Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group Discussion Task 1 With Answer
Group Discussion Task 1 With Answer
Uploaded by
Farah IzzatiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Group Discussion Task 1 With Answer
Group Discussion Task 1 With Answer
Uploaded by
Farah IzzatiCopyright:
Available Formats
GROUP DISCUSSION CFD 20302 FOOD CHEMISTRY 1
Group Discussion
CFD 20302 FOOD CHEMISTRY
Question 1:
Discuss the definition of food chemistry and give TWO (2) examples of component
that is important in food.
Food chemistry is concerned with the composition of food and the changes that
it undergoes during processing and under storage. included here are the major
food constituents, carbohydrates, lipids and proteins (macromolecules) and
some of the main reactions between them, including the maillard reaction, a
common reaction between sugars and proteins.
Question 2:
Explain the difference between water and ice.
Ice Water
Water is a unique substance that
covers about 70 percent of the
earths surface, and it is essential
Ice is the solid form of water. It is
Definition for life forms. It is formed by the
formed when water freezes.
combination of two atoms of
hydrogen and one atom of
oxygen.
Specific Heat 0.49 kcal/(kgC) 1 kcal/(kgC)
Density Less Higher
No regular arrangement of
Structure Crystalline structure molecules. Have more compactly
arranged molecule
AIDA SAFINA ARIDI JAN 2017
GROUP DISCUSSION CFD 20302 FOOD CHEMISTRY 2
Question 3:
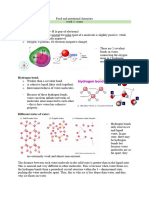
Draw and label the structure of water molecule.
Question 4:
Water is the major constituent of most foods. Although it brings no energy to
food, its existence plays a very important role. Explain the major function of water
to the food product.
Technological need: Knowledge of the water content of food is necessary
for the efficient conduct of the operations of harvesting, drying, storage or
processing. It is a key parameter for evaluating and controlling the risks of
deterioration during storage of foodstuffs.
Universal Solvent. The many biochemical interactions occurring in living
organismshuman, animal, and plantcould not occur in the absence of
a solvent environment. Water is considered to be the earths universal
AIDA SAFINA ARIDI JAN 2017
GROUP DISCUSSION CFD 20302 FOOD CHEMISTRY 3
solvent. The fluid substance, mostly water, within and around the cell is a
solvent that contains many dissolved substances called solutes. Combining
a solvent and a solute result in either a solution, a colloidal dispersion, a
suspension, or an emulsion. These mixtures differ from each other based
on the size or solubility of their solutes.
Heat Transfer. Water both transfers and moderates the effects of heat. A
potato heated by itself in a pan will burn. but surrounding that same potato
with water ensures that the heat will be evenly distributed. Water also
transfers heat more efficiently, which explains why a potato heats faster in
boiling water than in the oven.
Question 5:
As a food technology student, it is important for you to understand the water
activity in food product. Explain the concept of water activity and give two
examples how water activity can affect the quality of the product produced.
Water activity or aw is the partial vapor pressure of water in a substance
divided by the standard state partial vapor pressure of water. In the field
of food science, the standard state is most often defined as the partial
vapor pressure of pure water at the same temperature. Using this
particular definition, pure distilled water has a water activity of exactly
one.
Higher aw substances tend to support more microorganisms. Bacteria
usually require at least 0.91, and fungi at least 0.7.
Food designers use water activity to formulate shelf-stable food. If a
product is kept below a certain water activity, then mold growth is
inhibited. This results in a longer shelf life.
Controlling non-enzymatic browning reactions. Food such as carbohydrate
and protein are prone to non- enzymatic browning reaction called Maillard
reaction. The increase in aw, will also increase in Maillard reaction
therefore to control Maillard reaction
AIDA SAFINA ARIDI JAN 2017
GROUP DISCUSSION CFD 20302 FOOD CHEMISTRY 4
Question 6:
Explain the properties of water molecule. Give appropriate example of application
to each properties that you explain.
Water has a high specific heat. Specific heat is the amount of energy
required to change the temperature of a substance. Because water has a
high specific heat, it can absorb large amounts of heat energy before it
begins to get hot. It also means that water releases heat energy slowly
when situations cause it to cool. Water's high specific heat allows for the
moderation of the Earth's climate and helps organisms regulate their body
temperature more effectively.
Water is also a good solvent, due to its polarity. Substances that will mix
well and dissolve in water (e.g. salts) are known as hydrophilic ("water-
loving") substances, while those that do not mix well with water (e.g. fats
and oils), are known as hydrophobic ("water-fearing") substances.
Question 7:
Briefly explain what is pH and why pH is important in food. Relate your explanation
with water properties and give example of low acidic and basic food product.
Atoms can gain or lose electrons in order to form ions in a process called
ionization (compounds formed in this way are called ionic compounds).
When ionic compounds dissolve in water, their ions separate from one
another in a process called dissociation. One interesting feature of water
and many other covalent compounds is that they too can dissociate into
ions.
pH (potential of hydrogen) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or
basicity of an aqueous solution. It is approximately the negative of the base
10 logarithm of the molar concentration, measured in units of moles per
liter, of hydrogen ions. Hydrogen ions are spontaneously generated in pure
water by the dissociation (ionization) of a small percentage of water
molecules.
When water dissociates, one of the hydrogen nuclei leaves its electron
behind with the oxygen atom to become a hydrogen ion, while the oxygen
and other hydrogen atoms become a hydroxide ion. Since the hydrogen
AIDA SAFINA ARIDI JAN 2017
GROUP DISCUSSION CFD 20302 FOOD CHEMISTRY 5
ion has no electron to neutralize the positive charge on its proton, it has a
full unit of positive charge and is symbolized as H+. The hydroxide ion
retains the electron left behind and thus has a full unit of negative charge,
symbolized by OH-. The hydrogen ion (proton) does not wander long by
itself before it attaches to the oxygen atom of a second un-ionized water
molecule to form a hydronium ion (H3O +)
Low acidic food is vinegar and lemon juice
Basic food product is baking soda
Question 8:
Explain the difference between free water and bound water.
Water that can be extracted easily from foods by squeezing or cutting or
pressing is known as free water. This is water in or on the surface that will
evaporate with a moisture balance.
water that cannot be extracted easily is termed as bound water. It may be
caught in capillaries, fibers or held onto via chemical reactions.
AIDA SAFINA ARIDI JAN 2017
GROUP DISCUSSION CFD 20302 FOOD CHEMISTRY 6
Rules:
1. 15 minutes to discuss and prepare the materials.
2. Stay in your group, do not mingle around other group.
3. Discuss your task seriously!
AIDA SAFINA ARIDI JAN 2017
You might also like
- HIRARC Table MIGDocument3 pagesHIRARC Table MIGFarah Izzati33% (3)
- HIRARC Table Arc WeldingDocument1 pageHIRARC Table Arc WeldingFarah Izzati67% (6)
- WaterpropertiestextDocument38 pagesWaterpropertiestextapi-261447125No ratings yet
- Workplace Inspection Checklist PDFDocument4 pagesWorkplace Inspection Checklist PDFFarah Izzati100% (2)
- Practical 5 JKKP Form JKKP 8Document5 pagesPractical 5 JKKP Form JKKP 8Farah Izzati100% (1)
- BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES-waterDocument4 pagesBIOLOGICAL MOLECULES-watertsteadmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Biological Molecules: WaterDocument15 pagesChapter 1: Biological Molecules: WaterChong Hyen100% (1)
- 1.1 WaterDocument15 pages1.1 Waterjennymarimuthu3No ratings yet
- EMGBS-Bio 11. U.2 NoteDocument77 pagesEMGBS-Bio 11. U.2 Notenafhire2021No ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument8 pagesBiological MoleculeststeadmanNo ratings yet
- Biological ChemistryDocument62 pagesBiological ChemistryCapital AceNo ratings yet
- Lec4 Role of Water in Food and Its Shelf LifeDocument17 pagesLec4 Role of Water in Food and Its Shelf LifeDIBINo ratings yet
- Properties of WaterDocument154 pagesProperties of WaterGayathri AnandNo ratings yet
- (CLEAN) - Experiment2 With AnswersDocument4 pages(CLEAN) - Experiment2 With AnswersLemon AdeNo ratings yet
- Water's Most Important Biochemical Role: The SolventDocument2 pagesWater's Most Important Biochemical Role: The SolventMöhä HàmouliliNo ratings yet
- Biol 325 Notes - BiochemistryDocument27 pagesBiol 325 Notes - BiochemistryKargboNo ratings yet
- 5 Water LectureDocument37 pages5 Water Lecturevanessa biliyaNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Water1Document7 pages2.4 Water1SaaraNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument161 pagesBiology NotesBlohsh KeenenNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Notes - 31 Chemical Elements and WaterDocument2 pagesIB Biology Notes - 31 Chemical Elements and WaterJohn Philip D. NapalNo ratings yet
- Updated Biochemistry Notes 2022Document17 pagesUpdated Biochemistry Notes 2022vandytommy308No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document12 pagesUnit 2Yitbarek TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Chap04 - Science of Water Sources - Part 1Document68 pagesChap04 - Science of Water Sources - Part 1gua leeNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Water and LifeDocument9 pagesModule 3 - Water and LifeAlmira M BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Cayamba (Anaphys M1L2)Document2 pagesCayamba (Anaphys M1L2)Eljen Dave CayambaNo ratings yet
- Critical Book Report Paper As A Product of Critical Books Review Assignment Material Water (H O)Document13 pagesCritical Book Report Paper As A Product of Critical Books Review Assignment Material Water (H O)Maya JenitaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry WaterDocument3 pagesBiochemistry WaterRory DrewNo ratings yet
- Water Is A Vital and Ubiquitous Compound Essential For Life On EarthDocument2 pagesWater Is A Vital and Ubiquitous Compound Essential For Life On EarthSADAFAL SINGHNo ratings yet
- Food and Nutritional Chemistry Week 5 WaterDocument7 pagesFood and Nutritional Chemistry Week 5 WaterlucyNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen/Hydrolysis: James Ivan Villareal Christopher Joseph Baisa Anne Mari F. FernandoDocument13 pagesHydrogen/Hydrolysis: James Ivan Villareal Christopher Joseph Baisa Anne Mari F. FernandoClarold DaigoNo ratings yet
- Biology: An Introduction: Specific Learning OutcomesDocument6 pagesBiology: An Introduction: Specific Learning OutcomesDerrick de los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chem Project ASWATHDocument22 pagesChem Project ASWATHAswathNo ratings yet
- Gchem2 Q3 Las WK1 Day4Document2 pagesGchem2 Q3 Las WK1 Day4mae.joan.reposposaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 2 Properties of WaterDocument26 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 2 Properties of WaterSahar GhanemNo ratings yet
- Chemicals of Life 1 3Document30 pagesChemicals of Life 1 3kitderoger_391648570No ratings yet
- Title of Assignment: Water PropertiesDocument10 pagesTitle of Assignment: Water PropertiesAriful IslamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Oceanography PDFDocument34 pagesChemical Oceanography PDFLia Kusumawati100% (1)
- Water For Pharmaceutical UseDocument40 pagesWater For Pharmaceutical UseKeith OmwoyoNo ratings yet
- Handout 3Document8 pagesHandout 3Naomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Biology-Biological-Molecules-Part - HTML: WaterDocument3 pagesBiology-Biological-Molecules-Part - HTML: Watersy ing ingNo ratings yet
- AFS 2211 - FUNDAMENTALS OF FOOD CHEMISTRY - Water PDFDocument40 pagesAFS 2211 - FUNDAMENTALS OF FOOD CHEMISTRY - Water PDFderrickNo ratings yet
- Water: Water Molecule's StructureDocument2 pagesWater: Water Molecule's StructureCheong Yong XuanNo ratings yet
- Properties of Water: Points/Mrcwaterwalk - Waterpro Pertiesqu..Document47 pagesProperties of Water: Points/Mrcwaterwalk - Waterpro Pertiesqu..Alicia JaneNo ratings yet
- Molecules of Life: 1.1 WATER 1.2 Carbohydrates 1.3 Lipids 1.4 Proteins 1.5 Dna & RnaDocument40 pagesMolecules of Life: 1.1 WATER 1.2 Carbohydrates 1.3 Lipids 1.4 Proteins 1.5 Dna & RnaRAFIQHAH SAFIAH BINTI MOHD SHAHNo ratings yet
- Molecules of Life: 1.1 WATER 1.2 Carbohydrates 1.3 Lipids 1.4 Proteins 1.5 Dna and Rna MoleculesDocument40 pagesMolecules of Life: 1.1 WATER 1.2 Carbohydrates 1.3 Lipids 1.4 Proteins 1.5 Dna and Rna MoleculesJack Si Yi WeiNo ratings yet
- Adv Cert in FS - Water - Protein - RC 2023Document53 pagesAdv Cert in FS - Water - Protein - RC 2023brrfjyk2g2No ratings yet
- What Is WaterDocument8 pagesWhat Is WaterKicki AnderssonNo ratings yet
- CBR Water Genchem Task 1Document19 pagesCBR Water Genchem Task 1Maya JenitaNo ratings yet
- Exercise6 Water DELAVEGADocument11 pagesExercise6 Water DELAVEGABuH BuHNo ratings yet
- 02 01 Properties of WaterDocument4 pages02 01 Properties of Waterphantomtree309No ratings yet
- Inorganic Compounds PPT 23-24Document24 pagesInorganic Compounds PPT 23-24gsturkozNo ratings yet
- Expressing The Significance of Water in Living MatterDocument6 pagesExpressing The Significance of Water in Living MatterJacinth ManuelNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules AS Bio 2022Document20 pagesBiological Molecules AS Bio 2022MrTechnomasterNo ratings yet
- Role of PH & Redox ReactionsDocument10 pagesRole of PH & Redox Reactionsmj recillaNo ratings yet
- Role of PH & Redox ReactionsDocument10 pagesRole of PH & Redox Reactionsmj recillaNo ratings yet
- Water Is A TransparentDocument1 pageWater Is A Transparentshubh cards bhilwara Wedding cardsNo ratings yet
- 02 WaterDocument4 pages02 WaterSadia BatoolNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة ٢Document7 pagesالمحاضرة ٢Mahmoud KhlifaNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument6 pagesPDF DocumentKevin MaharajNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Wonders of Water 1Document11 pagesExploring The Wonders of Water 1Shadrak Aldrick LimNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Biochemistry: BiomoleculesDocument91 pagesAspects of Biochemistry: BiomoleculesGeo NalobNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument29 pagesChemistry Projectvisw2101No ratings yet
- Principles of Chem ProjectDocument13 pagesPrinciples of Chem ProjectzeinabNo ratings yet
- Oil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandOil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Discussion Exp 2 PicklingDocument2 pagesDiscussion Exp 2 PicklingFarah Izzati100% (6)
- Test 1 - Sept16 AnswerDocument5 pagesTest 1 - Sept16 AnswerFarah IzzatiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2.2 Thevenin Theorem: Nur Humaira, Nur Faranisya, Nur Farah Izzati, Nurain Firzana, Nur SyafiqahDocument10 pagesTutorial 2.2 Thevenin Theorem: Nur Humaira, Nur Faranisya, Nur Farah Izzati, Nurain Firzana, Nur SyafiqahFarah IzzatiNo ratings yet
- Exp.5-Reaction of Alkanes, Alkenes, and CycloalkanesDocument27 pagesExp.5-Reaction of Alkanes, Alkenes, and CycloalkaneszazoNo ratings yet
- Surface ChemistryDocument58 pagesSurface ChemistryAtie IekahNo ratings yet
- Thesis Zinc OxideDocument6 pagesThesis Zinc Oxideotmxmjhld100% (1)
- Bonding Process by AdhesivesDocument2 pagesBonding Process by AdhesivesPritam100% (1)
- 1 PCCC3 3C NielsenDocument17 pages1 PCCC3 3C NielsenchemengNo ratings yet
- How To Properly Size A Steam TrapDocument4 pagesHow To Properly Size A Steam TrapJessicalba Lou100% (2)
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Syllabus, 2&16 Mark QuestionsDocument43 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Syllabus, 2&16 Mark Questionsdellibabu509No ratings yet
- Nist SP 250-91Document131 pagesNist SP 250-91QC GLOBALINSIGNIANo ratings yet
- Chemiluminescence ExamplesDocument3 pagesChemiluminescence ExamplesJex RoinderNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Unsteady State Heat TransferDocument26 pagesExperiment 5 Unsteady State Heat TransferFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- Ascorbic Acid Encapsulation in A Glassy Carbohydrate Matrix Via Hot Melt Extrusion: Preparation and Characterization.Document7 pagesAscorbic Acid Encapsulation in A Glassy Carbohydrate Matrix Via Hot Melt Extrusion: Preparation and Characterization.Chus Otto BellostaNo ratings yet
- Thesis PDFDocument190 pagesThesis PDFHien TranNo ratings yet
- FrictionDocument14 pagesFrictionManvendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Analysis - To - Determine - Optimum - Steam - Pressure - Before DeaeratorDocument9 pagesAnalysis - To - Determine - Optimum - Steam - Pressure - Before DeaeratorMas ZuhadNo ratings yet
- Three Phases of Matter: La Fortuna CollegeDocument3 pagesThree Phases of Matter: La Fortuna CollegePpm NovaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning TechnologyDocument285 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning Technologyangel100% (1)
- IB Chemistry Questions and Answers PDFDocument5 pagesIB Chemistry Questions and Answers PDFMAK Mind Attracts KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingDocument10 pagesCSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Biochem Basics PreviewDocument14 pagesBiochem Basics PreviewspeareeD :3No ratings yet
- Drug Receptor InteractionsDocument29 pagesDrug Receptor InteractionscsujithaNo ratings yet
- Hansen Solubility ParameterDocument82 pagesHansen Solubility ParameterAji PratamaNo ratings yet
- Journal MEKDocument9 pagesJournal MEKRiska Ika100% (1)
- Unit 3 Fiber Optics Lecture 1 PDFDocument38 pagesUnit 3 Fiber Optics Lecture 1 PDFshivangi SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics AssinmentDocument9 pagesChemical Kinetics AssinmentKhushi TiwariNo ratings yet
- Wet Gas Seal On Centrifugal Pump - Eagle BrugmannDocument30 pagesWet Gas Seal On Centrifugal Pump - Eagle BrugmannEliyanto E BudiartoNo ratings yet
- An Improved Synthesis of 5-Amino-3-NitroDocument16 pagesAn Improved Synthesis of 5-Amino-3-Nitrokby36No ratings yet
- Selecting The Right Insulation Material PDFDocument6 pagesSelecting The Right Insulation Material PDFShahab Z AhmedNo ratings yet
- HP Steam Methane Reformer Vs Electrolysis TechnologyDocument2 pagesHP Steam Methane Reformer Vs Electrolysis Technologyaegean227No ratings yet
- Karl-Fischer TitrationDocument19 pagesKarl-Fischer TitrationSomnath BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Ammonia RecoveryDocument136 pagesAmmonia RecoveryWagus GinanjarNo ratings yet