Professional Documents
Culture Documents
29 ST Gabriel S Paper 22011
29 ST Gabriel S Paper 22011
Uploaded by
Bin Ren0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views13 pageschem
Original Title
29 St Gabriel s Paper 22011
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentchem
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views13 pages29 ST Gabriel S Paper 22011
29 ST Gabriel S Paper 22011
Uploaded by
Bin Renchem
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 13
St. Gabriel’s Secondary School
2011 ‘O’ Preliminary Examination
Subject Chemistry
Paper 5072/2
Level/Stream : 4 Express
Duration 1 hr 45 minutes
Date : 20 September 2011
Setters : Mr. Anthony Phoon
Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
Additional Materials: Answer Paper and Periodic Table
READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST
Write your name and index number on all the work you hand in.
Wiite in dark blue or black pen on both sides of the paper.
You may use a soft pencil for any diagrams, graphs or rough working.
Do not use staples, paper clips, highlighters, glue or correction fluid.
Section A
Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
Section B
Answer all three questions, the last question is in the form
eitherfor. FOR EXAMINER'S USE
Write your answers on the lined paper provided and, if necessary, | Section A
continue on separate answer paper. a
At the end of the examination, fasten all your work securely
together. B8
‘The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each an
question or part question. 89 Either
A ; 83 6R
copy of the Data Sheets printed at bottom of page 13.
A copy of the Periodic Table is printed on page 14, Tour
‘This question paper consists of 14 printed pages including this cover page.
[Turn over
Paper 2
Section A
Answer all questions in this section in the space provided.
The total mark for this section is 50.
Choose from the following compounds to answer the questions (a) to (e) below.
Ammonium chloride
Calcium oxide
Copper (tt) nitrate
Ethene
Nitrogen monoxide
Potassium iodide
of-felol|=l
Sulfuric acid
Use the letters ‘A’ to ‘G' to represent the compounds. Each letter may be used once, more than
‘once or not at all.
‘Which compound
(2) - is most likely to reduce the temperature of water when dissolved ty
(b) forms a yellow precipitate with silver nitrate, i
(€) is used as a test for the presence of an oxidizing agent, .. a
(4) _ is likely to produce a black solid with acidified potassium manganate(Vil), 1
(e) _ is used by farmers to reduce soil acidity? ... tt]
{f) Draw the monomer that is used to produce the polymer shown here:
tm
CH; H Diagram of p@homer:
v3 4
fe
koe hi
(g) A solution of sodium carbonate reacts with hitric acid to produce sodium nitrate, carbon
dioxide and Weer. Write aa ‘onic equation to illustrate this reaction. State symbols are [1]
not required.
2 Potassium chlorate (KCIO,) is a compound that is often used in the making of fireworks. It can
| bbe produced by passing chlorine gas into a concentrated solution of potassium hydroxide.
fa) Balance the following equation to show the reaction-ts produce potassium chlorate.
Ch (9) +6KOH (aq) > _KC10g (aq) +_éRF(aq) +_ 1,0 () "a
{b) Its known that the oxidation number of Botassium is +1 and that of oxyget is -2.
Calculate the oxidation number of chlorine in potassium chloride and potassium chlorate
respectively. Hence, explain whether chlorine is an oxidizing agent or a reducing agent
or both a
(c) "By referring to your answer in (b) and a suitable property of halogens, state whether the
answer to (b) is usual or unusual. (1)
Potassium chlorate can be used to produce oxygen candles which are used as emergency
‘oxygen supplies for firemen and coal-mine rescue crews. Devices that contain oxygen candles
are often filled with a fiter of lithium hydroxide which is used to absorb carbon dioxide. The
equation is shown here:
2LiOH (aq) + CO2 (g) —> LixCO, (aq) + HO (1)
(d)__ Explain why the reaction is a neutralization reaction. (1
(f) Draw a dot-and-cross atagram to show the structure of lithium hydroxide. Show ‘only the
(2) ifamansypically exhales 50 dm? of carbon dioxide per hour, calculate the mass of
lithium hydroxide fequired to last a rescuer who needs to use an oxygen candle for
24 hours.
(31
valence shells.
2]
In an experiment, 10.0 cm® of 1.0 molidm? aqueous copper) sulfate was placed in a conicat
flask. From a burette, 50.0 cm? of 1.0 molidm® aqueous ammohia was slowly added, The flask
was swirled to ensure even mixing of reactants. A probe which measured electrical
conductivity of a solution was also placed in the conical flask and it measured the electrical
conductivity throughout the entire experiment.
Cu™(aq) + 20H(aq) + Cu(OH).(s)
{a) Calculate the number of moles of copper) ions in the mixture.
a
(B) Calculate the number of moles of hydroxide ions from aqueous ammonia in the mixture.
(You may assume aqueous ammonia fully ionizes in this reaction.)
(1)
(c) Making use of your results in (a) and (b), and knowledge of qualitative analysis of
chemicals, describe the observations as all of the aqueous ammonia is slowly added to
the copperifl) silfate solution. Explain the observations,
2
{d1- Desoribe and explain the ¢lrnges in electrical conductivity from the start of the
‘experiment til all the aqueous ammonia has been added.
8)
There are many ways that we can protect the environment. One such way involves the
recycling of metals such as aluminium. Aluminium is a metal that is extracted from the
electrolysis ofits ore which is known as bauxite. To conserve aluminium we can recover it
from drink cans.
(@) Give two reasons why metals such as aluminium should be recycled instead of being
extracted from its ore.
[2]
(6) Fuel cells can be used to replace fossil fuels as a means of'producing electricity. A type
of fuel cellis shown in the diagram below. Bélow the diagram, write down an equation to
illustrate the reaction that occurs at the anode and at the cathode. State symbols are not
required,
Anodic reaction:
(1)
Cathodic reaction:
O)
Make use of your equations to explain how electricity is generated in a fuel cell
ft]
A carbon sink is any natural or artificial reservoir or process that accumulates and stores
carbon-containing compounds for a period of time.
fe) ‘Name one natural carbon sink and describe how it works as a carbon sink.
(e) Explain why carbon monoxide is a pollutant and how its production or release into the
atmosphere can be minimized.
(2]
(21
[2]
a
Copper(ll) nitrate, graphite and co
per can conduct electricity. Consequently they can be used
as materials for electrolysis.
(@) Compare and contrast the ways that copper(I nitrate, graphite and copper conduct
electricity by completing the table.
ie Type(s) of particles State(s) of matter during
Material involved in conducting which it conducts
electricity electricity
Copper(tl) nitrate
Graphite
Copper BB)
(6) Two solutions of copperill) nitrate were separately electrolyzed using copper electrodes and
Graphite electrodes. State how thagsbservations are different by completing the table.
r ‘Anode Cathode Electrolyte
Using copper
Using graphite
[4]
|
(¢) Write an equation to show what happens at the anode when Silvérchitrdte.solution is
electrolyzed using coffer electrodes,
TH
(4) A plastic cup needs to be electroplated with a layer of cop,
per. Explain why it needs to be
Coated with metalic paint before electroplating.
i)
‘The equation for the tgaction of calcium carbonate with hydrachlorig, acid is
CaCO; + 2HCI> CaCl + H,O + CO,
5 q of calcium carbonate granules were added to an excess of dilute hydrochloric acid at 30 °C
and #ts volume was recorded at regular intervals.
fa)
})
(c)
500 cm* of carbon dioxide gas was produced in the experiment. Calculate the
percentage purity of the sample of calcium carbonate granules.
fl
Using the axes below, sketch a graph to show how the rate of this reaction changes with
time. Label this graph (b). or
On the same axes, sketch the graph that you would expect when the experiment wore
repeated at the same temperature with
(i) the same volume and concentration of acid, but with § g of calcium carbonate
powder. Label this graph (ci).
(li) 2.59 of calcium carbonate granules and same volume of acid, but with acid of half
the original concentration. Label this graph (cit. QI
Section B [30 marks]
Write your answers on the foolscap provided,
Answer all three questions from this section,
‘The last question is in the form of either/or and only one altemative should be attempted.
B7 Electrode potential is a way to represent the amount of energy needed for a reaction to occur.
AS such, it can show us how readily a reaction occurs. tn simple terms,
Glectrode potential, the more readily a reaction tends to occur
Electrode reaction
the more positive an
Electrode potential/V |
AID AP +3e +1.66
Ca> Ca +20 42.87
[ Cu> Cu® #26 ~0.34
FedFe*+2e [ay
Fe > Fe +3e +0.04
%Ch+e> ct +1.36
Khteor [F084
CRO? + 7H + 3e > CP + THEO 413300 °
|
(@) Arrange copper, aluminium,
electrode potential
(b) By examining your answer in (a),
electrode potential.
(c) The electrode potential of the reaction Hg Hg + 2e is
above data, suggest whethérst idacts with hydrochloric
(4) Aminer has a choice of extracting iron from two mines
fron and caleium according to decreasing (highest first)
(th
State the relationship between reactivity of metals and
1]
-0.85 V. By referring to the
acid. Explain your answer. 21
One mine is filled mainly with
iron(l) suide while the other is mostly iron( tt) oxide. By ‘eferring to the data, explain
‘which 7s the cheaper mine from which to extract iron,
8)
(2) A student believes that the relative oxidizing ability of different substances can be
deduced from their electrode potentials. Explain whether acidified potassium
Br. fy
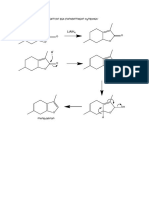
B8 An organic compound citronellol is shown in the diagram below. It is used in the perfume
industry.
{a) Draw the compound that is formed when it reacts with methanoic acid. (1)
(b) Draw the compound that is formed when several identical molecules of citronelicl is
allowed to react at 150 °C.in the presence of nickel powder. 1
(c) _Citronellol is boiled under reflux with acidified potassium dichromate(VI).
{i) Describe what you would expect to observe.
(i) Using structures, show this reaction, I
Unlike inorganic substances, organic substances are often distilled using a method called
steam distillation. The apparatus for this separation technique is shown below. This method is
particularly effective as it allows the organic substance to be distilled at a lower temperature
than its boiling point. Unfortunately, the distillate is a mixture of water and the organic
substance.
{d) Suggest two reasons why most organic substances cannot be separated using simple
distillation, (21
(e) Using a suitable diagram, briefly explain how the organic substance (of density 0.8
glom*) can be separated from water, both of which are in the distillate, 2)
(f) Both protein and Nylon are polyamides. When protein and Nylon are separately broken
down using sodium hydroxide, the resulting monomers of protein were found to have a
fixed boiling point while the monomers of Nylon did not have a fixed boiling point. By
referring to monomers, suggest a reason for this. U1
BS Either
The graph below illustrates t
he trends in boiling points of chlorides of elements in the third period of
the Periodic Table,
1500
1000 Boiling points
500
Temperature / °C
MgCl, PCiz SCh
(a) Explain, in terms of structure ar
ind bonding, the difference in boling points of MgCl, 13]
and SCh. .
(b) Explain, in terms of structure, the difference in boiling points of PC), and SCh, (2)
Chlorine is an important element which is used in many industries, One such use from many
Years back was to make chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). CFCs were ‘sometimes used as
Propeliants in aerosols and as refrigerants. “They tend to'be ‘relatively stable until they reach the
Stratospheric region where they decompose and chlorine atoms, which are formed in the
decomposition reaction, react with ozone molecules. These reactions lead to
layer.
‘holes’ in the ozone
Piluoromethane, CHeFajs a hydrofiuorocarbon, ican be used to replace CFCs in aerosols as it
does not lead to depletion of the ozone layer.
(4) ()_ Explain why holes in the ozone layer can be harmful to our health, 2
(li) Draw a dot-and-cross diagram to show the bonding in difluoromethane, CHF,
showing only the valence shells. 2)
(ili) Suggest a reason why hydroflurocarbons have no effect on the ozone layer. tt]
BO Or
‘Ammonia is manufactured by the Haber process
No+3H, — 2NHs.
The graph below shows the yield of ammonia at different temperature and pressure
conditions.
70
asqec | fF —
60 molt
2 OyrC
3 50
459°C
é 40
50q°c
& 30+--
5 T+
37 po rssre
104
gz an
°
© "50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400
pressure/atinosphere
(a) By referring to the graphs, choose the combination of conditions that gives the highest «
yield of ammonia. (1
(b) The conditions for producing ammonia in industries are 450 °C, 250 atm and iron
powder. Explain why these conditions are chosen instead of the ones that you have
listed in (a). [3]
(c) The Haber process is an exothermic reaction,
{i) Draw the energy profile diagram of this reaction without a catalyst.
(i) On the same axes as (i), draw the energy profile diagram of this reaction with a
catalyst. Label the diagram ‘with catalyst’. 2]
(d) A student reacted 5 g of ammonium chloride with 100 cm? of 0.5 molidm® calcium
hydroxide according to the equation, ZNH.CI +/Ca(OH), >CaCh + NH +PH.0.
(i) Write the ionic equation for this teabtict,
(ii) Calculate the expected volume of ammonia gas produced;
(iii)Explain why the volume of ammonia gas is less than expected.
(4]
End of Paper 2
DATA Sheet ~
Colours of some common metal hydroxides
‘Aluminium hydroxide | White Tron(ily hydroxide Green Zine hydroxide | white
Caicium hydroxide | White lron(ili) hydroxide | Red-brown ~ |
Copperill) hydroxide | Light blue Lead{il) hydroxide White ~
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Miconium Ctac29: Quaternary Ammonium SaltDocument1 pageMiconium Ctac29: Quaternary Ammonium Saltanon_993394650No ratings yet
- DM's Guild - The Elemental Spellbook (5e) PDFDocument24 pagesDM's Guild - The Elemental Spellbook (5e) PDFbalim01100% (1)
- AQUISEL Tubos Instrucciones-EnglishDocument20 pagesAQUISEL Tubos Instrucciones-Englishkukuh100% (1)
- Carnot EngineDocument1 pageCarnot EngineBin RenNo ratings yet
- CSIR Chemical Sciences Solved December 2012 PDFDocument57 pagesCSIR Chemical Sciences Solved December 2012 PDFBin RenNo ratings yet
- I. Differential Equations of Fluid Flow (Note S1)Document5 pagesI. Differential Equations of Fluid Flow (Note S1)Bin RenNo ratings yet
- Oxides of Nitrogen FINALDocument20 pagesOxides of Nitrogen FINALBin RenNo ratings yet
- Y2 B&SiDocument6 pagesY2 B&SiBin RenNo ratings yet
- Csir Chemistry Previous Years Questions With Answer PDFDocument187 pagesCsir Chemistry Previous Years Questions With Answer PDFBin RenNo ratings yet
- 06 G482 ALL QuestionsDocument244 pages06 G482 ALL QuestionsBin RenNo ratings yet
- H OH K H OH A: PH of Any Acid/Base SolutionDocument9 pagesH OH K H OH A: PH of Any Acid/Base SolutionBin RenNo ratings yet
- 2010 s4 Physics Tanjong Katong Sec PrelimDocument37 pages2010 s4 Physics Tanjong Katong Sec PrelimBin RenNo ratings yet
- IJC2009 Chem H2Prelim Paper 3Document12 pagesIJC2009 Chem H2Prelim Paper 3Bin RenNo ratings yet
- Propose A Mechanism For This Transformation SynthesisDocument1 pagePropose A Mechanism For This Transformation SynthesisBin RenNo ratings yet
- 2864 June 2005Document13 pages2864 June 2005Bin RenNo ratings yet
- Acidity of Organic CompoundsDocument1 pageAcidity of Organic CompoundsBin RenNo ratings yet
- 3A Cart of Mass 250g Is Placed On A Frictionless Horizontal Air TrackDocument1 page3A Cart of Mass 250g Is Placed On A Frictionless Horizontal Air TrackBin RenNo ratings yet
- The Lolium Alkaloids Have A Striking Saturated Heterocyclic SkeletonDocument1 pageThe Lolium Alkaloids Have A Striking Saturated Heterocyclic SkeletonBin RenNo ratings yet
- Erifon CLS Series: Key Benefits DescriptionDocument2 pagesErifon CLS Series: Key Benefits DescriptionEsdras Albuquerque100% (1)
- Catalytic Dewaxing ProcessDocument45 pagesCatalytic Dewaxing ProcessBóng Đá- Quán bia tổng hợpNo ratings yet
- 11stema8 Group 4Document13 pages11stema8 Group 4Daniel JohnsNo ratings yet
- Eratii Katalog 2017Document28 pagesEratii Katalog 2017Srdjan BastaNo ratings yet
- 1 Kinetics Formative Lab #1 - Factors Affecting ROR (Alka Seltzer)Document4 pages1 Kinetics Formative Lab #1 - Factors Affecting ROR (Alka Seltzer)Cecilia LindbergNo ratings yet
- Innershield Product GuideDocument44 pagesInnershield Product Guidewmajordan13No ratings yet
- Arc Spray TechnologyDocument11 pagesArc Spray TechnologyVictor PATIÑONo ratings yet
- Columbus MERV 10 P-100 Media Air Filter - Joe W. Fly Co., Inc.Document2 pagesColumbus MERV 10 P-100 Media Air Filter - Joe W. Fly Co., Inc.TreyflyNo ratings yet
- General EducationDocument11 pagesGeneral EducationhomidiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Part 1Document18 pagesChapter 18 Part 1roman ottleyNo ratings yet
- Chem7a BSN-1-J Module2 Group5 DapulaseDocument4 pagesChem7a BSN-1-J Module2 Group5 DapulaseKiana JezalynNo ratings yet
- Visual Guide To OPCW Science and TechnologyDocument25 pagesVisual Guide To OPCW Science and TechnologyWacel HamaniNo ratings yet
- F Acial Wash Normal SkinDocument17 pagesF Acial Wash Normal Skinmuhammadalfian4258No ratings yet
- US Chevron Spec. PSV - Sizing and Selection of Pressure Relief ValvesDocument20 pagesUS Chevron Spec. PSV - Sizing and Selection of Pressure Relief Valves울프No ratings yet
- Book 1Document18 pagesBook 1NURFADILLANo ratings yet
- Workover Well ControlDocument31 pagesWorkover Well Controlelsayed amerNo ratings yet
- Cheese: Processing and Sensory PropertiesDocument7 pagesCheese: Processing and Sensory PropertiesBianca AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Surface Typochemistry of Hydrothermal PyriteDocument13 pagesSurface Typochemistry of Hydrothermal PyriteGuillaume LepêcheurNo ratings yet
- FIBROTHAL Handbook Heating and Insulation SystemsDocument44 pagesFIBROTHAL Handbook Heating and Insulation SystemsMuhammad AbrarNo ratings yet
- Byk - P 4102 - TDS - 1643511993Document2 pagesByk - P 4102 - TDS - 1643511993swapon kumar shillNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Molecular Biology of The Cell Sixth EditionDocument30 pagesTest Bank For Molecular Biology of The Cell Sixth EditionglendavictoriabbkNo ratings yet
- Rheology of Cross-Linked Poly (Sodium Acrylate) /sodium Silicate HydrogelsDocument9 pagesRheology of Cross-Linked Poly (Sodium Acrylate) /sodium Silicate HydrogelsRatri HiusenaNo ratings yet
- AISC Design Guide 27 Structural Stainless SteelDocument159 pagesAISC Design Guide 27 Structural Stainless Steelfzhou100% (2)
- Cummins Onan 12HDKCC.D.G - Service ManualDocument60 pagesCummins Onan 12HDKCC.D.G - Service ManualCOGERA EnergiaNo ratings yet
- Bookqasw 1Document46 pagesBookqasw 1Procurement SectionNo ratings yet
- Tensile Testing: ASTM and Other Test Standards For Tensile Strength Testing of MaterialsDocument1 pageTensile Testing: ASTM and Other Test Standards For Tensile Strength Testing of MaterialsBBA730No ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry Method QuestionnaireDocument20 pagesClinical Chemistry Method Questionnairedr_4uNo ratings yet