Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enzymes: Regulation of Activities Homeostasis Compartmentation
Enzymes: Regulation of Activities Homeostasis Compartmentation
Uploaded by
Yheng GaosaiiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Insulin PresentationDocument43 pagesInsulin Presentationinnocence faded100% (2)
- Chapter 27Document3 pagesChapter 27Yheng GaosaiiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter 9: Enzymes: Regulation of ActivitiesDocument2 pagesBiochemistry Chapter 9: Enzymes: Regulation of ActivitiesJethro Floyd QuintoNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM ReviewerDocument3 pagesBIOCHEM ReviewerKyla RamonesNo ratings yet
- Biochem QuizDocument2 pagesBiochem QuizNicole MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument13 pagesAcute PancreatitisJacob BorongNo ratings yet
- Hormones III: Cytokinins: Cytokinins Are Adenine DerivativesDocument2 pagesHormones III: Cytokinins: Cytokinins Are Adenine DerivativesNurul AlifahNo ratings yet
- Biology Chap 9 Form 4Document10 pagesBiology Chap 9 Form 4Nurin Irdina FarisshNo ratings yet
- IUBMB Life - 2022 - Cerone - Desaturases Structural and Mechanistic Insights Into The Biosynthesis of Unsaturated FattyDocument16 pagesIUBMB Life - 2022 - Cerone - Desaturases Structural and Mechanistic Insights Into The Biosynthesis of Unsaturated FattyRamanan ThirumoorthyNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry - Activity 2Document3 pagesFood Chemistry - Activity 2Leda PeñaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Nutrition & The Human Digestive System: 9.3 Absorption 9.4 AssimilationDocument9 pagesChapter 9: Nutrition & The Human Digestive System: 9.3 Absorption 9.4 Assimilation静宁No ratings yet
- Enzymes: Non-Starch Polysaccharides (NSP)Document6 pagesEnzymes: Non-Starch Polysaccharides (NSP)amamùra maamarNo ratings yet
- MBG312 Chp23 BDDocument47 pagesMBG312 Chp23 BDBaran KirdarNo ratings yet
- Biology 3 Tuto 1Document43 pagesBiology 3 Tuto 1Firdaus ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Bile Acid Malabsorption May 2020Document9 pagesBile Acid Malabsorption May 2020MUTHMAINNAHNo ratings yet
- Bharucha 2010Document5 pagesBharucha 2010Yanuar PramanaNo ratings yet
- The Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Kidney Physiology and DiseaseDocument19 pagesThe Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Kidney Physiology and DiseaseDiego RodriguezNo ratings yet
- On The Function of Bile Salts and Proteins As Cofactors of LipaseDocument4 pagesOn The Function of Bile Salts and Proteins As Cofactors of Lipasevanapalli_uitmNo ratings yet
- A Balancing Act of Lipids: Excess Cholesterol Contributes To Intestinal TumorigenesisDocument1 pageA Balancing Act of Lipids: Excess Cholesterol Contributes To Intestinal TumorigenesisBeatrice RossNo ratings yet
- Critical Review: Protein TurnoverDocument7 pagesCritical Review: Protein TurnoverSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Place Where It Acts Name of The EnzymeDocument2 pagesPlace Where It Acts Name of The EnzymeValery AcostaNo ratings yet
- RuminantDocument23 pagesRuminantAndres Felipe CHAVES GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Protein DigestionDocument2 pagesProtein Digestionshane.abrugar9116No ratings yet
- Intro To DigestionDocument18 pagesIntro To DigestionelizabethNo ratings yet
- Aoc 2 - BiocatalysisDocument22 pagesAoc 2 - BiocatalysisUsha gowdaNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction Lecture1: Introduction: NPTEL: IIT KharagpurDocument6 pagesModule 1: Introduction Lecture1: Introduction: NPTEL: IIT KharagpurShruti PantNo ratings yet
- Barecuatro - BSN1 11L - Pre Finals ActivityDocument12 pagesBarecuatro - BSN1 11L - Pre Finals ActivityAngelica Claire BarecuatroNo ratings yet
- Enzim&Protein RevDocument52 pagesEnzim&Protein Revkamilah rafaNo ratings yet
- Hypertonic Stress in The Kidney: A Necessary Evil: Min Seong Kwon, Sun Woo Lim and H. Moo KwonDocument7 pagesHypertonic Stress in The Kidney: A Necessary Evil: Min Seong Kwon, Sun Woo Lim and H. Moo Kwoncrina1980No ratings yet
- CMFRI Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesCMFRI Digestive SystemNOORDIYANA MAT NOORDINNo ratings yet
- Gut Kidney Cross TalkDocument37 pagesGut Kidney Cross TalkAbdelrahman MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption: Digestive ProcessDocument6 pagesDigestion and Absorption: Digestive ProcessJoao KasprowiczNo ratings yet
- D'Adamo: Nap Professional ServicesDocument4 pagesD'Adamo: Nap Professional ServicesdrmauraNo ratings yet
- Physio 7 From A.SDocument14 pagesPhysio 7 From A.SAhmed AmarNo ratings yet
- Water Physiology Essentiality, Metabolism, And.8Document6 pagesWater Physiology Essentiality, Metabolism, And.8Patricia ChirinosNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal PhysiologyDocument6 pagesGastrointestinal PhysiologyPedro RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Enzyme: Holoenzyme-BiochemicallyDocument8 pagesEnzyme: Holoenzyme-BiochemicallyStefanie LucresiaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Ap08 PDFDocument12 pagesWorksheet Ap08 PDFIvonneDiazNo ratings yet
- Bile Acids As Inflammatory Mediators and Modulators of Intestinal PermeabilityDocument24 pagesBile Acids As Inflammatory Mediators and Modulators of Intestinal Permeabilitymahsagh7477No ratings yet
- Fluids & Electrolytes AssDocument6 pagesFluids & Electrolytes AssDudil GoatNo ratings yet
- COMPLETE REPORT FERMENTATionDocument45 pagesCOMPLETE REPORT FERMENTATionIntan AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Fcimb 02 00086Document15 pagesFcimb 02 00086Aleksandra Sanja MartinovicNo ratings yet
- Lab12 Fisiología DigestivaDocument7 pagesLab12 Fisiología DigestivacesamavNo ratings yet
- Ass 1 - BCH 2602Document7 pagesAss 1 - BCH 2602grimsdellaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Microbes, and Fiber: Small Versus Large IntestineDocument7 pagesAnatomy, Microbes, and Fiber: Small Versus Large IntestinedidiNo ratings yet
- Biology VocabDocument17 pagesBiology VocabMuhammad Amin Suhaimi100% (1)
- Abscisic AcidDocument14 pagesAbscisic AcidMadhusmita BalNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0092867423000442Document32 pagesPi Is 0092867423000442ANo ratings yet
- Isolation of ProteinDocument3 pagesIsolation of ProteinReysa Gabrielle PileNo ratings yet
- Baron 1963 Serum Enzymes in Clinical Practice Clinical Enzymology With Particular Reference To Liver DiseaseDocument5 pagesBaron 1963 Serum Enzymes in Clinical Practice Clinical Enzymology With Particular Reference To Liver DiseaseEzereonye PeterNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: ADP ADP Phosphorylation (Kinase) PDocument7 pagesBiochemistry: ADP ADP Phosphorylation (Kinase) PVivek VinayakumarNo ratings yet
- EB Cell MembraneDocument68 pagesEB Cell MembraneKera Maria AllengerNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology - Kapitola 21 PDFDocument41 pagesHuman Physiology - Kapitola 21 PDFpummygNo ratings yet
- Lehninger 5º Edicion - Capitulo 15Document45 pagesLehninger 5º Edicion - Capitulo 15Paz VazquezNo ratings yet
- Kim 2011Document6 pagesKim 2011Nicolas Riffo LepeNo ratings yet
- What Is BiochemistryDocument4 pagesWhat Is BiochemistryMary Angel JuanNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document 1Document9 pagesUntitled Document 1Zwen Zyronne Norico LumiwesNo ratings yet
- Efectos No Fisiologicos de Oligosacaridos No DigeriblesDocument6 pagesEfectos No Fisiologicos de Oligosacaridos No DigeribleslccapiramNo ratings yet
- Linus Pauling - Ascorbic Acid and The Glycosaminoglycans - An Orthomolecular Approach To Cancer and Other DiseasesDocument21 pagesLinus Pauling - Ascorbic Acid and The Glycosaminoglycans - An Orthomolecular Approach To Cancer and Other DiseasesFilipos ConstantinNo ratings yet
- On Digestive Proteolysis: Being the Cartwright Lectures for 1894From EverandOn Digestive Proteolysis: Being the Cartwright Lectures for 1894No ratings yet
- Posterior and Anterior MediastinumDocument6 pagesPosterior and Anterior MediastinumYheng GaosaiiNo ratings yet
- Superior MediastinumDocument4 pagesSuperior MediastinumYheng GaosaiiNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument19 pagesHeartYheng GaosaiiNo ratings yet
Enzymes: Regulation of Activities Homeostasis Compartmentation
Enzymes: Regulation of Activities Homeostasis Compartmentation
Uploaded by
Yheng GaosaiiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Enzymes: Regulation of Activities Homeostasis Compartmentation
Enzymes: Regulation of Activities Homeostasis Compartmentation
Uploaded by
Yheng GaosaiiCopyright:
Available Formats
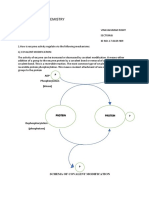
CHAPTER 9
ENZYMES: REGULATION COMPARTMENTATION
OF ACTIVITIES ensures metabolic efficiency & simplifies regulation
HOMEOSTASIS LYSOSOME
the ability of animals to maintain a constant intracellular many of the enzymes that degrade proteins and
environment despite changes in their external polysaccharides resides here
surroundings
term coined by Walter Cannon FATTY ACID BIOSYNTHESIS
occurs in the cytosol
VIBRIO CHOLERAE FATTY ACID OXIDATION
the causative agent of cholera takes place within mitochondria
disables sensor-response pathways in intestinal
epithelial cells by ADP-ribosylating the GTP-binding NOTE:
proteins (G-proteins) that link cell surface receptors to For any reaction or series of reactions, the change in free
adenylyl cyclase energy that takes place when metabolite flow proceeds
The consequent activation of the cyclase leads to the in the forward direction is equal in magnitude but
unrestricted flow of water into the intestines, resulting opposite in sign from that required to proceed in the
in: reverse direction.
massive diarrhea
dehydration
YERSINIA PESTIS
the causative agent of plague
elaborates a protein-tyrosine phosphatase that
hydrolyzes phosphoryl groups on key cytoskeletal
proteins
You might also like
- Insulin PresentationDocument43 pagesInsulin Presentationinnocence faded100% (2)
- Chapter 27Document3 pagesChapter 27Yheng GaosaiiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter 9: Enzymes: Regulation of ActivitiesDocument2 pagesBiochemistry Chapter 9: Enzymes: Regulation of ActivitiesJethro Floyd QuintoNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM ReviewerDocument3 pagesBIOCHEM ReviewerKyla RamonesNo ratings yet
- Biochem QuizDocument2 pagesBiochem QuizNicole MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument13 pagesAcute PancreatitisJacob BorongNo ratings yet
- Hormones III: Cytokinins: Cytokinins Are Adenine DerivativesDocument2 pagesHormones III: Cytokinins: Cytokinins Are Adenine DerivativesNurul AlifahNo ratings yet
- Biology Chap 9 Form 4Document10 pagesBiology Chap 9 Form 4Nurin Irdina FarisshNo ratings yet
- IUBMB Life - 2022 - Cerone - Desaturases Structural and Mechanistic Insights Into The Biosynthesis of Unsaturated FattyDocument16 pagesIUBMB Life - 2022 - Cerone - Desaturases Structural and Mechanistic Insights Into The Biosynthesis of Unsaturated FattyRamanan ThirumoorthyNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry - Activity 2Document3 pagesFood Chemistry - Activity 2Leda PeñaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Nutrition & The Human Digestive System: 9.3 Absorption 9.4 AssimilationDocument9 pagesChapter 9: Nutrition & The Human Digestive System: 9.3 Absorption 9.4 Assimilation静宁No ratings yet
- Enzymes: Non-Starch Polysaccharides (NSP)Document6 pagesEnzymes: Non-Starch Polysaccharides (NSP)amamùra maamarNo ratings yet
- MBG312 Chp23 BDDocument47 pagesMBG312 Chp23 BDBaran KirdarNo ratings yet
- Biology 3 Tuto 1Document43 pagesBiology 3 Tuto 1Firdaus ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Bile Acid Malabsorption May 2020Document9 pagesBile Acid Malabsorption May 2020MUTHMAINNAHNo ratings yet
- Bharucha 2010Document5 pagesBharucha 2010Yanuar PramanaNo ratings yet
- The Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Kidney Physiology and DiseaseDocument19 pagesThe Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Kidney Physiology and DiseaseDiego RodriguezNo ratings yet
- On The Function of Bile Salts and Proteins As Cofactors of LipaseDocument4 pagesOn The Function of Bile Salts and Proteins As Cofactors of Lipasevanapalli_uitmNo ratings yet
- A Balancing Act of Lipids: Excess Cholesterol Contributes To Intestinal TumorigenesisDocument1 pageA Balancing Act of Lipids: Excess Cholesterol Contributes To Intestinal TumorigenesisBeatrice RossNo ratings yet
- Critical Review: Protein TurnoverDocument7 pagesCritical Review: Protein TurnoverSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Place Where It Acts Name of The EnzymeDocument2 pagesPlace Where It Acts Name of The EnzymeValery AcostaNo ratings yet
- RuminantDocument23 pagesRuminantAndres Felipe CHAVES GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Protein DigestionDocument2 pagesProtein Digestionshane.abrugar9116No ratings yet
- Intro To DigestionDocument18 pagesIntro To DigestionelizabethNo ratings yet
- Aoc 2 - BiocatalysisDocument22 pagesAoc 2 - BiocatalysisUsha gowdaNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction Lecture1: Introduction: NPTEL: IIT KharagpurDocument6 pagesModule 1: Introduction Lecture1: Introduction: NPTEL: IIT KharagpurShruti PantNo ratings yet
- Barecuatro - BSN1 11L - Pre Finals ActivityDocument12 pagesBarecuatro - BSN1 11L - Pre Finals ActivityAngelica Claire BarecuatroNo ratings yet
- Enzim&Protein RevDocument52 pagesEnzim&Protein Revkamilah rafaNo ratings yet
- Hypertonic Stress in The Kidney: A Necessary Evil: Min Seong Kwon, Sun Woo Lim and H. Moo KwonDocument7 pagesHypertonic Stress in The Kidney: A Necessary Evil: Min Seong Kwon, Sun Woo Lim and H. Moo Kwoncrina1980No ratings yet
- CMFRI Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesCMFRI Digestive SystemNOORDIYANA MAT NOORDINNo ratings yet
- Gut Kidney Cross TalkDocument37 pagesGut Kidney Cross TalkAbdelrahman MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption: Digestive ProcessDocument6 pagesDigestion and Absorption: Digestive ProcessJoao KasprowiczNo ratings yet
- D'Adamo: Nap Professional ServicesDocument4 pagesD'Adamo: Nap Professional ServicesdrmauraNo ratings yet
- Physio 7 From A.SDocument14 pagesPhysio 7 From A.SAhmed AmarNo ratings yet
- Water Physiology Essentiality, Metabolism, And.8Document6 pagesWater Physiology Essentiality, Metabolism, And.8Patricia ChirinosNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal PhysiologyDocument6 pagesGastrointestinal PhysiologyPedro RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Enzyme: Holoenzyme-BiochemicallyDocument8 pagesEnzyme: Holoenzyme-BiochemicallyStefanie LucresiaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Ap08 PDFDocument12 pagesWorksheet Ap08 PDFIvonneDiazNo ratings yet
- Bile Acids As Inflammatory Mediators and Modulators of Intestinal PermeabilityDocument24 pagesBile Acids As Inflammatory Mediators and Modulators of Intestinal Permeabilitymahsagh7477No ratings yet
- Fluids & Electrolytes AssDocument6 pagesFluids & Electrolytes AssDudil GoatNo ratings yet
- COMPLETE REPORT FERMENTATionDocument45 pagesCOMPLETE REPORT FERMENTATionIntan AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Fcimb 02 00086Document15 pagesFcimb 02 00086Aleksandra Sanja MartinovicNo ratings yet
- Lab12 Fisiología DigestivaDocument7 pagesLab12 Fisiología DigestivacesamavNo ratings yet
- Ass 1 - BCH 2602Document7 pagesAss 1 - BCH 2602grimsdellaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Microbes, and Fiber: Small Versus Large IntestineDocument7 pagesAnatomy, Microbes, and Fiber: Small Versus Large IntestinedidiNo ratings yet
- Biology VocabDocument17 pagesBiology VocabMuhammad Amin Suhaimi100% (1)
- Abscisic AcidDocument14 pagesAbscisic AcidMadhusmita BalNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0092867423000442Document32 pagesPi Is 0092867423000442ANo ratings yet
- Isolation of ProteinDocument3 pagesIsolation of ProteinReysa Gabrielle PileNo ratings yet
- Baron 1963 Serum Enzymes in Clinical Practice Clinical Enzymology With Particular Reference To Liver DiseaseDocument5 pagesBaron 1963 Serum Enzymes in Clinical Practice Clinical Enzymology With Particular Reference To Liver DiseaseEzereonye PeterNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: ADP ADP Phosphorylation (Kinase) PDocument7 pagesBiochemistry: ADP ADP Phosphorylation (Kinase) PVivek VinayakumarNo ratings yet
- EB Cell MembraneDocument68 pagesEB Cell MembraneKera Maria AllengerNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology - Kapitola 21 PDFDocument41 pagesHuman Physiology - Kapitola 21 PDFpummygNo ratings yet
- Lehninger 5º Edicion - Capitulo 15Document45 pagesLehninger 5º Edicion - Capitulo 15Paz VazquezNo ratings yet
- Kim 2011Document6 pagesKim 2011Nicolas Riffo LepeNo ratings yet
- What Is BiochemistryDocument4 pagesWhat Is BiochemistryMary Angel JuanNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document 1Document9 pagesUntitled Document 1Zwen Zyronne Norico LumiwesNo ratings yet
- Efectos No Fisiologicos de Oligosacaridos No DigeriblesDocument6 pagesEfectos No Fisiologicos de Oligosacaridos No DigeribleslccapiramNo ratings yet
- Linus Pauling - Ascorbic Acid and The Glycosaminoglycans - An Orthomolecular Approach To Cancer and Other DiseasesDocument21 pagesLinus Pauling - Ascorbic Acid and The Glycosaminoglycans - An Orthomolecular Approach To Cancer and Other DiseasesFilipos ConstantinNo ratings yet
- On Digestive Proteolysis: Being the Cartwright Lectures for 1894From EverandOn Digestive Proteolysis: Being the Cartwright Lectures for 1894No ratings yet
- Posterior and Anterior MediastinumDocument6 pagesPosterior and Anterior MediastinumYheng GaosaiiNo ratings yet
- Superior MediastinumDocument4 pagesSuperior MediastinumYheng GaosaiiNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument19 pagesHeartYheng GaosaiiNo ratings yet