Professional Documents
Culture Documents
State Court Organization 1998
State Court Organization 1998
Uploaded by
losangelesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
State Court Organization 1998
State Court Organization 1998
Uploaded by
losangelesCopyright:
Available Formats
U.S.
Department of Justice
Office of Justice Programs
Bureau of Justice Statistics
State Court Organization
1998
Victim-offender relationship in violent crimes
(rape/sexual assault, robbery, and assault) by sex of victim
Courts and judges
Judicial selection and service
Judicial branch
Appellate courts
Trial courts
The jury
The sentencing context
Court structure
Part I: Courts and judges
Coming to grips with the number and variety of courts is found in Alabama (Court of Civil Appeals), Alaska,
the essential starting point for anyone interested in court Hawaii, and Idaho.
organization. The fundamental distinction is between
trial courts, which are courts of first instance that decide Trial courts are listed state by state in Table 3,
a dispute by examining the facts, and appellate courts, distinguishing between courts of general jurisdiction (GJ)
which review the trial court’s application of law to those and courts of limited (or special) jurisdiction (LJ).
facts. General jurisdiction trial courts are always the highest
trial court in a state where felony criminal cases and high
How many appellate courts have been established in the stakes civil suits are adjudicated. They often exercise
United States? Table 1 provides the answer. There are some form of appellate review over outcomes in limited
two basic kinds of appellate courts. Courts of last resort jurisdiction courts or decisions by administrative
(COLR) have final jurisdiction over appeals. Each state agencies, exercising what is termed incidental appellate
has a COLR. Oklahoma and Texas split final appellate jurisdiction (Table 29).
review between separate civil and criminal COLRs.
Intermediate appellate courts (IAC) hear initial appeals, A limited jurisdiction trial court, one or more of which is to
the outcome of which is subject to further review by the be found in all but five states and the District of
state’s COLR. Courts of last resort typically were Columbia, typically holds preliminary hearings in felony
established in the state’s constitution and sit in one cases and typically has jurisdiction over misdemeanor
location, the state capital. Intermediate appellate courts, and ordinance violation cases (Table 45 details the
a more contemporary institution, have multiple locations jurisdiction over felony cases by courts of limited
in 21 states. In 10 states, each location serves a region jurisdiction). Civil jurisdiction is restricted to a fixed
within the state and has its own chief judge and a maximum amount, and typically includes a separate
permanently assigned complement of judges (Table 1). category of small claims cases for which simplified
Other state appellate courts travel en banc to various procedures are established. Juvenile, domestic
locations, while still other courts travel in smaller panels. relations, and drug cases are typically heard in a court of
How many judges are authorized to serve and were general jurisdiction, however, there is a trend to create
actually serving, as of July 1, 1998, on each court? The special courts reserved for special dockets for these
number of appellate judgeships, authorized and serving, case types. See Table 33 and 34 detailing the use of
for the state and federal courts is shown in Table 2. The family and drug courts.
combined full-time federal and state appellate bench has
1,474 members. Most appellate judges serve on Table 3 also indicates the number of judges authorized
intermediate appellate courts (1,108). for and serving on each trial court statewide. Some
courts use part-time or senior judges to help with
The allocation of judgeships to appellate courts caseloads, the resulting judicial power is therefore
illustrates the divergence between the federal and state expressed as full-time equivalent positions. Courts
courts, as well as state court diversity. All COLRs are typically also make use of quasi-judicial staff to hear
established with an odd number of justices, in contrast to cases as referees, commissioners, or hearing officers.
the structure of the jury as a decision-making institution, Quasi-judicial officers are usually appointed by the trial
which usually entails an even number of jurors. This bench for a fixed period of time and can be dismissed by
follows the federal model. However, state COLRs have that bench. General jurisdiction trial courts are usually
fewer justices than the U.S. Supreme Court. The most divided into circuits or districts. In some states (e.g.,
common arrangement is a seven judge COLR, found in California) the county serves as the judicial district. Most
27 states and Puerto Rico. Five justices serve on states, however, construct judicial districts that embrace
COLRs in 18 state courts, including the Oklahoma Court a number of counties. Limited jurisdiction trial courts
of Criminal Appeals. Seven courts, including both Texas vary in whether they possess jurisdiction across a county
COLRs and the Oklahoma Supreme Court (Civil COLR), or serve a specific local government unit, such as a city
follow the federal nine-justice model (as does the District or village. Jurisdiction beyond a specific county is rare;
of Columbia). exceptions are for those courts with special jurisdiction
that applies statewide (water courts and workers’
Intermediate appellate courts often undertake review compensation courts are examples).
through panels of three or more judges rather than by
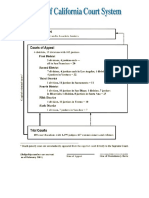
the full court sitting en banc (see Table 23). California The information contained in this section is basic
has the largest state IAC, with 93 authorized judgeships. because there is no generic court system in the United
This court is divided into nine divisions. (Table 1) There States. Even the nomenclature varies. Supreme Courts
are 179 authorized judgeships for the 13 circuits of the are usually courts of last resort, but in New York the
U.S. Circuit Courts of Appeal. Three judge IACs are designation “supreme” is assigned to the main trial court,
Courts and judges 7
while The Court of Appeals is the state’s court of last Select Bibliography:
resort. Justices and a Chief Justice usually serve on
courts of last resort, but a number of COLRs have Carl Baar, One Trial Court: Possibilities and Limitations,
judges and a chief judge. Judge is the standard title for Ottawa: Canadian Judicial Council, 1991.
those serving on intermediate appellate courts.
Howard Ball, “The Federal Court System,” Encyclopedia
The closest to a generic form of court structure in the of the American Judicial System, Vol. II, R. Janosik
United States is a court system with two appellate courts, (Ed.). New York: Charles Scribner’s, 1987.
one a court of last resort and one an intermediate
appellate court, and two or more trial courts. But many Marie T. Finn (Ed.) The American Bench: Judges of the
states, and the federal courts, do not neatly fit that Nation, Ninth Edition 1997/98, Sacramento: Forster-
pattern, and even those states that do add diversity in Long, 1993 [includes maps of federal and state
how the allocation of subject matter jurisdiction to courts judicial boundaries].
is made, how appellate review is designated as being on
a mandatory (appeal of right) or discretionary (through a Henry Glick, “State Court Systems,” Encyclopedia of the
petition) basis, and in the use made of quasi-judicial American Judicial System, Vol. II, R. Janosik (Ed.).
officers. New York: Charles Scribner’s, 1987.
Erick B. Low, “Accessing the Judicial System: The
State’s Response,” The Book of the States, 1994-95
Edition, Vol. 30. Lexington, KY: The Council of State
Governments.
8 State Court Organization, 1998
Table 1. Appellate Courts in the United States
Number of court locations that have:
Separate administrative rules Chief justice/judge Place of session
Alabama
1
Supreme Court 1 1 Montgomery
1
Court of Civil Appeals 1 1 Montgomery
1
Court of Criminal Appeals 1 1 Montgomery
Alaska
2
Supreme Court 1 1 Anchorage, Fairbanks, Juneau
Court of Appeals 1 1 Anchorage
Arizona
Supreme Court 1 1 Phoenix
Court of Appeals 2 2 Phoenix (16 judges)
Tucson (6 judges)
Arkansas
Supreme Court 1 1 Little Rock
Court of Appeals 0 1 Little Rock
California
Supreme Court – 1 3 cities
3 4
Courts of Appeal – 9 6 districts , 9 locations
Colorado
5
Supreme Court 1 1 Denver
Court of Appeals 1 1 Denver
Connecticut
6
Supreme Court 1 1 Hartford
6
Appellate Court 1 1 Hartford
Delaware
Supreme Court 0 1 Dover
District of Columbia
Court of Appeals 1 1 Washington DC
Florida
7
Supreme Court 1 1 Tallahassee
9
District Courts of Appeal 0 58 Varies by district
Georgia
Supreme Court 1 1 Atlanta
10
Court of Appeals 1 1 Atlanta
Hawaii
Supreme Court 1 1 Honolulu
Intermediate Court of Appeals 1 1 Honolulu
Idaho
11
Supreme Court 1 1 Varies
12
Court of Appeals 1 1 Varies
Illinois
Supreme Court 1 1 Springfield
13
Appellate Court 5 5 5 cities or districts
Indiana
Supreme Court 1 1 Indianapolis
Court of Appeals 1 1 Indianapolis
14
Tax Court 1 –
Iowa
Supreme Court 1 1 Des Moines
Court of Appeals 1 1 Des Moines
Kansas
15
Supreme Court 1 1 Topeka
15
−
16
Court of Appeals 1 1
Kentucky
Supreme Court 1 1 Frankfort
Court of Appeals 1 1 Varies
Courts and judges 9
Table 1. Appellate Courts in the United States
Number of court locations that have:
Separate administrative rules Chief justice/judge Place of session
Louisiana
Supreme Courts 1 1 New Orleans
17
Courts of Appeal 5 5 Varies by circuit
Maine
18
Supreme Judicial Court 1 1 Portland
Maryland
Court of Appeals 1 1 Annapolis
Court of Special Appeals 1 1 Annapolis
Massachusetts
Supreme Judicial Court 1 1 Boston
Appeals Court 1 1 Boston
Michigan
Supreme Court 1 1 Lansing
19
Court of Appeals 1 1 4 designated cities
Minnesota
Supreme Court 1 1 St. Paul
Court of Appeals 1 1 Hennepin and Ramsey Counties
Mississippi
Supreme Court 1 1 Jackson
Court of Appeals 1 1 Jackson
Missouri
Supreme Court 1 1 Jefferson City
20
Court of Appeals 3 3 Varies
Montana
Supreme Court 1 1 Helena
Nebraska
Supreme Court 1 1 Lincoln
Court of Appeals 1 1 Lincoln
Nevada
21
Supreme Court 1 1 Carson City
New Hampshire
Supreme Court 1 1 Concord
New Jersey
Supreme Court 1 1 Trenton
22
Superior Court, Appellate Division 1 1 Varies
New Mexico
Supreme Court 1 1 Santa Fe
23
Court of Appeals 1 1 Varies
New York
Court of Appeals 1 1 Albany
24
Supreme Court, Appellate Div. 4 4 Varies
North Carolina
Supreme Court 1 1 Raleigh
Court of Appeals 1 1 Raleigh
North Dakota
25
Supreme Court 1 1 Bismarck
Ohio
Supreme Court 1 1 Columbus
26
Courts of Appeals 12 12 Varies
Oklahoma
Supreme Court 1 1 Oklahoma City
Court of Criminal Appeals 1 1 Oklahoma City
Court of Civil Appeals 1 1 Oklahoma City and Tulsa (divisions of 3)
10 State Court Organization, 1998
Table 1. Appellate Courts in the United States
Number of court locations that have:
Separate administrative rules Chief justice/judge Place of session
Oregon
Supreme Court 1 1 Salem
Court of Appeals 1 1 Salem
Pennsylvania
Supreme Court 1 1 Pittsburgh, Harrisburg, and Philadelphia
27
Superior Court 1 1 “Ride circuit” throughout the state
28
Commonwealth Court 1 1 “Ride circuit” throughout the state
Puerto Rico
Supreme Court 1 1 San Juan
Court of Appeals 1 1 San Juan and throughout the island
Rhode Island
Supreme Court 1 1 Providence
South Carolina
Supreme Court 1 1 Columbia
Court of Appeals 1 1 Columbia
South Dakota
Supreme Court 1 1 Pierre
Tennessee
Supreme Court 1 1 Knoxville, Nashville, and Jackson
29
Court of Appeals 1 1 Varies
29
Court of Criminal Appeals 1 1 Varies
Texas
Supreme Court 1 1 Austin
Court of Criminal Appeals 1 1 Austin
30
Courts of Appeals 14 14 Designated for each of the 14 IACs
Utah
Supreme Court 1 1 Salt Lake City
Court of Appeals 1 1 Salt Lake City
Vermont
31
Supreme Court 1 1 Montpelier
Virginia
Supreme Court 1 1 Richmond
Court of Appeals 1 0 Richmond, Norfolk, Salem, and Alexandria
Washington
Supreme Court 1 1 Olympia
34 32 33
Courts of Appeals 3 3 Varies by division
West Virginia
Supreme Court of Appeals 1 1 Charleston
Wisconsin
34
Supreme Court 1 1 Madison
Court of Appeals 1 1 Milwaukee, Waukesha, Wausau, and Madison
Wyoming
35
Supreme Court 1 1 Cheyenne
38
Federal
U.S. Supreme Court 1 1 Washington DC
U.S. Courts of Appeals 1 14 Each of the 14 courts of appeal has a designated
city to conduct court
FOOTNOTES:
Alabama: California:
1 3
Sometimes sessions for oral argument are held in other cities. There are ninety-three authorized judgeships. As of June 1998, ninety
judgeships are filled. There is an administrative presiding judge in each of the
Alaska:
2
The supreme court holds regular sessions in other cities occasionally.
Courts and judges 11
Table 1. Appellate Courts in the United States
three multi-division districts, and the presiding judges serve this function in the Ohio:
26
other three districts. District One—Cincinnati; District Two—Dayton; District Three—Lima; District
4
District One—San Francisco; District Two—Los Angeles, Ventura; District Four—Portsmouth; District Five—Canton; District Six—Toledo; District Seven—
Three—Sacramento; District Four—San Diego, San Bernadino, Santa Ana; Youngstown; District Eight—Cleveland; District Nine—Akron; District Ten—
District Five—Fresno; District Six—San Jose. Columbus; District Eleven—Warren; District Twelve—Middleton.
Pennsylvania:
27
Colorado: One set of rules for three locations.
5 38
Twice each year the court will travel and hold arguments at a public school as Commonwealth court usually meets in Pittsburgh, Harrisburg, and Philadelphia,
part of a public education program. with one en banc session per argument week.
Connecticut: Tennessee:
6 29
One day each year the court meets at a Connecticut law school or university. Eastern Section—Knoxville; Middle Section—Nashville; Western Section—
Jackson.
Florida:
7
The supreme court facility for all seven justices is located in the state capital. Texas:
8 30
There are five district courts of appeal (DCA) that are located in five different District One—Houston; District Two—Fort Worth; District Three—Austin; District
judicial districts throughout the state. The first district has fifteen judges; the Four—San Antonio; District Five—Dallas; District Six—Texarkana; District
second, fourteen; the third, eleven; the fourth, twelve, and the fifth, nine. The chief Seven—Amarillo; District Eight—El Paso; District Nine—Beaumont; District Ten—
judge for each DCA is chosen by a majority of the court, and if there is no majority, Waco; District Eleven—Eastland; District Twelve—Tyler; District Thirteen—
by the chief justice. Corpus Christi; District Fourteen—Houston.
9
District One—Tallahassee; District Two—Tampa; District Three—Miami; District
Four—West Palm Beach; District Five—Daytona Beach. Vermont:
31
Georgia: Special court sessions are held at Vermont Law School and at trial courts.
10
Court may sit outside Atlanta by special court order.
Washington:
32
Idaho: There is one presiding judge over all divisions, as well as a chief judge in each
11
Boise, Coeur d’Alene, Idaho Falls, Lewiston, Moscow, Pocatello, and Twin Falls. of the three divisions. All have local administrative rules in addition to general
12
Boise, Coeur d’Alene, Idaho Falls, Lewiston, Moscow, Pocatello, Twin Falls, administrative rules.
33
Blackfoot, and Hailey. Division I—Seattle; Division II—Tacoma; Division III—Spokane.
Illinois: Wisconsin:
13 34
Court sits in Chicago, Elgin, Ottawa, Springfield and Mount Vernon. Although it is not customary, in October of 1993 the court sat in Green Bay as
part of a more general public information/education program. The court has
Indiana: continued this practice, traveling to selected sites in Wisconsin approximately
14
Tax court does not have a chief judge; but one permanently assigned judge. once a year.
Kansas: Wyoming:
15 35
Both the COLR and IAC operate under the same rules of appellate practice On occasion the court sits at the Wyoming Law School and various community
although each court drafts its own internal operating procedures. colleges and high schools.
16
Judges are authorized to sit in any courthouse in the state.
Federal:
36
Louisiana: The federal military appeals system, established primarily by federal legislation,
17
First Circuit–Baton Rouge, LA; Second Circuit–Shreveport, LA; Third Circuit– Articles 66 and 67 of the Uniform Code of Military Justice, 10 U.S.C. §§ 866, 867,
Lake Charles, LA; Fourth Circuit–New Orleans, LA; Fifth Circuit–Jefferson, LA created four intermediate appellate courts and one court of last resort, whose
decisions are subject to review by the U.S. Supreme Court. The intermediate
Maine: courts are: the U.S. Air Force Court of Criminal Appeals, U.S. Army Court of
18
The justices have permanent chambers in the superior courthouse near their Criminal Appeals, U.S. Navy-Marine Corps Court of Criminal Appeals, and the
residence. The supreme court is not lodged in its own building. U.S. Coast Guard Court of Criminal Appeals. The court of last resort is the U.S.
Court of Appeals for the Armed Forces. While the courts of criminal appeals are
Michigan: governed by joint rules issued by the Judge Advocates General of the respective
19
All IAC judges rotate throughout court locations in the state, although there are services (General Counsel of the Department of Transportation for the Coast
four designated election districts (1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th). Guard), the chief judge of each court is authorized to issue internal rules for that
court. Accordingly, the internal rules vary according to service needs.
Missouri:
20
Eastern District—St. Louis; Western District—Kansas City; Southern District—
Springfield.
Nevada:
21
Court sits in Las Vegas three times a year. (In January 1999, court will expand
to seven justices and will commence to meet in panels.)
New Jersey:
22
Judges not assigned to permanent locations.
New Mexico:
23
Oral argument often scheduled in different locations.
New York:
24
First Department—New York City; Second Department—Brooklyn; Third
Department—Albany; Fourth Department—Rochester.
North Dakota:
25
Court sits in special session at the law school.
12 State Court Organization, 1998
Table 2. Number of Appellate Court Justices
Number of Court of Last Resort (COLR) justices Number of Intermediate Appellate Court (IAC) justices
Authorized Serving Authorized Serving
1 1
Alabama 9 9 10 10
Alaska 5 5 3 3
Arizona 5 5 22 22
Arkansas 7 7 12 12
California 7 7 93 93
Colorado 7 7 16 16
2 2
Connecticut 7 7 9 9
Delaware 5 5 ~ ~
District of Columbia 9 9 ~ ~
Florida 7 7 61 61
Georgia 7 7 10 10
Hawaii 5 5 4 4
Idaho 5 5 3 3
Illinois 7 7 53 53
3 3
Indiana 5 5 16 16
Iowa 9 9 6 6
Kansas 7 7 10 10
Kentucky 7 7 14 14
4 4
Louisiana 7 8 55 54
Maine 7 7 ~ ~
Maryland 7 7 13 13
5
Massachusetts 7 7 14 16
Michigan 7 7 28 28
Minnesota 7 7 16 16
Mississippi 9 9 10 10
Missouri 7 7 32 32
Montana 7 7 ~ ~
Nebraska 7 7 6 6
Nevada 5 5 ~ ~
New Hampshire 5 5 ~ ~
New Jersey 7 7 32 32
New Mexico 5 5 10 10
6 6
New York 7 7 71 63
North Carolina 7 7 12 12
North Dakota 5 5 ~ ~
Ohio 7 7 66 66
7 7
Oklahoma 14 14 12 12
Oregon 7 7 10 10
8 8
Pennsylvania 7 7 24 24
Puerto Rico 7 7 33 33
Rhode Island 5 5 ~ ~
South Carolina 5 5 9 9
South Dakota 5 5 ~ ~
9 9
Tennessee 5 5 24 24
10 10
Texas 18 18 80 80
Utah 5 5 7 7
Vermont 5 5 ~ ~
Virginia 7 7 10 10
Washington 9 9 23 21
West Virginia 5 5 ~ ~
Wisconsin 7 7 16 16
Wyoming 5 5 ~ ~
Federal:
US Supreme Court 9 9 ~ ~
11
US Courts of Appeals ~ ~ 179 153
Legend: ~=Not applicable Courts and judges 13
Table 2. Number of Appellate Court Justices
Note: Information is current as of July 1, 1998.
FOOTNOTES:
Alabama:
1
Five judges on court of criminal appeals; five judges on court of civil appeals.
Connecticut:
2
Figure does not include senior justice in supreme court or senior judge in
appellate court.
Indiana:
3
One judge in the Indiana Tax Court.
Louisiana:
4
One judge elected to a temporary judgeship on the courts of appeal was
assigned, effective 1/1/93 to sit on the supreme court. Appointment will expire on
or before December 31, 2000.
Massachusetts:
5
Figure includes three recall justices.
New York:
6
Figure includes fifty-six justices on appellate divisions of supreme court and
fifteen on appellate terms of supreme court.
Oklahoma:
7
Figure includes 9 justices in the supreme court and 5 justices in the court of
criminal appeals
Pennsylvania:
8
Figure includes15 justices in the superior court and 9 in the commonwealth court.
Tennessee:
9
Figure includes twelve judges on the court of appeals; twelve judges on the court
of criminal appeals.
Texas:
10
Figure includes nine justices in the supreme court and nine justices in the court
of criminal appeals.
Federal:
11
Figure includes the court of appeals for the federal circuit. Information is current
as of June 1, 1997.
14 State Court Organization, 1998 Legend: ~=Not Applicable
Table 3. Trial Courts and Trial Court Judges of the United States
Court Type Full-time Court Type Full-time
G = General jurisdiction Authorized G = General jurisdiction Authorized
L = Limited jurisdiction Judges L = Limited jurisdiction Judges
Alabama Georgia
G Circuit Court 131 G Superior Court 169
L District Court 99 L Juvenile Court 28
L Municipal Court 242 L Civil Court 3
L Probate Court 68 L State Court 51
L Probate Court 159
Alaska
L Magistrate Court ~
G Superior Court 32
L Municipal Court of Columbus 1
L District Court 17
L County Recorder's Court 9
~ Magistrates Division 67
L Municipal/City Courts of Atlanta 307
Arizona
1 Hawaii
G Superior Court 134 9
G Circuit Court 27
L Justice of the Peace Court 84 10
G Family Court 15
L Municipal Court 84
L District Court 22
Arkansas
2 Idaho
G Circuit Court 30
2 G District Court 37
G Chancery and Probate Court 33
~ Magistrate’s Division 81
L Municipal Court 110
L City Court 81 Illinois
L Police Court 4 G Circuit Court 865
L Court of Common Pleas 4
Indiana
L County Court 75
G Superior Court 182
L Justice of the Peace 55
G Circuit Court 96
California G Probate Court 1
G Superior Court 807 L County Court 13
L Municipal Court 673 L City Court 47
L Town Court 25
Colorado
L Small Claims Court of Marion 9
G District Court 115
3 County
G Denver Probate Court
4
G Denver Juvenile Court Iowa
5 11
G Water Court G District Court 179
6
L County Court 47
6 Kansas
L Municipal Court 250
G District Court 156
Connecticut L Municipal Court 259
7
G Superior Court 89
Kentucky
L Probate Court 133
G Circuit Court 97
Delaware L District Court 126
G Court of Chancery 5
Louisiana
G Superior Court 17
G District Court 204
L Justice of the Peace Court 57
G Juvenile & Family Courts 18
L Family Court 13
L Justice of the Peace Court 390
L Court of Common Pleas 7
L Mayor’s Court 250
L Alderman's Court 8
L City and Parish Courts 73
District of Columbia
Maine
G Superior Court 59 12
G Superior Court 16
8 13
Florida L District Court 27
14
G Circuit Court 468 L Probate Court
L County Court 263 L Administrative Court 2
Maryland
G Circuit Court 140
L District Court 101
L Orphan’s Court 66
Legend: ~=Not applicable Courts and judges 15
Table 3. Trial Courts and Trial Court Judges of the United States
Court Type Full-time Court Type Full-time
G = General jurisdiction Authorized G = General jurisdiction Authorized
L = Limited jurisdiction Judges L = Limited jurisdiction Judges
Massachusetts New Mexico
G Superior Court 80 G District Court 72
L District Court 172 L Magistrate Court 59
L Probate/Family Court 49 L Metropolitan Court 15
L Juvenile Court 37 L Municipal Court 85
L Housing Court 9 L Probate Court 33
L Boston Municipal Court 11
New York
L Land Court 4 29
G Supreme Court 369
15
Michigan G County Court 127
16 30
G Circuit Court 210 L Court of Claims 72
G Court of Claims ~ L Surrogates' Court ~
17
L District Court 259 L Family Court 124
L Probate Court 92 L District Court 50
L Municipal Court 6 L City Court 158
L NYC Civil Court 120
Minnesota
L NYC Criminal Court 107
G District Court 254
L Town and Village Justice Court 2,300
Mississippi
North Carolina
G Circuit Court 49 31
G Superior Court 99
L Chancery Court 45 32
L District Court 204
L County Court 24
L Family Court 1 North Dakota
33
L Municipal Court 215 G District Court 44
L Justice Court 191 L Municipal Court 79
Missouri Ohio
18
G Circuit Court 310 G Court of Common Pleas 372
19
L Municipal Court 331 L Municipal Court 202
L County Court 55
Montana 34
L Court of Claims ~
G District Court 37 35
L Mayors Court 428
G Workers' Compensation Court 1
G Water Court 1 Oklahoma
L Justice of the Peace Court 73 G District Court 223
L Municipal Court 3 L Municipal Court Not of Record 350
20
L City Court 36 L Municipal Court of Record 23
L Worker's Compensation Court 9
Nebraska
21 L Court of Tax Review 3
G District Court 53
22
L Separate Juvenile Court 8 Oregon
36
L County Court 59 G Circuit Court 160
37
L Workers' Compensation Court 7 G Tax Court 1
L County Court 7
Nevada
23 L Justice Court 30
G District Court 48
24 L Municipal Court 141
L Justice Court 67
25
L Municipal Court 18 Pennsylvania
G Court of Common Pleas 386
New Hampshire
L Philadelphia Municipal Court 25
G Superior Court 28
L District Justice Court 549
L District Court 14
26 L Philadelphia Traffic Court 7
L Municipal Court 0
L Pittsburgh City Magistrates 6
L Probate Court 4
Puerto Rico
New Jersey
27 G Superior Court 168
G Superior Court 384 38
L District Subsection 42
L Tax Court 12
28 L Municipal Court 105
L Municipal Court 40
16 State Court Organization, 1998 Legend: ~=Not applicable
Table 3. Trial Courts and Trial Court Judges of the United States
Court Type Full-time Court Type Full-time
G = General jurisdiction Authorized G = General jurisdiction Authorized
L = Limited jurisdiction Judges L = Limited jurisdiction Judges
Rhode Island Vermont
G Superior Court 22 G Superior Court 12
L Workers' Compensation Court 10 G District Court 17
42
L District Court 13 G Family Court ~
L Family Court 12 L Probate Court ~
L Probate Court 39 L Environmental Court 1
L Municipal Court 21
Virginia
South Carolina G Circuit Court 147
G Circuit Court 46 L District Court 222
L Family Court 52
Washington
L Magistrate Court 300 43
G Superior Court 167
L Probate Court 46
L District Court 113
L Municipal Court 300
L Municipal Court 102
L Administrative Law Division 6
West Virginia
South Dakota
G Circuit Court 62
G Circuit Court 37
L Magistrate Court 156
44
Tennessee L Municipal Court ~
G Circuit Court 85
Wisconsin
G Chancery Court 33 45
G Circuit Court 234
G Criminal Court 31 46
L Municipal Court 217
G Probate Court 2
L Juvenile Court 16 Wyoming
39
L Municipal Court 231 G District Court 17
40 47
L General Sessions Court 156 L Justice of the Peace Court 0
48
L Municipal Court 2
Texas
L County Court 19
G District Courts 396
49
L Constitutional County Court 254 Federal
L County Courts at Law 181 U.S. District Court 642
L Justice of the Peace Court 842 U.S. Magistrate 436
L Municipal Court 1,122 U.S. Bankruptcy 326
L Statutory Probate 16
Utah
G District Court 70
41
L Justice Court 128
L Juvenile Court 22
Note: Information is current as of July 1, 1998.
Note: See the court structure charts in section eight of this volume for data on commissioners, referees, magistrates, and other quasi-judicial officers
and part-time judges.
FOOTNOTES:
Arizona: Florida:
1 8
Total includes the superior court judge/judges who also serve on the tax court. The court system uses retired judges on a part-time basis. County judges are
assigned to serve on the circuit bench by administrative order of the Supreme
Arkansas: Court.
2
In addition to 30 circuit judges and 33 chancery/probate judges, 43 judges have
the statutory authority to hear cases in both Circuit and Chancery Courts. The Hawaii:
9
total number of general jurisdiction judges in the state is 106. Total number of circuit court judges equals 29, however 2 judges are assigned to
the family court.
10
Colorado: District family court judges.
3
The Denver probate court has 1 district court judge serving and 1 magistrate.
4
The Denver juvenile court has 3 district court judges serving and 3 magistrates. Iowa:
5 11
The water court is served by 7 judges from the district court, full-time referee and Includes 112 authorized district judges, 54 district associate judges, 12
6 part-time water referees. associate juvenile judges, and one associate probate judge.
6
Denver County Court and Municipal Court are not part of the state judicial
system. Maine:
12
Active retired justices of the Superior Court serve as senior judges.
13
Connecticut: Active retired judges of the District Court serve as senior judges.
7 14
There are also 61 trial referees and 17 superior court senior judges. All are part-time judges.
Legend: ~=Not applicable Courts and judges 17
Table 3. Trial Courts and Trial Court Judges of the United States
Michigan: Ohio:
15 34
Michigan has a family court division that became operational on January 1, Judges are assigned by supreme court.
35
1998, but data is not yet available. These are mayors.
16
The court of claims operates within the 30th Circuit Court.
17
There are 14 part-time judges with a full-time equivalency of approximately Oregon:
36
seven FTE. 160 as of 1/1/98; the total will change to 163 effective 1/1/99. There are 94 senior
(retired) judges who serve as needed and when available.
37
Missouri: Tax court has 1 judge and 5 magistrates.
18
334 total: 135 circuit judges, 175 associate circuit judges, 15 family court
commissioners, one family court referee, one family court hearing officer, one
drug commissioner, 3 probate and 3 deputy probate commissioners. Puerto Rico:
19 38
This number represents the established municipal courts. The Judicial Reform Act of 1994 establishes the eventual abolition of the district
subsection. The superior division has concurrent jurisdiction with the district
Montana: subsection during the process of its abolition.
20
Also, 41 justices of the peace who also serve as city court judges.
Tennessee:
39
Nebraska: Municipal court number is estimated, number is unknown.
21 40
The district court has 53 judges as of 7/1/98 to be increased to 54 by 7/1/2000. Some judges serve in another capacity so juvenile judge numbers overlap in
22
The separate juvenile court has 8 judges as of 7/1/98 to be increased to 9 by juvenile and general sessions courts.
7/1/2000.
Nevada: Utah:
23 41
3 additional district judges January 1999 (will be 51). Justice courts are formed at the option of local governments, therefore no specific
24
2 additional justices of the peace January 1999 (will be 69). number of judges is fixed by statute or rule.
25
Also served by 11 justices of the peace.
Vermont:
42
New Hampshire: District and superior court judges are assigned to preside in family court.
26
The municipal court has 2 part-time judges.
Washington:
43
New Jersey: Authorized number. May be higher than judges actually seated.
27
Excludes appellate division judges.
28
40 of the current 390 municipal court judges serve full-time. The remaining West Virginia:
44
judges sit part-time. Also, many municipal court judges sit in more than one court. No full-time and 22 part-time judges.
New York: Wisconsin:
29 45
Also has 50 “acting” supreme court judges and 12 quasi-judicial staff. The court Reserve judges are retired judges who serve as needed and when available. FTE
also uses full-time certified retired justices of supreme court. reserve judge service estimate includes case-specific assignments (calculated at
30
50 court of claims judges also sit on the supreme court. an average of 2.5 days per assignment) and general assignments.
46
Municipal courts are local option, and locally funded and administered. In the
North Carolina: event of a municipal judicial vacancy, for whatever reason, the chief judge of the
31
There is statutory authority for use of emergency and retired judges. This district must either assign another municipal judge or transfer pending municipal
authority is used regularly, as justified by need, although unable to translate for cases to circuit court. (SCR-70.24)
any typical year how many "FTE" positions such use incurs.
32
District court also has 696 magistrates of which 32 are part-time. Wyoming:
47
There are 10 justices of the peace (part-time).
48
North Dakota: Also has 73 part-time judges.
33
Number of authorized judges drops to 43 effective 1/1/99, and may be reduced to
42 by the year 2001. Federal:
49
As of January 1, 1999.
18 State Court Organization, 1998
You might also like
- Domingue, P.R. (2001) - The Historical Development of The Mixed Legal System of Mauritius.Document125 pagesDomingue, P.R. (2001) - The Historical Development of The Mixed Legal System of Mauritius.jess tannoo100% (2)
- Understanding Federal CourtsDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Federal CourtswoodspatNo ratings yet
- California Court Structure State PDFDocument3 pagesCalifornia Court Structure State PDFenri0% (1)
- Political Law Bar Q&ADocument88 pagesPolitical Law Bar Q&AClaire Culminas100% (1)
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University LucknowDocument16 pagesDr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University Lucknowjinisha sharmaNo ratings yet
- State Supreme Court: Appellate JurisdictionDocument4 pagesState Supreme Court: Appellate JurisdictionmirmoinulNo ratings yet
- State Court Organization 1998Document36 pagesState Court Organization 1998losangelesNo ratings yet
- CourtsDocument26 pagesCourtsCriss DeeaNo ratings yet
- Courts and The Legal ProcessDocument3 pagesCourts and The Legal ProcessBonifaceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document30 pagesChapter 2masemolaguyNo ratings yet
- Lunenburg, Fred C The Judicial System FOCUS V6 N1 2012-1Document4 pagesLunenburg, Fred C The Judicial System FOCUS V6 N1 2012-1mazumdertanisha100No ratings yet
- Judicial Interpretation and DiscretionDocument18 pagesJudicial Interpretation and DiscretionRajiv YadavNo ratings yet
- Courts in The USADocument2 pagesCourts in The USAStanley GorayNo ratings yet
- The U.S. Legal System: A Short Description: Federal Judicial CenterDocument4 pagesThe U.S. Legal System: A Short Description: Federal Judicial CenterNaumPelicudaNo ratings yet
- Hierarchy and Functions of Courts & Justice System in USA - OverviewDocument8 pagesHierarchy and Functions of Courts & Justice System in USA - OverviewStruat Christoper John BroadNo ratings yet
- The System of CourtsDocument3 pagesThe System of CourtsSergei IvanovNo ratings yet
- Comparing Federal & State CourtsDocument2 pagesComparing Federal & State Courtsmiguez871No ratings yet
- CourtComparisons Article 3 CourtDocument9 pagesCourtComparisons Article 3 CourtAnonymous puqCYDnQNo ratings yet
- MGMT 260 CH 3 SlidesDocument22 pagesMGMT 260 CH 3 SlidesqhaweseithNo ratings yet
- The Judicial SystemDocument54 pagesThe Judicial Systemapi-213462480No ratings yet
- Ilovepdf - Com-49-63 (6) - 231215 - 055529Document19 pagesIlovepdf - Com-49-63 (6) - 231215 - 055529Надія ЛяшкоNo ratings yet
- SupremecourtprecedentDocument11 pagesSupremecourtprecedentNeelu PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Lecture #8 Courts 22 AccDocument50 pagesLecture #8 Courts 22 AccprocmadzNo ratings yet
- Judicial Stucture and Jurisdiction of USA (OM)Document19 pagesJudicial Stucture and Jurisdiction of USA (OM)Niruta PaudelNo ratings yet
- American Court System GleimDocument8 pagesAmerican Court System GleimpfreteNo ratings yet
- Appealing To The Supreme CourtDocument6 pagesAppealing To The Supreme Courtsandicb100% (1)
- Introduction To Legal System Small Group F2014Document18 pagesIntroduction To Legal System Small Group F2014Yale Law LibraryNo ratings yet
- Courts ReadingDocument3 pagesCourts Readingapi-328061525No ratings yet
- Criminal Courts - Chapter 7Document23 pagesCriminal Courts - Chapter 7Ishani TarkarNo ratings yet
- American Government Chapter 13 2020Document54 pagesAmerican Government Chapter 13 2020Gikonyo MararoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Federal Court SystemDocument5 pagesIntroduction To The Federal Court SystemAlexandraNo ratings yet
- Fed. Judiciary OutlineDocument4 pagesFed. Judiciary OutlineSweet PeaNo ratings yet
- State Court Organization 1998Document54 pagesState Court Organization 1998losangelesNo ratings yet
- CheckPoint - Court System Structure IDocument1 pageCheckPoint - Court System Structure IBubba HotepNo ratings yet
- Original JurisdictionDocument8 pagesOriginal JurisdictionMarianna NajaryanNo ratings yet
- Usa Jurisidiction Federal and Supreme CourtDocument13 pagesUsa Jurisidiction Federal and Supreme CourtB.C. Harker100% (2)
- Law and Ethics For Today's Journalist: A Concise Guide: by Joe Mathewson Chapter 1: CourtsDocument16 pagesLaw and Ethics For Today's Journalist: A Concise Guide: by Joe Mathewson Chapter 1: CourtsemzekonisNo ratings yet
- DuhartOlympiaSt 2017 PLAINENGLISHTABLE LegalWritingQuickStudDocument3 pagesDuhartOlympiaSt 2017 PLAINENGLISHTABLE LegalWritingQuickStudenriNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - ABEL CASTRUITA - Double Take Dual Court SystemDocument9 pagesKami Export - ABEL CASTRUITA - Double Take Dual Court System1613405No ratings yet
- Analysis On Judicial SystemDocument11 pagesAnalysis On Judicial SystemRitika RitzNo ratings yet
- Judicial Branch in A Flash ReadingsDocument2 pagesJudicial Branch in A Flash Readingsapi-261009456100% (1)
- Checkpoint: Court System Structure Tanesha Brenno 11-16-10 Sara RogersDocument4 pagesCheckpoint: Court System Structure Tanesha Brenno 11-16-10 Sara RogersTanesha BrennoNo ratings yet
- Court Role and StructureDocument22 pagesCourt Role and StructureМаксим ВласенкоNo ratings yet
- Good Morning UsaDocument4 pagesGood Morning UsamvanishcNo ratings yet
- Comparing FederalDocument3 pagesComparing FederalYana FishkaNo ratings yet
- Court StructureDocument2 pagesCourt StructureanushiiiiNo ratings yet
- Courts of RecordDocument7 pagesCourts of RecordSue RhoadesNo ratings yet
- Judical BranchDocument19 pagesJudical BranchGabriel BlountNo ratings yet
- Court Systems PowerpointDocument23 pagesCourt Systems Powerpointkasun jiwanthaNo ratings yet
- The American Court System: An Outline and Guiding PrinciplesDocument2 pagesThe American Court System: An Outline and Guiding Principlesтатьяна васильковаNo ratings yet
- The Oklahoma JudiciaryDocument10 pagesThe Oklahoma JudiciaryRocky AllenNo ratings yet
- Law II - Texts - Sem. II 2015-2016Document6 pagesLaw II - Texts - Sem. II 2015-2016iuliaiulianaNo ratings yet
- US Court System & Legal InstitutionsDocument31 pagesUS Court System & Legal Institutionso.boborakhimovNo ratings yet
- Courts of Record ListingDocument14 pagesCourts of Record ListingKrimsonNo ratings yet
- State Court Organization 1998Document57 pagesState Court Organization 1998losangelesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Court SystemDocument4 pagesIntroduction To The Court SystemJorge Alberto AraujoNo ratings yet
- The Court System in USDocument3 pagesThe Court System in USQuế Lương LýNo ratings yet
- American Gopo Review 15.1 JudiciaryDocument3 pagesAmerican Gopo Review 15.1 JudiciaryCaitlin RiveraNo ratings yet
- Courts and Court SystemsDocument4 pagesCourts and Court SystemsnazarabbasNo ratings yet
- The Judicial System of The UsaDocument2 pagesThe Judicial System of The UsaAlina BelousovaNo ratings yet
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Overview of US Court System and StructureFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Overview of US Court System and StructureNo ratings yet
- 02359-b04-03 AppendixDocument146 pages02359-b04-03 AppendixlosangelesNo ratings yet
- Omb Bulletin No. 06-01Document2 pagesOmb Bulletin No. 06-01losangeles100% (1)
- Executive Office of The President Executive Office of The PresidentDocument13 pagesExecutive Office of The President Executive Office of The Presidentlosangeles100% (1)
- 02352-b03-04 AttachDocument141 pages02352-b03-04 AttachlosangelesNo ratings yet
- 02368-b06-01 CorrectionDocument1 page02368-b06-01 Correctionlosangeles100% (1)
- Executive Office of The President: Attachment BDocument5 pagesExecutive Office of The President: Attachment Blosangeles100% (1)
- Executive Office of The President Executive Office of The PresidentDocument4 pagesExecutive Office of The President Executive Office of The Presidentlosangeles100% (1)
- Executive Office of The PresidentDocument23 pagesExecutive Office of The Presidentlosangeles100% (1)
- b04 04Document16 pagesb04 04losangeles100% (1)
- Attachment BDocument4 pagesAttachment BlosangelesNo ratings yet
- Executive Office of The PresidentDocument20 pagesExecutive Office of The PresidentlosangelesNo ratings yet
- 02360-b04-03 AttachmentDocument5 pages02360-b04-03 AttachmentlosangelesNo ratings yet
- 02358-b04-02 Supp1Document7 pages02358-b04-02 Supp1losangelesNo ratings yet
- Major Savings and Reforms in The President's 2008 Budget: EbruaryDocument211 pagesMajor Savings and Reforms in The President's 2008 Budget: EbruarylosangelesNo ratings yet
- 02338-Expanding Egov 2005Document12 pages02338-Expanding Egov 2005losangelesNo ratings yet
- Executive Office of The President Executive Office of The PresidentDocument5 pagesExecutive Office of The President Executive Office of The PresidentlosangelesNo ratings yet
- Bulletin No. 00 - 03 To The Heads of Executive Departments and Establishments SubjectDocument13 pagesBulletin No. 00 - 03 To The Heads of Executive Departments and Establishments SubjectlosangelesNo ratings yet
- Program Assessment Rating Tool (PART) 2008 Budget: This PDF Is Also Available in Excel Format atDocument31 pagesProgram Assessment Rating Tool (PART) 2008 Budget: This PDF Is Also Available in Excel Format atlosangelesNo ratings yet
- Executive Office of The President: What Are The Legal Authorities Under Which OMB Is Requiring Agency Action?Document3 pagesExecutive Office of The President: What Are The Legal Authorities Under Which OMB Is Requiring Agency Action?losangelesNo ratings yet
- SpecDocument424 pagesSpeclosangelesNo ratings yet
- Director Rob Portman February 5, 2007Document8 pagesDirector Rob Portman February 5, 2007losangelesNo ratings yet
- Department of Transportation: Since 2001, The AdministrationDocument5 pagesDepartment of Transportation: Since 2001, The AdministrationlosangelesNo ratings yet
- HistDocument336 pagesHistlosangeles100% (1)
- Object Class Analysis: Budget of The U.S. GovernmentDocument128 pagesObject Class Analysis: Budget of The U.S. GovernmentlosangelesNo ratings yet
- TreasuryDocument4 pagesTreasurylosangelesNo ratings yet
- Shibu Soren Vs Dayanand Sahay & Ors. 19 July, 2001 PDFDocument18 pagesShibu Soren Vs Dayanand Sahay & Ors. 19 July, 2001 PDFPiyush KulshreshthaNo ratings yet
- Flavio K - Macasaet & Associates, Inc. vs. Com. On Audit 173 SCRA 352, May 12, 1989Document6 pagesFlavio K - Macasaet & Associates, Inc. vs. Com. On Audit 173 SCRA 352, May 12, 1989MarkNo ratings yet
- Human Rights AlertDocument120 pagesHuman Rights AlertHuman Rights Alert - NGO (RA)No ratings yet
- RA 7975 - Strengthening The Functional and Struct Org of The Sandiganbayan EtcDocument6 pagesRA 7975 - Strengthening The Functional and Struct Org of The Sandiganbayan EtcCrislene CruzNo ratings yet
- BAgatsing V Ramirez, GR No., 74 SCRA 306Document15 pagesBAgatsing V Ramirez, GR No., 74 SCRA 306Sheena Reyes-BellenNo ratings yet
- CJSDocument2 pagesCJSJovie Masongsong100% (2)
- Advanced Civil Procedure Matsikidze 2018Document166 pagesAdvanced Civil Procedure Matsikidze 2018Cornelius ChigomeNo ratings yet
- Gonzales v. ComelecDocument2 pagesGonzales v. ComelecRenz FactuarNo ratings yet
- T.N. Godavarman Thirumulpad v. Union of India (WP (Civil) No. 202 of 1995)Document3 pagesT.N. Godavarman Thirumulpad v. Union of India (WP (Civil) No. 202 of 1995)Soumiki GhoshNo ratings yet
- An Assignment On The Judicial System of BangladeshDocument8 pagesAn Assignment On The Judicial System of BangladeshManjare Hassin Raad80% (5)
- Forensic Medicine and Power of CourtsDocument25 pagesForensic Medicine and Power of CourtsVikas Bhargav ForensicsNo ratings yet
- Co Owner Rights and Liabilities 2009 (1) Scale 679Document9 pagesCo Owner Rights and Liabilities 2009 (1) Scale 679Sridhara babu. N - ಶ್ರೀಧರ ಬಾಬು. ಎನ್No ratings yet
- AppealsDocument25 pagesAppealsYogesh MittalNo ratings yet
- 05 - University of Santo Tomas vs. Board of Tax Appeals, 93 Phil., 376, No. L-5701 June 23, 1953Document4 pages05 - University of Santo Tomas vs. Board of Tax Appeals, 93 Phil., 376, No. L-5701 June 23, 1953Galilee RomasantaNo ratings yet
- LTP Legal ResearchDocument4 pagesLTP Legal ResearchNiharika GumasteNo ratings yet
- SecularismDocument31 pagesSecularismIMRAN ALAM100% (2)
- Callangan vs. PeopleDocument12 pagesCallangan vs. PeopleisaaabelrfNo ratings yet
- B.law AssignmentDocument13 pagesB.law AssignmentHarshita B ManjunathNo ratings yet
- C5 LandBank V ColarinaDocument7 pagesC5 LandBank V ColarinaApol GimenezNo ratings yet
- Marbury v. Madison, 5 U.S. 137 (1803)Document25 pagesMarbury v. Madison, 5 U.S. 137 (1803)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law Project PDFDocument13 pagesConstitutional Law Project PDFHarsh GautamNo ratings yet
- 12 Rodriguez vs. SandiganbayanDocument18 pages12 Rodriguez vs. SandiganbayandoraemoanNo ratings yet
- Delhi High Court Judgment On Delimitation of Powers of LG and CMDocument194 pagesDelhi High Court Judgment On Delimitation of Powers of LG and CMLatest Laws TeamNo ratings yet
- Estrella Vs ComElecDocument8 pagesEstrella Vs ComElecJohnday MartirezNo ratings yet
- Perfecto vs. MeerDocument27 pagesPerfecto vs. MeerindiraNo ratings yet
- Doctrines in Political LawDocument13 pagesDoctrines in Political LawJames PagdangananNo ratings yet
- 0june 2017 TheHindu Editorial DigestDocument60 pages0june 2017 TheHindu Editorial DigestSaranyaNo ratings yet
- Asturias Sugar Central, Inc. vs. Commissioner of CustomsDocument8 pagesAsturias Sugar Central, Inc. vs. Commissioner of Customsvince005100% (1)