Professional Documents
Culture Documents
,, ,,, and The
,, ,,, and The
Uploaded by
SaswataCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Copart Fees - USA and Canada MembersDocument9 pagesCopart Fees - USA and Canada MembersMike Villegas100% (1)
- Guitar Center PDFDocument3 pagesGuitar Center PDFVeronica FaithNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Investment Science by David LuenbergerDocument2 pagesSolution Manual For Investment Science by David Luenbergeryoogs0% (1)
- Social Commerce - Consumer Behaviour in Online Environments PDFDocument289 pagesSocial Commerce - Consumer Behaviour in Online Environments PDFace187No ratings yet
- IFMMDocument8 pagesIFMMRanan AlaghaNo ratings yet
- Possible Macro-Finance QuestionsDocument30 pagesPossible Macro-Finance QuestionsPATRICIA TRUJILLO SANZNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy Module 5Document6 pagesMonetary Policy Module 5Idyelle Princess Salubo MalimbanNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Establishing A Monetary Union On The Integration of Financial MarketsDocument19 pagesThe Effects of Establishing A Monetary Union On The Integration of Financial MarketsKaustubh BomewarNo ratings yet
- If Assignmengt 1Document6 pagesIf Assignmengt 1Noor AmjadNo ratings yet
- Bisp MPDocument5 pagesBisp MPkab riyadhNo ratings yet
- Investigating The Asymmetric Impact of Oil Prices On GCC Stock MarketsDocument41 pagesInvestigating The Asymmetric Impact of Oil Prices On GCC Stock MarketsNacNo ratings yet
- Vietnamese Dong: Pros For A Fixed/Pegged RateDocument2 pagesVietnamese Dong: Pros For A Fixed/Pegged RateAnisur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Module 5 ActivityDocument15 pagesModule 5 Activitysandrini salinasNo ratings yet
- Bretton Woods SystemDocument12 pagesBretton Woods SystemAadi SarinNo ratings yet
- AFW 3331 T1 Answers1Document7 pagesAFW 3331 T1 Answers1Zhang MengNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Impact of Exchange Rate On Foreign TradeDocument15 pagesAssignment On Impact of Exchange Rate On Foreign TradeSheikh Munirul Hakim67% (3)
- Unit - 4: Exchange Rate and Its Economic Effects: Learning OutcomesDocument20 pagesUnit - 4: Exchange Rate and Its Economic Effects: Learning Outcomesganeshnavi2008No ratings yet
- Government Influence On Exchange Rates Presented by (1) 11111111111111Document16 pagesGovernment Influence On Exchange Rates Presented by (1) 11111111111111Faizan AbidNo ratings yet
- Common Currency in AsiaDocument8 pagesCommon Currency in AsiaAbhishekGuptaNo ratings yet
- MPRA Paper 104145Document45 pagesMPRA Paper 104145Thùy LinhhNo ratings yet
- Appendix II: Fixed Vs Flexible Exchange RatesDocument4 pagesAppendix II: Fixed Vs Flexible Exchange RatesMasara OwenNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange Market Foreign Exchange Traders Interest Rates Country's DebtDocument9 pagesForeign Exchange Market Foreign Exchange Traders Interest Rates Country's DebtBP JoshieNo ratings yet
- Fixed Exchange Rate System - Introduction: Monetary DisciplineDocument3 pagesFixed Exchange Rate System - Introduction: Monetary DisciplineUmairAfzalNo ratings yet
- BBMF2103 ITF Tutorial 5Document8 pagesBBMF2103 ITF Tutorial 5christyyjx-wp20No ratings yet
- Workers and Unions Structural AdjustmentsDocument47 pagesWorkers and Unions Structural AdjustmentsveeerajNo ratings yet
- Politica MonetaraDocument9 pagesPolitica MonetaraCostache Madalina AlexandraNo ratings yet
- An Assignment On: D.Pradeep KumarDocument4 pagesAn Assignment On: D.Pradeep Kumarpradeep3673No ratings yet
- Advantages N Disadvantages of Fixed Xchange RateDocument3 pagesAdvantages N Disadvantages of Fixed Xchange RateMohammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- Fixed Exchange RatesDocument2 pagesFixed Exchange RatesMuhammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- General Assessment of The Macroeconomic Situation: The Recovery Is Strengthening Albeit Slowly and UnevenlyDocument82 pagesGeneral Assessment of The Macroeconomic Situation: The Recovery Is Strengthening Albeit Slowly and UnevenlygbbajajNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 MacroDocument27 pagesUnit 5 MacroBhavani venkatesanNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument7 pagesProjectRajeshwari ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Economic Note 51 PDFDocument34 pagesEconomic Note 51 PDFWanMuhammadSyafiqNo ratings yet
- Relevance To IndiaDocument2 pagesRelevance To Indiasairaj bhatkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document23 pagesChapter 11Fazila AzharNo ratings yet
- A Level Exchange Rate SystemDocument6 pagesA Level Exchange Rate SystemFokerNo ratings yet
- International Financial Management: by Jeff MaduraDocument32 pagesInternational Financial Management: by Jeff MaduraBe Like ComsianNo ratings yet
- Rapport Gfi FINAL (2Document19 pagesRapport Gfi FINAL (2karimaelidris96No ratings yet
- Monetary and Fiscal Policy in The Euro AreaDocument17 pagesMonetary and Fiscal Policy in The Euro Areausman098No ratings yet
- MPRA Paper 28245Document32 pagesMPRA Paper 28245Ali HbashahNo ratings yet
- What Are The Main Advantages and Disadvantages of Fixed Exchange RatesDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Main Advantages and Disadvantages of Fixed Exchange RatesGaurav Sikdar0% (1)
- Exchange Rate Volatility and Economic Growth in Nigeria by Moguluwa Sochima 2Document13 pagesExchange Rate Volatility and Economic Growth in Nigeria by Moguluwa Sochima 2leonxchima SmogNo ratings yet
- Regional Economic Outlook: Dealing With Shocks Evidence From Old EU Members and Serbia by Abdelmoneim YoussefDocument9 pagesRegional Economic Outlook: Dealing With Shocks Evidence From Old EU Members and Serbia by Abdelmoneim Youssefabdelmoneim_youssefNo ratings yet
- Impact of The Currency Exchange RateDocument2 pagesImpact of The Currency Exchange RateLawrence JimenoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document6 pagesChapter 6jon doeeNo ratings yet
- Q1) Factors Affecting Exchange Rates: Interest and Inflation RatesDocument7 pagesQ1) Factors Affecting Exchange Rates: Interest and Inflation RatesMandar SangleNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Exchange RateDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting Exchange Rateparthiban25No ratings yet
- ECO 111 - Qu NH Trâm 180055 (2) 9Document10 pagesECO 111 - Qu NH Trâm 180055 (2) 9tramhtqqs180055No ratings yet
- Objectives and Targets of Monetary PolicyDocument30 pagesObjectives and Targets of Monetary PolicynadeemhumdardNo ratings yet
- Prepared For Members and Committees of CongressDocument24 pagesPrepared For Members and Committees of CongressFami mikaelNo ratings yet
- CRS Report For Congress: Fixed Exchange Rates, Floating Exchange Rates, and Currency Boards: What Have We Learned?Document27 pagesCRS Report For Congress: Fixed Exchange Rates, Floating Exchange Rates, and Currency Boards: What Have We Learned?Husnina HasniNo ratings yet
- IMT Covid19Document3 pagesIMT Covid19shiv sharmaNo ratings yet
- Wellington Middle East UnrestDocument5 pagesWellington Middle East UnrestmariovassarNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate Regime Currency Foreign Exchange Market Floating CurrencyDocument6 pagesExchange Rate Regime Currency Foreign Exchange Market Floating Currencypradeep3673100% (1)
- Floating Exchange RateDocument2 pagesFloating Exchange RateMuhammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- Rbi Monetory TechniquesDocument4 pagesRbi Monetory TechniquesDarshan JainNo ratings yet
- Investigating The Asymmetric Impact of Oil Prices On GCC - 2021 - Economic ModelDocument16 pagesInvestigating The Asymmetric Impact of Oil Prices On GCC - 2021 - Economic ModelThảo Trần Thị ThuNo ratings yet
- MPRA Paper 22484 (KuwaiKt)Document29 pagesMPRA Paper 22484 (KuwaiKt)pappu khanNo ratings yet
- Ifm 1Document7 pagesIfm 1Nickson KamarajNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Floating Exchange RatesDocument3 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Floating Exchange RatesSyedAshirBukhari50% (2)
- Chapter 6: Government Influence On Exchange Rate Exchange Rate System Fixed Exchange Rate SystemDocument5 pagesChapter 6: Government Influence On Exchange Rate Exchange Rate System Fixed Exchange Rate SystemMayliya Alfi NurritaNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate Movements: Changes in ExportsDocument11 pagesExchange Rate Movements: Changes in ExportsamitNo ratings yet
- Diss Final IntroDocument11 pagesDiss Final IntroRam SinghNo ratings yet
- Course 405: Production Technologies: Surender KumarDocument56 pagesCourse 405: Production Technologies: Surender KumarSaswataNo ratings yet
- 04Foster&Rosenzweig JPE1995Document35 pages04Foster&Rosenzweig JPE1995SaswataNo ratings yet
- Coursework Petroleum Processes and ControlDocument2 pagesCoursework Petroleum Processes and ControlSaswataNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Random Variables and Their Distributions: Rohini Somanathan Course 003, 2016Document16 pagesTopic 2: Random Variables and Their Distributions: Rohini Somanathan Course 003, 2016SaswataNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignment 13 - SolutionsDocument4 pagesHomework Assignment 13 - SolutionsSaswataNo ratings yet
- Optical Instruments Type 1Document8 pagesOptical Instruments Type 1SaswataNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument2 pagesVectorsSaswataNo ratings yet
- Practice MidtermDocument8 pagesPractice MidtermghaniaNo ratings yet
- 2019 Business Agility Institute Report PDFDocument24 pages2019 Business Agility Institute Report PDFUsman SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1 Thru 8 Review Questions Rev 2Document108 pagesChapters 1 Thru 8 Review Questions Rev 2wilchaNo ratings yet
- Duong Thanh Uyen - k204090478 - Acr4.2Document48 pagesDuong Thanh Uyen - k204090478 - Acr4.2Thanh UyênNo ratings yet
- SwagDocument15 pagesSwagPr ManagerNo ratings yet
- Staff ListDocument2 pagesStaff Listaslam vpNo ratings yet
- Ride - Along - Form - LSPD-.docx MMDocument2 pagesRide - Along - Form - LSPD-.docx MMmohammedbader976No ratings yet
- Fasb 155 PDFDocument2 pagesFasb 155 PDFDanNo ratings yet
- IPE 336 - Session 2014Document10 pagesIPE 336 - Session 2014ridoy2146No ratings yet
- 0455 s09 QP 2Document4 pages0455 s09 QP 2Thalansh BatraNo ratings yet
- Target CostingDocument17 pagesTarget CostingJashan VirkNo ratings yet
- Flexible Budgets and Variance Analysis: © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Slide 12-1Document14 pagesFlexible Budgets and Variance Analysis: © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Slide 12-1nowthisisitkoolNo ratings yet
- Bahrain and Qatar Report - 3rd Quarter 2008Document4 pagesBahrain and Qatar Report - 3rd Quarter 2008ahmadtebiNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting Ifrs 2nd Edition Warfield Test BankDocument35 pagesIntermediate Accounting Ifrs 2nd Edition Warfield Test Banksportfulscenefulzb3nhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AccountingDocument30 pagesIntroduction To AccountingCherie LeeNo ratings yet
- C - Report 18 PDFDocument32 pagesC - Report 18 PDF30 Novita Kusuma WardhaniNo ratings yet
- New StatementDocument15 pagesNew Statementankitks53No ratings yet
- Segmentation and PositioningDocument10 pagesSegmentation and Positioningsujeetleopard100% (1)
- Commodity MarketsDocument35 pagesCommodity MarketschandanmiddhaNo ratings yet
- PelDocument29 pagesPelSalman AmjadNo ratings yet
- DT 102 LibrariesGuide enDocument95 pagesDT 102 LibrariesGuide enhaseena_lalNo ratings yet
- DTDC Courier Cargo LTDDocument3 pagesDTDC Courier Cargo LTDDeepakkmrgupta786No ratings yet
- Midterm - Quiz - AEC6Document4 pagesMidterm - Quiz - AEC6aprilNo ratings yet
- Hall & Jones (1999)Document35 pagesHall & Jones (1999)Charly D WhiteNo ratings yet
- Applying International Financial Reporting Standards Picker 3rd Edition Test BankDocument7 pagesApplying International Financial Reporting Standards Picker 3rd Edition Test BankDebbie Platt100% (34)
,, ,,, and The
,, ,,, and The
Uploaded by
SaswataOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
,, ,,, and The
,, ,,, and The
Uploaded by
SaswataCopyright:
Available Formats
Background
Members states of GCC : Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab
Emirates
What is the need of implementation of a common Monetary Union by GCC ?
GCC was set up in 1981. One of the motives of setting up GCC was to increase trade between
its member states [Greater Economic Integration].
At the end of 2007 to further the motive of Economic integration of member states of GCC, a
common market was formally agreed between the member states. Once the policy of common
market is implemented, it will allow free movement of labour, capital and goods between the
member states. For the proper functioning and implementation of the common market policy, it
was important to introduce a common currency which will help in eliminating the transaction
costs in bilateral exchanges between the member states. This will lead to greater efficiency in
economic transaction between the member states & will also help in economic integration of the
member states.
Formation of GCC monetary Union was seen to be essential to ensure enhanced economic
stability and economic integration of the member states.
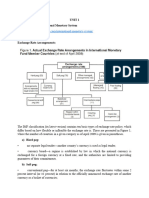
Fixed Exchange Rate Regime of GCC
GCC follows a fixed exchange rate regime where the currency is pegged to the US dollar.
Oil is the chief commodity of export in GCC member states and oil prices are fixed in dollars (here
fixed means negotiated in terms of dollars). But, the decrease in oil prices has resulted in declining
revenues and current account deficits. The economic growth in US will be robust in the next few
years. The US economy is expanding but at the same time the GCC economies are contracting over
low oil prices and geo political instability. With the US economy expanding, it is gradually expected
to increase its interest rates. Decline in oil prices will also lead to currency depreciation in the GCC
member states. But, due to the substantial amount of FOREX reserves at the disposal of GCC
member states, they will be able to resist substantial currency depreciation for some period of time.
Although reserves ensure stability in the medium run but in the long run, currency depreciation will
lead to high rate of inflation. GCC banks in response to increase in rate of interest by US Federal
Reserve and to limit inflation will need to increase the interest rates. As a result growth and
investment will be negatively impacted.
[It is normally argued that depreciation in currency increases export competitiveness but this is not
likely to have a large impact on GCC member states due to following factors :
1. Equilibrium in oil market is set in international market
2. States like Iran, Venezuela , Russia also control substantial reserves of oil. In case of increase in
export competitiveness of GCC member states, these nations are expected to act counteractively
through their monetary policy to ensure that the advantage of GCC countries in export
competiveness does not last long ]
More over countries like Kuwait, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates may have
sufficient central bank reserves to withstand this period of currency depreciation and low
economic growth in the medium run but Oman and Bahrain do not have sufficient reserves for
them to last such a period of economic growth for more than 3-4 years.
2. Disadvantage of a currency union -
Member states of GCC will lose the ability of using an independent monetary policy to stimulate the
economy in times of asymmetric or unexpected shocks. There is a possibility that the economic
shocks may adversely affect some nations and not others. Such a scenario will further lead to
political instability and the reduced flexibility of the currency union will compound the effect of the
economic shock. There are further chances of instability in such a system owing to the fact that it
depends on how smaller nations are affected by such a system and how a dominant member exerts
its influence on other member states.
Conclusion
The current exchange rate arrangements of the Gulf Cooperation Council is not sustainable in the
long run as it is pegged against dollar which is although a credible anchor but still the economic setup
of the US economy is vastly different from the economic set up of GCC member states. So, certain
economic factors ( in this case oil price change) which may affect GCC member states in one way,
may affect US economy in the other way or its effect may be negligible. Macroeconomic adjustments
(rise in interest rates in this case) of US economy will be forced on the GCC monetary union which
may makes the matters even worse for the GCC member States. It is advisable that the GCC pegs its
currency against the currency of a nation which has similar economic conditions as that of GCC and
is stable in the long run.
You might also like
- Copart Fees - USA and Canada MembersDocument9 pagesCopart Fees - USA and Canada MembersMike Villegas100% (1)
- Guitar Center PDFDocument3 pagesGuitar Center PDFVeronica FaithNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Investment Science by David LuenbergerDocument2 pagesSolution Manual For Investment Science by David Luenbergeryoogs0% (1)
- Social Commerce - Consumer Behaviour in Online Environments PDFDocument289 pagesSocial Commerce - Consumer Behaviour in Online Environments PDFace187No ratings yet
- IFMMDocument8 pagesIFMMRanan AlaghaNo ratings yet
- Possible Macro-Finance QuestionsDocument30 pagesPossible Macro-Finance QuestionsPATRICIA TRUJILLO SANZNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy Module 5Document6 pagesMonetary Policy Module 5Idyelle Princess Salubo MalimbanNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Establishing A Monetary Union On The Integration of Financial MarketsDocument19 pagesThe Effects of Establishing A Monetary Union On The Integration of Financial MarketsKaustubh BomewarNo ratings yet
- If Assignmengt 1Document6 pagesIf Assignmengt 1Noor AmjadNo ratings yet
- Bisp MPDocument5 pagesBisp MPkab riyadhNo ratings yet
- Investigating The Asymmetric Impact of Oil Prices On GCC Stock MarketsDocument41 pagesInvestigating The Asymmetric Impact of Oil Prices On GCC Stock MarketsNacNo ratings yet
- Vietnamese Dong: Pros For A Fixed/Pegged RateDocument2 pagesVietnamese Dong: Pros For A Fixed/Pegged RateAnisur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Module 5 ActivityDocument15 pagesModule 5 Activitysandrini salinasNo ratings yet
- Bretton Woods SystemDocument12 pagesBretton Woods SystemAadi SarinNo ratings yet
- AFW 3331 T1 Answers1Document7 pagesAFW 3331 T1 Answers1Zhang MengNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Impact of Exchange Rate On Foreign TradeDocument15 pagesAssignment On Impact of Exchange Rate On Foreign TradeSheikh Munirul Hakim67% (3)
- Unit - 4: Exchange Rate and Its Economic Effects: Learning OutcomesDocument20 pagesUnit - 4: Exchange Rate and Its Economic Effects: Learning Outcomesganeshnavi2008No ratings yet
- Government Influence On Exchange Rates Presented by (1) 11111111111111Document16 pagesGovernment Influence On Exchange Rates Presented by (1) 11111111111111Faizan AbidNo ratings yet
- Common Currency in AsiaDocument8 pagesCommon Currency in AsiaAbhishekGuptaNo ratings yet
- MPRA Paper 104145Document45 pagesMPRA Paper 104145Thùy LinhhNo ratings yet
- Appendix II: Fixed Vs Flexible Exchange RatesDocument4 pagesAppendix II: Fixed Vs Flexible Exchange RatesMasara OwenNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange Market Foreign Exchange Traders Interest Rates Country's DebtDocument9 pagesForeign Exchange Market Foreign Exchange Traders Interest Rates Country's DebtBP JoshieNo ratings yet
- Fixed Exchange Rate System - Introduction: Monetary DisciplineDocument3 pagesFixed Exchange Rate System - Introduction: Monetary DisciplineUmairAfzalNo ratings yet
- BBMF2103 ITF Tutorial 5Document8 pagesBBMF2103 ITF Tutorial 5christyyjx-wp20No ratings yet
- Workers and Unions Structural AdjustmentsDocument47 pagesWorkers and Unions Structural AdjustmentsveeerajNo ratings yet
- Politica MonetaraDocument9 pagesPolitica MonetaraCostache Madalina AlexandraNo ratings yet
- An Assignment On: D.Pradeep KumarDocument4 pagesAn Assignment On: D.Pradeep Kumarpradeep3673No ratings yet
- Advantages N Disadvantages of Fixed Xchange RateDocument3 pagesAdvantages N Disadvantages of Fixed Xchange RateMohammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- Fixed Exchange RatesDocument2 pagesFixed Exchange RatesMuhammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- General Assessment of The Macroeconomic Situation: The Recovery Is Strengthening Albeit Slowly and UnevenlyDocument82 pagesGeneral Assessment of The Macroeconomic Situation: The Recovery Is Strengthening Albeit Slowly and UnevenlygbbajajNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 MacroDocument27 pagesUnit 5 MacroBhavani venkatesanNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument7 pagesProjectRajeshwari ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Economic Note 51 PDFDocument34 pagesEconomic Note 51 PDFWanMuhammadSyafiqNo ratings yet
- Relevance To IndiaDocument2 pagesRelevance To Indiasairaj bhatkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document23 pagesChapter 11Fazila AzharNo ratings yet
- A Level Exchange Rate SystemDocument6 pagesA Level Exchange Rate SystemFokerNo ratings yet
- International Financial Management: by Jeff MaduraDocument32 pagesInternational Financial Management: by Jeff MaduraBe Like ComsianNo ratings yet
- Rapport Gfi FINAL (2Document19 pagesRapport Gfi FINAL (2karimaelidris96No ratings yet
- Monetary and Fiscal Policy in The Euro AreaDocument17 pagesMonetary and Fiscal Policy in The Euro Areausman098No ratings yet
- MPRA Paper 28245Document32 pagesMPRA Paper 28245Ali HbashahNo ratings yet
- What Are The Main Advantages and Disadvantages of Fixed Exchange RatesDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Main Advantages and Disadvantages of Fixed Exchange RatesGaurav Sikdar0% (1)
- Exchange Rate Volatility and Economic Growth in Nigeria by Moguluwa Sochima 2Document13 pagesExchange Rate Volatility and Economic Growth in Nigeria by Moguluwa Sochima 2leonxchima SmogNo ratings yet
- Regional Economic Outlook: Dealing With Shocks Evidence From Old EU Members and Serbia by Abdelmoneim YoussefDocument9 pagesRegional Economic Outlook: Dealing With Shocks Evidence From Old EU Members and Serbia by Abdelmoneim Youssefabdelmoneim_youssefNo ratings yet
- Impact of The Currency Exchange RateDocument2 pagesImpact of The Currency Exchange RateLawrence JimenoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document6 pagesChapter 6jon doeeNo ratings yet
- Q1) Factors Affecting Exchange Rates: Interest and Inflation RatesDocument7 pagesQ1) Factors Affecting Exchange Rates: Interest and Inflation RatesMandar SangleNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Exchange RateDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting Exchange Rateparthiban25No ratings yet
- ECO 111 - Qu NH Trâm 180055 (2) 9Document10 pagesECO 111 - Qu NH Trâm 180055 (2) 9tramhtqqs180055No ratings yet
- Objectives and Targets of Monetary PolicyDocument30 pagesObjectives and Targets of Monetary PolicynadeemhumdardNo ratings yet
- Prepared For Members and Committees of CongressDocument24 pagesPrepared For Members and Committees of CongressFami mikaelNo ratings yet
- CRS Report For Congress: Fixed Exchange Rates, Floating Exchange Rates, and Currency Boards: What Have We Learned?Document27 pagesCRS Report For Congress: Fixed Exchange Rates, Floating Exchange Rates, and Currency Boards: What Have We Learned?Husnina HasniNo ratings yet
- IMT Covid19Document3 pagesIMT Covid19shiv sharmaNo ratings yet
- Wellington Middle East UnrestDocument5 pagesWellington Middle East UnrestmariovassarNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate Regime Currency Foreign Exchange Market Floating CurrencyDocument6 pagesExchange Rate Regime Currency Foreign Exchange Market Floating Currencypradeep3673100% (1)
- Floating Exchange RateDocument2 pagesFloating Exchange RateMuhammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- Rbi Monetory TechniquesDocument4 pagesRbi Monetory TechniquesDarshan JainNo ratings yet
- Investigating The Asymmetric Impact of Oil Prices On GCC - 2021 - Economic ModelDocument16 pagesInvestigating The Asymmetric Impact of Oil Prices On GCC - 2021 - Economic ModelThảo Trần Thị ThuNo ratings yet
- MPRA Paper 22484 (KuwaiKt)Document29 pagesMPRA Paper 22484 (KuwaiKt)pappu khanNo ratings yet
- Ifm 1Document7 pagesIfm 1Nickson KamarajNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Floating Exchange RatesDocument3 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Floating Exchange RatesSyedAshirBukhari50% (2)
- Chapter 6: Government Influence On Exchange Rate Exchange Rate System Fixed Exchange Rate SystemDocument5 pagesChapter 6: Government Influence On Exchange Rate Exchange Rate System Fixed Exchange Rate SystemMayliya Alfi NurritaNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate Movements: Changes in ExportsDocument11 pagesExchange Rate Movements: Changes in ExportsamitNo ratings yet
- Diss Final IntroDocument11 pagesDiss Final IntroRam SinghNo ratings yet
- Course 405: Production Technologies: Surender KumarDocument56 pagesCourse 405: Production Technologies: Surender KumarSaswataNo ratings yet
- 04Foster&Rosenzweig JPE1995Document35 pages04Foster&Rosenzweig JPE1995SaswataNo ratings yet
- Coursework Petroleum Processes and ControlDocument2 pagesCoursework Petroleum Processes and ControlSaswataNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Random Variables and Their Distributions: Rohini Somanathan Course 003, 2016Document16 pagesTopic 2: Random Variables and Their Distributions: Rohini Somanathan Course 003, 2016SaswataNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignment 13 - SolutionsDocument4 pagesHomework Assignment 13 - SolutionsSaswataNo ratings yet
- Optical Instruments Type 1Document8 pagesOptical Instruments Type 1SaswataNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument2 pagesVectorsSaswataNo ratings yet
- Practice MidtermDocument8 pagesPractice MidtermghaniaNo ratings yet
- 2019 Business Agility Institute Report PDFDocument24 pages2019 Business Agility Institute Report PDFUsman SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1 Thru 8 Review Questions Rev 2Document108 pagesChapters 1 Thru 8 Review Questions Rev 2wilchaNo ratings yet
- Duong Thanh Uyen - k204090478 - Acr4.2Document48 pagesDuong Thanh Uyen - k204090478 - Acr4.2Thanh UyênNo ratings yet
- SwagDocument15 pagesSwagPr ManagerNo ratings yet
- Staff ListDocument2 pagesStaff Listaslam vpNo ratings yet
- Ride - Along - Form - LSPD-.docx MMDocument2 pagesRide - Along - Form - LSPD-.docx MMmohammedbader976No ratings yet
- Fasb 155 PDFDocument2 pagesFasb 155 PDFDanNo ratings yet
- IPE 336 - Session 2014Document10 pagesIPE 336 - Session 2014ridoy2146No ratings yet
- 0455 s09 QP 2Document4 pages0455 s09 QP 2Thalansh BatraNo ratings yet
- Target CostingDocument17 pagesTarget CostingJashan VirkNo ratings yet
- Flexible Budgets and Variance Analysis: © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Slide 12-1Document14 pagesFlexible Budgets and Variance Analysis: © 2007 Pearson Education Canada Slide 12-1nowthisisitkoolNo ratings yet
- Bahrain and Qatar Report - 3rd Quarter 2008Document4 pagesBahrain and Qatar Report - 3rd Quarter 2008ahmadtebiNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting Ifrs 2nd Edition Warfield Test BankDocument35 pagesIntermediate Accounting Ifrs 2nd Edition Warfield Test Banksportfulscenefulzb3nhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AccountingDocument30 pagesIntroduction To AccountingCherie LeeNo ratings yet
- C - Report 18 PDFDocument32 pagesC - Report 18 PDF30 Novita Kusuma WardhaniNo ratings yet
- New StatementDocument15 pagesNew Statementankitks53No ratings yet
- Segmentation and PositioningDocument10 pagesSegmentation and Positioningsujeetleopard100% (1)
- Commodity MarketsDocument35 pagesCommodity MarketschandanmiddhaNo ratings yet
- PelDocument29 pagesPelSalman AmjadNo ratings yet
- DT 102 LibrariesGuide enDocument95 pagesDT 102 LibrariesGuide enhaseena_lalNo ratings yet
- DTDC Courier Cargo LTDDocument3 pagesDTDC Courier Cargo LTDDeepakkmrgupta786No ratings yet
- Midterm - Quiz - AEC6Document4 pagesMidterm - Quiz - AEC6aprilNo ratings yet
- Hall & Jones (1999)Document35 pagesHall & Jones (1999)Charly D WhiteNo ratings yet
- Applying International Financial Reporting Standards Picker 3rd Edition Test BankDocument7 pagesApplying International Financial Reporting Standards Picker 3rd Edition Test BankDebbie Platt100% (34)