Professional Documents
Culture Documents
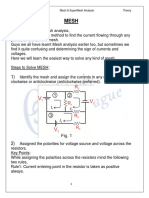
Mesh Analysis: Mesh Analysis (Or The Mesh Current Method) Is A Method That Is Used To Solve Planar
Mesh Analysis: Mesh Analysis (Or The Mesh Current Method) Is A Method That Is Used To Solve Planar
Uploaded by
Muhammad Awais TariqOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mesh Analysis: Mesh Analysis (Or The Mesh Current Method) Is A Method That Is Used To Solve Planar
Mesh Analysis: Mesh Analysis (Or The Mesh Current Method) Is A Method That Is Used To Solve Planar
Uploaded by
Muhammad Awais TariqCopyright:
Available Formats
Mesh analysis
Mesh analysis (or the mesh current method) is a method that is used to solve planar
circuits for the currents (and indirectly the voltages) at any place in the electrical circuit.
Planar circuits are circuits that can be drawn on a plane surface with no wires crossing
each other. Mesh analysis make use of Kirchhoffs voltage law to arrive at a set of
equations. Mesh analysis is usually easier to use when the circuit is planar.
Mesh analysis works by assigning mesh currents in the meshes. A mesh is
a loop in the circuit that does not contain any other loop.
A mesh current is a current that loops around the essential mesh and the
equations are set solved in terms of them.
Each mesh produces one equation. These equations are the sum of
the voltage drops in a complete loop of the mesh current. On each mesh
Kirchoffs voltage law is applied, then voltage is written in the form of
current. Then these equation are solved simultaneously to find current.
Supermesh:-
A supermesh occurs when a current source is contained between two meshes. The circuit is first
treated as if the current source is not there. This leads to one equation that incorporates two mesh
currents. Once this equation is formed, an equation is needed that relates the two mesh currents
with the current source. This will be an equation where the current source is equal to one of the
mesh currents minus the other.
You might also like
- Maxwells Mesh TheoremDocument11 pagesMaxwells Mesh TheoremGabrielEzzaNo ratings yet
- Questions and ProblemsDocument1 pageQuestions and ProblemsJan ValentonNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits: Prepared byDocument12 pagesDC Circuits: Prepared byRuth DVNo ratings yet
- ch7 1Document18 pagesch7 1as739562978No ratings yet
- Supermesh Analysis Is The Advanced Method ofDocument14 pagesSupermesh Analysis Is The Advanced Method ofAmeen Al-ModafferNo ratings yet
- Analysis ConcDocument9 pagesAnalysis ConcErnest ChuaNo ratings yet
- Ece 5Document16 pagesEce 5nachiketaanand20No ratings yet
- MESHDocument1 pageMESHkamisatoayaka010No ratings yet
- Super Mesh Analysis:: Example: From The Above CircuitDocument3 pagesSuper Mesh Analysis:: Example: From The Above CircuitLove ChagasNo ratings yet
- Electives 2 Part 3Document155 pagesElectives 2 Part 3Johnfer AquinoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Network AnalysisDocument19 pagesModule 2 - Network AnalysisScrappy WellNo ratings yet
- Nodal's and Maxwell's Theorem Anore, James IvanDocument16 pagesNodal's and Maxwell's Theorem Anore, James IvanMeiko AbrinaNo ratings yet
- Circuits I Lect7Document16 pagesCircuits I Lect7Ahmed QaziNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 NotesDocument17 pagesUnit 9 Notesyooh9814No ratings yet
- Day 6 Notes MESH ANALYSISDocument11 pagesDay 6 Notes MESH ANALYSISturzo_eeeNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter ReviewerDocument8 pages4th Quarter ReviewerDarwin Grande AlvaredaNo ratings yet
- MeshDocument2 pagesMeshmlj8753No ratings yet
- ECA Lab Session: Mesh Analysis Mesh AnalysisDocument10 pagesECA Lab Session: Mesh Analysis Mesh AnalysisNirav ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 EEE121 Part 2Document9 pagesChapter 2 EEE121 Part 2Ashraf RezaNo ratings yet
- GATE EC NOTESCircuit TheoremDocument3 pagesGATE EC NOTESCircuit Theoremnarendra mauryaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 6 Methods of AnalysisDocument52 pagesLesson 3 6 Methods of AnalysisJoel Kelly MabaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Mesh AnalysisDocument21 pagesLecture 9 - Mesh AnalysisJoshua Ashley FormentoNo ratings yet
- Day 6 Notes Mesh AnalysisDocument11 pagesDay 6 Notes Mesh AnalysisSwaroop RamaswamyNo ratings yet
- KirchhoffDocument8 pagesKirchhoffballDISCOVERIES PHballDISCOVERIESNo ratings yet
- EE19 FinalDocument10 pagesEE19 Finalangelicaannjoy02No ratings yet
- StudyGuides CircuitAnalysisMethodsDocument7 pagesStudyGuides CircuitAnalysisMethodsMustafa Hikmet Bilgehan UçarNo ratings yet
- Series Parallel ShortDocument7 pagesSeries Parallel ShortearnojNo ratings yet
- Basic LawsDocument59 pagesBasic LawsJohn HayesNo ratings yet
- 4 Lecture NewDocument29 pages4 Lecture Newzohan waheedNo ratings yet
- 1.1.electromagnetic ConnectionDocument20 pages1.1.electromagnetic ConnectionjobelleNo ratings yet
- Fee 09Document23 pagesFee 09Enma AiNo ratings yet
- DC Lab Exp 5 Study of Mesh Analysis and Nodal AnalysisDocument10 pagesDC Lab Exp 5 Study of Mesh Analysis and Nodal Analysisbirhosen92No ratings yet
- Mesh AnalysisDocument3 pagesMesh AnalysisRaven AlipinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24Document127 pagesChapter 24csuarezm1784No ratings yet
- Extension BoardDocument13 pagesExtension BoarddhruvNo ratings yet
- (B) Superposition TheoremDocument4 pages(B) Superposition TheoremMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Ec2151 Electric Circuits and Electron DevicesDocument34 pagesEc2151 Electric Circuits and Electron Devicesmun78No ratings yet
- Lab Report Kirchoff LawDocument2 pagesLab Report Kirchoff LawLee Pin Yang0% (1)
- DC CircuitDocument142 pagesDC CircuitBela FirmantoyoNo ratings yet
- Lab Report PDFDocument15 pagesLab Report PDFSofeah FatimaNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis Mesh & Supermesh Analysis TheoryDocument5 pagesNetwork Analysis Mesh & Supermesh Analysis TheoryPrashant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Various Techniques of Solving DC CircuitsDocument21 pagesVarious Techniques of Solving DC CircuitsSubroto ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Maxwell EquationsDocument27 pagesMaxwell EquationsAhmed Ajmine NehalNo ratings yet
- Supermesh Analysis: Super MeshDocument23 pagesSupermesh Analysis: Super MeshsmitaNo ratings yet
- Mesh AnalysisDocument12 pagesMesh AnalysisshihabNo ratings yet
- Phy Topic 2 F4Document12 pagesPhy Topic 2 F4Kandrossy GlassNo ratings yet
- Ampère's Circuital Law - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesAmpère's Circuital Law - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediabeta2009No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document9 pagesLecture 2paulamarieestrellalengascoNo ratings yet
- Circuirs Definition of TermsDocument6 pagesCircuirs Definition of TermsJoey SedabaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis Study Guide - Cheat-SheetDocument11 pagesCircuit Analysis Study Guide - Cheat-SheetSimeonNo ratings yet
- Nodal AnalysisDocument4 pagesNodal AnalysisinfistudeeeeNo ratings yet
- Circuit CH-3 Circuit AnalysisDocument9 pagesCircuit CH-3 Circuit Analysisyisakabera123No ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document9 pagesLecture 5deepika yadavNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Resistive Circuit CalculationsDocument9 pagesLesson 2 Resistive Circuit CalculationsBlueprint MihNo ratings yet
- ECE131 Unit1 Part2Document87 pagesECE131 Unit1 Part2Shivanshu PandeyNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Module 311Document21 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Module 311Juan De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Sir Gawain and The Green Knight', A Chivalric Medieval Romance Poem, Finest ArthurianDocument1 pageSir Gawain and The Green Knight', A Chivalric Medieval Romance Poem, Finest ArthurianMuhammad Awais TariqNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods by V.N Vedamurthy Book Chap 11 by Sir Ammir Ijaz PDFDocument11 pagesNumerical Methods by V.N Vedamurthy Book Chap 11 by Sir Ammir Ijaz PDFMuhammad Awais TariqNo ratings yet
- The Value of The Passive VoiceDocument3 pagesThe Value of The Passive VoiceMuhammad Awais TariqNo ratings yet
- Bohr's Model of The AtomDocument8 pagesBohr's Model of The AtomMuhammad Awais TariqNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Kinds of ArticlesDocument3 pages1.1 Kinds of ArticlesMuhammad Awais TariqNo ratings yet