Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kinematics 1 Assignment 1
Kinematics 1 Assignment 1
Uploaded by
Sangeeta Bansal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
69 views10 pageskinematics assignment for iit jee by Arjun Sir
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentkinematics assignment for iit jee by Arjun Sir
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
69 views10 pagesKinematics 1 Assignment 1
Kinematics 1 Assignment 1
Uploaded by
Sangeeta Bansalkinematics assignment for iit jee by Arjun Sir
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 10
Motion in One
Dimension
ppp 4.1
General Kinematics 1
RR 01
1, The ratio of the numerical values of the average velocity
and average speed of a body is always
(a) Unity (b)_ Unity or less
(©) Unity or more (4) Less than unity
2. Which of the following options is correct for the object
having a straight line motion represented by the following
graph?
o
(a) The object moves with constantly increasing velocity
from 0 t0 A and then it moves with constant velocity.
(b) Velocity of the object increases uniformly
(©) Average velocity is zero
(€) The graph shown is impossible
‘The numerical ratio of displacement to the distance covered
is always
(a) Less than one
(b) Equal to one
(©) Equal to or less than one
(A) Equal to or greater than one
4, A particle moves along a straight line path. After some time
it comes to rest. The motion is with constant acceleration
whose direction with respect to the direction of velocity
(a) positive throughout motion
(b) negative throughout motion
(©) first positive then neg
(@) first negative then positive
5. If acar covers 2/5" of the total distance with v, speed and
3/5" distance with v>, then average speed is
@ Lim Ate
© @ 2
ann I+
6. One car moving on a straight road covers one-third of the
distance with 20 km/hr and the rest with 60 km/hr. The
average speed is
(a) 40 kev/hr (b) 80 km/hr
(©) 46% ke (@) 36knvbr
7. Arman walks on a straight road from his home to a market
2.5 km away with a speed of 5 knvh, Finding the market
closed, he instantly turns and walks back home with a
speed of 7.5 km/h, The average speed of the man over the
interval of time 0 to 40 min is equal to
@) Skmh (b) 2 mm
© 2 km/h @ Shon
42 Mechanics |
8. Consider the acceleration, velocity and displacement of
a tennis ball as it falls to the ground and bounces back.
Directions of which of these changes in the process
(a) Velocity only
(b) Displacement and velocity
(©) Acceleration, velocity and displacement
(@) Displacement and acceleration
9. The position of a particle moving in the
time ris given by x= (3r—61) metres,
Select the correct statement about the moving particle from
the following
(a) The acceleration of the particle is zero at
(b) The velocity of the particle is zero at
(©) The velocity of the particle is zero at ¢
(d) The velocity and acceleration of the particle are never
10. The acceleration ‘a’ in m/s? of a particle is given by
a= 37 + 21+ 2 where ris the time. If the particle stars
‘out with a velocity w= 2 mvs at r= 0, then the velocity at
the end of 2 second is
(a) 12 mis (b) 18 ms
(©) 27 ms (@) 36mis
11, The x and y coordinates of a particle at any time rare given
‘second
byx= 744+ 4? and y= Si, where xand yae in metre and
tin seconds. The acceleration of particle at = 5 sis
(a) Zero (b) 8 m/s?
(©) 20 mvs? (@) 40. mvs?
Mulltiple Correct Answers
12. Which of the following four statements are correc
of possible values of the time for which the particle is at
distance ‘a’ from its starting point may be:
(a) One (b) Two
(©) Three (d) Four
14, Fora particle moving in straight line with increasing speed
the appropriate sign of acceleration a and velocity v can,
be
(@) a>Oandv>0
© a>Oandv<0
(b) a@0
15. Refer to the graph in figure. Match the following,
Column T Column It
(ay | f (p) [Has v > 0 and a > OJ
{throughout
(B) (q) |has.x>0 throughout and|
has a point with v= 0 and
appoint with a= 0
oO] F (© |has @ point with zero
displacement for t > 0
(a) A body can have zero velocity and still be accelerated
(b) A body can have a constant velocity and still have a
varying speed o> ]
(c) A body can have a constant speed and still have a H
warping velocity = (| F (© |hasvo |)
(d) The direction of the velocity of a body can change
when its acceleration is constant
13. A particle is moving on the x-axis. If initial velocity
> 0, and acceleration a <0 and a is constant then number A js
Answers Key
Single Correct Answer Type ‘Multiple Correct Answers Type
1. (b) 2. (c) 3 4. (b) 5. (d) 12. (a,c,d) 13. (a b,c) 14. (a,b)
é ® 7.) -& (b)-% ©) 10.) ics undead yal
15. (A,B), (C>5), Dp),
‘Motion in One Dimension 43
ppPr 4.2
General Kinematics 2
5 o
1. Arradius vector of point A relative to the origin varies with
time tas # = ati ~ br°7 where a and b are constants. Find
the equation of point’s trajectory.
2. The speed of a body moving on a straight track varies
s 4
according to v gees for 0<1<5secandv=31+8
for f> 5 sec. If distances are in meters, find the distance
‘moved by a particle at the end of 10 sec.
Teste correct answer
3. The acceleration of a particle is increasing linearly wi
time 1 as bt. The particle starts from the origin with an
initial velocity vp, The distance travelled by the particle in
time twill be
1 1
(@) vot + oe (b) volt sor
1
© w+obP © wer dor
4. A body starts from the origin and moves along the
X-axis such that the velocity at any instant is given by
(P21, where ris in sec and velocity in m/s. What is the
acceleration ofthe particle, when itis 2 m from the origin?
(a) 28 m/s? (b) 22 mvs? (c) 12 mis? (d) 10 mis?
5. The relation between time and distance is 1 = ca? + A,
where of and B are constants. The retardation is
(@) 2oy?—(b) 28? (©) 2a (a) 2B
6. The relation 3¢= 3x +6 describes the displacement of a
particle in one direction where x is in metres and rin sec.
‘The displacement, when velocity is zero, is
(@) 24 metres (b) 12 metres
(© S metres @ Zero
7. If the velocity of a particle is given by
v= (180 ~ 16x)! mis, then its acceleration will be
(@) Zero (b) Smis* (c) -8mv/s* (d) 4 mvs?
2 2 (154208)
ae
Answers Key
8. A particle moves along x-axis as
x= 4(t—2)4 a(t—2)°
Which of the following is true?
(@) The initial velocity of partie is 4
(b) The acceleration of particle is 2a
(©) The particle is at origin at
(d) None of these
9. The position vector of a particle is given as
/? — 4t + 6)i + (1°). The time after which the velocity
vector and acceleration vector becomes perpendicular to
‘each other is equal to
(a) 1 sec
(c) 15sec
(b) 2sec
(4) not possible
|
10. A particle of mass m moves along a curve y =27, When
particle has x-co-ordinate as 1/2 m and x-component of
velocity as 4 mvs, then
(a) the position coordinate of particle are (1/2, 1/4)m
(b) the velocity of particle will be along the line
4x—4y-120.
(c) the magnitude of velocity at that instant is 42 m/s
(d) the magnitude of velocity at that instant is 22 m/s
11. The velocity of a particle moving in the positive direction of
a-axis varies as v= 10V/x . Assuming that at ¢ = 0, particle
was at x=0.
(a) The initial velocity of the particle is zero.
(b) The initial velocity of the particle is 2.5 mvs.
(©) The acceleration of the particle is 2.5 mis”.
(d) The acceleration of the particle is 50 m/s.
12. A particle moves along x-axis such that its position varies
with time as x= S0r— 51°. Select the correct alternative(s).
(a) The particle has travelled 130 m distance by t= 6s.
(b) Atr=4sand 1 12s, the particle is at 120 m distance
from starting point.
(©) The particle will never be at a distance of 130:m from
starting point.
(@) During the whole motion, the particle does not have
same velocity at 2 different instants.
Single Correct Answer Type
3. © 4.) 5. (@)
&) 9% @)
Multiple Correct Answers Type
10. (a,b,c) ML. (ad) 12 (a,b,d)
6@ 2©
ppp 4.3
Motion with Constant Acceleration
|
1. A particle moving along a straight line with a constant
acceleration of ~4 m/s? passes through a point A on the
line with a velocity of +8 m/s at some moment. Find the
distance travelled by the particle in 5 seconds after that
moment.
A driver having a definite reaction time is capable of
stopping his car over a distance of 30 m on seeing a red
traffic signal, when the speed of the caris 72 km/hr and over
a distance of 10 m when the speed is 36 knvhr. Find the
distance over which he can stop the car if it were running
at a speed of 54 km/hr. Assume that his reaction time and,
the deceleration of the car remains same in all the three
cases.
ee |
3. A particle experiences a constant acceleration for 20 see
after starting from rest. Ift travels a distance , inthe first,
10 sec and a distance S; in the next 10 sec, then
(@) S\=5, (b) 5, =5y3
© S,=S/2 @ 5,=Sy4
4. A body is moving from rest under constant acceleration
and let 5, be the displacement in the first (p ~ 1) sec and
‘, be the displacement in the first p sec. The displacement
in (p? —p + 1)" sec will be
(a) S,+5, (b) SS ©) S,-S, @) SYS
5. A particle travels 10 m in first 5 sec and 10 m in next 3
sec. Assuming constant acceleration what is the distance
travelled in next 2 sec
(@) 83m (b) 9.3m
(©) 103m (@) None of above
6. A particle starts from rest, accelerates at 2 m/s* for 10s and
then goes for constant speed for 30 s and then decelerates
7. Acar starts from rest and moves with uniform acceleration
@ ona straight road from time t= 0 to t = T. After that, a
constant deceleration brings it to rest. In this process the
average speed of the car is
3aT
2
8. A body is moving with uniform acceleration describes 40m,
in the first 5 sec and 65 m in next 5 sec. Its initial velocity
will be
(a) 4 ms (b) 2.5 mis
(©) 55ms (@) lms
9. A car, starting from rest, accelerates atthe rate f through a
distance S, then continues at constant speed for time t and
of © of wa
then decelerates at the rate £ to come to rest. Ifthe total
distance traversed is 15 S, then
@ s
a1
© S=>f
10. A man is 45 m behind the bus when the bus start
accelerating from rest with acceleration 2.5 m/s?. With
what minimum velocity should the man start running to
catch the bus?
(a) 12m/s (b) 14mv/s () 1Sm/s (A) 16 m/s
11, A card is travelling on a straight level road with a uniform
speed of 60 km/h. It is followed by another car B which
is moving with a speed of 70 km/h, When the distance
between them is 2.5 km, the car B is given a deceleration
of 20 krwvh. After how much time will B catch up with A
(@) Lhe (b) W2hr (©) V4br (4) Whe
12. The speed of a body moving with uniform acceleration is
u. This speed is doubled while covering a distance S. When
itcovers an additional distance S, its speed would become
at 4 mv/s* till it stops. What is the distance travelled by it? @ Bu (o) V5u
(@) 750m (b) 800m (©) 700m () 850m
© Viv @ Viu
Answers Key
Subjective Type Single Correct Answer Type
1. 26m. 2. 18.75 m 30 4@ 5@ 6@ 10
& () 9% (c) 10. (c) 11. (d) 12. @)
‘Motion in One Dimension 4.5
ppp 4.4
Motion Under Gravity
HS 8te crt nse
1. A body is released from the top of a tower of height h. It
takes sec to reach the ground, Where will be the ball after
time 1/2 sec?
(a) At h/2 from the ground
(b) At h/4 from the ground
(©) Depends upon mass and volume of the body
(@) At3h/4 from the ground
2. A ball is projected upwards from a height h above the
surface of the earth with velocity v. The time at which the
ball strikes the ground is
2, 2g © fi. 2]
& g
© zl je @ xf re]
8 ¥ ® A
@ =
ge
3. A body is projected vertically up with a velocity v and
after some time it returns to the point from which it was
projected. The average velocity and average speed of the
body for the total time of flight are
(@) 3/2 and v/2 (b) Oand w2
(©) Oando (6) ¥/2 ando
4, Two bodies are thrown simultaneously from a tower with
same initial velocity vp: one vertically upwards, the other
vertically downwards. The distance between the two bodies
after time ris
(a) 2vot ther (b) 2vor
© vt +4 ge @) vot
5. A body falling from a high Minaret travels 40 meters in
the last 2 seconds ofits fall to ground. Height of Minaret
iin meters is (take g = 10 m/s?)
@ 6 45 (@s 50
6. A man drops a ball downside from the roof of a tower of
height 400 meters. At the same time another ball is thrown,
upside with a velocity 50 meter/sec from the surface of the
‘tower, then they will meet at which height from the surface
of the tower
(a) 100 meters (b) 320 meters
(©) 80 meters (4) 240 meters
7. Ifa freely falling body travels in the last second, a distance
equal tothe distance travelled by itin the first three second,
the time of the travel is
(a) Gsec (b) Ssec (c) 4sec (d) 3 sec
8, A body is projected up with a speed ‘u’ and the time taken
by it is 7 to reach the maximum height H. Pick out the
correct statement
(@) Itreaches H/2 in 7/2 sec
(b) It acquires velocity w/2 in T72 sec
(©) Its velocity is w/2 at H/2
(@) Same velocity at 27
9. A body freely falling from the rest has a velocity ‘v’ after it
falls through a height ‘a’. The distance it has to fall down
for its velocity to become double, is
(a) 2h (b) 4h) Gh A) Bh
10. A man throws balls with the same speed vertically upwards
‘one after the other at an interval of 2 seconds. What should
be the speed of the throw so that more than two balls are
in the sky at any time (Given g = 10 m/s*)
(a) Atleast 0.8 m/s
(b) Any speed less than 20 m/s
(©) Only with speed 20 m/s
(@) More than 20 m/s
|
11. A stone is projected vertically upwards at = 0 second. The
net displacement of stone is zero in time interval between
= 0 second to 1 = T seconds. Pick up the CORRECT
statement.
(@) Fromimer= =
second tot= z second, the average
4
velocity is zero.
(b) The change in velocity from time
; ‘in veloci Tr
is same as change in velocity from += second to
T
= steond
(©) The distance travelled from = 0 to second is
larger than distance travelled from t = ft second to
ar
second
4
4.8 Mechanics |
(@) The distance travelled from += 7 second to zB
4
second is half the distance traveled romr= second
tor=Tsecond.
12. A person, standing on the roof of a 40 m high tower, throws
a ball vertically upwards with speed 10 m/s. Two seconds
later, he throws another ball again in vertical direction (use
= 10 mv/s*), Both the balls hit the ground simultaneously.
(a) The first ball hits the ground after 4 seconds.
(b) The second ball was projected vertically downwards
with speed 5 m/s.
(©) The distance travelled by the first ball is 10 m greater
(a) cover a distance of 50 m til it strikes the ground,
(©) have adisplacement of 50 m tll itreaches the ground,
(©) reach the ground in 4 seconds.
(@ begin to move down instantaneously.
EE Gnpretension 5
‘A man is standing on top of a building 100 m high. He throws
two balls vertically, one at t = 0 and after a time interval (less
than 2 seconds). The later ball is thrown at a velocity of half the
first. At¢= 2s, both the balls reach to their maximum heights. At
this time the vertical gap between first and second ball is + 15m,
14. The speed of first ball is
than the distance travelled by the second ball. (@) 20ms (&) 10 m/s
(@) Both balls hit the ground with same velocities. (©) Sms @ 15 m/s
13. A balloon starts rising from the ground with an acceleration 15. ‘The time interval between the throw of balls is
of 1.25 ms. After 8 seconds, a stone is released from the (a) 1.2 sec (b) 05 sec
balloon. After releasing, the stone will: (©) 08 sec @ I sec
Answers Key
Single Correct Answer Type ‘Multiple Correct Answers Type
L@ 20 36 46 5% I. @b,o) 12 @ed) 13. @0)
6. ©) 7.0) 8) 9%) 10. @) cei
4 @ 15. @
Motion in One Dimension 4.7
ppPe 4.5
Relative Motion in One Dimension
|
L
3.
6.
‘A 120 m long train is moving in a direction with speed
20 mis. A train B moving with 30 mvs in the opposite
direction and 130 m long crosses the first train in atime
(@ 6s (b) 365
© 385 (d) None of these
A210 meter long train is moving due North at a of 25 m/s.
‘A small bird is flying due South alittle above the train with
speed 5 m/s. The time taken by the bird to cross the train
is
@6s (7s ©9s @ 10s
A police jeep is chasing with, velocity of 45 km/h, a thief
‘in another jeep moving with velocity 153 knvh. Police fires
a bullet with muzzle velocity of 180 mvs. The velocity it
will strike the car of the thief is
(@) 150 ms (b) 27 ms
(© 450 mis (4) 250 mis
The distance between two particles is decreasing at the
rate of 6 m/sec. If these particles travel with same speeds
and in the same direction, then the separation increase at
the rate of 4 m/sec. The particles have speeds as
(@) Smisec; | m/sec (b) 4 m/sec; 1 m/sec
(© 4 m/sec; 2 m/sec —_(@) 5 m/sec; 2 m/sec
‘A boat moves with a speed of 5 knvh relative to water in
a river flowing with a speed of 3 knvh and having a width
of I-km. The minimum time taken around a round trip is
@) Smin (b) 60 min
(©) 20min (@) 30min
An express train is moving with a velocity », Its driver
finds another train is moving on the same track in the
same direction with velocity v». To escape collision, driver
applies a retardation a on the train. The minimum time of
escaping collision will be
@ AS ) gett
(©) None (@) Both
A thief is running away on a straight road in jeep moving
witha speed of 9 ms“. A police man chases him on a motor
‘cycle moving at a speed of 10 ms“. If the instantaneous
separation of the jeep from the motorcycle is 100 m, how
Jong will it take for the police to catch the thie
@ 1s) 19s © %s @ 100s
8. Two trains one of length 100 m and another of length
125 m, are moving in mutually opposite directions along
parallel lines, meet each other, each with speed 10 mi. If
their acceleration are 0.3 m/s? and 0.2 m/s? respectively,
then the time they take to pass each other will be
@ 5s) 10s © 15s @) 208
9. ‘Two cars are moving in the same direction with the same
speed 30 km/hr. They are separated by a distance of 5 km,
the speed of a car moving in the opposite direction if it
‘meets these two cars at an interval of 4 minutes, will be
(a) 40 kwvhr (b) 45 km/hr
(©) 30 km/hr (@) 15 km/hr
A boat takes two hours to travel 8 km and back in still
‘water. Ifthe velocity of water is 4 kmh, the time taken for
going upstream 8 km and coming back is
(a) 2h
(b) 2h 40 min
(©) 1h20min
(@) Cannot be estimated with the information given
BERD Matipteconect answers
11, A man in a lift ascending with an upward acceleration
“a’ throws a ball vertically upwards with a velocity ‘v"
with respect to himself and catches it after ‘t,’ seconds.
Afterwards when the lift is descending with the same
acceleration ‘a’ acting downwards the man again throws
the ball vertically upwards with the same velocity with
respect to him and catches it after ‘f,’ seconds?
(@) the acceleration of the ball wart. ground is g when it
10.
isin air
(©) the velocity v ofthe ball relative tothe lftis eae)
ifs
(© the acceleration a ofthe tit is SHA)
(@) the velocity ‘v’ of the ball relative to the man is
hb
(ath)
48 Mechanics |
|
Aboy in the elevator shoots a bulletin a vertical upward direction
from a height of 1.5 m above the floor of the elevator. There is
12. Find the acceleration of the elevator in upward direction,
(nis?)
@ 5 (&) 525° © 5.75 (d) 625
13. Find the displacement of the bullet relative to ground during
no roof in the elevator, The floor of the elevator is at 50 m from its flight:
ground at the instant when velocity of the elevator is 10 mvs in @ 500m (b) 40m
upward direction, The bullet strikes the floor of the elevator in © 25m @ 30m .
2 seconds. The initial speed of the bullet is 15 mvs relative to 14 Find the maximum height reached by the bullet relative to
the elevator, the ground:
@ 85m (b) 82m
(© 82.75m (@) 85.25 m
nO mi 15, Find the distance travelled by bullet during its flight:
15 @ 320m (b) 300m
“ © 500m @ 350m
Answers Key
Single Correct Answer Type ‘Multiple Correct Answers Type
L@ 20 3@ 4@ 5@ I. (@c,4)
6@ 7 BH) O10) oraprehension Type
2@ B® WO 16. @
Motion in One Dimension 4.9
Understanding Motion Through Graph
HE Sine conect ansver
1. The x- graph shown in
figure represents
(a) Constant velocity
(b) Velocity of the body is
continuously changing
() Instantaneous velocity
(4) The body travels with
constant speed upto time f, and then stops
2. An object is moving with a uniform acceleration which
is parallel to its instantaneous direction of motion. The
displacement (s) and velocity (v) graph of this object is
4
Displacement
Time ()
As
@ © c
4s
© @
3. The velocity-time graph of a body moving in a straight
line is shown in the figure. The displacement and distance
travelled by the body in 6 sec are respectively
5
‘
{3
ae
7
S17T ps se
2 0)
(a) 8m, 16m (b) 16m,8m
(©) 16m, 16m (@) 8m,8m
4, The acceleration-time graph of a body is shown below
t
The most probable velocity-time graph of the body is
6
v vA
(a) pons (b)
ee) Yo an
vA vA
© @
[An
5. A ball is thrown vertically upwards. Which of the following
graph/graphs represent velocity-time graph of the ball
‘during its flight (air resistance is neglected).
@) hNSZ ) {
Lee oh
‘A ball is thrown vertically upwards. Which of the following
plots represents the speed-time graph of the ball during its
height if the air resistance is not ignored?
INE WY
oz Or
1
© 1 @
Ta Tie
4 4
© @ y
me Tie
A batsman hits a sixer and the ball touches the ground
outside the cricket ground. Which of the following graph
describes the variation of the cricket ball’s vertical velocity
with time between the time ¢, as it hits the bat and time
1, when it touches the ground?
oF ,® i
= -
Velocity
a straight line is shown in figure.
y
2m
am
‘Then the acceleration displacement graph is.
a aN
2m
2m
f@ ) 3
ae mis)
2m amis,
© *@
-2mist 2m
9. ‘The position-time (x-1) graphs for
two children A and B returning from
their school O to their homes P and
respectively along straight line
ppath (taken as x-axis) are shown in
figure.
Choose the correct statement (8):
(a) A lives closer to the school than B
(b) A starts from the school earlier than B
(©) A and B have equal average velocities from 0 tof.
(@) Bovertakes A on the way
10. A particle can travel from point A to B from two different
(a) Average velocity along the two paths must be equal
(©) The particle may travel along both the pathy
unaccelerated
(©) The direction of instantaneous velocity along the path
1 and 2 can be same for a maximum of two point on
the paths.
(@ The average and instantaneous velocity along path |
can have same direction.
in
11, In each of the situations assume that particle was initially
atrestat origin and there after it moved rectilinearly. Some
of the graph in left column represent the same motion as
represented by graphs in right column match these graph,
Column I (Column I 4
Kay { oy x
——
'
(@) ‘
—|—-:
@ ;
i
ke !
}
© 1 © i }
Ji, os
3 ; }
paths 1 and 2, as shown, in same interval of time. Then > , io
which of the following is incorrect? =
tell gg '
AD xy TG
4 ’
Answers Key
Single Correct Answer Type Multiple Correct Answers Type |
L@ 20 3@ 40 5@ 9 (@,b.d) 10. (@,c,d) |
6 720 &© - nipe
IL (A,B 49),(C+9,0>p)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Bio Lab QuestionsDocument1 pageBio Lab Questionsfuriex100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Centrifugal Pump Test RigDocument4 pagesCentrifugal Pump Test RigVaidish Sumaria100% (1)
- OMR Sheet Has Been Attached at The End: EST Erial ODocument8 pagesOMR Sheet Has Been Attached at The End: EST Erial OSangeeta BansalNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument4 pagesConic SectionsSangeeta BansalNo ratings yet
- A RK y (First T Exam Nation 2015-2016) : Nswe e ErmDocument9 pagesA RK y (First T Exam Nation 2015-2016) : Nswe e ErmSangeeta BansalNo ratings yet
- Probabi IltyDocument4 pagesProbabi IltySangeeta BansalNo ratings yet
- Presidium Indirapuram Multiple Choice Questions Class X Session 2016-17Document2 pagesPresidium Indirapuram Multiple Choice Questions Class X Session 2016-17Sangeeta BansalNo ratings yet
- Amity International School Mayur Vihar Physics Worksheet Class Ix MotionDocument1 pageAmity International School Mayur Vihar Physics Worksheet Class Ix MotionSangeeta BansalNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals: HapterDocument12 pagesQuadrilaterals: HapterSangeeta BansalNo ratings yet
- Amity International School, Mayur Vihar English Recap Sheet Direct and Indirect Speech Class IXDocument1 pageAmity International School, Mayur Vihar English Recap Sheet Direct and Indirect Speech Class IXSangeeta BansalNo ratings yet
- SolidWorks Sketch Relations SummaryDocument2 pagesSolidWorks Sketch Relations Summaryxitta00No ratings yet
- Forms of Energy (Tutorial Part 2)Document21 pagesForms of Energy (Tutorial Part 2)asapamoreNo ratings yet
- Safely Exceeding Buckling Loads in Long Horizontal Wells - Case Study in Shale PlaysDocument13 pagesSafely Exceeding Buckling Loads in Long Horizontal Wells - Case Study in Shale PlaysMejbahul SarkerNo ratings yet
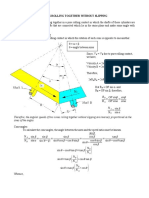
- Cones Rolling Together Without Slipping: R R OP sinα sinα N NDocument2 pagesCones Rolling Together Without Slipping: R R OP sinα sinα N NAllaine VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Science Pre BoardDocument6 pagesScience Pre BoardvspkpracticalNo ratings yet
- GaN HEMT LargesignalmodelthesisDocument83 pagesGaN HEMT LargesignalmodelthesisNorozyNo ratings yet
- Blok Design Receive Blok Design Cannel OptikDocument1 pageBlok Design Receive Blok Design Cannel Optikbpr platinmods4No ratings yet
- Lecture 13 (Evaluation of Heat and Mass Transfer Coefficients)Document7 pagesLecture 13 (Evaluation of Heat and Mass Transfer Coefficients)KaleemNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Grade 6 MathDocument11 pagesReviewer Grade 6 MathOlive L. GabunalNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Assignment 4 PDFDocument6 pagesDifferentiation Assignment 4 PDFAmandeep DhillonNo ratings yet
- Review Questions in Forensic Ballistics PDF FreeDocument5 pagesReview Questions in Forensic Ballistics PDF FreeRevie Sawadan GaanoNo ratings yet
- 07a70203 PowersystemoperationandcontrolDocument8 pages07a70203 PowersystemoperationandcontrolSamiullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Surface Properties and Activation Energy of Superplastically Carburized Duplex Stainless SteelDocument5 pagesSurface Properties and Activation Energy of Superplastically Carburized Duplex Stainless SteelElina AkbarzadeNo ratings yet
- ASTM E1289-08 (2022) Standard Specification For Reference Specimen For Sound Transmission LossDocument6 pagesASTM E1289-08 (2022) Standard Specification For Reference Specimen For Sound Transmission LossJ MrNo ratings yet
- Analisis Isotop Dalam Bidang Geosains, Pertambangan Dan LingkunganDocument38 pagesAnalisis Isotop Dalam Bidang Geosains, Pertambangan Dan LingkunganEka Djatnika NugrahaNo ratings yet
- History of RadiocarbonDocument33 pagesHistory of Radiocarbongerasimos2010No ratings yet
- Separation Variable DasarDocument9 pagesSeparation Variable DasarChristian Paskah WNo ratings yet
- TMT128Document8 pagesTMT128greatNo ratings yet
- Oil-Less Diaphragm Vacuum Pumps & Compressors: Peration Aintenance AnualDocument8 pagesOil-Less Diaphragm Vacuum Pumps & Compressors: Peration Aintenance AnualhermitagecinqNo ratings yet
- 2018 Book IntroductoryQuantumMechanicsDocument641 pages2018 Book IntroductoryQuantumMechanicsAlfangNo ratings yet
- Automatic Waste SegregationDocument6 pagesAutomatic Waste SegregationDeepak ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Practice Test-02 - Arjuna NEET (2025) - 09.06.2024 - QuestionsDocument18 pagesPractice Test-02 - Arjuna NEET (2025) - 09.06.2024 - Questionskenyen.jarekNo ratings yet
- Lecture CetrifugationDocument27 pagesLecture CetrifugationIranna UdachanNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 Tray DryerDocument9 pagesExp 2 Tray DryerMawareNo ratings yet
- Modulo 4 b2 Ame Question Quiz Part1Document8 pagesModulo 4 b2 Ame Question Quiz Part1Angel RuizNo ratings yet
- Ecoduo330 EnglDocument2 pagesEcoduo330 EnglMario Vargas VegaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines ExamDocument5 pagesElectrical Machines ExamBapeNo ratings yet
- 01 - Kitchenhood Suppression System PDFDocument24 pages01 - Kitchenhood Suppression System PDFGulf JobzNo ratings yet