Phyiscs Final RevisionDocument2 pagesIB Phyiscs Final Revisionjungwoohan72No ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry FaderuDocument76 pagesPhysical Chemistry FaderumikinaniNo ratings yet
- Physics Topic 3 Study GuideDocument5 pagesPhysics Topic 3 Study GuideSai 0235No ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of ParticlesDocument14 pagesKinetic Theory of ParticlesMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- Materials Science and Engineering IDocument33 pagesMaterials Science and Engineering IJose MussanoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 PhysicsDocument245 pagesModule 2 PhysicsEmre ÖzerNo ratings yet
- CHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0101 AkDocument4 pagesCHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0101 AkKyla Dave LiganNo ratings yet
- 2A The Structure of The Atom-AnswerDocument6 pages2A The Structure of The Atom-AnswerSiti Nursahidah0% (1)
- Delivery SystemsDocument28 pagesDelivery SystemscNo ratings yet
- Temperature C: Structure of AtomDocument6 pagesTemperature C: Structure of AtomAnonymous 7NBHZUtQBcNo ratings yet
- Thermal PropertiesDocument6 pagesThermal PropertiesMordecai ChimedzaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Atomic BondingDocument34 pagesStructure and Atomic BondingGjgfgNo ratings yet
- Third Form Packet WorkDocument19 pagesThird Form Packet WorkLizbeth Chi100% (1)
- Note ChemDocument28 pagesNote ChemHoàng Kim LongNo ratings yet
- Matter and Substances.: 4.1 Changes in The States of Matter. Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument15 pagesMatter and Substances.: 4.1 Changes in The States of Matter. Kinetic Theory of MatterElly EllynaNo ratings yet
- PHY111A 1.1.1 - Kinetic Particle Model PDFDocument28 pagesPHY111A 1.1.1 - Kinetic Particle Model PDFanton petrovNo ratings yet
- Cell Practise: 1 Day 1 Main Points To Revise: Key Terms: Term DefinitionDocument3 pagesCell Practise: 1 Day 1 Main Points To Revise: Key Terms: Term DefinitionDony GregorNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument15 pagesChemistryREGALA XENIANo ratings yet
- Reviewer (Gen Science)Document3 pagesReviewer (Gen Science)Sophia LantinNo ratings yet
- A. GED Science (Chemistry)Document43 pagesA. GED Science (Chemistry)May Zin PhyoNo ratings yet
- Key Words: Apparatus For Measuring The Amount of Heat Involved in A Chemical ReactionDocument2 pagesKey Words: Apparatus For Measuring The Amount of Heat Involved in A Chemical ReactionChutimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Structure of The Atom A MatterDocument9 pagesChapter 2: The Structure of The Atom A MatterMSKNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 MatterDocument47 pagesTopic 1 MatterAidah HanidaNo ratings yet
- Thermal PhysicsDocument19 pagesThermal PhysicsMaya SinghNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY NOTES Class 9 CBSEDocument13 pagesCHEMISTRY NOTES Class 9 CBSERamRakh YadavNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Topic 3 Particle Model of Matter Knowledge OrganiserDocument3 pagesAQA Physics Topic 3 Particle Model of Matter Knowledge OrganiserGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- G10 Science Q4 - Week 2 - Molecular Kinetic TheoryDocument24 pagesG10 Science Q4 - Week 2 - Molecular Kinetic TheoryMelissa Ganituen-BautistaNo ratings yet
- Medical PhysicsDocument371 pagesMedical PhysicsAhmed khanNo ratings yet
- B Thermal PhysicsDocument16 pagesB Thermal PhysicsTravis TeohNo ratings yet
- 1 - Nature of Matter and Chemical ChangeDocument6 pages1 - Nature of Matter and Chemical ChangeSagi IbiNo ratings yet
- Intramolecular Forces (Chemical Bonding) : Ionic BondDocument27 pagesIntramolecular Forces (Chemical Bonding) : Ionic BondVince ShaneNo ratings yet
- Rebyuwer Sa Asignaturang AghamDocument5 pagesRebyuwer Sa Asignaturang AghamjoshuaNo ratings yet
- 403 ThermalDocument31 pages403 ThermalranaNo ratings yet
- Cie Igcse Physics Chapter 2 2023 OnwDocument10 pagesCie Igcse Physics Chapter 2 2023 OnwZeinab ElkholyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 2: Subatomic Particle Symbol Relative Mass Relative Electric ChargeDocument2 pagesChemistry Chapter 2: Subatomic Particle Symbol Relative Mass Relative Electric ChargestevetehNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy.Document7 pagesThermal Energy.romaehab201912No ratings yet
- Waja Chemistry The Structure of The AtomDocument8 pagesWaja Chemistry The Structure of The AtomChewfun KhooNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Intensive Revision SP 2019 NEWESTDocument1 pageIntensive Revision SP 2019 NEWESTteoh6234No ratings yet
- Solubility Equilibria: End of Chapter 16Document8 pagesSolubility Equilibria: End of Chapter 16teoh6234No ratings yet
- Ch39 Periodic Relationship Among The OxidesDocument69 pagesCh39 Periodic Relationship Among The Oxidesteoh6234No ratings yet
- STPM Trial 2012 Chemistry Qa KelantanDocument42 pagesSTPM Trial 2012 Chemistry Qa Kelantanteoh6234100% (2)
- A Sample of M Oxide Contains 2.7 G of Element X and 2.4 G of Oxygen. What Is The Empirical Formula of This Compound? (Relative Atomic Mass: X 27, O 16)Document1 pageA Sample of M Oxide Contains 2.7 G of Element X and 2.4 G of Oxygen. What Is The Empirical Formula of This Compound? (Relative Atomic Mass: X 27, O 16)teoh6234No ratings yet
- Calculation of Relative Molecular MassDocument1 pageCalculation of Relative Molecular Massteoh6234No ratings yet
- New AccountDocument1 pageNew Accountteoh6234No ratings yet
- Date:: Private Retirement Scheme Account Detai LSDocument1 pageDate:: Private Retirement Scheme Account Detai LSteoh6234No ratings yet