Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CPG Uti
CPG Uti
Uploaded by
Nomar NonatoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CPG Uti
CPG Uti
Uploaded by
Nomar NonatoCopyright:
Available Formats
The Pharmaceutical Journal 687
cpd
Dealing with urinary tract infections
This article discusses urinary tract infections, specific patient groups and the appropriate
referral and management of these patients
INDRAN BALAKRISHNAN MRCP, FRCPATH, CONSULTANT AND HONORARY SENIOR LECTURER IN MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY, AND VICTORIA HILL MSC,
MRPHARMS, INTERIM MEDICAL SPECIALTIES PHARMACIST, ROYAL FREE HAMPSTEAD NHS TRUST
Reflect
Evaluate Plan
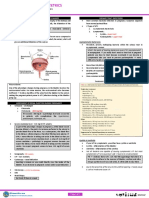
Kidney
Act
Ureter REFLECT
1 How is urinary tract infection diagnosed?
JACOPIN/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY)
2 What options are available for urine collection
in children?
Bladder
3 What strategies are used for prophylaxis?
Prostate
Urethra Before reading on, think about how this article
may help you to do your job better.
Anatomy of male and female genitourinary tracts
AROUND 20 per cent of women develop a Symptoms and when to refer Admission to hospital is required in a few
urinary tract infection (UTI) at some time The symptoms associated with cystitis are situations, for example, patients who are
incidence rises sharply around puberty and usually pain on urination (dysuria), urgency severely ill with acute pyelonephritis or
remains high thereafter. In contrast, UTI (inability to delay urination), frequency bacteraemia secondary to UTI. Although it
becomes common in men only after the age of (urinating small volumes more often) and may be possible to manage mild to moderate
50 years. suprapubic pain. The presence of cloudy or pyelonephritis with oral antibiotics, the nausea
smelly urine or blood in the urine and vomiting that are a feature of more severe
Types and terms (haematuria) indicates a need to refer the infection do not allow this. In these cases,
UTIs are best divided into two categories: patient to a GP. Urinary frequency following 4872 hours of intravenous therapy,
infections involving only the lower urinary accompanied by symptoms of thirst and it is usually possible to discharge the patient
tract (the components of the urinary tract unexplained weight loss can indicate diabetes on suitable oral treatment after the acute
below the ureter, ie, the bladder and urethra) and also prompts referral. symptoms and signs have settled. Patients
and infections involving both upper and lower If bacteraemia is associated with the infected with a multi-resistant pathogen
tracts. infection, the patient is also likely to be (eg, extended-spectrum beta-lactamase
Cystitis is the term applied to bladder systemically unwell, with fever and rigors.
inflammation, the commonest cause of which Such features are more characteristic
is infection of urine in the bladder. of upper UTI, in which case they are KEY POINTS
Upper UTI involves the ureters and kidneys. associated with loin pain (and tenderness,
When the kidneys are involved, the term
acute pyelonephritis is applied.
which a clinician may find on examination)
and vomiting.
Refer men, children under 16, pregnant
women, those with diabetes, heart or renal
Infection in a tract that is anatomically and However, none of these features is solely conditions, cloudy or smelly urine,
physiologically normal is termed indicative of UTI and similar presentations haematuria, or thirst and unexplained
uncomplicated because there are no risk can be seen in other urinary tract disorders weight loss.
factors that predispose to infection.
Anatomical or physiological abnormalities, or
such as urethritis, calculi and herpetic lesions.
Presentation can also be non-specific,
Guidelines recommend that women with
symptomatic lower urinary tract infection
both, in the urinary tract (eg, obstruction due particularly in the elderly, in whom confusion should receive empirical antibiotic
to any cause, vesico-ureteric reflux or may be a predominant feature. treatment but, on average, antibiotics
neurological disorders) predispose to Patients with symptoms of cystitis and who shorten symptom duration by about a day.
recurrent UTIs, and infection in patients with
such abnormalities is deemed complicated.
are male (see Panel 1, p688), under 16 (see
Panel 2), or pregnant (see Panel 3), or who
Use of prophylactic antibiotics for recurrent
UTIs is usually restricted to six to 12
Upper UTIs are also sometimes categorised have diabetes, heart disease or renal months.
as complicated. conditions should be referred to their GP.
(Vol 287) 10/17 December 2011
www.pjonline.com
688 The Pharmaceutical Journal
cpd
PANEL 1: URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN MALES
In males, UTIs usually aect infants and the In elderly men, prostatic hypertrophy
Any condition that
elderly. In boys, infection is often due to a predisposes to incomplete bladder emptying. prevents complete voiding
developmental anomaly known as posterior Recurrent UTI can be caused by a reservoir of of urine predisposes to
urethral valves (see Resources). An
obstructing membrane prevents the ow of
bacteria becoming established in the
prostate a condition called chronic bacterial
infection
urine out of the bladder, resulting in vesico- prostatitis. This is usually asymptomatic in
ureteric reux (see Panel 2). The anomaly can itself. Diagnosis requires simultaneous
usually be seen using cystourethrography. quantitative cultures of urethral (ie, initial)
Excluding infants and the elderly, UTI in men urine, mid-stream urine, expressed prostatic patients develop bacteriuria, of whom 2 to 6
is 10-fold less likely than in women. If secretions (obtained by prostatic massage) per cent develop symptoms of UTI. The risk
infection presents, imaging of the urinary tract and urine voided after massage. Treatment of acquiring bacteriuria is approximately 5 per
is indicated because the likelihood of an requires prolonged courses (four to eight cent for each day of catheterisation.
anatomical abnormality is high. Urine culture weeks) of antibiotics that are able to penetrate
should always be performed in symptomatic the prostate. Ciprooxacin is the most Diagnosis and testing
men. commonly used antibiotic for the treatment of Urine specimens for diagnosis of infection
All UTIs in men are considered complicated, prostatitis, although treatment must be guided include mid-stream urine and suprapubic
and longer courses of antibiotics are required. by culture results. aspirates and are discussed further in Panel 4.
Dipstick testing
PANEL 2: URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN Urine dipstick testing for nitrites and
leucocyte esterase provides a rapid and
In infants the prevalence of bacteria in urine Children with a UTI should undergo imaging economical means of screening for UTI.
(bacteriuria) is 1 to 2 per cent but it is more studies (such as 99mTc-DMSA scintigraphy) in Bacteria tend to break down urinary nitrates
common in boys than in girls due to posterior order to identify those with vesico-ureteric to nitrites, which are not found in normal
urethral valves. In pre-school children, reux, upper tract involvement and renal urine, and leucocyte esterase is produced by
prevalence of bacteriuria is about 4.5 per cent scarring. the increased neutrophils present during
in girls and 0.5 per cent in boys.1 Children should be encouraged to drink infection.
Vesico-ureteric reux, a condition in which adequate amounts of uid. Delayed urination The combined negative predictive value of
incompetence of the vesico-ureteric valve should be avoided. Trimethoprim and nitrites and leucocyte esterase of 98 per cent
allows backow of urine through the ureters nitrofurantoin are both commonly used as allows UTI to be excluded with condence in
during bladder contraction, is seen in 30 to 50 prophylaxis in vesico-ureteric reux. The many patient groups. On the other hand, the
per cent of symptomatic children. antibiotic is continued until the child outgrows relatively low positive predictive value of this
It can be caused by a variety of the reux (usually around ve or six years of technique (38 per cent) must be considered.3
abnormalities, including delayed development age). For those who develop an infection while The detection of proteinuria and haematuria
of the vesico-ureteral junction and a short taking prophylactic antibiotics, treatment with by dipstick testing is unreliable, with a high
intravesical ureter. This incompetence can a dierent agent should be initiated rather rate of false positives and false negatives, and
resolve with age but reux leads to renal than a higher dose of the prophylactic agent.2 is, therefore, of comparatively little diagnostic
scarring, chronic pyelonephritis and eventual Surgical correction of vesico-ureteric reux value.
end-stage renal disease. It is made worse by is usually reserved for children in whom In addition, dipstick testing has been found
infection. Development or progression of renal antibiotics fail to prevent infection or in whom to be unreliable in pregnant women, children
scarring is unlikely after ve years of age. reux persists. under three years of age and patients with
urinary tracts with structural anomalies or
diabetes mellitus, or who are
producing enterobacteriaeceae) for which Risk factors immunocompromised. Urine specimens from
there are limited eective oral therapeutic Risk factors for UTI include: these patients must be cultured regardless of
options may also require hospital admission. the dipstick result.
Organisms
Anatomical or physiological urinary
tract abnormalities Microscopy
UTI accounts for around 23 per cent of Sexual activity Microscopy can be used to detect haematuria
hospital-acquired infections. Over 95 per cent Pregnancy (ie, erythrocytes in the urine), white cells in
are unimicrobial, the most common family of Urinary tract procedures (eg, cytoscopy) urine (pyuria) and bacteriuria.
micro-organisms involved being Diabetes mellitus Haematuria, although a feature of cystitis, is
Enterobacteriaceae. Catheterisation
Being immunocompromised not always present and is seen in many other
In normal urinary tracts Escherichia coli is
the most common pathogen. Recurrent
conditions (eg, neoplasia, calculi). Pyuria
indicates inammation within the urinary
infection, however, is a feature of Any condition that prevents complete tract. It is suggestive but not diagnostic of
anatomically or physiologically abnormal voiding of urine predisposes to infection. In infection. For example, neutropenic patients
urinary tracts, and other micro-organisms, children, the most common is vesico-ureteric will have UTI without pyuria. Bacteriuria,
such as Proteus spp, Enterobacter spp, reux (see Panel 2).
Enterococcus spp, Staphylococcus spp and Prostatic hypertrophy can often cause
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, are more common in urinary tract obstruction and, in elderly The authors will be available to answer
these cases. women, bladder prolapse can lead to questions on this topic until 23 December 2011
The prevalence of antibiotic-resistant incomplete voiding. Many neurological
infections tends to be higher in patients with disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, can also Ask the
recurrent infections, in those who have had
multiple antibiotic exposures for other
illnesses and in nosocomial (eg, urinary
aect voiding.
Urinary catheterisation provides a portal of
entry for pathogens into the urinary tract
expert
www.pjonline.com/expert
catheter related) infection. between 20 and 30 per cent of catheterised
10/17 December 2011 (Vol 287)
www.pjonline.com
The Pharmaceutical Journal 689
cpd
but those who fail to respond to first-line
PANEL 3: URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN PREGNANT WOMEN therapy (usually trimethoprim or
nitrofurantoin see later) should have their
The urinary tract of pregnant women The evidence as to whether eliminating urine cultured to inform subsequent
undergoes considerable physiologic alteration bacteriuria early in gestation reduces the treatment.
from around seven weeks into gestation until subsequent risk of prematurity is conicting.
term. The ureters and renal pelvis dilate, However, screening (by semi-quantitative Susceptibility testing
ureteric peristalsis is reduced and bladder culture) and treatment of bacteriuria in Antibiotic susceptibility testing is performed
tone reduces. These changes predispose pregnancy is undertaken in order to reduce whenever there is isolation of an organism
women to both upper and lower UTI. the risk of developing acute pyelonephritis deemed significant. The range of antibiotics
The prevalence of asymptomatic bacteriuria and other complications. It should be tested will vary with local epidemiology,
in pregnancy ranges from 4 to 7 per cent.1 It performed routinely at the rst antenatal prescribing practices and policies.
increases with age, parity, diabetes mellitus, visit and the presence of bacteriuria
sexual activity and history of UTI. There is an should be conrmed with a second urine Complications of UTI
inverse relationship with socio-economic specimen. Of patients with a UTI, 1 to 4 per cent
status. Around 1 to 1.5 per cent of pregnant Teratogenicity is a serious consideration develop bacteraemia and, of these, 1330 per
women develop a UTI this proportion when planning treatment , but any risks cent die.5
increases to 25 per cent when bacteriuria has associated with the antimicrobial therapy Perinephric and intrarenal abscesses are
been present earlier in pregnancy, compared must be balanced against the potential recognised complications of urosepsis.
with less than 1 per cent for women in whom consequences of untreated infection. Perinephric abscesses are relatively
bacteriuria has been absent. With a lack of evidence to support the use of uncommon and usually complicate infections
Between 10 and 30 per cent of women with specic antibiotics, choice should be based on where urinary obstruction exists. Intrarenal
bacteriuria in the rst trimester develop an safety. Tetracyclines and quinolones are abscesses are being increasingly recognised as
upper UTI in the second or third trimester and contraindicated, as is trimethoprim in the rst a complication of acute pyelonephritis. The
this can adversely aect both mother and trimester. Nitrofurantoin carries a risk of development of an abscess necessitates
fetus. Prematurity and low birth weight are neonatal haemolysis near term. inpatient investigation and treatment. Imaging
increased in pregnant women who have had The duration of treatment for bacteriuria in techniques include ultrasonography and
bacteriuria; the risk is greater with upper UTI. pregnancy is three to seven days. computed tomography percutaneous
aspiration can often be performed under
radiological guidance both to provide
particularly in combination with pyuria, is, accepted as indicative of infection. Smaller specimens for microbiological analysis as well
however, highly suggestive of infection. In numbers (1001,000 colony forming as for therapeutic drainage. Antimicrobial
children below three years of age, the sole units/ml) and multiple isolates often reflect treatment should target the pathogens isolated.
presence of bacteriuria is accepted as evidence contaminated specimens but can, in some Surgical drainage may be necessary if
of urinary tract infection.2 situations, be significant, particularly when percutaneous drainage is not possible
patients are symptomatic. Any isolate from a (approximately 10 per cent), particularly with
Culture suprapubic aspirate is likely to be significant larger abscesses. After good drainage,
Semi-quantitative culture is the mainstay of regardless of colony count. complete resolution of symptoms should
diagnosis. This technique makes it easier for Culture is the only option for catheter occur in most cases with two weeks of
the laboratory to distinguish infection from samples but multiple isolates are frequently antimicrobial therapy.
contamination an important consideration obtained. These usually reflect catheter
given that the urethra, in contrast to the colonisation rather than UTI and do not Treatment
bladder, is not sterile. require treatment in the absence of symptoms. Symptomatic UTIs
Counts greater than 100,000 colony forming Routine urine culture is not required to Female patients presenting to the pharmacy
units/ml of a single isolate are generally manage lower UTIs in non-pregnant women with cystitis and who do not need to be
PANEL 4: ADVICE ON TAKING A URINE SAMPLE
As far as possible, urine urine should not be collected. Suprapubic aspirates Urine can
specimens should be collected Women should clean external be obtained from the bladder by
before starting antibiotic genitalia with soap and water. needle aspiration. This is the gold
treatment because treatment is They should hold labia apart and standard for diagnosis because it
likely to hamper laboratory empty the bladder. Men should minimises the risk of urethral
diagnosis. empty the bladder (after contamination.
Specimens need to be either retracting foreskin if Suprapubic aspiration is
processed promptly or uncircumcised). suitable for obtaining samples
JRG BEUGE | DREAMSTIME.COM
refrigerated after collection in The urine should be collected in from young children and babies.
order to minimise bacterial a sterile container placed in line It may also be used for adults in
multiplication. This is particularly of the urine stream, stopping some cases.
important for semiquantitative collection before urination is
analysis. complete. Catheter specimens Catheter
For toddlers, a potty washed specimens of urine may be
Midstream urine Midstream with hot water (60C) and washing required from patients with
urine specimens are appropriate up liquid can be used for indwelling urinary catheters and
for most patients. This method collection. poor control of micturition. bacteriuria in catheter specimens
minimises contamination from For infants a urine collection Neither dipstick testing nor of urine for febrile urinary tract
the urethra by using the rst part pad in a nappy may be used but microscopy should be used to infection identied by clinical
of the stream to remove specimens are easily diagnose UTI in these specimens. criteria has been measured as
commensal ora. Early stream contaminated. The positive predictive value of only 11 per cent.4
(Vol 287) 10/17 December 2011
www.pjonline.com
690 The Pharmaceutical Journal
cpd
as empiric treatment, but therapy should be
adjusted according to sensitivities.
PRACTICE POINTS
The evidence base for Upper UTI (or pyelonephritis) requires a
longer duration of antibiotic treatment (10 to Reading is only one way to undertake CPD
recommendation of agents 14 days). Empiric treatment options include a and the regulator will expect to see various
such as sodium or second or third generation cephalosporin, co- approaches in a pharmacists CPD portfolio.
potassium citrate amoxiclav, quinolone or an aminoglycoside
such as gentamicin. This empiric treatment is 1 Review questions to ask patients to
solutions for symptomatic often given intravenously for 4872 hours, presenting with cystitis.
reliefs limited and then switched, where possible, to oral
therapy guided by microbiological results.
2 Make sure your healthcare assistants know
which groups should be referred.
In light of the emergence and rapid spread 3 Review the appropriateness of prophylactic
of resistance in organisms known to cause antibiotics.
UTIs (eg, extended-spectrum beta-lactamase
producing E coli), certain relatively old Consider making this activity one of your
referred can be oered urine alkalinising antibacterial agents are being reintroduced. nine CPD entries this year.
agents such as sodium or potassium citrate For example, fosfomycin, which is unlicensed
solutions for symptomatic relief. However, in the UK, is seeing increased use for lower
the evidence base for recommendation is UTI and temocillin is used for upper and inconsistent and the required dose is unclear.
limited and, in mild cases, symptoms are complicated UTI. Both antibiotics achieve Patients taking warfarin should use cranberry
likely to resolve without treatment. high urinary concentrations uncomplicated products with caution.6 Women with normal
Caution is needed in patients taking drugs UTI in most patient groups can be treated upper urinary tracts may also nd
such as angiotensin-converting enzyme with a single dose of fosfomycin due to its methanamine hippurate helpful in reducing
inhibitors, potassium-sparing diuretics or slow excretion into the urine. the occurrence of symptomatic UTI.
lithium and drugs reliant on acidic urine for An application to switch trimethoprim from If an infection develops while a patient is
their excretion, which would include POM to P was withdrawn last year. It has taking antibiotic prophylaxis, a dierent agent
nitrofurantoin. been shown that in countries with fewer should be used for treatment, rather than a
General advice that can be given includes restrictions on antimicrobial supply resistance higher dose of the same antibiotic.
maintaining adequate hydration and ensuring rates are higher. Improving prescribing Antibiotic prophylaxis is not recommended
frequent urination; evidence to support a link practice can contribute to reducing in catheterised patients. One meta-analysis
with lifestyle factors is, however, limited. antimicrobial resistance. showed no signicant reduction of bacteriuria
If symptoms persist the woman should be Recurrent infection may be caused by either and a two-fold increase in antimicrobial
referred to her GP. Current guidelines the same or a dierent organism, therefore the resistant bacteria (although not in those
recommend that women with symptomatic same antimicrobial agent may be used again receiving methenamine).6
lower UTI should receive empirical antibiotic unless resistance is known. Recurrence relates Genitourinary atrophy may increase the risk
treatment.6 According to Clinical Knowledge to patient risk factors for reinfection rather of bacteriuria. Oestrogen therapy has
Summaries, on average, antibiotics shorten the than resistance to the antibiotic. Relapse demonstrated variable ecacy in reducing the
duration of symptoms by about a day. involves the same organism and suggests risk of symptomatic UTI, but it is clear that
treatment failure, potentially due to this is less eective than antibiotic prophylaxis.
Asymptomatic UTIs anatomical reasons that should be Two systematic reviews of vaginal oestrogen
In asymptomatic bacteriuria the potential risks investigated. administration both report considerable
of not treating and the expected benets of inconsistency of results; some studies show
treatment need to be balanced against the side Prophylaxis signicant reduction in risk of recurrent UTI
eects of the agent used. Recurrent UTI in women is dened as three while others show no signicant eect and
Asymptomatic bacteriuria can be associated episodes in the past 12 months or two in the even a trend towards harmful eects.
with permanent renal impairment from preceding six months. In addition to Oestrogen therapy may have a role in some
chronic pyelonephritis in pre-school children investigation, antibiotic prophylaxis should be patients, but it is not recommended for
and poor outcomes in pregnancy so treatment considered for those who have frequent routine prevention of recurrent UTI in
in these cases is essential. recurrences, especially if they are debilitating, postmenopausal women.
Given the serious consequences of persistent result in hospital admission or require
bacteriuria in these patients, a post-treatment parenteral treatment. Suitable regimens Resources
urine specimen should be obtained to ensure
bacteriological cure.
include trimethoprim 100mg on and
nitrofurantoin 50100mg on. Prophylactic
Further information about posterior urethral
valves is available at www.gosh.nhs.uk
The elderly are more susceptible to the side
eects of antibiotic therapy, and treatment of
antibiotics should be taken at night when
urine ow is low.
Afrom
summary of updated international guidelines
the Infectious Diseases Society of
UTI is not associated with improvement in Use of any antibiotic over an extended America and the European Society for
overall outcome. Moreover, the infection is period carries a risk of resistance developing, Microbiology and Infectious Diseases for the
much more likely to recur. In view of these so prophylaxis is usually restricted to six to 12 treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and
factors, treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria months. The available evidence does not pyelonephritis are available at
is not indicated in this population. support longer duration of use.7 www.escmid.org (accessed 20 August 2011).
In children, the small benet of reduced risk
Options of UTI should be weighed against the References available online.
First-line antibiotic choices for uncomplicated increased risk of developing resistant
lower UTI include nitrofurantoin and organisms. Available online until 9 January 2012
trimethoprim. In women and children, Women with frequent recurrences can be
symptomatic cure can be achieved with
courses of short duration, usually for three
advised to take cranberry products on the
basis that they inhibit the adhesion of bacteria
Check your
days. Men should be treated for at least seven
days.
In pregnancy, penicillins (eg, amoxicillin) or
to the urinary tract epithelium, therefore
preventing infection. However, the potential
for benet varies, depending on patient group,
learning
www.pjonline.com/check
rst generation cephalosporins are preferred dose and duration. Study results are
10/17 December 2011 (Vol 287)
www.pjonline.com
You might also like
- Freebie Bundle-50 PagesDocument75 pagesFreebie Bundle-50 PagesKarla Seravalli86% (7)
- DigestiveSystemSE - Activity CDocument11 pagesDigestiveSystemSE - Activity CYang Yang50% (2)
- (3F) Pediatrics - Pediatric HistoryDocument9 pages(3F) Pediatrics - Pediatric HistoryNomar Nonato100% (2)
- Group 1 Urinarytractinfections 2Document34 pagesGroup 1 Urinarytractinfections 2blessiejamNo ratings yet
- To Promote Good Hygiene and Physical Comfort.: Coli (E. Coli), NormallyDocument2 pagesTo Promote Good Hygiene and Physical Comfort.: Coli (E. Coli), NormallyFran LanNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. NCM 109Document16 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia. NCM 109Niña Jean Tormis AldabaNo ratings yet
- Funda Sample ScenarioDocument2 pagesFunda Sample ScenarioGadez JeanpelNo ratings yet
- Is Antibiotic Treatment Indicated in A Patient With A Positive Urine Culture But No SymptomsDocument4 pagesIs Antibiotic Treatment Indicated in A Patient With A Positive Urine Culture But No Symptomstsiko111No ratings yet
- Risk For Fluid VolumeDocument1 pageRisk For Fluid VolumeMariella BadongenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan TemplateDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan TemplatetonnifritzcutamoraNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections Core Curriculum 2024Document11 pagesUrinary Tract Infections Core Curriculum 2024Amanda EscorciaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection Core Curriculum 2024Document11 pagesUrinary Tract Infection Core Curriculum 2024JESSICA VELAZQUEZNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection in Adult WomenDocument15 pagesRecurrent Urinary Tract Infection in Adult WomenSEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections Core Curriculum 2024 American Journal KidneyDocument11 pagesUrinary Tract Infections Core Curriculum 2024 American Journal Kidneycharliz diazNo ratings yet
- Iaat12i5p615 PDFDocument6 pagesIaat12i5p615 PDFsuresh kumar bakhtianiNo ratings yet
- Pyelonephritis 508Document8 pagesPyelonephritis 508Dery ZhibharanyNo ratings yet
- M1 - Urinary DisordersDocument2 pagesM1 - Urinary DisordersjuiceNo ratings yet
- Silvaqueenie Rose Multiple SclerosisDocument5 pagesSilvaqueenie Rose Multiple SclerosisQueenie SilvaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationLeizel ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Peritonitis Bacteriana EspontaneaDocument1 pagePeritonitis Bacteriana EspontaneaInstituto Mexicano Seguro SocialNo ratings yet
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument2 pagesImpaired Urinary EliminationSiafei RabeNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Urinary Tract InfectionDocument10 pagesCase Study - Urinary Tract InfectionJiffy198867% (3)
- UTIsDocument25 pagesUTIsAnamul MasumNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Cholecystitis (Gallbladder Inflammation) ObjectiveDocument17 pagesCase Study of Cholecystitis (Gallbladder Inflammation) Objectivetalia hamedNo ratings yet
- Aquino NCP UtiDocument3 pagesAquino NCP UtiGianne ObaldoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Infectious Disease:: 6. Urinary Tract Infections and ProstatitisDocument26 pagesPharmacotherapy of Infectious Disease:: 6. Urinary Tract Infections and ProstatitisDigafe TolaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Incontinence - DiagnosisDocument2 pagesUrinary Incontinence - DiagnosisHoney Roselle MorenoNo ratings yet
- CC Orina PurpuraDocument2 pagesCC Orina PurpuraSusan RamosNo ratings yet
- Group Iv - Urinary Elimination PDFDocument96 pagesGroup Iv - Urinary Elimination PDFMeshezabel AsentistaNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Pseudocyst Mimicking A Left Kidney Abscess: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesPancreatic Pseudocyst Mimicking A Left Kidney Abscess: A Case Reportdarlen bahriNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection UTI and Dementia FactsheetDocument10 pagesUrinary Tract Infection UTI and Dementia FactsheettoobaziNo ratings yet
- Does My Patient Need To Be Screened or Treated For A Urinary Tract InfectionDocument4 pagesDoes My Patient Need To Be Screened or Treated For A Urinary Tract Infectiontsiko111No ratings yet
- F. NCP ProperDocument4 pagesF. NCP ProperAle SandraNo ratings yet
- Rinary Ract Nfections: Classification Pathophysiology Risk Factors Clinical Manifestation DiagnosticsDocument27 pagesRinary Ract Nfections: Classification Pathophysiology Risk Factors Clinical Manifestation DiagnosticsDARYmagpantayNo ratings yet
- Constipation: Patient Name: Shehzad Age: 45 Ward: Emergency BDocument2 pagesConstipation: Patient Name: Shehzad Age: 45 Ward: Emergency BShafiq Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument9 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasiamardsz100% (1)
- Educational Module For Nursing Assistants in Long-Term Care Facilities: Urinary Tract Infections and Asymptomatic BacteriuriaDocument35 pagesEducational Module For Nursing Assistants in Long-Term Care Facilities: Urinary Tract Infections and Asymptomatic BacteriuriaPH Ph GnsoNo ratings yet
- Coralie Therese D. Dimacali, MD, FPCP, FPSNDocument48 pagesCoralie Therese D. Dimacali, MD, FPCP, FPSNJose Ph YuNo ratings yet
- Awais - Revision. 2015Document24 pagesAwais - Revision. 2015Michael Stevent Cuellar RodriguezNo ratings yet
- IVU en El Adulto MayorDocument8 pagesIVU en El Adulto MayorAndres Sebastian TorresNo ratings yet
- Davao Doctors College Nursing Program Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesDavao Doctors College Nursing Program Nursing Care PlanPRINCESS KOBAYASHINo ratings yet
- Subjective: Nephrolithiasis Is STO: After 8 Diagnostics: STO: Fully MetDocument3 pagesSubjective: Nephrolithiasis Is STO: After 8 Diagnostics: STO: Fully MetSebastianNo ratings yet
- CDU Care Plan. UTIDocument7 pagesCDU Care Plan. UTImutiso mutieNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection in Children: DR Nada Qawasmi Alquds Faculty of MedicineDocument25 pagesUrinary Tract Infection in Children: DR Nada Qawasmi Alquds Faculty of Medicineولاء إبراهيمNo ratings yet
- OB - Renal and Urinary Tract Disorders (RCB)Document5 pagesOB - Renal and Urinary Tract Disorders (RCB)Darren Mae MosadaNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced Urinary Tract Changes Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument5 pagesPregnancy Induced Urinary Tract Changes Urinary Tract InfectionsDilausan B MolukNo ratings yet
- Notes On Urinary DisordersDocument3 pagesNotes On Urinary DisordersJAY TOM BOLIVARNo ratings yet
- University of The Assumption: College of Nursing Level Ii Related Nursing Experience Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesUniversity of The Assumption: College of Nursing Level Ii Related Nursing Experience Nursing Care PlanEugene MananganNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Free Nursing LecturesDocument8 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Free Nursing Lecturesmeshael_29No ratings yet
- Clinical Analysis: I. Patient's ProfileDocument19 pagesClinical Analysis: I. Patient's ProfileKathleen DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Deficient Knowledge Related To Urinary Tract Infection: "Di Ako Aware About Sa UTI"as Verbalized by The ClientDocument2 pagesDeficient Knowledge Related To Urinary Tract Infection: "Di Ako Aware About Sa UTI"as Verbalized by The ClientSeanmarie CabralesNo ratings yet
- Activity On NCM MakingDocument4 pagesActivity On NCM MakingJollan Marie BuenvenidaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement For Urinary Tract InfectionDocument7 pagesThesis Statement For Urinary Tract Infectionaflnbwmjhdinys100% (2)
- MONIS, Clemcy Pearl A. (NCP 103)Document5 pagesMONIS, Clemcy Pearl A. (NCP 103)Clemcy Pearl MonisNo ratings yet
- Uti Asbu Guidance FinalDocument14 pagesUti Asbu Guidance FinalJohn Vincent Dy OcampoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of ConstipationDocument8 pagesEvaluation of ConstipationAndrea GallegoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument14 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionSilva RahmaNo ratings yet
- Hematuria, (Blood in Urine) A Simple Guide to The Condition, Related Diseases And Use in Diagnosis of DiseasesFrom EverandHematuria, (Blood in Urine) A Simple Guide to The Condition, Related Diseases And Use in Diagnosis of DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- A Simple Guide to Pancreatitis, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Pancreatitis, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Insights into Acute Cystitis: Understanding, Management, and Future DirectionsFrom EverandComprehensive Insights into Acute Cystitis: Understanding, Management, and Future DirectionsNo ratings yet
- Post-cholecystectomy Bile Duct InjuryFrom EverandPost-cholecystectomy Bile Duct InjuryVinay K. KapoorNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide To Nocturia, (Excessive Night Urination) Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide To Nocturia, (Excessive Night Urination) Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- JAAPA Article - Staying Up To Date With JNC 8 HTN Guideline - H FeldmanDocument7 pagesJAAPA Article - Staying Up To Date With JNC 8 HTN Guideline - H FeldmanNomar NonatoNo ratings yet
- Wedding MassDocument19 pagesWedding MassNomar NonatoNo ratings yet
- Price ListDocument6 pagesPrice ListNomar NonatoNo ratings yet
- December 2010 Nurse Licensure Examination ResultsDocument595 pagesDecember 2010 Nurse Licensure Examination ResultsFilipino Nurses CentralNo ratings yet
- 11 Humss B Perdev Group 9 Brain Theory - 20231017 - 100244 - 0000Document22 pages11 Humss B Perdev Group 9 Brain Theory - 20231017 - 100244 - 0000Marilou PerochoNo ratings yet
- Mid Im 2020 AnatomyDocument178 pagesMid Im 2020 AnatomyXzailheene Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- Acit TrainingDocument23 pagesAcit TrainingTheoNo ratings yet
- Psychology: Test Booklet NoDocument24 pagesPsychology: Test Booklet NokodalidhanaNo ratings yet
- O&G CompendiumDocument676 pagesO&G Compendiumwalefamous100% (1)
- ATCM JOURNAL September 2014 - 21Document60 pagesATCM JOURNAL September 2014 - 21Ivonne Flores FernándezNo ratings yet
- Yogic Sthula VyayamaDocument11 pagesYogic Sthula VyayamaGerardo Antonio Contreras Guerrero100% (7)
- Frog Dissection Worksheet With Virtual DissectionDocument3 pagesFrog Dissection Worksheet With Virtual DissectionTyrone Marius EarnestNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Stabilizer Muscles A Systematic ReviewDocument11 pagesCharacteristics of Stabilizer Muscles A Systematic ReviewIvan MuñozNo ratings yet
- Ba MintonDocument15 pagesBa MintonKristel Joyce FortusNo ratings yet
- Mechanosensitive Ion Channels Contribute To MechanDocument9 pagesMechanosensitive Ion Channels Contribute To MechanHugues PetitjeanNo ratings yet
- DXN Ganoderma: Meet The King of HerbsDocument10 pagesDXN Ganoderma: Meet The King of HerbsBir Tamang TheengNo ratings yet
- Microbial Biopolymer: Pullulan Gellan Gum Dextran Xanthan GumDocument93 pagesMicrobial Biopolymer: Pullulan Gellan Gum Dextran Xanthan GumDewi WijayantiNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Lectures PDFDocument88 pagesOphthalmology Lectures PDFsharenNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan 7Document61 pagesTeaching Plan 7dinman_rituraj1683No ratings yet
- Inotropic Drugs: DR S A Jayaratne Dept of PharmacologyDocument21 pagesInotropic Drugs: DR S A Jayaratne Dept of PharmacologyanojanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System and Sense Organ in FishDocument6 pagesNervous System and Sense Organ in FishAdarsh SenNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics in Total Hip Arthroplasty: Dr. Jose AustineDocument48 pagesBiomechanics in Total Hip Arthroplasty: Dr. Jose AustinePankaj VatsaNo ratings yet
- BIO.1.Test Bank (MEO) 2nd EditionDocument247 pagesBIO.1.Test Bank (MEO) 2nd Editionshady.1422026No ratings yet
- 39.2 Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy: Ahmad Assalia, M.D. Michel Gagner, M.D., FACS, FRCSCDocument13 pages39.2 Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy: Ahmad Assalia, M.D. Michel Gagner, M.D., FACS, FRCSCimherestudyingNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesIsolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesJearweine FormaranNo ratings yet
- Haematology and Some Serum Parameters of BroilersDocument13 pagesHaematology and Some Serum Parameters of BroilersDanladi Idris HassanNo ratings yet
- Surgery I #3 - Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument9 pagesSurgery I #3 - Fluid and ElectrolytesCarl Earvin L. Favorito100% (1)
- Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis-CouplandDocument3 pagesFlowering Pathway in Arabidopsis-CouplandJay Prakash MauryaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care The Mechanical VentilatedDocument11 pagesNursing Care The Mechanical VentilatedIchal faisNo ratings yet
- EntomologyDocument50 pagesEntomologyapi-19960301100% (1)
- Read The Given Passage and Answer The Questions That FollowDocument3 pagesRead The Given Passage and Answer The Questions That Followapi-3850829No ratings yet
- Botanical Actions Reference Sheet: Botanical Action Description Physiology ExamplesDocument2 pagesBotanical Actions Reference Sheet: Botanical Action Description Physiology ExamplesDeo DoktorNo ratings yet