Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Combustion Tutorial Question
Combustion Tutorial Question
Uploaded by
Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ENG790s2 Lab Sheet - Hilton Combustion Unit-1Document8 pagesENG790s2 Lab Sheet - Hilton Combustion Unit-1Moiz Subhan100% (1)
- ANSYS Fluent Tutorial Isothermal FlowDocument20 pagesANSYS Fluent Tutorial Isothermal FlowSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Student Practice Questions For Chemical Engineering Calculations For CombustionDocument6 pagesStudent Practice Questions For Chemical Engineering Calculations For CombustionDonPedrew60% (5)
- Combustion Engineering - Topic 1-4Document8 pagesCombustion Engineering - Topic 1-4JosafatNo ratings yet
- CombustionDocument78 pagesCombustionhansley100% (1)
- Theoretical and Actual CombustionDocument14 pagesTheoretical and Actual CombustionErma Sulistyo R100% (1)
- Che219 Case1 Gaseous and LiquidDocument9 pagesChe219 Case1 Gaseous and LiquidMargaret FloresNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 CombustionDocument23 pagesCHAPTER 3 CombustionChris ZiyuenNo ratings yet
- Fuels and CombDocument1 pageFuels and CombChristian M. Mortel0% (1)
- ASKNAKLSDocument3 pagesASKNAKLSGarcia RaphNo ratings yet
- Sheet (1) - Combustion and Furnaces - MEP363-Fall-2019Document1 pageSheet (1) - Combustion and Furnaces - MEP363-Fall-2019ahmed khaledNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Fuels and CombustionDocument2 pagesTutorial Fuels and CombustionPranav MishraNo ratings yet
- Combustion HandoutDocument16 pagesCombustion HandoutAbdallah Irfaan Ramjan100% (1)
- M2-Combustion ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesM2-Combustion ThermodynamicsKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Exercicios CombustaoDocument19 pagesExercicios CombustaoFeno'c FenosseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 PDFDocument66 pagesChapter 13 PDFdany arkanNo ratings yet
- CHPT 14Document30 pagesCHPT 14Ysabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering, Iit Madras ME5105: Applied Thermodynamics Tutorials 6 & 7 (Combustion & Chemical Equilibrium)Document3 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering, Iit Madras ME5105: Applied Thermodynamics Tutorials 6 & 7 (Combustion & Chemical Equilibrium)Krishna Kalikiri100% (1)
- BEng MB 0506 AnswerDocument6 pagesBEng MB 0506 AnswerStanley SibandaNo ratings yet
- Set No. 1Document8 pagesSet No. 1rajaraghuramvarmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2666aokiNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 - Combustion - Sp24Document2 pagesSheet 2 - Combustion - Sp24Cursed PirateNo ratings yet
- L36 - Combustion ReactionsDocument25 pagesL36 - Combustion ReactionsGermano Menzel100% (1)
- Powerplant Engineering A/Y 2018/2019: Addis Ababa Science and Technology UniversityDocument2 pagesPowerplant Engineering A/Y 2018/2019: Addis Ababa Science and Technology Universitydmc constructionNo ratings yet
- Tutorial CombustionDocument2 pagesTutorial CombustionAllen R KerkettaNo ratings yet
- Problem SetsDocument2 pagesProblem Setsanjocyl aumentadoNo ratings yet
- Chap.13.THERMOchemical Examples IIDocument19 pagesChap.13.THERMOchemical Examples IIKidus Yado GirmaNo ratings yet
- Liquid FuelsDocument12 pagesLiquid FuelsCharles MayoNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 - Combustion Reaction (And Solution)Document12 pagesSheet 2 - Combustion Reaction (And Solution)ahmed.hasaballaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - 2-Fuel and Combustions Cont.Document47 pagesChapter 3 - 2-Fuel and Combustions Cont.Habtamu Tkubet Ebuy100% (1)
- ME 6163: Combustion Engineering: (Moran Ex. 13.2)Document2 pagesME 6163: Combustion Engineering: (Moran Ex. 13.2)Wasi UddinNo ratings yet
- Reacting Gas MixturesDocument2 pagesReacting Gas MixturesAxel Flores GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Combustion ChemistryDocument17 pagesCombustion Chemistryrajeev50588No ratings yet
- Combustion 2222222222222222222Document52 pagesCombustion 2222222222222222222Habtamu Tkubet EbuyNo ratings yet
- m1 ProblemsDocument2 pagesm1 ProblemsHaris AbdulahNo ratings yet
- Examen Muestra CombustiónDocument1 pageExamen Muestra CombustiónMarco TorresNo ratings yet
- CombustionDocument4 pagesCombustionAbotaleb EsaidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - CombustionDocument21 pagesChapter 5 - CombustionMohd SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 - Energy Conversion SystemDocument1 pageHomework 2 - Energy Conversion SystemBry RieraNo ratings yet
- Gaseous FuelsDocument5 pagesGaseous FuelsShane PatulotNo ratings yet
- Liquid FuelsDocument8 pagesLiquid FuelsCharles Bonn Kirby MayoNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document18 pagesWeek 5Aaron Choco De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Combustion Reactions Tutorial Questions - CHE221Document2 pagesCombustion Reactions Tutorial Questions - CHE221Chidiebere Chikwendu-OgbodoNo ratings yet
- Dry Reforming of Methane AnalysisDocument6 pagesDry Reforming of Methane Analysistabrejalamdps19No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignmentMitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Co Co H o Ho: CH Ao Bco Dho CH Ao Co HoDocument43 pagesCo Co H o Ho: CH Ao Bco Dho CH Ao Co HocaportNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1ahmed.hasaballaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Combustion (Chapter 5 - Mec551) 1) : APRIL 2009Document3 pagesTutorial - Combustion (Chapter 5 - Mec551) 1) : APRIL 2009Muhammad FirdawsNo ratings yet
- Thermo Chemistry of Fuel-Air MixturesDocument34 pagesThermo Chemistry of Fuel-Air Mixturesmahmudul adilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Fuels and CombustionDocument6 pagesChapter 3 - Fuels and CombustionHectorCabzNo ratings yet
- L36 - Combustion ReactionsDocument25 pagesL36 - Combustion ReactionsĐặng Tấn PhátNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1saurabhNo ratings yet
- HWK Set 2 - CombustionDocument2 pagesHWK Set 2 - CombustionEliot KhNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 Basic Combustion Chemistry PDFDocument77 pagesChap 2 Basic Combustion Chemistry PDFMelvin MhdsNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument4 pagesQuestionsDean Joyce Alboroto0% (1)
- CPC 9Document8 pagesCPC 9rajaraghuramvarmaNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Natural Gas: From Coal, Dry Biomass, and Power-to-Gas ApplicationsFrom EverandSynthetic Natural Gas: From Coal, Dry Biomass, and Power-to-Gas ApplicationsTilman J. SchildhauerNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Hydrogen Production TechnologiesFrom EverandHydrogen Production TechnologiesMehmet SankirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document6 pagesChapter 3Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Eeib413 Pci Final Exam Sem 2 2017 - 18Document7 pagesEeib413 Pci Final Exam Sem 2 2017 - 18Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering Putrajaya Campus Test 1 Examination SEMESTER 2 2017/2018Document3 pagesCollege of Engineering Putrajaya Campus Test 1 Examination SEMESTER 2 2017/2018Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Fluent Tutorial Mix Flow ElbowDocument13 pagesANSYS Fluent Tutorial Mix Flow ElbowSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- 1 - Rapid-P0002-0100-Pmg-Prc-0001-1084 - A - Code 3 PDFDocument12 pages1 - Rapid-P0002-0100-Pmg-Prc-0001-1084 - A - Code 3 PDFSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- ASME V Article 6 Liquid PenetrantDocument1 pageASME V Article 6 Liquid PenetrantSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- COEB442 Chapter 1Document28 pagesCOEB442 Chapter 1Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction and CombustionDocument1 pageChemical Reaction and CombustionSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Universiti Tenaga Nasional: College of EngineeringDocument15 pagesUniversiti Tenaga Nasional: College of EngineeringSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Long Report Lab 7Document15 pagesLong Report Lab 7Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: Hardness of The Specimen (HRB)Document1 pageObjectives:: Hardness of The Specimen (HRB)Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- MOM Lab 8 NEWDocument7 pagesMOM Lab 8 NEWSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- MOM Lab 8 NEWDocument7 pagesMOM Lab 8 NEWSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Universiti Tenaga Nasional: College of EngineeringDocument7 pagesUniversiti Tenaga Nasional: College of EngineeringSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Oct 2016 Mark Sheet LogbookpdfDocument2 pagesOct 2016 Mark Sheet LogbookpdfSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
Combustion Tutorial Question
Combustion Tutorial Question
Uploaded by
Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Combustion Tutorial Question
Combustion Tutorial Question
Uploaded by
Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauCopyright:
Available Formats
HH MEHB312 Tut5
Department Of Mechanical Engineering
College Of Engineering
Universiti Tenaga Nasional
MEHB312 Thermodynamics 2
Tutorial 5 (Chemical Reaction & Combustion)
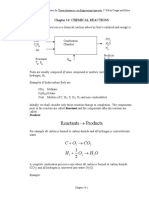
1. For the combustion of Heptane (C7 H1 6) in air, find:
(a) the stoichiometric air/fuel ratio by mass
(b) the % excess air and the % O2 (by volume) in the dry products of complete combus-
tion when air/fuel ratio is 20
(c) the % CO (by volume) in the dry exhaust products when the air/fuel ratio is 12,
assuming that the fuel is all converted into CO, CO2 and H2 O
[Ans: (a)15.1 (b)32.5, 5.46 (c)11.3]
2. A fuel gas has the following volumetric analysis:
Methane (CH4 ) 80%, Ethane (C2 H6 ) 15%, Hydrogen (H2 ) 5%
Calculate:
(a) the stoichiometric air/fuel ratio both by mass and by volume (same T, p for air and
fuel) [Ans: 17.0, 10.2]
(b) the lower calorific value at 25 C, both per kg and per m3 at 1 atm
[Ans: 49.9 MJ/kg, 35.5 MJ/m3 ]
(c) an analysis by % mass of the products of complete combustion with 100% excess air
[Ans: 8.0% CO2 , 6.2% H2 O, 11.3% O2 , 74.5% N2 ]
3. The ultimate analysis of a coal by mass is: 87% Carbon, 4% Hydrogen, 9% Ash. Calculate
the air/fuel ratio and % excess air used by a boiler burning the coal if an Orsat analysis of
the flue gas shows 9.9% CO2 , 2.5% CO, 8.3% O2 (79.3% N2 by difference) [Ans: 16.9, 50%]
4. Methane gas with 100% excess air is preheated to 400 K and burns in a steady flow
combustion chamber. Find the adiabatic flame temperature. [Ans: 1288 C]
Updated: July 11, 2006 Page 1 of 1
You might also like
- ENG790s2 Lab Sheet - Hilton Combustion Unit-1Document8 pagesENG790s2 Lab Sheet - Hilton Combustion Unit-1Moiz Subhan100% (1)
- ANSYS Fluent Tutorial Isothermal FlowDocument20 pagesANSYS Fluent Tutorial Isothermal FlowSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Student Practice Questions For Chemical Engineering Calculations For CombustionDocument6 pagesStudent Practice Questions For Chemical Engineering Calculations For CombustionDonPedrew60% (5)
- Combustion Engineering - Topic 1-4Document8 pagesCombustion Engineering - Topic 1-4JosafatNo ratings yet
- CombustionDocument78 pagesCombustionhansley100% (1)
- Theoretical and Actual CombustionDocument14 pagesTheoretical and Actual CombustionErma Sulistyo R100% (1)
- Che219 Case1 Gaseous and LiquidDocument9 pagesChe219 Case1 Gaseous and LiquidMargaret FloresNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 CombustionDocument23 pagesCHAPTER 3 CombustionChris ZiyuenNo ratings yet
- Fuels and CombDocument1 pageFuels and CombChristian M. Mortel0% (1)
- ASKNAKLSDocument3 pagesASKNAKLSGarcia RaphNo ratings yet
- Sheet (1) - Combustion and Furnaces - MEP363-Fall-2019Document1 pageSheet (1) - Combustion and Furnaces - MEP363-Fall-2019ahmed khaledNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Fuels and CombustionDocument2 pagesTutorial Fuels and CombustionPranav MishraNo ratings yet
- Combustion HandoutDocument16 pagesCombustion HandoutAbdallah Irfaan Ramjan100% (1)
- M2-Combustion ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesM2-Combustion ThermodynamicsKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Exercicios CombustaoDocument19 pagesExercicios CombustaoFeno'c FenosseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 PDFDocument66 pagesChapter 13 PDFdany arkanNo ratings yet
- CHPT 14Document30 pagesCHPT 14Ysabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering, Iit Madras ME5105: Applied Thermodynamics Tutorials 6 & 7 (Combustion & Chemical Equilibrium)Document3 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering, Iit Madras ME5105: Applied Thermodynamics Tutorials 6 & 7 (Combustion & Chemical Equilibrium)Krishna Kalikiri100% (1)
- BEng MB 0506 AnswerDocument6 pagesBEng MB 0506 AnswerStanley SibandaNo ratings yet
- Set No. 1Document8 pagesSet No. 1rajaraghuramvarmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2666aokiNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 - Combustion - Sp24Document2 pagesSheet 2 - Combustion - Sp24Cursed PirateNo ratings yet
- L36 - Combustion ReactionsDocument25 pagesL36 - Combustion ReactionsGermano Menzel100% (1)
- Powerplant Engineering A/Y 2018/2019: Addis Ababa Science and Technology UniversityDocument2 pagesPowerplant Engineering A/Y 2018/2019: Addis Ababa Science and Technology Universitydmc constructionNo ratings yet
- Tutorial CombustionDocument2 pagesTutorial CombustionAllen R KerkettaNo ratings yet
- Problem SetsDocument2 pagesProblem Setsanjocyl aumentadoNo ratings yet
- Chap.13.THERMOchemical Examples IIDocument19 pagesChap.13.THERMOchemical Examples IIKidus Yado GirmaNo ratings yet
- Liquid FuelsDocument12 pagesLiquid FuelsCharles MayoNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 - Combustion Reaction (And Solution)Document12 pagesSheet 2 - Combustion Reaction (And Solution)ahmed.hasaballaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - 2-Fuel and Combustions Cont.Document47 pagesChapter 3 - 2-Fuel and Combustions Cont.Habtamu Tkubet Ebuy100% (1)
- ME 6163: Combustion Engineering: (Moran Ex. 13.2)Document2 pagesME 6163: Combustion Engineering: (Moran Ex. 13.2)Wasi UddinNo ratings yet
- Reacting Gas MixturesDocument2 pagesReacting Gas MixturesAxel Flores GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Combustion ChemistryDocument17 pagesCombustion Chemistryrajeev50588No ratings yet
- Combustion 2222222222222222222Document52 pagesCombustion 2222222222222222222Habtamu Tkubet EbuyNo ratings yet
- m1 ProblemsDocument2 pagesm1 ProblemsHaris AbdulahNo ratings yet
- Examen Muestra CombustiónDocument1 pageExamen Muestra CombustiónMarco TorresNo ratings yet
- CombustionDocument4 pagesCombustionAbotaleb EsaidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - CombustionDocument21 pagesChapter 5 - CombustionMohd SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 - Energy Conversion SystemDocument1 pageHomework 2 - Energy Conversion SystemBry RieraNo ratings yet
- Gaseous FuelsDocument5 pagesGaseous FuelsShane PatulotNo ratings yet
- Liquid FuelsDocument8 pagesLiquid FuelsCharles Bonn Kirby MayoNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document18 pagesWeek 5Aaron Choco De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Combustion Reactions Tutorial Questions - CHE221Document2 pagesCombustion Reactions Tutorial Questions - CHE221Chidiebere Chikwendu-OgbodoNo ratings yet
- Dry Reforming of Methane AnalysisDocument6 pagesDry Reforming of Methane Analysistabrejalamdps19No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignmentMitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Co Co H o Ho: CH Ao Bco Dho CH Ao Co HoDocument43 pagesCo Co H o Ho: CH Ao Bco Dho CH Ao Co HocaportNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1ahmed.hasaballaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Combustion (Chapter 5 - Mec551) 1) : APRIL 2009Document3 pagesTutorial - Combustion (Chapter 5 - Mec551) 1) : APRIL 2009Muhammad FirdawsNo ratings yet
- Thermo Chemistry of Fuel-Air MixturesDocument34 pagesThermo Chemistry of Fuel-Air Mixturesmahmudul adilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Fuels and CombustionDocument6 pagesChapter 3 - Fuels and CombustionHectorCabzNo ratings yet
- L36 - Combustion ReactionsDocument25 pagesL36 - Combustion ReactionsĐặng Tấn PhátNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1saurabhNo ratings yet
- HWK Set 2 - CombustionDocument2 pagesHWK Set 2 - CombustionEliot KhNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 Basic Combustion Chemistry PDFDocument77 pagesChap 2 Basic Combustion Chemistry PDFMelvin MhdsNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument4 pagesQuestionsDean Joyce Alboroto0% (1)
- CPC 9Document8 pagesCPC 9rajaraghuramvarmaNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Natural Gas: From Coal, Dry Biomass, and Power-to-Gas ApplicationsFrom EverandSynthetic Natural Gas: From Coal, Dry Biomass, and Power-to-Gas ApplicationsTilman J. SchildhauerNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Hydrogen Production TechnologiesFrom EverandHydrogen Production TechnologiesMehmet SankirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document6 pagesChapter 3Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Eeib413 Pci Final Exam Sem 2 2017 - 18Document7 pagesEeib413 Pci Final Exam Sem 2 2017 - 18Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering Putrajaya Campus Test 1 Examination SEMESTER 2 2017/2018Document3 pagesCollege of Engineering Putrajaya Campus Test 1 Examination SEMESTER 2 2017/2018Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Fluent Tutorial Mix Flow ElbowDocument13 pagesANSYS Fluent Tutorial Mix Flow ElbowSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- 1 - Rapid-P0002-0100-Pmg-Prc-0001-1084 - A - Code 3 PDFDocument12 pages1 - Rapid-P0002-0100-Pmg-Prc-0001-1084 - A - Code 3 PDFSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- ASME V Article 6 Liquid PenetrantDocument1 pageASME V Article 6 Liquid PenetrantSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- COEB442 Chapter 1Document28 pagesCOEB442 Chapter 1Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction and CombustionDocument1 pageChemical Reaction and CombustionSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Universiti Tenaga Nasional: College of EngineeringDocument15 pagesUniversiti Tenaga Nasional: College of EngineeringSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Long Report Lab 7Document15 pagesLong Report Lab 7Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: Hardness of The Specimen (HRB)Document1 pageObjectives:: Hardness of The Specimen (HRB)Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- MOM Lab 8 NEWDocument7 pagesMOM Lab 8 NEWSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- MOM Lab 8 NEWDocument7 pagesMOM Lab 8 NEWSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Universiti Tenaga Nasional: College of EngineeringDocument7 pagesUniversiti Tenaga Nasional: College of EngineeringSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Oct 2016 Mark Sheet LogbookpdfDocument2 pagesOct 2016 Mark Sheet LogbookpdfSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet