Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shoulder Joint
Shoulder Joint
Uploaded by
Dr santosh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views6 pagesThe shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral articulation, is a ball and socket synovial joint formed between the head of the humerus and the glenoid cavity of the scapula. It is surrounded by a fibrous capsule attached to the scapula and humerus that is strengthened by ligaments and muscles. The joint allows for multi-axial movement of the arm, including flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and medial and lateral rotation. Dislocations are common for this joint due to its shallow socket and lax capsule.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral articulation, is a ball and socket synovial joint formed between the head of the humerus and the glenoid cavity of the scapula. It is surrounded by a fibrous capsule attached to the scapula and humerus that is strengthened by ligaments and muscles. The joint allows for multi-axial movement of the arm, including flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and medial and lateral rotation. Dislocations are common for this joint due to its shallow socket and lax capsule.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views6 pagesShoulder Joint
Shoulder Joint
Uploaded by
Dr santoshThe shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral articulation, is a ball and socket synovial joint formed between the head of the humerus and the glenoid cavity of the scapula. It is surrounded by a fibrous capsule attached to the scapula and humerus that is strengthened by ligaments and muscles. The joint allows for multi-axial movement of the arm, including flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and medial and lateral rotation. Dislocations are common for this joint due to its shallow socket and lax capsule.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
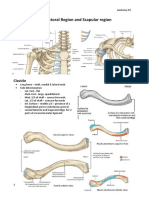
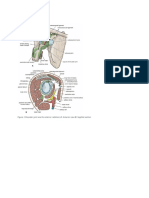
Shoulder joint - it is an articulation bet humerus &
scapula & also known as glenohumeral articulation
Type - synovial
Subtype - ball & socket i.e. multi axial
Bones taking part -
1. Head of humerus
2. Glenoid cavity of scapula
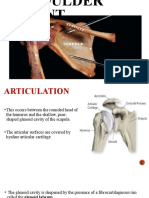
Articular surfaces
1. In humerus- head of humerus forming ball
2. Glenoid cavity - forming shallow cavity it is
small as compare to head but deepened by
glenoid labrum attached to peripheral margin
Articular capsule - it consist of two parts
1. Fibrous capsule
2. Synovial membrane
Fibrous capsule – it is fibrous envelop of joint
Attachment -
1. At the scapula - margins of glenoid cavity &
encloses the origin of long head of biceps
2. At the humerus - anatomical neck of
humerus
Texture - 3 L lean lax loose
Characteristics -
1. Weakest part - its lower & medial part due
to long head of triceps
2. Deficiencies - above at intertubercular
sulcus due to long head of biceps
3. Factor gives strength to capsule
Accessory ligament
1. Coracohumeral lig – it is thick band coracoids
process to neck of humerus it prevent lateral
rotation & abduction
2. Transverse humeral- bridges bet greater &
lesser tuberosity
3. Glenoidal labrum – it is fibrocartilagenous
rim it deepens the glenoid cavity
4. Glenohumeral lig
Muscles surrounding joint
1. Above - supraspinatus
2. Behind - infraspinatus & teres minor
3. In front - subscapularis
4. Below - long head of triceps
All muscles except triceps are closely attached to
capsule forming musculotendenous cuff
Synovial membrane -It lines inner surface of
fibrous capsule
1. Glenohumeral lig - it is thick band it has
three parts
Superior band attached to upper end of lesser
tubercle
Middle band is attached to lower end of lesser
tubercle
Inferior band is attached to lower part of
anatomical neck
Relation -
Superiorly – coracoacromial arch
Subacromial bursa
Supraspinatus
Deltoid
Inferiorly – long head of triceps
Anteriorly – subscapularis
Coracobrachialis
Short head of biceps
Posteriorly – deltoid
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
Long head of biceps
Movements –
Flexion - anterior fibers of deltoid
clavicular fibers of pect
major
Extension - posterior fibers of deltoid
Latissimus dorsi
Abduction - 1- 15 supraspinatus
15- 90 middle fibers of deltoid
90- 120 serratus anterior
Adduction - sternal fibers of pect major
Latissimus dorsi
Medial rotation - lady soldiers & majors
Latissimus dorsi
Subscapularies
Anterior fibers of deltoid
Two majors
Lateral rotation - tip
Teres minor
Infraspinatus
Post fibers of deltoid
Blood supply - anterior circumflex humeral artery
Posterior circumflex humeral artery
Sub scapular
All Branches of axillary artery
Suprascapular artery –thyrocervical
trunk – 1st part
subclavian artery
Nerve supply - axillary musculocuteneous &
suprascapular
Applied anatomy
1. Dislocation is common due to
disproportionate articular surfaces
2. Laxity of capsule
3. It is usually occurred when arm is forcefully
abducted
4. Frozen shoulder - due to adhesion between
rotator cuff & head of humerus
5. Shoulder tip pain - irritation of diaphragm
causes referred pain to the shoulder tip since
the root value of phrenic nerve supplying
diaphragm & suprascapular are same i.e. C3
C4
You might also like
- Teach Yourself Upper LimbDocument44 pagesTeach Yourself Upper LimbSambili Tonny100% (3)
- Lab 9 Gross Anatomy of The Muscular SystemDocument13 pagesLab 9 Gross Anatomy of The Muscular SystemJohn Lawrence YbanezNo ratings yet
- Radioanatomy of Shoulder Joint-Dr - NaziyaDocument82 pagesRadioanatomy of Shoulder Joint-Dr - Naziyaraghavmaster100% (1)
- Summary of Muscles in The ShoulderDocument3 pagesSummary of Muscles in The ShoulderDaniel GraceNo ratings yet
- Pectoral Girdle and Shoulder JointDocument55 pagesPectoral Girdle and Shoulder JointGaurav ThapaNo ratings yet
- The Shoulder JointDocument17 pagesThe Shoulder JointBhargavNo ratings yet
- The Shoulder JointDocument17 pagesThe Shoulder JointBhargavNo ratings yet
- Anat Compart 203Document52 pagesAnat Compart 203Saidu BobbojiNo ratings yet
- Final W5 L2 Shoulder JointDocument36 pagesFinal W5 L2 Shoulder JointOmar OsamaNo ratings yet
- Shoulder JTDocument30 pagesShoulder JTEVELYN EZEKWENo ratings yet
- Back of Thigh ClassDocument31 pagesBack of Thigh Classgrithika1706No ratings yet
- MSK SummaryDocument5 pagesMSK SummaryRahla KhanNo ratings yet
- Revison For Upper LimbDocument55 pagesRevison For Upper LimbbEdo 0No ratings yet
- Anatomy 03 - Pectoral and Scapular Region (Pre Med 101)Document10 pagesAnatomy 03 - Pectoral and Scapular Region (Pre Med 101)Navoda Dulshan PereraNo ratings yet
- Shoulder GirdleDocument38 pagesShoulder GirdleAnigha PrasadNo ratings yet
- 3 Shoulder Joint - Chapter Summary - Anatomy of The Shoulder Joint by Snell Medicine LectureDocument76 pages3 Shoulder Joint - Chapter Summary - Anatomy of The Shoulder Joint by Snell Medicine LectureRobin TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Back MusclesDocument4 pagesAnatomy of Back Musclesfatima wribagNo ratings yet
- Front of ForearmDocument19 pagesFront of ForearmAditya AnandNo ratings yet
- Back MusclesDocument38 pagesBack MusclesAsmithNo ratings yet
- 007superficial Back and Scapular & Deltoid RegionsDocument38 pages007superficial Back and Scapular & Deltoid RegionsEtsubNo ratings yet
- 1 LGDocument42 pages1 LGJoo Se HyukNo ratings yet
- Ospe-Ll 16Document35 pagesOspe-Ll 16Muthu GuhaanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Eman El Sawaf: Anatomy & Embr Yology Depar TmentDocument96 pagesDr. Eman El Sawaf: Anatomy & Embr Yology Depar TmentKareem DawoodNo ratings yet
- Scapular Region 9 Mar 2024Document32 pagesScapular Region 9 Mar 2024aamna.nadeem101No ratings yet
- Shoulder JointDocument17 pagesShoulder JointShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The ShoulderDocument79 pagesMuscles of The Shoulderali.algazali20No ratings yet
- 2 - Shoulder Girdle PDFDocument38 pages2 - Shoulder Girdle PDFMayra FlorNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy of The Human BodyDocument18 pagesGeneral Anatomy of The Human BodyVarenLagartoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Back of The Neck NewDocument63 pagesChapter 21 Back of The Neck NewMohan PalanimalaiNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Muscles' Summary Without O-IDocument7 pagesUpper Limb Muscles' Summary Without O-IMahmoud KamhawyNo ratings yet
- The Elbow JointDocument4 pagesThe Elbow JointMd Ahsanuzzaman PinkuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Trans UPPER EXTREMITIESDocument9 pagesAnatomy Trans UPPER EXTREMITIESSan LapuhapuNo ratings yet
- 02upper L SmmryDocument50 pages02upper L SmmryISMAIL HAMZANo ratings yet
- 805 - Front of ForearmDocument63 pages805 - Front of ForearmUkkNo ratings yet
- Back of Thigh & Popliteal FossaDocument50 pagesBack of Thigh & Popliteal Fossatechbaker786No ratings yet
- All Bat NotesDocument1,048 pagesAll Bat NotesAfk SystemNo ratings yet
- Clinical Anatomy of The Lower Limb Eng 2013Document49 pagesClinical Anatomy of The Lower Limb Eng 2013Dr-Brian T PhiliNo ratings yet
- neck-FUE FinalDocument84 pagesneck-FUE Finalhannalojo21No ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument5 pagesAnatomyhananabodeaf41No ratings yet
- Gluteal Region Gluteal RegionDocument21 pagesGluteal Region Gluteal RegionPraneethaNo ratings yet
- MUSCLES of The UPPER LIMBDocument12 pagesMUSCLES of The UPPER LIMBdncm.alejandroNo ratings yet
- Shoulder JointDocument4 pagesShoulder Jointcyrus kirwaNo ratings yet
- Ul- flexor - ForearmDocument29 pagesUl- flexor - Forearmkadambaric594No ratings yet
- 3rd ULMuscles of Pectoral RegionDocument19 pages3rd ULMuscles of Pectoral Regionx8w6df2fxwNo ratings yet
- Upper LimbDocument40 pagesUpper LimbKhadija AbouslimaNo ratings yet
- 0.5x ANATOMY LOWER LIMBSDocument24 pages0.5x ANATOMY LOWER LIMBSArijeet77No ratings yet
- 811 Anatomy of Shoulder JointDocument51 pages811 Anatomy of Shoulder JointAishwarya PatilNo ratings yet
- Flexor Region of The ForearmDocument13 pagesFlexor Region of The ForearmNeil DolendoNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Joint: DR Abdul Hafeez BalochDocument26 pagesShoulder Joint: DR Abdul Hafeez Balochmehrab kayaniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Ofthe Upper ArmDocument37 pagesAnatomy Ofthe Upper ArmBenjamin JonathanNo ratings yet
- MSK Upper LimbDocument24 pagesMSK Upper LimbAhmed QrariaNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb - Gluteal Region, Thigh & Hip JointDocument32 pagesLower Limb - Gluteal Region, Thigh & Hip Jointewijayapala100% (1)
- Anatomy: ST ND TH TH Th. RD TH TH THDocument11 pagesAnatomy: ST ND TH TH Th. RD TH TH THskNo ratings yet
- MUSCLES TabulatedDocument12 pagesMUSCLES Tabulateddncm.alejandroNo ratings yet
- Lower Anatomy PT 2120Document29 pagesLower Anatomy PT 2120mahmoudmyoussef2001No ratings yet
- General Myology, Muscles of The Upper Limb: Petr Hájek, MD., PHDDocument39 pagesGeneral Myology, Muscles of The Upper Limb: Petr Hájek, MD., PHDTodesengelNo ratings yet
- Front of Forearm LecturesDocument19 pagesFront of Forearm LecturesInsyirah JohariNo ratings yet
- 2021 4.2.3 Muscle ListDocument2 pages2021 4.2.3 Muscle ListAlyssa JacobsNo ratings yet
- Upper ExtremityDocument216 pagesUpper ExtremityChester VergilNo ratings yet
- The Arm PDFDocument19 pagesThe Arm PDFMayra FlorNo ratings yet
- 2 Shoulder Girdle JointsDocument29 pages2 Shoulder Girdle JointsFarrukh ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Thoracic DuctDocument2 pagesThoracic DuctDr santosh100% (1)
- Azygos VeinDocument2 pagesAzygos VeinDr santoshNo ratings yet
- CerebrumDocument12 pagesCerebrumDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Angle of Louis or Sterna AngleDocument1 pageAngle of Louis or Sterna AngleDr santoshNo ratings yet
- BreastDocument6 pagesBreastDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Thalamus-: Disposition - It Lies Obliquely With Its Long AxisDocument8 pagesThalamus-: Disposition - It Lies Obliquely With Its Long AxisDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Lateral Ventricle: Number - Two in Number One On Each SideDocument4 pagesLateral Ventricle: Number - Two in Number One On Each SideDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesCentral Nervous SystemDr santoshNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument3 pagesMusclesDr santoshNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument29 pagesCardioDr santoshNo ratings yet
- BoneDocument4 pagesBoneDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Obturator NerveDocument3 pagesObturator NerveDr santoshNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument8 pagesPancreasDr santosh100% (1)
- PONSDocument1 pagePONSDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Paper Pattern of 1st Year BHMSDocument3 pagesPaper Pattern of 1st Year BHMSDr santosh100% (2)
- Shoulder Joint BiomechanicsDocument129 pagesShoulder Joint BiomechanicsKhan SalimNo ratings yet
- Manual Therapy: L.A. Watson, T. Pizzari, S. BalsterDocument10 pagesManual Therapy: L.A. Watson, T. Pizzari, S. BalsterPau StraitNo ratings yet
- 1 Anatomy-MSKDocument86 pages1 Anatomy-MSKashim tiwariNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Shoulder JointDocument44 pagesAnatomy of The Shoulder JointAuza Moses Ibrahim100% (1)
- Shoulder Dislocation TechniquesDocument9 pagesShoulder Dislocation TechniqueskenthepaNo ratings yet
- Os Complete Final AnswerDocument198 pagesOs Complete Final AnswerDeshini Balasubramaniam100% (4)
- Anatomy of The Shoulder Girdle and Scapulohumeral RhythmDocument30 pagesAnatomy of The Shoulder Girdle and Scapulohumeral RhythmthwisemanNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Impingement SyndromeDocument21 pagesShoulder Impingement SyndromeivannaOctavianiNo ratings yet
- The Acumoxa Treatment of Shoulder Impingement SyndromeDocument8 pagesThe Acumoxa Treatment of Shoulder Impingement SyndromeAngela PagliusoNo ratings yet
- Comjnmh 10 Years' Doc.4 - 1Document49 pagesComjnmh 10 Years' Doc.4 - 1Zaid KhanNo ratings yet
- AnatDocument31 pagesAnatBintang ParipurnaNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Shoulder ExaminationDocument4 pagesOrthopedic Shoulder Examinationapi-281340024No ratings yet
- Overview of The Anatomy of The Upper and Lower LimbsDocument59 pagesOverview of The Anatomy of The Upper and Lower LimbsCher TangNo ratings yet
- Dr. A. Samy TAG Upper Limb - 1Document20 pagesDr. A. Samy TAG Upper Limb - 1DRAHMEDFAHMYORTHOCLINICNo ratings yet
- Mobilization Techniques in SubjectsDocument9 pagesMobilization Techniques in SubjectsclemNo ratings yet
- Shoulder JointDocument32 pagesShoulder JointRafli Antariksa100% (1)
- SLAP Tear Management in AthletesDocument11 pagesSLAP Tear Management in AthletesErnesto Dávila RamírezNo ratings yet
- Bowen Therapy: ... and How It May Effectively Relieve A Range of ConditionsDocument43 pagesBowen Therapy: ... and How It May Effectively Relieve A Range of Conditionsina macNo ratings yet
- 2016 January-February PDFDocument45 pages2016 January-February PDFAndriusjo100% (2)
- Reverse Grip Bench Press-Ironman Sportsmedicine ColumnDocument5 pagesReverse Grip Bench Press-Ironman Sportsmedicine ColumnJohn PhungNo ratings yet
- 7C83 Taping For Trigger Points 1117Document71 pages7C83 Taping For Trigger Points 1117Jonathan C. De la Orta100% (1)
- Ao Alliance Handbook Nonoperative Fracture Treatment Complete PDFDocument164 pagesAo Alliance Handbook Nonoperative Fracture Treatment Complete PDFvicageoNo ratings yet
- Abp 10 Years PDFDocument44 pagesAbp 10 Years PDFUtsabNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb TransDocument18 pagesUpper Limb Transashley nicholeNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Scapular Kinematics Between Elevation and Lowering of The Arm in The Scapular PlaneDocument10 pagesComparison of Scapular Kinematics Between Elevation and Lowering of The Arm in The Scapular PlaneWallison LeaoNo ratings yet
- Jimed, Vol. 3, No. 2 Issn 2356-301XDocument5 pagesJimed, Vol. 3, No. 2 Issn 2356-301XDewi YulyantiNo ratings yet
- Glenoid LabrumDocument26 pagesGlenoid LabrumluizamgoNo ratings yet
- Willmore Smith 2016 Scapular Dyskinesis EvolutiontowardsandsystemsbasedapproachDocument11 pagesWillmore Smith 2016 Scapular Dyskinesis EvolutiontowardsandsystemsbasedapproachAhmed TawfiqNo ratings yet