Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
114 viewsP Alexander-Vaneaton What So What Now What Note Taking Chart For Module 3 v2
P Alexander-Vaneaton What So What Now What Note Taking Chart For Module 3 v2
Uploaded by
api-356979259This module discusses differentiation strategies for gifted students. It suggests flipping the classroom to allow students to learn basic material at home so they can delve more deeply into topics in class. Formative assessment and feedback are important to monitor student understanding and guide instruction. Students should be challenged with higher-order questions and complex, abstract activities that encourage independent learning and collaboration. The goals are to encourage students to progress at their own pace and engage in rigorous, self-directed study of broad, thematic concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Mercantilism Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesMercantilism Lesson Planapi-300665059100% (1)
- P Alexandervaneaton What So What Now What Note Taking Chart-E Docx v2Document6 pagesP Alexandervaneaton What So What Now What Note Taking Chart-E Docx v2api-356979259100% (1)
- J Gray Learning and Teaching Preferences - Learner Know Thyself Chart Rev20Document13 pagesJ Gray Learning and Teaching Preferences - Learner Know Thyself Chart Rev20api-528983071No ratings yet
- J Gray Special Populations in Gifted EducationDocument5 pagesJ Gray Special Populations in Gifted Educationapi-528983071No ratings yet
- L Bammann Viewpoint Matrix - Major Contributors in Gifted Education Sy21Document5 pagesL Bammann Viewpoint Matrix - Major Contributors in Gifted Education Sy21api-419982595No ratings yet
- P Alexandervaneaton What So What Now What Note Taking Chart-E Docx v2Document6 pagesP Alexandervaneaton What So What Now What Note Taking Chart-E Docx v2api-356979259100% (1)
- J Gray Testing and Evaluation Instruments Research OrganizerDocument5 pagesJ Gray Testing and Evaluation Instruments Research Organizerapi-528983071No ratings yet
- J Gray Special Population Subgroup Collaboration AgendaDocument2 pagesJ Gray Special Population Subgroup Collaboration Agendaapi-528983071No ratings yet
- J Gray Acceleration On A National Level Discussion PostDocument3 pagesJ Gray Acceleration On A National Level Discussion Postapi-528983071No ratings yet
- W Astin Implement The Strategies and Rubric - Module 4Document6 pagesW Astin Implement The Strategies and Rubric - Module 4api-325932544No ratings yet
- P Alexander Vaneaton Consider The Strategies Document RevisedDocument6 pagesP Alexander Vaneaton Consider The Strategies Document Revisedapi-356979259No ratings yet
- Kerley - Philosophy of Gifted EducationDocument2 pagesKerley - Philosophy of Gifted Educationapi-237403122100% (1)
- P Alexander Vaneaton Consider The Strategies Document RevisedDocument6 pagesP Alexander Vaneaton Consider The Strategies Document Revisedapi-356979259No ratings yet
- J Gray Gifted High Achieving or CreativeDocument2 pagesJ Gray Gifted High Achieving or Creativeapi-528983071No ratings yet
- J Gray Great Brains Dinner PartyDocument6 pagesJ Gray Great Brains Dinner Partyapi-528983071No ratings yet
- Theorists and Theories Design A T-Shirt & Compare and Contrast Part 1: Design The Theorist's T-ShirtDocument6 pagesTheorists and Theories Design A T-Shirt & Compare and Contrast Part 1: Design The Theorist's T-ShirtLeahNo ratings yet
- J Gray Test Blueprint Assignment RevDocument3 pagesJ Gray Test Blueprint Assignment Revapi-528983071No ratings yet
- J Gray Local Gifted Evaluation Procedures Exit TicketDocument1 pageJ Gray Local Gifted Evaluation Procedures Exit Ticketapi-528983071No ratings yet
- W Astin Implement The Strategies and Rubric - Module 2Document8 pagesW Astin Implement The Strategies and Rubric - Module 2api-325932544No ratings yet
- What Is A Performance TaskDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Performance Taskapi-356979259100% (1)
- Emily Hogarth Bright Vs Gifted Vs Creative ChartDocument4 pagesEmily Hogarth Bright Vs Gifted Vs Creative Chartapi-293546583No ratings yet
- Implement The Strategies 3Document2 pagesImplement The Strategies 3api-315325618No ratings yet
- J Gray Gifted Identification and Services DeterminationDocument4 pagesJ Gray Gifted Identification and Services Determinationapi-528983071No ratings yet
- J Gray Summary of Reading and Viewing Graphic OrganizerDocument4 pagesJ Gray Summary of Reading and Viewing Graphic Organizerapi-528983071No ratings yet
- Differentiation Inquiry CycleDocument1 pageDifferentiation Inquiry Cycleapi-383417172No ratings yet
- 7067 19099 1 PBDocument6 pages7067 19099 1 PBwen monteNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 4 Unit 4 LP 4 UPDATEDDocument45 pagesProf Ed 4 Unit 4 LP 4 UPDATEDAniway Rose Nicole BaelNo ratings yet
- High Leverage Instructinal PracticesDocument3 pagesHigh Leverage Instructinal Practicesapi-557677748No ratings yet
- Week 1Document3 pagesWeek 1Ro De NavaNo ratings yet
- PSTMLS-Lesson 1-TransesDocument3 pagesPSTMLS-Lesson 1-TransesjkthmsvtchNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment Toolkit: An Annotated Menu of PossibilitiesDocument18 pagesFormative Assessment Toolkit: An Annotated Menu of PossibilitiesEnglishNo ratings yet
- Gifted ChildrenDocument17 pagesGifted ChildrenBharat Singh100% (4)
- 21st Century Facilitating SkillsDocument5 pages21st Century Facilitating SkillsPeter Patrick LlemitNo ratings yet
- Week 6 - Unit 5.1: Learning Processes: Curriculum and Course Design - PER 3260Document22 pagesWeek 6 - Unit 5.1: Learning Processes: Curriculum and Course Design - PER 3260Alexandra Bachero BeltránNo ratings yet
- Cadaa - Module 4 - EDUC 126Document6 pagesCadaa - Module 4 - EDUC 126Elfe Grace L. CadaaNo ratings yet
- Discussion 5 InclusiveDocument15 pagesDiscussion 5 InclusiveNora ZarahNo ratings yet
- Eliciting, Giving Instructions and Setting Up Activities (Gower, Phillips & Walters, 1995)Document7 pagesEliciting, Giving Instructions and Setting Up Activities (Gower, Phillips & Walters, 1995)AshleyBlueNo ratings yet
- 1 2 3 4 MergedDocument9 pages1 2 3 4 MergedAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Strategies LESSON 1 HEALTHEDDocument3 pagesTeaching Strategies LESSON 1 HEALTHEDAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Oh 4 12 2020Document9 pagesCSTP 1 Oh 4 12 2020api-483530581No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Matuchniak 0423Document6 pagesCSTP 1 Matuchniak 0423api-572629820No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Mack 050324Document8 pagesCSTP 1 Mack 050324api-679292788No ratings yet
- Apst 3.3 Range of Teaching Strategies LogDocument2 pagesApst 3.3 Range of Teaching Strategies Logapi-525572712No ratings yet
- Classroom BehaviorsDocument2 pagesClassroom BehaviorsJinky OmboyNo ratings yet
- Episode 5Document2 pagesEpisode 5viaxine m. pangilinanNo ratings yet
- TEEP A4 6pp - Accelerated LearningDocument6 pagesTEEP A4 6pp - Accelerated Learninganand raviNo ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Haro 12 12 19Document9 pagesCSTP 1 Haro 12 12 19api-467608657No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Mitchell 7Document6 pagesCSTP 1 Mitchell 7api-203432401No ratings yet
- CSTP ClassroomDocument13 pagesCSTP Classroomapi-333564329100% (1)
- My 21st Century Classroom Facilitating SkillsDocument1 pageMy 21st Century Classroom Facilitating SkillsGhebre PalloNo ratings yet
- Study Skill by Dr. Sontang SimamoraDocument26 pagesStudy Skill by Dr. Sontang SimamoraLucy WijayaNo ratings yet
- Sweeney - CSTP Self-Assessment Spring 2021Document76 pagesSweeney - CSTP Self-Assessment Spring 2021Ryan SweeneyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Teaching and LearningDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Teaching and LearningAnne Martha Acuña NeronaNo ratings yet
- Online Teaching and Learning ChallengesDocument2 pagesOnline Teaching and Learning ChallengesShez MerchantNo ratings yet
- Jot2 Task 2 Template 1 Shalena FordeDocument23 pagesJot2 Task 2 Template 1 Shalena Fordeapi-464924175No ratings yet
- Building Inclusive ClassroomDocument12 pagesBuilding Inclusive ClassroomCristobal CantorNo ratings yet
- Sweeney CSTP 1 Semester 4Document14 pagesSweeney CSTP 1 Semester 4Ryan SweeneyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2Document22 pagesLesson 1.2Leah Jean PolitaNo ratings yet
- Theme 1 - SlidesDocument18 pagesTheme 1 - Slidesmogobaphumzile06No ratings yet
- J Hemphill Meeting Student Needs Through Rigor and Differentiation Reflection 1Document3 pagesJ Hemphill Meeting Student Needs Through Rigor and Differentiation Reflection 1api-445922230No ratings yet
- Group Instructional Design - Multiple Intelligences & Flipped ClassroomDocument9 pagesGroup Instructional Design - Multiple Intelligences & Flipped ClassroomSAVIRA MARETTANo ratings yet
- CSTP 1 SheppardDocument9 pagesCSTP 1 Sheppardapi-378917002No ratings yet
- Sned 4 Group 3 NotesDocument7 pagesSned 4 Group 3 Notesjase.lacuna.swuNo ratings yet
- P Alexander-Vaneaton Implement The Strategies Module4 v2Document2 pagesP Alexander-Vaneaton Implement The Strategies Module4 v2api-356979259No ratings yet
- P Alexander Vaneaton Rank and Order Technology Tools v2Document2 pagesP Alexander Vaneaton Rank and Order Technology Tools v2api-356979259No ratings yet
- What Is A Performance TaskDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Performance Taskapi-356979259100% (1)
- Learning Outcome Topic Methodology Resources AssessmentDocument5 pagesLearning Outcome Topic Methodology Resources AssessmentJp Isles MagcawasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ESP DAY 2Document2 pagesLesson Plan in ESP DAY 2Krystal Claire Dioso MarimonNo ratings yet
- Division of Davao City Erico T. Nograles National High SchoolDocument4 pagesDivision of Davao City Erico T. Nograles National High SchoolDaniel MagnoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Format TemplateDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Format TemplateNurul HusnaNo ratings yet
- SN Yr 4 DLPDocument1 pageSN Yr 4 DLPAnonymous jHgxmwZNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Reading Year 2 English KSSR Topic 5 I Am SpecialDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Reading Year 2 English KSSR Topic 5 I Am SpecialnonsensewatsonNo ratings yet
- PPUFrameworkDocument2 pagesPPUFrameworkAsmanono100% (3)
- Final Research PresentationDocument5 pagesFinal Research Presentationapi-289775724No ratings yet
- Module 1: Adapting College Life in PHILSCADocument2 pagesModule 1: Adapting College Life in PHILSCAAngelo IbañezNo ratings yet
- Group 4: Caparas Sayago Vidauretta Quirogo TerolDocument16 pagesGroup 4: Caparas Sayago Vidauretta Quirogo TerolIane Aliño NavarroNo ratings yet
- Sptve 7 Exploratory: Week 5 & 6: Performance Task 3Document3 pagesSptve 7 Exploratory: Week 5 & 6: Performance Task 3Gerean VillasNo ratings yet
- Baker College Lesson Plan PersonalityDocument2 pagesBaker College Lesson Plan Personalityapi-356006116No ratings yet
- Formal Classroom ObservationDocument3 pagesFormal Classroom Observationapi-660475328No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Understand The Meaning of Colors in EnglishDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Understand The Meaning of Colors in EnglishVanessa QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Foundational Resources - Equitable Learning PracticesDocument84 pagesFoundational Resources - Equitable Learning PracticesVicente MoralesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Organic Compounds: SummaryDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Organic Compounds: SummaryMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- W5Document16 pagesW5NURSYAZWANI BINTI TOLOS MoeNo ratings yet
- Academic Audit FormatDocument8 pagesAcademic Audit FormatUma Shankar YaligarNo ratings yet
- Edu 270 Lesson Plan 2Document2 pagesEdu 270 Lesson Plan 2api-271353489No ratings yet
- Teacher Interview Questions Tell Me A Little About YourselfDocument2 pagesTeacher Interview Questions Tell Me A Little About YourselfLORENA ALEXANDRA HUAMAN BUENONo ratings yet
- NEPPeerObsFeedbackProtocol PDFDocument2 pagesNEPPeerObsFeedbackProtocol PDFBeverly A. OmotoyNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning With Technology: Effectiveness of ICT Integration in SchoolsDocument18 pagesTeaching and Learning With Technology: Effectiveness of ICT Integration in SchoolsWanda Nugroho YanuartoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Current Topics in Digital Philology - Uppsala University, SwedenDocument2 pagesSyllabus For Current Topics in Digital Philology - Uppsala University, SwedenterawNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4.2Document2 pagesQuiz 4.2Seniorito Louiesito100% (1)
- DR Marzano Webinar Becoming Reflective TeacherDocument71 pagesDR Marzano Webinar Becoming Reflective TeachercsshyamalaNo ratings yet
- Social Studies Lesson Plan Covered WagonDocument4 pagesSocial Studies Lesson Plan Covered Wagonapi-309983676No ratings yet
- The Monsters Are Due On Maple Street Act 2Document2 pagesThe Monsters Are Due On Maple Street Act 2api-594077974No ratings yet
- Week 1 Lesson 1Document3 pagesWeek 1 Lesson 1dayah3101No ratings yet
- Emily Jarema Resume 2015 CompleteDocument4 pagesEmily Jarema Resume 2015 Completeapi-248987146No ratings yet
P Alexander-Vaneaton What So What Now What Note Taking Chart For Module 3 v2
P Alexander-Vaneaton What So What Now What Note Taking Chart For Module 3 v2
Uploaded by
api-3569792590 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
114 views5 pagesThis module discusses differentiation strategies for gifted students. It suggests flipping the classroom to allow students to learn basic material at home so they can delve more deeply into topics in class. Formative assessment and feedback are important to monitor student understanding and guide instruction. Students should be challenged with higher-order questions and complex, abstract activities that encourage independent learning and collaboration. The goals are to encourage students to progress at their own pace and engage in rigorous, self-directed study of broad, thematic concepts.
Original Description:
Original Title
p alexander-vaneaton what so what now what note taking chart for module 3 v2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis module discusses differentiation strategies for gifted students. It suggests flipping the classroom to allow students to learn basic material at home so they can delve more deeply into topics in class. Formative assessment and feedback are important to monitor student understanding and guide instruction. Students should be challenged with higher-order questions and complex, abstract activities that encourage independent learning and collaboration. The goals are to encourage students to progress at their own pace and engage in rigorous, self-directed study of broad, thematic concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
114 views5 pagesP Alexander-Vaneaton What So What Now What Note Taking Chart For Module 3 v2
P Alexander-Vaneaton What So What Now What Note Taking Chart For Module 3 v2
Uploaded by
api-356979259This module discusses differentiation strategies for gifted students. It suggests flipping the classroom to allow students to learn basic material at home so they can delve more deeply into topics in class. Formative assessment and feedback are important to monitor student understanding and guide instruction. Students should be challenged with higher-order questions and complex, abstract activities that encourage independent learning and collaboration. The goals are to encourage students to progress at their own pace and engage in rigorous, self-directed study of broad, thematic concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
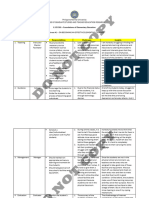
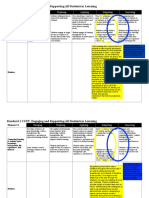
Area to Consider Modu What? This can be a So What?
(Why is this
le bulleted list. important?) Provide dee
meaningful, thoughtful
responses.
Inst Differentiation 3 Gifted students, Students should be
ruc though uniquely encouraged to move th
tio different, as a group at their own pace.
n need a specific type of Information should not
differentiated rigor to repetitive but more
help them thrive. advanced for learners
Flipping the classroom move quickly through
can be an effective curriculum. Content sh
instructional strategy be broad and thematic
for differentiating Activities should be
instruction for gifted intellectually demandin
and talented students. Questioning should be
higher level and initiat
inquiry. Activities shou
encourage self-directe
learning.
Students learn the bas
information at home th
before the lesson is
presented. When they
to class they can exten
their knowledge on the
content that they have
already previewed. Te
sometimes do this thro
technology, using vide
assign to the class to w
and learn about conten
Students who are talen
enough to learn from t
videos may then advan
their learning in class a
they have been provid
the option to skip pass
teaching of information
already know or can le
more quickly alone tha
the pace of whole clas
instruction.
Rigor 3 Teachers should ask Questions asked by tea
questions that promote should promote studen
rigor. demonstrate understa
Differentiation require students to ana
continues to be or evaluate, requires s
necessary for gifted to predict, design or cr
learners under the and that asks students
common core apply a skill or
understanding.
The standards were wr
with the notion that th
would have to be alter
both gifted and studen
with disabilities.
Blooms/Depth of 3 Learning builds on itself Students learn knowled
Knowledge as we move from one stages that build on
segment of Bloom's themselves. The lowe
Taxonomy and Depth of level is recalling knowl
Knowledge to the next. which is considered sim
and concrete and build
to creating which is
considered complex an
abstract. Depth of
knowledge should be u
to assess learning, and
evaluate alignment be
curriculum and instruc
ranges from level one,
is simple recall, to leve
where students are ex
to provide extended
reasoning.
Assessment 3 Teachers can use the With the correct amou
internet to create guidance, students can
student lessons that a more meaningful
promote collaboration, understanding of conc
increase when they are allowed
communication and self-guided research co
increase inquiry of with collaboration. Stu
relevant topics. have had conversation
Formative assessment have allowed them to
is an important part of deeper into the. With
evaluation of students deeper investigations,
learning. students have engage
Students thoughts the other in meaningful
day of an assessment conversations which
demonstrates a higher
of understanding.
Students need constan
feedback throughout t
unit. Teachers also ne
monitor what students
already know verses w
they need to know prio
the summative assess
For this reason formati
assessment should be
often and feedback sh
be a part of the proces
make it meaningful. It
important to realize th
summative assessmen
be used as a formative
is particularly true if at
end of the unit a stude
performs poorly on the
summative. This now
become useful informa
to the teacher as it pro
feedback on what the
student understands. T
teacher can then decid
reassessment, making
reassessment the new
formative assessment.
Students tend to panic
try to understand why
are being tested or the
meaning or reason for
testing. My interpretat
this picture is that it
suggests some might h
anxiety on test day as
students have
demonstrated. On the
of the unannounced qu
administered, students
questioning why we we
having a quiz and said
of the same comments
the one on this picture
we being quizzed so yo
see what we know? D
this quiz count as a gra
Will it affect my averag
Aff Social Needs 3 A students social Parents and teachers ar
ecti adjustment may alter likely to recommend a
ve the students student who is not socia
Ne consideration into a adjusted due to the
eds gifted program. evaluators view of the
student versus the stud
capabilities.
Emotional Needs 3 There is a relationship Students who are aware
between emotional their feelings are more
giftedness and to be able to differentia
emotional intelligence. their feelings and are m
likely to create better a
deeper relationships.
Intellectual Needs 3 Creative people have a The idea of a grim futur
(ie perfectionism, reputation for being perpetuated onto those
underachievement, mentally unstable. as artistic. Most things
etc) Structured inquiry do is judge and unfairly
experiences can help compared to other
learners develop skills accomplishments. As a
for coping with result, many artistic pe
problems that have no have inherited emotion
clear solutions, dealing anxiety of how they wil
with challenges, and judged. Greeks in the p
adapting procedures to believed that creative p
the demands of were different. Romans
different situations. a similar yet less bleak
Unrealistic expectation
those who are gifted or
perfectionist can lead to
stress, anxiety, depress
and suicide. These
expectations cause stud
to be overly critical. As
result they tend to focu
others perceptions of t
achievements which lea
high levels of anxiety a
depression. There is,
however, a healthy form
perfectionism that lead
students perseverance
achievement and high
standards.
You 3 Gifted students ability Gifted students who fe
r to work with others. their work was appreci
Ow by teachers and fellow
n students reported the
strongest preference to
with others. Independ
learning activities are m
like what students are
accustomed to doing in
school and thus has be
more comfortable for t
3 Risk taking to promote Students with a growth
a growth mindset. mindset are more likel
view challenging work
opportunity to learn an
grow. Students must b
allowed to struggle an
make mistakes in orde
feel comfortable trying
different strategies wh
first ones tried don't w
Modified from the What? So What? Now What? Chart on page 177 in
Advancing Differentiation
Resources Used for Research: You must have a minimum of 2; however, you
should include any resources used on this chart by adding additional numbers
in the appropriate box(es). Type directly in each box.
Topic Resources UsedTitle and/or Link
Differentiation 1. Sandra Berger: Differentiating curriculum for gifted students
2. Del Siegle, PhD: Technology Differentiating Instruction by Flipping the
Classroom
Rigor 1. Rigor_Teacher_Questions_by_Quadrant
2. Kate Ash: Gifted Learners Poised to Join The Conversation
Blooms/Depth of 1. treeTopSecret presents Bloom's Taxonomy and Depth of Knowledge
Knowledge 2.
Assessment 1. Rick Wormeli: Formative and Summative Assessment
https://www.youtube.com/watch?
v=rJxFXjfB_B4&index=7&list=PLzFz35PAA7-
cxi75IW6y4UGeN0oCtn3Y81%26url%3D
2. Wondering + Online Inquiry = Learning
3. Assessment image from pinterst
Social Needs 1. Issues in the Social and Emotional Adjustment of Gifted Children
2.
Emotional Needs Emotional Intelligence and Giftedness
Issues in the Social and Emotional Adjustment of Gifted Children
Intellectual Needs 1. Elizabeth Gilbert: Your elusive creative genius
https://www.ted.com/talks/elizabeth_gilbert_on_genius
2. Wondering and online inquiry.
Own Topics 1. Do gifted students really prefer to work alone?
2. Even Genuises Works Hard
You might also like
- Mercantilism Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesMercantilism Lesson Planapi-300665059100% (1)
- P Alexandervaneaton What So What Now What Note Taking Chart-E Docx v2Document6 pagesP Alexandervaneaton What So What Now What Note Taking Chart-E Docx v2api-356979259100% (1)
- J Gray Learning and Teaching Preferences - Learner Know Thyself Chart Rev20Document13 pagesJ Gray Learning and Teaching Preferences - Learner Know Thyself Chart Rev20api-528983071No ratings yet
- J Gray Special Populations in Gifted EducationDocument5 pagesJ Gray Special Populations in Gifted Educationapi-528983071No ratings yet
- L Bammann Viewpoint Matrix - Major Contributors in Gifted Education Sy21Document5 pagesL Bammann Viewpoint Matrix - Major Contributors in Gifted Education Sy21api-419982595No ratings yet
- P Alexandervaneaton What So What Now What Note Taking Chart-E Docx v2Document6 pagesP Alexandervaneaton What So What Now What Note Taking Chart-E Docx v2api-356979259100% (1)
- J Gray Testing and Evaluation Instruments Research OrganizerDocument5 pagesJ Gray Testing and Evaluation Instruments Research Organizerapi-528983071No ratings yet
- J Gray Special Population Subgroup Collaboration AgendaDocument2 pagesJ Gray Special Population Subgroup Collaboration Agendaapi-528983071No ratings yet
- J Gray Acceleration On A National Level Discussion PostDocument3 pagesJ Gray Acceleration On A National Level Discussion Postapi-528983071No ratings yet
- W Astin Implement The Strategies and Rubric - Module 4Document6 pagesW Astin Implement The Strategies and Rubric - Module 4api-325932544No ratings yet
- P Alexander Vaneaton Consider The Strategies Document RevisedDocument6 pagesP Alexander Vaneaton Consider The Strategies Document Revisedapi-356979259No ratings yet
- Kerley - Philosophy of Gifted EducationDocument2 pagesKerley - Philosophy of Gifted Educationapi-237403122100% (1)
- P Alexander Vaneaton Consider The Strategies Document RevisedDocument6 pagesP Alexander Vaneaton Consider The Strategies Document Revisedapi-356979259No ratings yet
- J Gray Gifted High Achieving or CreativeDocument2 pagesJ Gray Gifted High Achieving or Creativeapi-528983071No ratings yet
- J Gray Great Brains Dinner PartyDocument6 pagesJ Gray Great Brains Dinner Partyapi-528983071No ratings yet
- Theorists and Theories Design A T-Shirt & Compare and Contrast Part 1: Design The Theorist's T-ShirtDocument6 pagesTheorists and Theories Design A T-Shirt & Compare and Contrast Part 1: Design The Theorist's T-ShirtLeahNo ratings yet
- J Gray Test Blueprint Assignment RevDocument3 pagesJ Gray Test Blueprint Assignment Revapi-528983071No ratings yet
- J Gray Local Gifted Evaluation Procedures Exit TicketDocument1 pageJ Gray Local Gifted Evaluation Procedures Exit Ticketapi-528983071No ratings yet
- W Astin Implement The Strategies and Rubric - Module 2Document8 pagesW Astin Implement The Strategies and Rubric - Module 2api-325932544No ratings yet
- What Is A Performance TaskDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Performance Taskapi-356979259100% (1)
- Emily Hogarth Bright Vs Gifted Vs Creative ChartDocument4 pagesEmily Hogarth Bright Vs Gifted Vs Creative Chartapi-293546583No ratings yet
- Implement The Strategies 3Document2 pagesImplement The Strategies 3api-315325618No ratings yet
- J Gray Gifted Identification and Services DeterminationDocument4 pagesJ Gray Gifted Identification and Services Determinationapi-528983071No ratings yet
- J Gray Summary of Reading and Viewing Graphic OrganizerDocument4 pagesJ Gray Summary of Reading and Viewing Graphic Organizerapi-528983071No ratings yet
- Differentiation Inquiry CycleDocument1 pageDifferentiation Inquiry Cycleapi-383417172No ratings yet
- 7067 19099 1 PBDocument6 pages7067 19099 1 PBwen monteNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 4 Unit 4 LP 4 UPDATEDDocument45 pagesProf Ed 4 Unit 4 LP 4 UPDATEDAniway Rose Nicole BaelNo ratings yet
- High Leverage Instructinal PracticesDocument3 pagesHigh Leverage Instructinal Practicesapi-557677748No ratings yet
- Week 1Document3 pagesWeek 1Ro De NavaNo ratings yet
- PSTMLS-Lesson 1-TransesDocument3 pagesPSTMLS-Lesson 1-TransesjkthmsvtchNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment Toolkit: An Annotated Menu of PossibilitiesDocument18 pagesFormative Assessment Toolkit: An Annotated Menu of PossibilitiesEnglishNo ratings yet
- Gifted ChildrenDocument17 pagesGifted ChildrenBharat Singh100% (4)
- 21st Century Facilitating SkillsDocument5 pages21st Century Facilitating SkillsPeter Patrick LlemitNo ratings yet
- Week 6 - Unit 5.1: Learning Processes: Curriculum and Course Design - PER 3260Document22 pagesWeek 6 - Unit 5.1: Learning Processes: Curriculum and Course Design - PER 3260Alexandra Bachero BeltránNo ratings yet
- Cadaa - Module 4 - EDUC 126Document6 pagesCadaa - Module 4 - EDUC 126Elfe Grace L. CadaaNo ratings yet
- Discussion 5 InclusiveDocument15 pagesDiscussion 5 InclusiveNora ZarahNo ratings yet
- Eliciting, Giving Instructions and Setting Up Activities (Gower, Phillips & Walters, 1995)Document7 pagesEliciting, Giving Instructions and Setting Up Activities (Gower, Phillips & Walters, 1995)AshleyBlueNo ratings yet
- 1 2 3 4 MergedDocument9 pages1 2 3 4 MergedAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Strategies LESSON 1 HEALTHEDDocument3 pagesTeaching Strategies LESSON 1 HEALTHEDAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Oh 4 12 2020Document9 pagesCSTP 1 Oh 4 12 2020api-483530581No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Matuchniak 0423Document6 pagesCSTP 1 Matuchniak 0423api-572629820No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Mack 050324Document8 pagesCSTP 1 Mack 050324api-679292788No ratings yet
- Apst 3.3 Range of Teaching Strategies LogDocument2 pagesApst 3.3 Range of Teaching Strategies Logapi-525572712No ratings yet
- Classroom BehaviorsDocument2 pagesClassroom BehaviorsJinky OmboyNo ratings yet
- Episode 5Document2 pagesEpisode 5viaxine m. pangilinanNo ratings yet
- TEEP A4 6pp - Accelerated LearningDocument6 pagesTEEP A4 6pp - Accelerated Learninganand raviNo ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Haro 12 12 19Document9 pagesCSTP 1 Haro 12 12 19api-467608657No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Mitchell 7Document6 pagesCSTP 1 Mitchell 7api-203432401No ratings yet
- CSTP ClassroomDocument13 pagesCSTP Classroomapi-333564329100% (1)
- My 21st Century Classroom Facilitating SkillsDocument1 pageMy 21st Century Classroom Facilitating SkillsGhebre PalloNo ratings yet
- Study Skill by Dr. Sontang SimamoraDocument26 pagesStudy Skill by Dr. Sontang SimamoraLucy WijayaNo ratings yet
- Sweeney - CSTP Self-Assessment Spring 2021Document76 pagesSweeney - CSTP Self-Assessment Spring 2021Ryan SweeneyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Teaching and LearningDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Teaching and LearningAnne Martha Acuña NeronaNo ratings yet
- Online Teaching and Learning ChallengesDocument2 pagesOnline Teaching and Learning ChallengesShez MerchantNo ratings yet
- Jot2 Task 2 Template 1 Shalena FordeDocument23 pagesJot2 Task 2 Template 1 Shalena Fordeapi-464924175No ratings yet
- Building Inclusive ClassroomDocument12 pagesBuilding Inclusive ClassroomCristobal CantorNo ratings yet
- Sweeney CSTP 1 Semester 4Document14 pagesSweeney CSTP 1 Semester 4Ryan SweeneyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2Document22 pagesLesson 1.2Leah Jean PolitaNo ratings yet
- Theme 1 - SlidesDocument18 pagesTheme 1 - Slidesmogobaphumzile06No ratings yet
- J Hemphill Meeting Student Needs Through Rigor and Differentiation Reflection 1Document3 pagesJ Hemphill Meeting Student Needs Through Rigor and Differentiation Reflection 1api-445922230No ratings yet
- Group Instructional Design - Multiple Intelligences & Flipped ClassroomDocument9 pagesGroup Instructional Design - Multiple Intelligences & Flipped ClassroomSAVIRA MARETTANo ratings yet
- CSTP 1 SheppardDocument9 pagesCSTP 1 Sheppardapi-378917002No ratings yet
- Sned 4 Group 3 NotesDocument7 pagesSned 4 Group 3 Notesjase.lacuna.swuNo ratings yet
- P Alexander-Vaneaton Implement The Strategies Module4 v2Document2 pagesP Alexander-Vaneaton Implement The Strategies Module4 v2api-356979259No ratings yet
- P Alexander Vaneaton Rank and Order Technology Tools v2Document2 pagesP Alexander Vaneaton Rank and Order Technology Tools v2api-356979259No ratings yet
- What Is A Performance TaskDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Performance Taskapi-356979259100% (1)
- Learning Outcome Topic Methodology Resources AssessmentDocument5 pagesLearning Outcome Topic Methodology Resources AssessmentJp Isles MagcawasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ESP DAY 2Document2 pagesLesson Plan in ESP DAY 2Krystal Claire Dioso MarimonNo ratings yet
- Division of Davao City Erico T. Nograles National High SchoolDocument4 pagesDivision of Davao City Erico T. Nograles National High SchoolDaniel MagnoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Format TemplateDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Format TemplateNurul HusnaNo ratings yet
- SN Yr 4 DLPDocument1 pageSN Yr 4 DLPAnonymous jHgxmwZNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Reading Year 2 English KSSR Topic 5 I Am SpecialDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Reading Year 2 English KSSR Topic 5 I Am SpecialnonsensewatsonNo ratings yet
- PPUFrameworkDocument2 pagesPPUFrameworkAsmanono100% (3)
- Final Research PresentationDocument5 pagesFinal Research Presentationapi-289775724No ratings yet
- Module 1: Adapting College Life in PHILSCADocument2 pagesModule 1: Adapting College Life in PHILSCAAngelo IbañezNo ratings yet
- Group 4: Caparas Sayago Vidauretta Quirogo TerolDocument16 pagesGroup 4: Caparas Sayago Vidauretta Quirogo TerolIane Aliño NavarroNo ratings yet
- Sptve 7 Exploratory: Week 5 & 6: Performance Task 3Document3 pagesSptve 7 Exploratory: Week 5 & 6: Performance Task 3Gerean VillasNo ratings yet
- Baker College Lesson Plan PersonalityDocument2 pagesBaker College Lesson Plan Personalityapi-356006116No ratings yet
- Formal Classroom ObservationDocument3 pagesFormal Classroom Observationapi-660475328No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Understand The Meaning of Colors in EnglishDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Understand The Meaning of Colors in EnglishVanessa QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Foundational Resources - Equitable Learning PracticesDocument84 pagesFoundational Resources - Equitable Learning PracticesVicente MoralesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Organic Compounds: SummaryDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Organic Compounds: SummaryMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- W5Document16 pagesW5NURSYAZWANI BINTI TOLOS MoeNo ratings yet
- Academic Audit FormatDocument8 pagesAcademic Audit FormatUma Shankar YaligarNo ratings yet
- Edu 270 Lesson Plan 2Document2 pagesEdu 270 Lesson Plan 2api-271353489No ratings yet
- Teacher Interview Questions Tell Me A Little About YourselfDocument2 pagesTeacher Interview Questions Tell Me A Little About YourselfLORENA ALEXANDRA HUAMAN BUENONo ratings yet
- NEPPeerObsFeedbackProtocol PDFDocument2 pagesNEPPeerObsFeedbackProtocol PDFBeverly A. OmotoyNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning With Technology: Effectiveness of ICT Integration in SchoolsDocument18 pagesTeaching and Learning With Technology: Effectiveness of ICT Integration in SchoolsWanda Nugroho YanuartoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Current Topics in Digital Philology - Uppsala University, SwedenDocument2 pagesSyllabus For Current Topics in Digital Philology - Uppsala University, SwedenterawNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4.2Document2 pagesQuiz 4.2Seniorito Louiesito100% (1)
- DR Marzano Webinar Becoming Reflective TeacherDocument71 pagesDR Marzano Webinar Becoming Reflective TeachercsshyamalaNo ratings yet
- Social Studies Lesson Plan Covered WagonDocument4 pagesSocial Studies Lesson Plan Covered Wagonapi-309983676No ratings yet
- The Monsters Are Due On Maple Street Act 2Document2 pagesThe Monsters Are Due On Maple Street Act 2api-594077974No ratings yet
- Week 1 Lesson 1Document3 pagesWeek 1 Lesson 1dayah3101No ratings yet
- Emily Jarema Resume 2015 CompleteDocument4 pagesEmily Jarema Resume 2015 Completeapi-248987146No ratings yet