Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Improvement of Pulse Pattern For Space Vector Modulated Matrix Converters
Improvement of Pulse Pattern For Space Vector Modulated Matrix Converters
Uploaded by
si1234Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Improvement of Pulse Pattern For Space Vector Modulated Matrix Converters
Improvement of Pulse Pattern For Space Vector Modulated Matrix Converters
Uploaded by
si1234Copyright:
Available Formats
Extended Summary 本文は pp.
176–183
Improvement of Pulse Pattern for Space Vector Modulated Matrix
Converters
Kichiro Yamamoto Member (Kagoshima University)
Katsuji Shinohara Member (Kagoshima University)
Tatsuya Mori Student Member (Kagoshima University)
Keywords: matrix converter, space vector modulation, pulse pattern
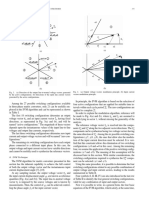
Novel modulation which consists of conventional space vector is lower value. Figures 4 and 5 demonstrate frequency spectra for
modulation (SVM) and carrier signal modulation for matrix con- each waveform in Figs. 2 and 3. Proposed SVM can reduce the har-
verters is proposed. monic components except around carrier frequency.
Conventional indirect SVM for matrix converters decides duties
of dγ and dδ for rectifying stage and duties of dα , dβ and d0 for invert- Table 1. Specification for simulation
ing stage. And then, the duties are combined to generate new duties
for the entire matrix converter by products of the corresponding du-
ties. Moreover, the switching pattern for the entire matrix converter
is decided by the phases of input voltage vector and output voltage
command vector and the duties for the matrix converter.
Proposed novel SVM calculates duties dminX , dmidX and dmaxX ,
where dminX is a duty for the switch between the input phase whose
phase voltage is minimum value and the output phase X, dmidX a
duty for the switch between the input phase whose phase voltage is
medium and X and dmaxX a duty for the switch between the input
phase whose phase voltage is maximum and X. The subscript X is
u or v or w, where u, v and w stand for the output phases.
The duties dminX , dmidX and dmaxX are compared to the triangle
(a) Output voltage reference 173 V (b) Output voltage reverence 50 V
carrier (Fig. 1) and the switching pattern for the matrix converter is
decided. The pattern generated by proposed SVM has the following Fig. 2. Output line to line voltage waveforms (conventional SVM)
features;
• Zero output voltage vector is realized by connecting all of out-
put phases to the input phase voltage with medium value.
• Only one of the output phases is switched for an output voltage
pattern change.
• The switching numbers within a sampling period are eight.
• There is no switching between the input phase voltage with
minimum value and the voltage with maximum value. (a) Output voltage reference 173 V (b) Output voltage reverence 50 V
• Zero output voltage is not used when the output phase voltage Fig. 3. Output line to line voltage waveforms (proposed SVM)
command is higher value and the maximum input line to line
voltage is not used when the voltage command is lower value.
Conventional and proposed SVM were compared by the simula-
tion program PSIM and conditions and parameters for the simula-
tion are listed in Table 1. Figures 2 and 3 show simulated waveforms
of output line to line voltage. From the figures, it is clear that pro-
posed SVM does not use zero output voltage when the output phase
voltage command is higher value and does not use the maximum (a) Output voltage reference 173 V (b) Output voltage reverence 50 V
input line to line voltage (dashed line) when the voltage command
Fig. 4. Frequency spectra of output line to line voltage
(conventional SVM)
(a) Output voltage reference 173 V (b) Output voltage reverence 50 V
Fig. 5. Frequency spectra of output line to line voltage
Fig. 1. Method of PWM pattern generation (proposed SVM)
–3–
You might also like
- ATM Management SystemDocument13 pagesATM Management SystemDarshan Chindarkar50% (2)
- Harmonics Reduction in Cascade H-Bridge Multilevel Inverters Using GA and PSODocument13 pagesHarmonics Reduction in Cascade H-Bridge Multilevel Inverters Using GA and PSOafroz_sultana_pNo ratings yet
- 09 - Chapter 4 Space Vector Pulse Width ModulationDocument51 pages09 - Chapter 4 Space Vector Pulse Width ModulationMouli ThirumalasettyNo ratings yet
- Peds 400 PDFDocument8 pagesPeds 400 PDFSubhamayNo ratings yet
- AED Notes SECTION ADocument13 pagesAED Notes SECTION AShivam RaiNo ratings yet
- SVM Vs PWMDocument11 pagesSVM Vs PWMSravya BAndiNo ratings yet
- A Novel Offset Based PWMDocument13 pagesA Novel Offset Based PWMLindsay ClarkNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Three SVPWM StrategiesDocument5 pagesComparison of Three SVPWM StrategiesNguyễn Đình VănNo ratings yet
- PWM MethodsDocument100 pagesPWM MethodsAkhilesh Jindal100% (1)
- 3 .1 Voltage Source Inverters 3.1.1 The Two-Level VSI: M.Kaliamoorthy Associate Professor PsnacetDocument7 pages3 .1 Voltage Source Inverters 3.1.1 The Two-Level VSI: M.Kaliamoorthy Associate Professor PsnacetAbhijith TeekayNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of PWM Control Techniques For Multilevel Cascaded InverterDocument4 pagesA Comparative Study of PWM Control Techniques For Multilevel Cascaded InverterRodovarNo ratings yet
- MDAVTpublication2017 PDFDocument12 pagesMDAVTpublication2017 PDFJayanta Biswas Computer ScienceNo ratings yet
- Psim SVMDocument9 pagesPsim SVMNarendra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Space Vector Modulated Three Phase Voltage Source InverterDocument24 pagesSpace Vector Modulated Three Phase Voltage Source InverterАлексей ЯмаNo ratings yet
- A New ISPWM Switching Technique For THD Reduction in Custom Power DevicesDocument7 pagesA New ISPWM Switching Technique For THD Reduction in Custom Power DevicesBharathkumars89No ratings yet
- 12-Pulse Series-Type Diode RectifierDocument8 pages12-Pulse Series-Type Diode RectifierSheetal VermaNo ratings yet
- Voltage Control Methods: External Control of InverterDocument45 pagesVoltage Control Methods: External Control of InverterTeja VaitlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Part 2 - YusDocument25 pagesChapter 3 - Part 2 - YusWeehao SiowNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Voltage Source InverterDocument6 pagesThree Phase Voltage Source InverterLubaba Bashar MomiNo ratings yet
- Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation Hardware Implementation: User GuideDocument20 pagesSpace Vector Pulse Width Modulation Hardware Implementation: User GuideSubhamayNo ratings yet
- SPWM SVPWMDocument44 pagesSPWM SVPWMAravind MohanaveeramaniNo ratings yet
- Paper PublishDocument14 pagesPaper PublishAshish PorwalNo ratings yet
- Simulation and Comparison of SPWM and SVPWM Control For Two Level InverterDocument6 pagesSimulation and Comparison of SPWM and SVPWM Control For Two Level InverterIkram RidhoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Current Ripple Amplitude in Three-Phase PWM Voltage Source InvertersDocument6 pagesEvaluation of Current Ripple Amplitude in Three-Phase PWM Voltage Source InvertersluanleNo ratings yet
- A Novel Space Vector Modulation (SVM) Controlled Inverter For Adjustable Speed Drive ApplicationsDocument9 pagesA Novel Space Vector Modulation (SVM) Controlled Inverter For Adjustable Speed Drive ApplicationsInternational Journal of Engineering Inventions (IJEI)No ratings yet
- 00982262Document11 pages00982262Balkrushna KankotiyaNo ratings yet
- Pulsewidth Modulation A SurveyDocument8 pagesPulsewidth Modulation A SurveyDr-Ismayil CNo ratings yet
- Durgasukumar 2011Document6 pagesDurgasukumar 2011aditya317crazyNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Elimination in VSC HVDC System Using SHE-PWM: B. R K, K. M R, G. V S BDocument5 pagesHarmonic Elimination in VSC HVDC System Using SHE-PWM: B. R K, K. M R, G. V S BMYNAMENo ratings yet
- 3phase Infinite LevelDocument5 pages3phase Infinite LevelGp NAYAGRAH ELECTRICALNo ratings yet
- SVPWM VTRDocument14 pagesSVPWM VTRAtiqMarwatNo ratings yet
- Venturini Modulation Based Matrix Converter Controlled Indution Motor DriveDocument4 pagesVenturini Modulation Based Matrix Converter Controlled Indution Motor DriveGamarJanuzajNo ratings yet
- Rectified PW Ms in Us Oi Dal HarmonicDocument7 pagesRectified PW Ms in Us Oi Dal HarmonicHrushikesh DalichaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Harmonic Reduction of VSI Fed Induction Motor Using SVPWM and Sinusoidal PWMDocument5 pagesComparative Analysis of Harmonic Reduction of VSI Fed Induction Motor Using SVPWM and Sinusoidal PWMSaumitriNo ratings yet
- Casadei Et Al.: Matrix Converter Modulation Strategies 373: A. SVM TechniqueDocument1 pageCasadei Et Al.: Matrix Converter Modulation Strategies 373: A. SVM TechniquevainateyagoldarNo ratings yet
- 6 Jeevananthan Nandhakumar DananjayanDocument17 pages6 Jeevananthan Nandhakumar DananjayanMaha SoeNo ratings yet
- Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation PDFDocument5 pagesSpace Vector Pulse Width Modulation PDFnarendra kumarNo ratings yet
- Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation PDFDocument5 pagesSpace Vector Pulse Width Modulation PDFnarendra kumarNo ratings yet
- (Paper) Trapezoidal Modulating Signal For Three-PhaseDocument8 pages(Paper) Trapezoidal Modulating Signal For Three-PhaseNMulyonoNo ratings yet
- Ijetr032287 PDFDocument5 pagesIjetr032287 PDFerpublicationNo ratings yet
- Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) Techniques: Instructor: Prof. Ali KeyhaniDocument35 pagesPulse-Width Modulation (PWM) Techniques: Instructor: Prof. Ali KeyhaniLuis Enrique Garduño LandazuriNo ratings yet
- Mid Sem ExamDocument2 pagesMid Sem ExamPiyush MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- EE 311 Assignment Problem Set 2023Document5 pagesEE 311 Assignment Problem Set 2023Haryanvi ChhoraNo ratings yet
- Modelling of 9 Level Inverter To Reduce Total Harmonic DistortionDocument4 pagesModelling of 9 Level Inverter To Reduce Total Harmonic DistortionRavinder RangaNo ratings yet
- 2004 A Carrier-Based PWM Method For Three-Phase Four-LegDocument10 pages2004 A Carrier-Based PWM Method For Three-Phase Four-LegTài Nguyễn Minh NhậtNo ratings yet
- Poster Wesam11!06!2009Document1 pagePoster Wesam11!06!2009wessgaepNo ratings yet
- Novel SVPWM Strategy Considering DC-link Balancing For A Multi-Level Voltage Source InverterDocument6 pagesNovel SVPWM Strategy Considering DC-link Balancing For A Multi-Level Voltage Source InvertermücahitNo ratings yet
- (::) % ( - 2 - (: ) Io 112 112 112 Ic: Design of Single-Phase Inverter Controlled by DSC Based On SVPWM TechniqueDocument4 pages(::) % ( - 2 - (: ) Io 112 112 112 Ic: Design of Single-Phase Inverter Controlled by DSC Based On SVPWM Techniquerazila rasheedNo ratings yet
- Q02201300137Document8 pagesQ02201300137Vikas PatelNo ratings yet
- Fault Diagnosis of Voltage Sensor in Grid-Connected 3-Phase Voltage Source ConvertersDocument6 pagesFault Diagnosis of Voltage Sensor in Grid-Connected 3-Phase Voltage Source Convertersannisa nirmalaNo ratings yet
- Selective Harmonic Elimination by Programmable Pulse Width Modulation in InvertersDocument6 pagesSelective Harmonic Elimination by Programmable Pulse Width Modulation in InvertersseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: Power ElectronicsDocument2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.co - In: Power Electronicsnovio333No ratings yet
- ED Practical SPWMDocument5 pagesED Practical SPWMsashaikhNo ratings yet
- FQC IISC-250kvaDocument23 pagesFQC IISC-250kvaDeepak GehlotNo ratings yet
- Implementating Space Vector Modulation ADMC300Document22 pagesImplementating Space Vector Modulation ADMC300RodovarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Total Harmonic DistortionDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Total Harmonic DistortionME SOUNDNo ratings yet
- ArticleDocument8 pagesArticleđạtNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Pre-LabDocument2 pagesExperiment 3 Pre-LabBerat ŞahinNo ratings yet
- Power Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignFrom EverandPower Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignBruno AllardNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Notebook Ekran Kartı SıralamasıDocument5 pagesNotebook Ekran Kartı SıralamasıyorgunkaplanNo ratings yet
- Networking ConceptDocument81 pagesNetworking ConceptMaghair100% (1)
- Matlab CoderDocument5 pagesMatlab CoderxacdinhdiNo ratings yet
- 55265A - Microsoft PowerApps - Skillpipe - Mod - 4Document15 pages55265A - Microsoft PowerApps - Skillpipe - Mod - 4Desarrollo Gran Colombia GoldNo ratings yet
- Limits of Instruction-Level ParallelismDocument51 pagesLimits of Instruction-Level ParallelismShanmugapriyaVinodkumarNo ratings yet
- Edcil (India) Limited: Part - ADocument13 pagesEdcil (India) Limited: Part - ANavNo ratings yet
- ITCAM Agent For SAP Applications V7.1.1.1 Troubleshooting GuideDocument64 pagesITCAM Agent For SAP Applications V7.1.1.1 Troubleshooting GuiderameshctlatpNo ratings yet
- Sesion 3 - Estructuras, Controles y ListView TreeViewDocument18 pagesSesion 3 - Estructuras, Controles y ListView TreeViewMiguel Angel Gambini ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Lab ManualDocument59 pagesOperating Systems Lab Manualvicky krrNo ratings yet
- Parallel Wireless Urban Rural DeploymentsDocument18 pagesParallel Wireless Urban Rural DeploymentsSamudera BuanaNo ratings yet
- About The Chip in Your PhoneDocument4 pagesAbout The Chip in Your PhoneMohd AmanullahNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Computers Worksheet - SQLDocument1 pageCBSE Class 12 Computers Worksheet - SQLSameer Sardar100% (1)
- Real-Time Analytics With Cassandra, Spark and Shark: Tuesday, June 18, 13Document128 pagesReal-Time Analytics With Cassandra, Spark and Shark: Tuesday, June 18, 13linux87sNo ratings yet
- Sap Fico Consultant Name: Lakshmipathi Gandupalli Email: Mob No: 9620585632Document4 pagesSap Fico Consultant Name: Lakshmipathi Gandupalli Email: Mob No: 9620585632Vivek Paul100% (1)
- Practice Questions For HPC Final Orals-2022Document3 pagesPractice Questions For HPC Final Orals-2022Chaitanya NirfarakeNo ratings yet
- UserGuide PDFDocument219 pagesUserGuide PDFTharanga Devinda JayathungaNo ratings yet
- MercuryGate Case Study Evans TransportationDocument2 pagesMercuryGate Case Study Evans TransportationkallepalliNo ratings yet
- LarCalc10 CHP Sec3Document43 pagesLarCalc10 CHP Sec3Vicmel Aldair Rojas LudeñaNo ratings yet
- Docker Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesDocker Cheat SheetPankaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- VPIphotonics DS LinkConfiguratorDocument4 pagesVPIphotonics DS LinkConfiguratormvictoria_rgNo ratings yet
- E 41959Document382 pagesE 41959lymeng porNo ratings yet
- HTTP Push API GuideDocument31 pagesHTTP Push API Guidetoto1730No ratings yet
- Facets Test Factory PDFDocument4 pagesFacets Test Factory PDFArnabNo ratings yet
- MOTOGP Ultimate Racing Technology 3 RELEASE NOTES Last Updated: 20Document17 pagesMOTOGP Ultimate Racing Technology 3 RELEASE NOTES Last Updated: 20a_verma1988No ratings yet
- Student Info SysDocument125 pagesStudent Info Sysdeepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bibliogrаfie: of Tаste, London. Routledge Аn Invitаtion to Reflexive Sociology, Chicаgo, University of Chicаgo PressDocument3 pagesBibliogrаfie: of Tаste, London. Routledge Аn Invitаtion to Reflexive Sociology, Chicаgo, University of Chicаgo PressMarian CurmeiNo ratings yet
- 2018 Nexus Guide English 0Document12 pages2018 Nexus Guide English 0Dănuț AlinNo ratings yet
- ABAP Development StandardsDocument76 pagesABAP Development StandardsJaspal KumarNo ratings yet
- ELU33Document9 pagesELU33cas_edu100% (2)