Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsFailure Mode and Effects Analysis (F.M.E.A.)
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (F.M.E.A.)
Uploaded by
RathnakrajaFailure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a technique used to consider all possible ways in which a process, design, or system could fail. It was first developed over 60 years ago and is now widely used in industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing. FMEA identifies potential failures, assesses their effects and causes, and determines how to minimize risks. When conducted during product development stages, FMEA can help reduce costs from scrap, rework, and warranty claims by building quality into the design.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Quality Core ToolsDocument14 pagesQuality Core Toolsالعاب الاطفال- jeux enfantsNo ratings yet
- CQI Wessex ISO-TS CORE TOOLS Presentation John Skinner 11dec12Document54 pagesCQI Wessex ISO-TS CORE TOOLS Presentation John Skinner 11dec12Gabryel BogdanNo ratings yet
- Quick Study For Computer Keyboard Short CutsDocument2 pagesQuick Study For Computer Keyboard Short Cutsmahazari100% (3)
- A Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing IndustryDocument8 pagesA Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing IndustryBONFRINGNo ratings yet
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (Fmea) : Mechanical Engineering, September 1993Document5 pagesFailure Modes and Effects Analysis (Fmea) : Mechanical Engineering, September 1993JeevanNo ratings yet
- GS-0002D, Design FMEADocument26 pagesGS-0002D, Design FMEAmesa142100% (1)
- Fmea SoproDocument9 pagesFmea SoprofernandoNo ratings yet
- Failure Modes and Effects AnalysisDocument5 pagesFailure Modes and Effects AnalysisBoBo KyawNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report - Atharva - Sanglikar - 19121236Document22 pagesSeminar Report - Atharva - Sanglikar - 19121236Atharva SanglikarNo ratings yet
- All Tools in OneDocument38 pagesAll Tools in Oneom_3334No ratings yet
- History of FMEA: FMEA Cause and Effect DiagramDocument8 pagesHistory of FMEA: FMEA Cause and Effect Diagramervikas34No ratings yet
- Development of Quality System For Engine AssemblyDocument55 pagesDevelopment of Quality System For Engine AssemblysvrbchaudhariNo ratings yet
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)Document9 pagesFailure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)yashar2500No ratings yet
- The 5 Core ToolDocument17 pagesThe 5 Core ToolRajesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- The 5 Core ToolDocument17 pagesThe 5 Core ToolRajesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- A Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing IndustryDocument9 pagesA Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing Industrysanjay chamoliNo ratings yet
- Minor Project (Research Report)Document50 pagesMinor Project (Research Report)Atul DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode Effect AnalysisDocument7 pagesFailure Mode Effect AnalysisRewati KumarNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effective AnalysisDocument197 pagesFailure Mode and Effective AnalysisHarsha MPNo ratings yet
- Design Failure Mode Effect Analysis of A Centrifugal Oil Cleaner and Plan For Validation of The DfmeaDocument8 pagesDesign Failure Mode Effect Analysis of A Centrifugal Oil Cleaner and Plan For Validation of The DfmeaEfren RodríguezsNo ratings yet
- PPAPDocument7 pagesPPAPsunnysunsationNo ratings yet
- Qgem Management Solution: Welcomes You To Failure Mode & Effects Analysis (Fmea) Training Course 4 EditionDocument103 pagesQgem Management Solution: Welcomes You To Failure Mode & Effects Analysis (Fmea) Training Course 4 EditionVINOTH100% (2)
- Introduction To FMEADocument57 pagesIntroduction To FMEAypo41956No ratings yet
- Cause-And-Effect Diagram Check Sheet: Control Charts: Histogram: Pareto Chart: Scatter Diagram StratificationDocument3 pagesCause-And-Effect Diagram Check Sheet: Control Charts: Histogram: Pareto Chart: Scatter Diagram StratificationAlain DoniNo ratings yet
- R.Hariharan, Lect / EeeDocument31 pagesR.Hariharan, Lect / EeeJinto AntonyNo ratings yet
- Fmea 101Document3 pagesFmea 101SukanthNo ratings yet
- Design, Structural Analysis and D-FMEA of Automobile Manual Transmission Gear-BoxDocument32 pagesDesign, Structural Analysis and D-FMEA of Automobile Manual Transmission Gear-BoxAtul DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Application of Fmea Method in A Manufacturing Organization Focused On QualityDocument7 pagesApplication of Fmea Method in A Manufacturing Organization Focused On QualityRudra DasNo ratings yet
- The Application of PFMEA For Roller Bearings ProductionDocument7 pagesThe Application of PFMEA For Roller Bearings ProductionEun Lay ChuanNo ratings yet
- f7f1 PDFDocument8 pagesf7f1 PDFAnurag JaiswarNo ratings yet
- Hazen Alrasyid (3333160102)Document14 pagesHazen Alrasyid (3333160102)Ihadz CleverleyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Product Quality Planning PDFDocument35 pagesAdvanced Product Quality Planning PDFThuận HoàngNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AIAGDocument9 pagesIntroduction To AIAGAngelo ZerellaNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effect AnalysisDocument9 pagesFailure Mode and Effect AnalysisameliaNo ratings yet
- Identification & Mitigation of Potential Failures of Automotive Hvac Air Management System Using Failure Mode & Effects AnalysisDocument8 pagesIdentification & Mitigation of Potential Failures of Automotive Hvac Air Management System Using Failure Mode & Effects Analysisashishmechengg31No ratings yet
- DET2009 LYZheng KC-FMEADocument12 pagesDET2009 LYZheng KC-FMEAvishal.khalane9No ratings yet
- FMEADocument42 pagesFMEAibal_machine100% (1)
- BY Kiran S Shinde Kishor L RasalDocument10 pagesBY Kiran S Shinde Kishor L RasalKiran ShindeNo ratings yet
- FMEA PresentationDocument68 pagesFMEA PresentationParas KumarNo ratings yet
- FMEADocument4 pagesFMEAMDR PRAPHUNo ratings yet
- Are The Tools That Help Us Greatly Reduce Quality Problems in The Launch of New Products Apqp & CP, Amef, Control Plan, SPC, R & R and PpapDocument4 pagesAre The Tools That Help Us Greatly Reduce Quality Problems in The Launch of New Products Apqp & CP, Amef, Control Plan, SPC, R & R and PpapSergio Cristobal Bonilla CegadorNo ratings yet
- Presentation On FmeaDocument15 pagesPresentation On FmeaA Veda SagarNo ratings yet
- Has Introduced The First International Guide On Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)Document2 pagesHas Introduced The First International Guide On Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)Ionut Eduard100% (2)
- FMEADocument29 pagesFMEAKarthik Kr100% (1)
- Fmea and FmecaDocument14 pagesFmea and FmecaLindsay SleijpenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Advanced Product Quality PlanningDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Advanced Product Quality PlanningAbraham GuerraNo ratings yet
- Assignments-Mba Sem-Iii: Subject Code: QM0004Document16 pagesAssignments-Mba Sem-Iii: Subject Code: QM0004Mithesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effective AnalysisDocument214 pagesFailure Mode and Effective AnalysisAddhew PraseetyoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Failure Mode?Document16 pagesWhat Is A Failure Mode?Cuenta PokemonNo ratings yet
- Publisher Namespringer, London Print Isbn978-1-84882-471-3 Online Isbn978-1-84882-472-0 Ebook PackagesDocument3 pagesPublisher Namespringer, London Print Isbn978-1-84882-471-3 Online Isbn978-1-84882-472-0 Ebook PackagesEva WatiNo ratings yet
- Fmea VviDocument52 pagesFmea VviBobby Edwin100% (2)
- Tcs InterviewDocument10 pagesTcs InterviewYogi GowdaNo ratings yet
- FmeaDocument1 pageFmeaRanjith RamNo ratings yet
- FMEA in ServicesDocument6 pagesFMEA in ServicesPratik IyerNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Management Assignment-1Document16 pagesMaintenance Management Assignment-1ishika SHANDILYANo ratings yet
- Foc FmeaDocument6 pagesFoc FmeaShimon PopaNo ratings yet
- TQM Assignment On Failure Mode Effect Analysis: Srideep Kumar Mohanta 215112033 2013-14Document13 pagesTQM Assignment On Failure Mode Effect Analysis: Srideep Kumar Mohanta 215112033 2013-14mechatronicsmkNo ratings yet
- Innovative Approach To FMEA Facilitation: Govind RamuDocument34 pagesInnovative Approach To FMEA Facilitation: Govind Ramukskr_44100% (1)
- FMEA konkret: Preventive risk analysis concretely with FMEA plus. The series of successful developers, trainers and presenters.From EverandFMEA konkret: Preventive risk analysis concretely with FMEA plus. The series of successful developers, trainers and presenters.No ratings yet
- List of Piping CodesDocument43 pagesList of Piping CodesRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Nonpolar Covalent Bonds: ChemistryDocument9 pagesNonpolar Covalent Bonds: ChemistryRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Inspection / TestDocument7 pagesMechanical Inspection / TestRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Causes and Cures of Common Welding TroublesDocument1 pageCauses and Cures of Common Welding TroublesRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Solid State Welding ProcessDocument17 pagesSolid State Welding ProcessRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Nonpolar Covalent Bonds: ChemistryDocument9 pagesNonpolar Covalent Bonds: ChemistryRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- B-16-05107 KMT Stellite HardfacingAlloys Brochure en LRDocument28 pagesB-16-05107 KMT Stellite HardfacingAlloys Brochure en LRromanosky11No ratings yet
- Difference Between DT & NDTDocument3 pagesDifference Between DT & NDTRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Metallurgists-Quiz No.6 (: Mutiple Choice QuestionsDocument6 pagesMetallurgists-Quiz No.6 (: Mutiple Choice QuestionsRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- What Is Stellite SteelDocument11 pagesWhat Is Stellite SteelRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- CNC Machining Cycle Time CalculationDocument4 pagesCNC Machining Cycle Time CalculationRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Location: C:/NSH DOCUMENTS/MISCELLANIOUS/Radiograph Refrences .. Folder Item DescriptionDocument2 pagesLocation: C:/NSH DOCUMENTS/MISCELLANIOUS/Radiograph Refrences .. Folder Item DescriptionRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Welding DictionaryDocument59 pagesWelding DictionaryRathnakraja100% (1)
- MMA Electrode ClassificationDocument3 pagesMMA Electrode ClassificationRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Weight CalculationDocument17 pagesWeight CalculationRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (F.M.E.A.)
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (F.M.E.A.)
Uploaded by
Rathnakraja0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesFailure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a technique used to consider all possible ways in which a process, design, or system could fail. It was first developed over 60 years ago and is now widely used in industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing. FMEA identifies potential failures, assesses their effects and causes, and determines how to minimize risks. When conducted during product development stages, FMEA can help reduce costs from scrap, rework, and warranty claims by building quality into the design.
Original Description:
FMEA
Original Title
FMEAina
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFailure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a technique used to consider all possible ways in which a process, design, or system could fail. It was first developed over 60 years ago and is now widely used in industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing. FMEA identifies potential failures, assesses their effects and causes, and determines how to minimize risks. When conducted during product development stages, FMEA can help reduce costs from scrap, rework, and warranty claims by building quality into the design.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesFailure Mode and Effects Analysis (F.M.E.A.)
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (F.M.E.A.)
Uploaded by
RathnakrajaFailure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a technique used to consider all possible ways in which a process, design, or system could fail. It was first developed over 60 years ago and is now widely used in industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing. FMEA identifies potential failures, assesses their effects and causes, and determines how to minimize risks. When conducted during product development stages, FMEA can help reduce costs from scrap, rework, and warranty claims by building quality into the design.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
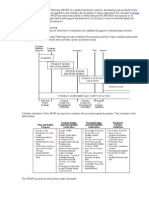
FAILURE MODE AND EFFECTS ANALYSIS (F.M.E.A.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis was first developed over 60 years
ago.
The Aerospace industry adopted FMEA during the 1960s. It is now in
widespread use in the Automotive industry.
Many manufacturers of automotive vehicles are now insisting that
suppliers use FMEA on new products and during product changes.
Its use in other industries is a comparatively recent phenomenon.
What is F.M.E.A ?
FMEA is a design and pre-product planning technique which structures
the engineers thought processes to consider every conceivable way in
which a component or product may fail. It is an analytical technique
which
Identifies potential failure modes
Assesses potential effects to a customer
Identifies potential causes of failure
Identifies needs for changes
Minimises potential cause of failure
Facilitates Inter-departmental dialogue
Facilitates identification of critical characteristics in a process
An FMEA enables engineers to look at all aspects of design and
process in formalised and structured way.
The potential problems are recorded, numerically assessed and
ranked in order, for action to be taken.
When to use FMEA
An FMEA study can be carried out at any stage during the
development of a product. However the ideal times to use this
technique are
At the original concept stage when specifications are being
established
As soon as the design is finalised but before any manufacturing of
tooling etc., is commenced
when the processing decisions are being made
when major changes are to be carried out, either to the design or
process alterations
After an FMEA study has been conducted and corrective actions
taken; i.e., re-assessment
Benefits of FMEA
FMEA is an upstream, off-line activity and represents a quality
prevention cost. It is concerned with building quality into the product
prior to manufacture. Properly conducted, it should therefore lead to
A reduction of scrap, and rework activities
Reduction in inspection and process control activities
Reduction of failure conditions
Reduction in warranty costs
Overall reduction in manufacturing costs
Improved customer satisfaction
You might also like
- Quality Core ToolsDocument14 pagesQuality Core Toolsالعاب الاطفال- jeux enfantsNo ratings yet
- CQI Wessex ISO-TS CORE TOOLS Presentation John Skinner 11dec12Document54 pagesCQI Wessex ISO-TS CORE TOOLS Presentation John Skinner 11dec12Gabryel BogdanNo ratings yet
- Quick Study For Computer Keyboard Short CutsDocument2 pagesQuick Study For Computer Keyboard Short Cutsmahazari100% (3)
- A Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing IndustryDocument8 pagesA Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing IndustryBONFRINGNo ratings yet
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (Fmea) : Mechanical Engineering, September 1993Document5 pagesFailure Modes and Effects Analysis (Fmea) : Mechanical Engineering, September 1993JeevanNo ratings yet
- GS-0002D, Design FMEADocument26 pagesGS-0002D, Design FMEAmesa142100% (1)
- Fmea SoproDocument9 pagesFmea SoprofernandoNo ratings yet
- Failure Modes and Effects AnalysisDocument5 pagesFailure Modes and Effects AnalysisBoBo KyawNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report - Atharva - Sanglikar - 19121236Document22 pagesSeminar Report - Atharva - Sanglikar - 19121236Atharva SanglikarNo ratings yet
- All Tools in OneDocument38 pagesAll Tools in Oneom_3334No ratings yet
- History of FMEA: FMEA Cause and Effect DiagramDocument8 pagesHistory of FMEA: FMEA Cause and Effect Diagramervikas34No ratings yet
- Development of Quality System For Engine AssemblyDocument55 pagesDevelopment of Quality System For Engine AssemblysvrbchaudhariNo ratings yet
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)Document9 pagesFailure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)yashar2500No ratings yet
- The 5 Core ToolDocument17 pagesThe 5 Core ToolRajesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- The 5 Core ToolDocument17 pagesThe 5 Core ToolRajesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- A Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing IndustryDocument9 pagesA Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing Industrysanjay chamoliNo ratings yet
- Minor Project (Research Report)Document50 pagesMinor Project (Research Report)Atul DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode Effect AnalysisDocument7 pagesFailure Mode Effect AnalysisRewati KumarNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effective AnalysisDocument197 pagesFailure Mode and Effective AnalysisHarsha MPNo ratings yet
- Design Failure Mode Effect Analysis of A Centrifugal Oil Cleaner and Plan For Validation of The DfmeaDocument8 pagesDesign Failure Mode Effect Analysis of A Centrifugal Oil Cleaner and Plan For Validation of The DfmeaEfren RodríguezsNo ratings yet
- PPAPDocument7 pagesPPAPsunnysunsationNo ratings yet
- Qgem Management Solution: Welcomes You To Failure Mode & Effects Analysis (Fmea) Training Course 4 EditionDocument103 pagesQgem Management Solution: Welcomes You To Failure Mode & Effects Analysis (Fmea) Training Course 4 EditionVINOTH100% (2)
- Introduction To FMEADocument57 pagesIntroduction To FMEAypo41956No ratings yet
- Cause-And-Effect Diagram Check Sheet: Control Charts: Histogram: Pareto Chart: Scatter Diagram StratificationDocument3 pagesCause-And-Effect Diagram Check Sheet: Control Charts: Histogram: Pareto Chart: Scatter Diagram StratificationAlain DoniNo ratings yet
- R.Hariharan, Lect / EeeDocument31 pagesR.Hariharan, Lect / EeeJinto AntonyNo ratings yet
- Fmea 101Document3 pagesFmea 101SukanthNo ratings yet
- Design, Structural Analysis and D-FMEA of Automobile Manual Transmission Gear-BoxDocument32 pagesDesign, Structural Analysis and D-FMEA of Automobile Manual Transmission Gear-BoxAtul DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Application of Fmea Method in A Manufacturing Organization Focused On QualityDocument7 pagesApplication of Fmea Method in A Manufacturing Organization Focused On QualityRudra DasNo ratings yet
- The Application of PFMEA For Roller Bearings ProductionDocument7 pagesThe Application of PFMEA For Roller Bearings ProductionEun Lay ChuanNo ratings yet
- f7f1 PDFDocument8 pagesf7f1 PDFAnurag JaiswarNo ratings yet
- Hazen Alrasyid (3333160102)Document14 pagesHazen Alrasyid (3333160102)Ihadz CleverleyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Product Quality Planning PDFDocument35 pagesAdvanced Product Quality Planning PDFThuận HoàngNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AIAGDocument9 pagesIntroduction To AIAGAngelo ZerellaNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effect AnalysisDocument9 pagesFailure Mode and Effect AnalysisameliaNo ratings yet
- Identification & Mitigation of Potential Failures of Automotive Hvac Air Management System Using Failure Mode & Effects AnalysisDocument8 pagesIdentification & Mitigation of Potential Failures of Automotive Hvac Air Management System Using Failure Mode & Effects Analysisashishmechengg31No ratings yet
- DET2009 LYZheng KC-FMEADocument12 pagesDET2009 LYZheng KC-FMEAvishal.khalane9No ratings yet
- FMEADocument42 pagesFMEAibal_machine100% (1)
- BY Kiran S Shinde Kishor L RasalDocument10 pagesBY Kiran S Shinde Kishor L RasalKiran ShindeNo ratings yet
- FMEA PresentationDocument68 pagesFMEA PresentationParas KumarNo ratings yet
- FMEADocument4 pagesFMEAMDR PRAPHUNo ratings yet
- Are The Tools That Help Us Greatly Reduce Quality Problems in The Launch of New Products Apqp & CP, Amef, Control Plan, SPC, R & R and PpapDocument4 pagesAre The Tools That Help Us Greatly Reduce Quality Problems in The Launch of New Products Apqp & CP, Amef, Control Plan, SPC, R & R and PpapSergio Cristobal Bonilla CegadorNo ratings yet
- Presentation On FmeaDocument15 pagesPresentation On FmeaA Veda SagarNo ratings yet
- Has Introduced The First International Guide On Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)Document2 pagesHas Introduced The First International Guide On Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)Ionut Eduard100% (2)
- FMEADocument29 pagesFMEAKarthik Kr100% (1)
- Fmea and FmecaDocument14 pagesFmea and FmecaLindsay SleijpenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Advanced Product Quality PlanningDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Advanced Product Quality PlanningAbraham GuerraNo ratings yet
- Assignments-Mba Sem-Iii: Subject Code: QM0004Document16 pagesAssignments-Mba Sem-Iii: Subject Code: QM0004Mithesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effective AnalysisDocument214 pagesFailure Mode and Effective AnalysisAddhew PraseetyoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Failure Mode?Document16 pagesWhat Is A Failure Mode?Cuenta PokemonNo ratings yet
- Publisher Namespringer, London Print Isbn978-1-84882-471-3 Online Isbn978-1-84882-472-0 Ebook PackagesDocument3 pagesPublisher Namespringer, London Print Isbn978-1-84882-471-3 Online Isbn978-1-84882-472-0 Ebook PackagesEva WatiNo ratings yet
- Fmea VviDocument52 pagesFmea VviBobby Edwin100% (2)
- Tcs InterviewDocument10 pagesTcs InterviewYogi GowdaNo ratings yet
- FmeaDocument1 pageFmeaRanjith RamNo ratings yet
- FMEA in ServicesDocument6 pagesFMEA in ServicesPratik IyerNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Management Assignment-1Document16 pagesMaintenance Management Assignment-1ishika SHANDILYANo ratings yet
- Foc FmeaDocument6 pagesFoc FmeaShimon PopaNo ratings yet
- TQM Assignment On Failure Mode Effect Analysis: Srideep Kumar Mohanta 215112033 2013-14Document13 pagesTQM Assignment On Failure Mode Effect Analysis: Srideep Kumar Mohanta 215112033 2013-14mechatronicsmkNo ratings yet
- Innovative Approach To FMEA Facilitation: Govind RamuDocument34 pagesInnovative Approach To FMEA Facilitation: Govind Ramukskr_44100% (1)
- FMEA konkret: Preventive risk analysis concretely with FMEA plus. The series of successful developers, trainers and presenters.From EverandFMEA konkret: Preventive risk analysis concretely with FMEA plus. The series of successful developers, trainers and presenters.No ratings yet
- List of Piping CodesDocument43 pagesList of Piping CodesRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Nonpolar Covalent Bonds: ChemistryDocument9 pagesNonpolar Covalent Bonds: ChemistryRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Inspection / TestDocument7 pagesMechanical Inspection / TestRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Causes and Cures of Common Welding TroublesDocument1 pageCauses and Cures of Common Welding TroublesRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Solid State Welding ProcessDocument17 pagesSolid State Welding ProcessRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Nonpolar Covalent Bonds: ChemistryDocument9 pagesNonpolar Covalent Bonds: ChemistryRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- B-16-05107 KMT Stellite HardfacingAlloys Brochure en LRDocument28 pagesB-16-05107 KMT Stellite HardfacingAlloys Brochure en LRromanosky11No ratings yet
- Difference Between DT & NDTDocument3 pagesDifference Between DT & NDTRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Metallurgists-Quiz No.6 (: Mutiple Choice QuestionsDocument6 pagesMetallurgists-Quiz No.6 (: Mutiple Choice QuestionsRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- What Is Stellite SteelDocument11 pagesWhat Is Stellite SteelRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- CNC Machining Cycle Time CalculationDocument4 pagesCNC Machining Cycle Time CalculationRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Location: C:/NSH DOCUMENTS/MISCELLANIOUS/Radiograph Refrences .. Folder Item DescriptionDocument2 pagesLocation: C:/NSH DOCUMENTS/MISCELLANIOUS/Radiograph Refrences .. Folder Item DescriptionRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Welding DictionaryDocument59 pagesWelding DictionaryRathnakraja100% (1)
- MMA Electrode ClassificationDocument3 pagesMMA Electrode ClassificationRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Weight CalculationDocument17 pagesWeight CalculationRathnakrajaNo ratings yet