Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jam
Jam
Uploaded by
Vaddi Meher0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Jam.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesJam
Jam
Uploaded by
Vaddi MeherCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
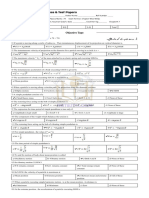
Syllabus - Physics (PH)
Physics
Mathematical Methods: Calculus of single and multiple variables, partial
derivatives, Jacobian, imperfect and perfect differentials, Taylor expansion, Fourier
series. Vector algebra, Vector Calculus, Multiple integrals, Divergence theorem,
Greens theorem, Stokes theorem. First order equations and linear second order
differential equations with constant coefficients. Matrices and determinants, Algebra
of complex numbers.
Mechanics and General Properties of Matter: Newtons laws of motion and
applications, Velocity and acceleration in Cartesian, polar and cylindrical coordinate
systems, uniformly rotating frame, centrifugal and Coriolis forces, Motion under a
central force, Keplers laws, Gravitational Law and field, Conservative and non-
conservative forces. System of particles, Center of mass, equation of motion of the
CM, conservation of linear and angular momentum, conservation of energy, variable
mass systems. Elastic and inelastic collisions. Rigid body motion, fixed axis
rotations, rotation and translation, moments of Inertia and products of Inertia,
parallel and perpendicular axes theorem. Principal moments and axes. Kinematics
of moving fluids, equation of continuity, Eulers equation, Bernoullis theorem.
Oscillations, Waves and Optics: Differential equation for simple harmonic
oscillator and its general solution. Superposition of two or more simple harmonic
oscillators. Lissajous figures. Damped and forced oscillators, resonance. Wave
equation, traveling and standing waves in one-dimension. Energy density and
energy transmission in waves. Group velocity and phase velocity. Sound waves in
media. Doppler Effect. Fermats Principle. General theory of image formation. Thick
lens, thin lens and lens combinations. Interference of light, optical path retardation.
Fraunhofer diffraction. Rayleigh criterion and resolving power. Diffraction gratings.
Polarization: linear, circular and elliptic polarization. Double refraction and optical
rotation.
Electricity and Magnetism: Coulombs law, Gausss law. Electric field and
potential. Electrostatic boundary conditions, Solution of Laplaces equation for
simple cases. Conductors, capacitors, dielectrics, dielectric polarization, volume and
surface charges, electrostatic energy. Biot-Savart law, Amperes law, Faradays law
of electromagnetic induction, Self and mutual inductance. Alternating currents.
Simple DC and AC circuits with R, L and C components. Displacement current,
Maxwells equations and plane electromagnetic waves, Poyntings theorem,
reflection and refraction at a dielectric interface, transmission and reflection
coefficients (normal incidence only). Lorentz Force and motion of charged particles
in electric and magnetic fields.
Kinetic theory, Thermodynamics: Elements of Kinetic theory of gases. Velocity
distribution and Equipartition of energy. Specific heat of Mono-, di- and tri-atomic
gases. Ideal gas, van-der-Waals gas and equation of state. Mean free path. Laws of
thermodynamics. Zeroth law and concept of thermal equilibrium. First law and its
consequences. Isothermal and adiabatic processes. Reversible, irreversible and
quasi-static processes. Second law and entropy. Carnot cycle. Maxwells
thermodynamic relations and simple applications. Thermodynamic potentials and
their applications. Phase transitions and Clausius-Clapeyron equation. Ideas of
ensembles, Maxwell-Boltzmann, Fermi-Dirac and Bose-Einstein distributions.
Modern Physics: Inertial frames and Galilean invariance. Postulates of special
relativity. Lorentz transformations. Length contraction, time dilation. Relativistic
velocity addition theorem, mass energy equivalence. Blackbody radiation,
photoelectric effect, Compton effect, Bohrs atomic model, X-rays. Wave-particle
duality, Uncertainty principle, the superposition principle, calculation of expectation
values, Schrdinger equation and its solution for one, two and three dimensional
boxes. Solution of Schrdinger equation for the one dimensional harmonic oscillator.
Reflection and transmission at a step potential, Pauli exclusion principle. Structure
of atomic nucleus, mass and binding energy. Radioactivity and its applications. Laws
of radioactive decay.
Solid State Physics, Devices and Electronics: Crystal structure, Bravais lattices
and basis. Miller indices. X-ray diffraction and Bragg's law; Intrinsic and extrinsic
semiconductors, variation of resistivity with temperature. Fermi level. p-n junction
diode, I-V characteristics, Zener diode and its applications, BJT: characteristics in CB,
CE, CC modes. Single stage amplifier, two stage R-C coupled amplifiers. Simple
Oscillators: Barkhausen condition, sinusoidal oscillators. OPAMP and applications:
Inverting and non-inverting amplifier. Boolean algebra: Binary number systems;
conversion from one system to another system; binary addition and subtraction.
Logic Gates AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR exclusive OR; Truth tables; combination of
gates; de Morgans theorem.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- B.SC Physics Syllabus (Semester Wise) 2015Document65 pagesB.SC Physics Syllabus (Semester Wise) 2015Waaiz MohammedNo ratings yet
- Semester - IVDocument3 pagesSemester - IVWaaiz MohammedNo ratings yet
- Semester - IIIDocument6 pagesSemester - IIIWaaiz MohammedNo ratings yet
- M.SC PhysicsDocument19 pagesM.SC PhysicsWaaiz MohammedNo ratings yet
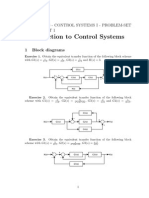
- Comparative Studies of Model Reference Adaptive Control SystemsDocument10 pagesComparative Studies of Model Reference Adaptive Control SystemsAmir AmkaNo ratings yet
- Physics Module Form 5 GCKL 2010Document29 pagesPhysics Module Form 5 GCKL 2010Jo Ey Goh75% (4)
- Satellite Design Course Spacecraft Configuration Structural Design Preliminary Design MethodsDocument85 pagesSatellite Design Course Spacecraft Configuration Structural Design Preliminary Design Methodsmegustalazorra100% (1)
- (Ebook Audio-Acoustics-Hifi Diy) Push-Pull Electrostatic Speaker Model Theory (By Shackman De)Document20 pages(Ebook Audio-Acoustics-Hifi Diy) Push-Pull Electrostatic Speaker Model Theory (By Shackman De)marcosNo ratings yet
- Mechanical-Shock Fragility of Products, Using Shock MachinesDocument8 pagesMechanical-Shock Fragility of Products, Using Shock MachinesAlevj Db0% (1)
- Solidworks SimulationDocument50 pagesSolidworks SimulationMark Chester KaraanNo ratings yet
- Lab DM6 Spring Mass System 2Document11 pagesLab DM6 Spring Mass System 2peng_pek92No ratings yet
- SDOF DynamicsDocument92 pagesSDOF DynamicsRonnie1478No ratings yet
- Spring Mass Experiment Student SheetDocument8 pagesSpring Mass Experiment Student SheetThảo Hà NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Noise Control in Textile MachineriesDocument40 pagesNoise Control in Textile MachineriesJagannath SardarNo ratings yet
- Solved MCQsDocument4 pagesSolved MCQsAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document6 pagesProblem Set 1Hector InbacuanNo ratings yet
- Waves & Vibrations All Quizzes and Midterm Answers - UpdatedDocument5 pagesWaves & Vibrations All Quizzes and Midterm Answers - UpdatedSara KhNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Transport Barge Nonlinear Roll Motions in A Seaway Using An Equivalent Linearization Procedure PDFDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Transport Barge Nonlinear Roll Motions in A Seaway Using An Equivalent Linearization Procedure PDFYao WeiNo ratings yet
- 1803Document254 pages1803dinhanhminhqtNo ratings yet
- Blevins 3Document9 pagesBlevins 3paulomarcalNo ratings yet
- 364 Pulp PDFDocument133 pages364 Pulp PDFਕੁਮਾਰ ਸੰਜੀਵNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory 2-MarksDocument16 pagesCircuit Theory 2-MarksJagadish Babu KondraguntaNo ratings yet
- Forced Vibration of Two Degrees of Freedom SystemDocument4 pagesForced Vibration of Two Degrees of Freedom Systemsethu sharanyaNo ratings yet
- 2 Motion Of A Simple Pendulum: θ mg tangent LDocument8 pages2 Motion Of A Simple Pendulum: θ mg tangent LLulu TojeenNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics WorksheetsDocument31 pages11 Physics WorksheetssbatrabatraNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines 1Document62 pagesTheory of Machines 1Jatin prasad TandanNo ratings yet
- Marchi Friction PaperDocument201 pagesMarchi Friction PaperRoger Lahoud100% (1)
- PRE BOARD EXAM (2021), PHYSICS XI (Chapter 7+9)Document3 pagesPRE BOARD EXAM (2021), PHYSICS XI (Chapter 7+9)Ghulam FaridNo ratings yet
- Labsheet Translation Mechanical SystemDocument33 pagesLabsheet Translation Mechanical SystemMuhammad Ehsan Abdul Halim0% (1)
- Dynamics of Machinery Question PapersDocument22 pagesDynamics of Machinery Question PapersMohan Babu S0% (1)
- Part 02 - Support Motion - TransmissibilityDocument14 pagesPart 02 - Support Motion - Transmissibilitymacynthia26No ratings yet
- CE 463.3 - Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 5 -SAP2000 Dynamic Analysis and P-Δ effectDocument16 pagesCE 463.3 - Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 5 -SAP2000 Dynamic Analysis and P-Δ effectHumberto Guerrero RojoNo ratings yet
- Damped Oscillations and Mechanical Waves: General Physics 1: Grade 12Document10 pagesDamped Oscillations and Mechanical Waves: General Physics 1: Grade 12jessNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mian Ashfaq Ali: Mechanical Vibrations ME-421Document13 pagesDr. Mian Ashfaq Ali: Mechanical Vibrations ME-421Talha MohsinNo ratings yet