Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tongue 1
Tongue 1
Uploaded by
Dr santosh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views5 pagesThe tongue is a muscular organ located in the mouth that helps with speech, swallowing, and chewing. It has two surfaces, two borders, an apex and a base. The base attaches to the back of the throat and voice box, while the apex lies against the front teeth. The tongue contains intrinsic muscles that allow it to change shape and two types of extrinsic muscles that control movement. Lymphatic drainage and nerve supply also vary across the different regions of the tongue.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe tongue is a muscular organ located in the mouth that helps with speech, swallowing, and chewing. It has two surfaces, two borders, an apex and a base. The base attaches to the back of the throat and voice box, while the apex lies against the front teeth. The tongue contains intrinsic muscles that allow it to change shape and two types of extrinsic muscles that control movement. Lymphatic drainage and nerve supply also vary across the different regions of the tongue.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views5 pagesTongue 1
Tongue 1
Uploaded by
Dr santoshThe tongue is a muscular organ located in the mouth that helps with speech, swallowing, and chewing. It has two surfaces, two borders, an apex and a base. The base attaches to the back of the throat and voice box, while the apex lies against the front teeth. The tongue contains intrinsic muscles that allow it to change shape and two types of extrinsic muscles that control movement. Lymphatic drainage and nerve supply also vary across the different regions of the tongue.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
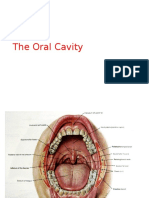
Tongue
It is muscular organ helps in speech swallowing &
mastication
Features
It has 2 surfaces 2 borders apex & base
Base - it is attach to the oropharynx & epiglottis
Apex - it is free & lies against incisior teeth
Two lateral borders – separating two surfaces
Superior surface - divided in to two parts by
sulcus terminalis anterior 2/3rd –it is rough due to
papillae & posterior 1/3rd it shows lingual tonsil
Inferior surface - it shows mid line fold of mucus
membrane called as frenulum at the lower end on
either side there is sublingual papillae it receives
submandibular duct
Muscles of tongue – two types extrinsic & intrinsic
Extrinsic
1. Genioglossus - originates from genial
tubercle of mandible & inserted in tip of
tongue
Nerve - hypoglossal
Action - protusion of tongue
2. Hyoglossus
Origin - from hyoid bone
Insertion - side of tongue
Nerve - hypoglossal
Action - depression of tongue
3. Styliglossus
Origin - from styloid process
Insertion - posterior part of tongue
Nerve - hypo
Action - retraction of tongue
Intrinsic muscles of tongue
1. Superior longitudinal –it lies along superior
surface
2. Inferior longitudinal - along inferior surface
3. Verticalis
4. Transverses
These muscles are present under mucus
membrane of tongue all are supplied by
hypoglossal nerve
Action - they changes the shape of tongue
Lymphatic drainage
1. Tip of tongue drains in to submental
2. Body of tongue drains in to submandibular &
jugulo-diagastric node
3. Posterior 1/3rd drains in to retro-pharyngeal
Nerve supply - it is divided in to two parts
Anterior 2/3rd & posterior 1/3rd
Tongue Anterior 2/3rd Posterior 1/3rd
Sensory Lingual 9th
Taste fibres Chord tympani 9th
Motor supply – all muscles are supplied by
hypoglossal except palatoglossus it is supplied by
pharyngeal plexus
Palatoglossus - it is extrinsic muscle
Origin –palatine aponeurosis
Insertion - superior part of tongue
Nerve - pharyngeal plexus
Action - elevation of tongue
It forms boundary of tonsillar fossa
Histology - it is lined by stratified squamous
epithelium on
The dorsum of tongue epithelium is specilised to
form papillae there are three types of papillae
present
1. Filiform - these papillae are pointed
2. Fungiform – rounded
3. Vallate - large taste buds are present in the
wall of papillae
Under epithelium intrinsic muscle forms bulk of
tongue they are longitudinal ,verticalis ,transverse
Lymphoid follicles are also present they may raised
above surface forming lingual tonsil
Seromucus glands are present which keeps the
tongue moist
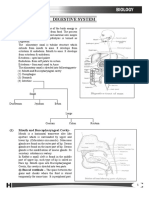
Development of tongue
1. The epithelium of anterior 2/3rd is formed by
endoderm of 1st & 2nd pouch
Two lingual swelling appears in 1st pouch in
the mid line
Medial tuberculum impar develops from 2nd
pouch & fuses in lingual swelling tuberculum
impar remains as a foramen caecum
2. Epithelium of posterior 1/3rd develops from
proximal part of hypobranchial eminence
3. Epithelium of root of tongue develops from
distal part hypobarnchial eminence
4. Eminence is formed fusion of 3rd 4th pouch
5. Muscles of tongue develops from occipital
myotomes ie mesoderm
Applied anatomy
1. Tongue tie –short frenulum causes difficulty
in speech
2. Micro glossia - small tongue
3. Macroglossia - tapering speech large tongue
4. Bifid tongue
5. Glossitis –oral ulcer or ulcers of mouth
6. Ca of tongue –causes excessive salivation
7. Diagnostic use of tongue
You might also like
- Guide To The Dissection of The Dog, 8th EditionDocument346 pagesGuide To The Dissection of The Dog, 8th Editionmaria da matosNo ratings yet
- CV MMiller FinalDocument3 pagesCV MMiller Finalmiller1755No ratings yet
- (F) Chapter 16 - Digestive System I, Oral Cavity and Associated StructuresDocument5 pages(F) Chapter 16 - Digestive System I, Oral Cavity and Associated StructuresAisle Malibiran PalerNo ratings yet
- TONGUE SeminarDocument82 pagesTONGUE SeminarArun MamachanNo ratings yet
- Sensory Organs - TongueDocument31 pagesSensory Organs - Tongueapi-324160601No ratings yet
- Embryology 2 Asr 3eny New 2024 PDFDocument6 pagesEmbryology 2 Asr 3eny New 2024 PDFHassan AwadNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument72 pagesTongueDrRj SameenNo ratings yet
- Tongue and PalateDocument103 pagesTongue and PalateHeba S RadaidehNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument162 pagesTongueDevendra ChhonkarNo ratings yet
- The TongueDocument7 pagesThe Tonguemanojchouhan2014No ratings yet
- Drain The Central Portion of The Anterior Two-Third of The Tongue Bilaterally Into The Deep Cervical Lymph NodesDocument3 pagesDrain The Central Portion of The Anterior Two-Third of The Tongue Bilaterally Into The Deep Cervical Lymph NodesÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument44 pagesTongueSidhartha BordoloiNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Applied Dental Sciences Tongue and Its Prosthodontic ImplicationsDocument5 pagesInternational Journal of Applied Dental Sciences Tongue and Its Prosthodontic ImplicationsMariatun Zahro NasutionNo ratings yet
- L1) Oral Cavity, Palate and TongueDocument39 pagesL1) Oral Cavity, Palate and Tongue3amroooni.a.aNo ratings yet
- Clinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016 PDFDocument29 pagesClinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016 PDFshagufta lailaNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument52 pagesTongueNANDANA BOSENo ratings yet
- Emberyology 2 LectDocument28 pagesEmberyology 2 LectOvidiu MarculescuNo ratings yet
- TONGUE Seminar by MeDocument84 pagesTONGUE Seminar by MeArpita SankhwarNo ratings yet
- Tongue (Including Clinical Significance)Document3 pagesTongue (Including Clinical Significance)Andra Bauer100% (1)
- Oral Cavity Salivary GlandsDocument36 pagesOral Cavity Salivary GlandsSaifNo ratings yet
- Pivotal Role of Tongue in Prosthodontic TreatmentDocument13 pagesPivotal Role of Tongue in Prosthodontic TreatmentAkshayaa BalajiNo ratings yet
- The Oral CavityDocument55 pagesThe Oral CavityMeren NagaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System at Head and NeckDocument8 pagesDigestive System at Head and NeckArinaNo ratings yet
- 14 Oral CavityDocument41 pages14 Oral Cavityhamokimo65No ratings yet
- Tongue & It's Applied AspectsDocument64 pagesTongue & It's Applied AspectsPrachi MulayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nose and TongueDocument40 pagesAnatomy of Nose and TongueDanial SharizulNo ratings yet
- The MouthDocument13 pagesThe MouthAjigotto ubiq.No ratings yet
- Mammalian System-01 (Digestive System)Document35 pagesMammalian System-01 (Digestive System)Saumya99No ratings yet
- 8d46the Oral CavityDocument33 pages8d46the Oral CavityChampak PaulNo ratings yet
- Oral Physiology and OcclusionDocument64 pagesOral Physiology and OcclusionFrances SyNo ratings yet
- Mouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsDocument52 pagesMouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsIrfan FalahNo ratings yet
- Tongue, Palate, Palatine Tonsils PDFDocument10 pagesTongue, Palate, Palatine Tonsils PDFChristopher PhilipsNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Document47 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Aditya FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Development and Anatomy of The Tongue2Document11 pagesDevelopment and Anatomy of The Tongue2Dr-AHmad Fasfous AL-QaisiNo ratings yet
- Tongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDocument100 pagesTongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDr Mohit Dhawan100% (19)
- Role of Tongue N Floor of Mouth in CD TRTDocument18 pagesRole of Tongue N Floor of Mouth in CD TRTashoorocksNo ratings yet
- Tongue AnatomyDocument3 pagesTongue Anatomykaruparthi sripravallikaNo ratings yet
- EssaysDocument176 pagesEssaysppdzssx7ghNo ratings yet
- Development of Head & Neck 2 Tongue Face & PalateDocument19 pagesDevelopment of Head & Neck 2 Tongue Face & Palatear921712No ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument3 pagesOral Cavityحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- The TongueDocument21 pagesThe Tonguemanojchouhan2014No ratings yet
- Development of TongueDocument2 pagesDevelopment of TongueCornelia GheorghitaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of AirwaysDocument6 pagesAnatomy of Airwaysgdubs215No ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY Tongue and OsephagusDocument8 pagesHISTOLOGY Tongue and OsephagusAkachukwu ObunikeNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesDigestive SystemchipsNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument79 pagesOral CavityueumanaNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument46 pagesTonguedeepak mauryaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 64: Anatomy of Tongue: Dr. Mohammad Rehan AsadDocument20 pagesLecture 64: Anatomy of Tongue: Dr. Mohammad Rehan AsadRehan Asad0% (1)
- H, NDocument20 pagesH, NNada Atef KoraitemNo ratings yet
- The TongueDocument39 pagesThe TongueNathanNo ratings yet
- Tongue, Deglutation and SpeechDocument65 pagesTongue, Deglutation and SpeechtamannaNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument100 pagesTongueAPARNA AARATHI SREEKUMARNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument105 pagesOral CavityAisha AbbasNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity (Mouth Cavity) : Dr. Aymen Ahmed Warille DR Moahip MohamedDocument57 pagesOral Cavity (Mouth Cavity) : Dr. Aymen Ahmed Warille DR Moahip MohamedNada MohammedNo ratings yet
- GIT TempDocument13 pagesGIT Tempdrahmed1028No ratings yet
- 16 The Mouth (Done)Document9 pages16 The Mouth (Done)osamaeNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument19 pagesOral CavityProy DCNo ratings yet
- TONGUEDocument63 pagesTONGUEAthulya Lakshmanan100% (1)
- 14-Oral CavityDocument37 pages14-Oral CavitySajid AliNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Thoracic DuctDocument2 pagesThoracic DuctDr santosh100% (1)
- Azygos VeinDocument2 pagesAzygos VeinDr santoshNo ratings yet
- CerebrumDocument12 pagesCerebrumDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Angle of Louis or Sterna AngleDocument1 pageAngle of Louis or Sterna AngleDr santoshNo ratings yet
- BreastDocument6 pagesBreastDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Thalamus-: Disposition - It Lies Obliquely With Its Long AxisDocument8 pagesThalamus-: Disposition - It Lies Obliquely With Its Long AxisDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Lateral Ventricle: Number - Two in Number One On Each SideDocument4 pagesLateral Ventricle: Number - Two in Number One On Each SideDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesCentral Nervous SystemDr santoshNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument3 pagesMusclesDr santoshNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument29 pagesCardioDr santoshNo ratings yet
- BoneDocument4 pagesBoneDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Obturator NerveDocument3 pagesObturator NerveDr santoshNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument8 pagesPancreasDr santosh100% (1)
- PONSDocument1 pagePONSDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Paper Pattern of 1st Year BHMSDocument3 pagesPaper Pattern of 1st Year BHMSDr santosh100% (2)
- Imaging of Skull Base: Pictorial Essay: M - S - H NDocument12 pagesImaging of Skull Base: Pictorial Essay: M - S - H NGeorge Harrison Jr.No ratings yet
- WSDDocument59 pagesWSDdiandrasafirinaNo ratings yet
- Resume - Parvin MoradiDocument3 pagesResume - Parvin Moradimohammadrezahajian12191No ratings yet
- Glaucoma Drainage DevicesDocument6 pagesGlaucoma Drainage Devicesmax paxNo ratings yet
- Incentive Spirometry1Document4 pagesIncentive Spirometry1Reisha FungoNo ratings yet
- Surgical Aseptic Technique Sterile FieldDocument18 pagesSurgical Aseptic Technique Sterile FieldAsiah IsmailNo ratings yet
- Lapkas Glaukoma Pemasangan Implan GDD Lapkas Glaukoma (AutoRecovered)Document14 pagesLapkas Glaukoma Pemasangan Implan GDD Lapkas Glaukoma (AutoRecovered)Vincent RoorohNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Sleep ApneaDocument21 pagesObstructive Sleep ApneaIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Fowlervs SORLreconstructionDocument6 pagesFowlervs SORLreconstructionAkbar GazaliNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 ReviewerDocument315 pagesNCM 118 ReviewerKarlo BallonNo ratings yet
- Decision Making ImplantDocument2 pagesDecision Making Implant김문규No ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument6 pagesAnaphyrhona esteibarNo ratings yet
- Catalog-Haiye Medical (2024.EN)Document17 pagesCatalog-Haiye Medical (2024.EN)sukrid.iceNo ratings yet
- Abdomen Radiography Interpretation: Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, IPB University Telp: +62 8111191333 (Abby Pratama)Document2 pagesAbdomen Radiography Interpretation: Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, IPB University Telp: +62 8111191333 (Abby Pratama)Intan PradikaNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Elevated Troponins: Susanne Korff, Hugo A Katus, Evangelos GiannitsisDocument7 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Elevated Troponins: Susanne Korff, Hugo A Katus, Evangelos GiannitsisRashad AlarikyNo ratings yet
- Indications and Utility in The Intensive Care Unit: NeuromonitoringDocument11 pagesIndications and Utility in The Intensive Care Unit: NeuromonitoringphilipNo ratings yet
- What To Expect After GallbladderDocument2 pagesWhat To Expect After GallbladderJennifer PorlaresNo ratings yet
- DC LPCDocument4 pagesDC LPCDianna RoseNo ratings yet
- CFR Vijayaraman WEBDocument8 pagesCFR Vijayaraman WEBacitri2No ratings yet
- Gross Examination LabmedDocument2 pagesGross Examination Labmediishayati100% (2)
- Cranial Nerve Examination OSCE GuideDocument34 pagesCranial Nerve Examination OSCE Guideluq9fifNo ratings yet
- Acute Cholecystitis SeminarDocument42 pagesAcute Cholecystitis SeminarNatnaelNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy and Physiology of The Stomach: Ian R. Daniels and William H. AllumDocument21 pagesThe Anatomy and Physiology of The Stomach: Ian R. Daniels and William H. Allummutia aNo ratings yet
- Fistula GenitaliaDocument35 pagesFistula GenitaliaFifi FruitasariNo ratings yet
- International Journal Orthodontics 3Document11 pagesInternational Journal Orthodontics 3helmysiswantoNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Laparoscopic Colon Surgery Milestones Education Best Practice Gregory Kouraklis PDFDocument46 pagesFull Chapter Laparoscopic Colon Surgery Milestones Education Best Practice Gregory Kouraklis PDFbernard.davis529100% (4)
- Termodiluicao PulmonarDocument7 pagesTermodiluicao PulmonarKarina ResendeNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 04-Nov-2022Document8 pagesAdobe Scan 04-Nov-2022The Killer gamingNo ratings yet