Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CE 204 Equation Sheet PDF
CE 204 Equation Sheet PDF
Uploaded by
spamandhamspamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CE 204 Equation Sheet PDF
CE 204 Equation Sheet PDF
Uploaded by
spamandhamspamCopyright:
Available Formats
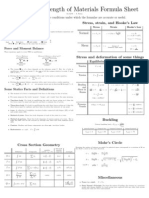
Centroids and Moments of Inertia
Q x = y d A = yA Q y = x d A = xA Ix = y2 dA I y = x2 d A
J =r2 dA J = Ix + Iy I = I + Ad 2
y y 1 3
I x' = bh
12 1
I x' = bh 3
1 3 36
I y' = b h
x 12 1 3
h h Ix = bh
C 1 12
I x = bh 3 x
x 3 C h/3
b 1
I y = b3h x
3 b
1
JC = bh(b 2 + h 2 )
12
y
8 4
Ix =Iy =
1
r4
y I x' = r
8 9 4
r 1
r 1
Ix = Iy = r4 JO = r4
x x 2
C 4r/3
8 O
x 1
O JO = r4
4
1-D Stress Components
P My VQ Tr
= = = =
A I It J
2V
3V 4V max = thin H VQ
max = rectangle max = solid circle A q= =
2A 3A x I
tube
y
3V
2
Shear stress distribution in a rectangle: =
1
2A
c
where y is measured from the neutral axis and c is the half-height of the beam (c = h/2)
1-D Deformations
TL
L
Torsional Deformation: =
PL P( x) JG
Axial Deformation: =
AE
= AE
dx L
T ( x)
0 =
0
JG
dx
Power in a circular shaft: P = 2 f T
Thermal Strain: T = (T )
Unrestrained Change in Length of Rod due to Temperature Change: T = (T )L
is the coefficient of thermal expansion and T is the change in temperature from a
reference temperature
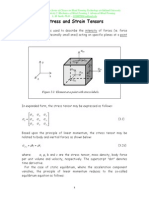
Relationships Between Stress and Strain
1 xy x = ( + 2G ) x + y + z
x = x y z xy =
E E E G
1 yz
y = x + y z yz = y = x + ( + 2G ) y + z
E E E G
1 xz
z = x y + z xz = z = x + y + ( + 2G ) z
E E E G
y (Defined for uniaxial Plane stress (z = yz = zx= 0) :
= = z
x x stress in the x-direction)
E E
x = x + y
E 1 2
1 2
G== E E
2(1 + ) y = x + y
1 2
1 2
E
=
(1 + )(1 2 ) z = ( +y)
1
x
You might also like
- HW1Document3 pagesHW1Naveen RajNo ratings yet
- Strain Gauge Based AccelerometerDocument13 pagesStrain Gauge Based Accelerometeranandakumarmts0% (1)
- Appendix D Review of Mechanics of Materials - 2009 - Elasticity Second Edition PDFDocument14 pagesAppendix D Review of Mechanics of Materials - 2009 - Elasticity Second Edition PDFJaimeNo ratings yet
- Chem 26.1 ATQ 1Document5 pagesChem 26.1 ATQ 1CeruleanBeingNo ratings yet
- Category 022 - Cement Concrete ProductsDocument12 pagesCategory 022 - Cement Concrete Productsshahrilzainul77100% (1)
- Structural Degrees of FreedomDocument24 pagesStructural Degrees of FreedomJibrilNo ratings yet
- Fatigue PDFDocument21 pagesFatigue PDFsuzilamatsallehNo ratings yet
- 06a SDOF System 1Document21 pages06a SDOF System 1maheshluintelNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy PrinciplesDocument12 pagesWork and Energy PrinciplesHernan Kennedy Ricaldi PorrasNo ratings yet
- Simple Stresses and Strains PDFDocument104 pagesSimple Stresses and Strains PDFyaminiNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Mechanics MaterialsDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet Mechanics MaterialsJames BuserNo ratings yet
- 3D Stress Components: Normal StressesDocument71 pages3D Stress Components: Normal Stressesengr_usman04No ratings yet
- Seismic Damper BuildingDocument2 pagesSeismic Damper BuildingTony RoseNo ratings yet
- Shaking Table Model Test and Numerical Analysis of A Complex High-Rise Building - Xilin Lu, Yin Zhou, Wensheng Lu - 2007Document34 pagesShaking Table Model Test and Numerical Analysis of A Complex High-Rise Building - Xilin Lu, Yin Zhou, Wensheng Lu - 2007Martin Dario Mazo QuingrejoNo ratings yet
- Statics and Strength of Materials Formula SheetDocument1 pageStatics and Strength of Materials Formula SheetRichard TsengNo ratings yet
- KLA AppNote StrainRateDocument6 pagesKLA AppNote StrainRatep dNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Testing TechniquesDocument54 pagesDynamic Testing TechniquesLuis Montoya100% (1)
- Solid Element Formulation OverviewDocument36 pagesSolid Element Formulation OverviewasdqwexNo ratings yet
- Plastic BendingDocument1 pagePlastic BendingmajmjudNo ratings yet
- Applications of Energy Methods: - Principle of Stationary Potential Energy - Castigliano's TheoremDocument33 pagesApplications of Energy Methods: - Principle of Stationary Potential Energy - Castigliano's TheoremSaurabh PednekarNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Damage Theories - Copy - 2Document10 pagesCumulative Damage Theories - Copy - 2faint27No ratings yet
- Shake Table II User Manual 2Document36 pagesShake Table II User Manual 2Sandro Zavala SotoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hydraulics: Chapter-1Document51 pagesIntroduction To Hydraulics: Chapter-1KarthikNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Architecture: Presented by Naveen Minj 19122035 P.B.V. Laxman 19122043Document15 pagesEarthquake Resistant Architecture: Presented by Naveen Minj 19122035 P.B.V. Laxman 19122043Ar Shubham JaiswalNo ratings yet
- MoM Summary PointsDocument39 pagesMoM Summary PointsAmmarNo ratings yet
- Fracture MechanicsDocument7 pagesFracture MechanicsDEEPAKNo ratings yet
- 84 TOP MOST Strength of Materials - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument24 pages84 TOP MOST Strength of Materials - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsJagadish MekaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Exam 1Document1 pageFormula Sheet For Exam 1chris ricaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials 2015 by S K MondalDocument471 pagesStrength of Materials 2015 by S K MondalNaman Jain100% (1)
- Failure Static LoadingDocument183 pagesFailure Static LoadingoperationmanagerNo ratings yet
- CE207 Final Exam Formula BookletDocument7 pagesCE207 Final Exam Formula BookletangrytemperNo ratings yet
- Strain Chap 04Document37 pagesStrain Chap 04Ricardo ColosimoNo ratings yet
- Ept474 2dofDocument118 pagesEpt474 2dofLeon OoNo ratings yet
- Structural ExamplesDocument85 pagesStructural Examplesfariasgarciarojas100% (1)
- 793 MPT Application SoftwareDocument542 pages793 MPT Application SoftwareClaudio Omar Andrade KucharskiNo ratings yet
- Ch18 Hexaedron ElementDocument10 pagesCh18 Hexaedron Elementlittle-wing100% (2)
- Dynamics and Vibrations - Notes - Free Undamped VibrationsDocument14 pagesDynamics and Vibrations - Notes - Free Undamped VibrationsPhatechand NaikNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain DiagramDocument4 pagesStress Strain DiagramMartine CastroNo ratings yet
- Modal AnalysisDocument26 pagesModal AnalysisTrinh Duy TanNo ratings yet
- 11 Problems - 11 Solutions: Case Histories of 11 Machinery Vibration Problems - Part 1Document7 pages11 Problems - 11 Solutions: Case Histories of 11 Machinery Vibration Problems - Part 1Ahmed El-ShafeiNo ratings yet
- Seismic Analysis of A Liquid Storage Tan PDFDocument5 pagesSeismic Analysis of A Liquid Storage Tan PDFMesfinNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Analysis of StructuresDocument57 pagesDynamic Analysis of StructuresYollanda LorenzaNo ratings yet
- Thick Cy FinalDocument5 pagesThick Cy FinalAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Theory of PlasticityDocument16 pagesLecture 2 Theory of PlasticityprashanthattiNo ratings yet
- CE 636 Stability of StructuresDocument5 pagesCE 636 Stability of StructuresMunther MohdNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Seismic Essentials in GroningenDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Seismic Essentials in GroningenKay Chan SothearaNo ratings yet
- Rotary ActuatorsDocument11 pagesRotary Actuatorskadir kayaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics and Applications of Different Types of Dampers As Seismic Energy DissipaterDocument4 pagesCharacteristics and Applications of Different Types of Dampers As Seismic Energy DissipaterKiran N S GowdaNo ratings yet
- Theory of ElasticityDocument59 pagesTheory of ElasticityAhsan SattarNo ratings yet
- Ordertracking: Users ManualDocument38 pagesOrdertracking: Users Manualbinh buiNo ratings yet
- Vibration Damping: Professor Mike BrennanDocument52 pagesVibration Damping: Professor Mike Brennanpuppyarav2726No ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations: Why Do We Study ?Document27 pagesMechanical Vibrations: Why Do We Study ?sagar kumarNo ratings yet
- Seismic Dampers and The Factors Affecting Its Efficacy A Review PaperDocument5 pagesSeismic Dampers and The Factors Affecting Its Efficacy A Review PaperInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Explicit Finite Element Method for Nonlinear Transient DynamicsFrom EverandIntroduction to the Explicit Finite Element Method for Nonlinear Transient DynamicsNo ratings yet
- Plates and Shells for Smart Structures: Classical and Advanced Theories for Modeling and AnalysisFrom EverandPlates and Shells for Smart Structures: Classical and Advanced Theories for Modeling and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Earthquake isolation method with variable natural frequencyFrom EverandEarthquake isolation method with variable natural frequencyNo ratings yet
- Stress - Principal Stresses - Strain EnergyDocument11 pagesStress - Principal Stresses - Strain EnergymanjusitNo ratings yet
- 2 D ElementsDocument14 pages2 D ElementsUpender DhullNo ratings yet
- NHA2430 Formulae SheetDocument10 pagesNHA2430 Formulae SheetomarNo ratings yet
- 1 Math Review: 2.1 Basic DefinitionsDocument6 pages1 Math Review: 2.1 Basic DefinitionsMia GheeNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids Week 7 LecturesDocument15 pagesMechanics of Solids Week 7 LecturesFlynn GouldNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of MaterialsDocument11 pagesMechanics of MaterialsMagesh KumarNo ratings yet
- ChE 210 Lecture 5 Material Balance With Chemical Reaction and Problems Involving Multiple UnitsDocument97 pagesChE 210 Lecture 5 Material Balance With Chemical Reaction and Problems Involving Multiple UnitsMay May MagluyanNo ratings yet
- Nurture Live Semi Major-01 19 Nov SoDocument11 pagesNurture Live Semi Major-01 19 Nov Sothorisking1No ratings yet
- Respiratory Mechanics and Gas ExchangeDocument14 pagesRespiratory Mechanics and Gas ExchangeNithyaa SathishNo ratings yet
- Capillary ElectrophoresisDocument16 pagesCapillary ElectrophoresisSaksham Sanwaria100% (1)
- PBR Guide Vol.1 - UnknownDocument13 pagesPBR Guide Vol.1 - Unknownwocukav1122100% (3)
- Achievement Test Review Part 2Document99 pagesAchievement Test Review Part 2amsi_qtpi100% (2)
- Extraction Copper PDFDocument2 pagesExtraction Copper PDFWilliamNo ratings yet
- Wrapidbond™ FST: A Visco-Elastic Adhesive Based System For Pipeline Corrosion ProtectionDocument2 pagesWrapidbond™ FST: A Visco-Elastic Adhesive Based System For Pipeline Corrosion ProtectionDinesh PillaiNo ratings yet
- Nano Particle Technology For Drug Delivery (2006)Document427 pagesNano Particle Technology For Drug Delivery (2006)prishly7108100% (3)
- 1 s2.0 S2090123213000969 MainDocument17 pages1 s2.0 S2090123213000969 Mainmarius_alex_32No ratings yet
- Chlorides and SulphatesDocument4 pagesChlorides and SulphatesRESHMYNo ratings yet
- 0 7 PIA Module 15 (Gas Turbine Engine) Sub Module 15.7 (Exhaust)Document25 pages0 7 PIA Module 15 (Gas Turbine Engine) Sub Module 15.7 (Exhaust)soophiakNo ratings yet
- Set6ans 10Document4 pagesSet6ans 10AndrewNo ratings yet
- Standard Cylinder DNC-63 - PPV-A: Data SheetDocument1 pageStandard Cylinder DNC-63 - PPV-A: Data SheetAnonymous 1JHrgYNo ratings yet
- A Serie MouvexDocument3 pagesA Serie Mouvexrasotto100% (1)
- Transport in PlantsDocument5 pagesTransport in PlantsAlex LochaiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Science Manual - Class 10 - Module 2Document80 pagesCBSE Science Manual - Class 10 - Module 2msujoyNo ratings yet
- CmosDocument207 pagesCmossuneeldvNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Rate ConversionDocument2 pagesCorrosion Rate ConversionBakti PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 CatalysisDocument31 pagesChapter 5 CatalysisHien HoangNo ratings yet
- Parte 5 PDFDocument215 pagesParte 5 PDFCATALINANo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Compressor Optimum Design and Manufacturing With Respect To Performance Reliability and CostDocument6 pagesReciprocating Compressor Optimum Design and Manufacturing With Respect To Performance Reliability and Costnnandha100% (1)
- Sika® Viscocrete®-180 G: Product Data SheetDocument3 pagesSika® Viscocrete®-180 G: Product Data SheetRyan PradanaNo ratings yet
- Collagen My SeminarDocument46 pagesCollagen My Seminarrupali100% (1)
- 220801bnejs3963 Cdfex0 33Document33 pages220801bnejs3963 Cdfex0 33tskmechNo ratings yet
- Notes On 150Mhz and DNADocument5 pagesNotes On 150Mhz and DNAoscarnine100% (1)
- Development and Analysis of Butt and Lap Welds in Micro Friction Stir Welding ( FSW)Document5 pagesDevelopment and Analysis of Butt and Lap Welds in Micro Friction Stir Welding ( FSW)HahaNo ratings yet