Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsSket 1
Sket 1
Uploaded by
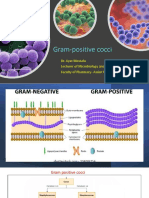
Xavier CirerStaphylococcus epidermitis commonly infects prosthetic joints and indwelling catheters by forming biofilms that stick to surfaces and resist antibiotics. It is treated with vancomycin and is part of normal skin flora. Staphylococcus saprophyticus causes urinary tract infections, especially in women, and is novobiocin resistant. Streptococcus pyogenes is the most common cause of pharyngitis and causes toxic shock syndrome. It produces exotoxins and M protein that allow it to evade the immune system and cause post-streptococcal complications. Streptococcus agalactiae commonly causes infections and meningitis in newborns.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- AABB Technical Manual 20th EditionDocument841 pagesAABB Technical Manual 20th Editionparag f80% (5)
- Method CMMEFDocument13 pagesMethod CMMEFAlexiel Nguyen0% (1)
- BLOOD TRANSFUSION NotesDocument7 pagesBLOOD TRANSFUSION NotesErl D. MelitanteNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Bacteria ChartDocument1 pageGram Positive Bacteria ChartAngelina IafanoNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The Skin and Eyes (Microbiology Chapter 21)Document82 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The Skin and Eyes (Microbiology Chapter 21)Katrina Isabel100% (1)
- BacteriologyDocument36 pagesBacteriologyMuhammad Furqaan Bari100% (1)
- Hematology NCLEX MCQDocument24 pagesHematology NCLEX MCQKo Ye100% (2)
- Sket 2Document6 pagesSket 2Xavier CirerNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology Edited 1Document65 pagesBacteriology Edited 1Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sketchy WordDocument9 pagesSketchy WordPäw Yusoph100% (1)
- Medical BacteriologyDocument108 pagesMedical BacteriologyTamarah YassinNo ratings yet
- Neisseria: Family Neisseriaceae With Four GeneraDocument26 pagesNeisseria: Family Neisseriaceae With Four GeneraAmit Mansukh MistryNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Diseases - TreatmentDocument7 pagesBacterial Diseases - Treatmentyasaira707No ratings yet
- LP Bacteria ChartDocument21 pagesLP Bacteria ChartTaman HoangNo ratings yet
- Microbiology - Bacteria Summary (Updated)Document26 pagesMicrobiology - Bacteria Summary (Updated)moZZeltovNo ratings yet
- Foundations in Microbiology: The Cocci of Medical Importance TalaroDocument71 pagesFoundations in Microbiology: The Cocci of Medical Importance TalaroOdurNo ratings yet
- 1 Gram Positive Bacterial InfectionDocument87 pages1 Gram Positive Bacterial InfectionCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Pyogenic CocciDocument4 pagesPyogenic CocciIvy LarrazabalNo ratings yet
- Neisseria, Diph, AnthraxDocument53 pagesNeisseria, Diph, AnthraxAyat MostafaNo ratings yet
- 1 Staph, Strep, NeisseriaDocument79 pages1 Staph, Strep, NeisseriaMj BrionesNo ratings yet
- Finasls 1 Staph Strep PDFDocument50 pagesFinasls 1 Staph Strep PDFFrancis ValdezNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus 1Document8 pagesStaphylococcus 1JohnWangerNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System, Mycobacteria MayDocument26 pagesRespiratory System, Mycobacteria MayMøhammed Amer KamelNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Aureus Infiection Thang 1 2007Document44 pagesStaphylococcus Aureus Infiection Thang 1 2007Nguyễn Tấn BìnhNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive CocciDocument55 pagesGram Positive CocciAyat MostafaNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases Affecting NVSDocument42 pagesInfectious Diseases Affecting NVSFATIMA LAVADIANo ratings yet
- Gram Pozitive CocciDocument47 pagesGram Pozitive CocciJedjdjdjdjdhjdNo ratings yet
- T'S Complied Ndbe Questions 2013-2015: FungiDocument34 pagesT'S Complied Ndbe Questions 2013-2015: FungiSheila JuddNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 BacteriologyDocument51 pagesUnit 4 BacteriologySharmila LamisharNo ratings yet
- Boards II Pages 1 121Document120 pagesBoards II Pages 1 121karate.b97No ratings yet
- Tangy Cleaned Up 2015Document41 pagesTangy Cleaned Up 2015Pass Boards100% (10)
- 760 Staphylococcus PPT UG LectureDocument47 pages760 Staphylococcus PPT UG Lectureridwan.biotekNo ratings yet
- ACE Edit 1 - 2Document142 pagesACE Edit 1 - 2Carly DyaNo ratings yet
- Unknown 10Document8 pagesUnknown 10Heran TeferiNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Chart FINALDocument27 pagesBacteria Chart FINALSteelers86100% (1)
- Diseases of The Skin and Eyes Wounds and BitesDocument22 pagesDiseases of The Skin and Eyes Wounds and BitesAmir IejieNo ratings yet
- Pathogenic Gram Negative CocciiDocument31 pagesPathogenic Gram Negative Cocciitemesgensemahegn55No ratings yet
- Gram Positive CocciDocument21 pagesGram Positive CocciRedelle Mae Nini100% (2)
- Bacterial Infections of The Skin, Soft TissuesDocument27 pagesBacterial Infections of The Skin, Soft TissuesSHIHAB UDDIN KAZI100% (1)
- Foundations in Microbiology: TalaroDocument71 pagesFoundations in Microbiology: Talaromertx013No ratings yet
- Coagulase +ve Coagulase - VeDocument41 pagesCoagulase +ve Coagulase - Veshrutik91No ratings yet
- Soal UasDocument10 pagesSoal UasDila ZeinNo ratings yet
- Microbiology TablesDocument19 pagesMicrobiology TablesRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- INFECTIONS Staphylococcal InfectionsDocument48 pagesINFECTIONS Staphylococcal InfectionsDr.P.NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Staph and Strep Skin InfectonsDocument60 pagesStaph and Strep Skin InfectonsteenaNo ratings yet
- StaphylococcusDocument39 pagesStaphylococcusAmmarNo ratings yet
- Infections of The SkinlllDocument7 pagesInfections of The SkinlllDanessa AlavataNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Study GuideDocument6 pagesChapter 21 Study GuideJaneNo ratings yet
- Skin and Soft-Tissue Infections: ImpetigoDocument26 pagesSkin and Soft-Tissue Infections: ImpetigoDr. Rizwanuddin QaziNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The Different Organ System SKINDocument102 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The Different Organ System SKINBea Bianca CruzNo ratings yet
- CB Part 3Document76 pagesCB Part 3Mohammad MambuayNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of Respiratory System AO Rev3Document40 pagesMicrobial Diseases of Respiratory System AO Rev3rahafahmed20043No ratings yet
- Acs Skabies InternationalDocument3 pagesAcs Skabies InternationalChandra AnggaraNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus: Medical Faculty - Hang Tuah UniversityDocument25 pagesStaphylococcus: Medical Faculty - Hang Tuah UniversityFranciska MawuntuNo ratings yet
- Perinatal Infection - Infeksi NeonatusDocument51 pagesPerinatal Infection - Infeksi NeonatusRiska PriyaniNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Summary DocumentDocument7 pagesMicrobiology Summary DocumentKNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci StaphylococciDocument41 pagesGram Positive Cocci StaphylococciZainab ElgehaniNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The Skin & EyesDocument52 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The Skin & EyesAna100% (3)
- 476 - MCB 201Document7 pages476 - MCB 201sonidave06No ratings yet
- Lecture-6 - Gram-Positive Cocci: Assist - Prof.Dr. Hiba Jasim HamzaDocument19 pagesLecture-6 - Gram-Positive Cocci: Assist - Prof.Dr. Hiba Jasim Hamzahussein.al-bohaija.nurs1765No ratings yet
- Pathologic andDocument6 pagesPathologic andAisha DoreenNo ratings yet
- 911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!From Everand911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- COVID 1984: The Pandemic, The Great Reset and the New World Order: A comprehensive and evidence-based investigation of the Covid-19 crisis, including data, facts, backgrounds, forecasts and solutionsFrom EverandCOVID 1984: The Pandemic, The Great Reset and the New World Order: A comprehensive and evidence-based investigation of the Covid-19 crisis, including data, facts, backgrounds, forecasts and solutionsNo ratings yet
- ABO Discrepancy Assignment Spring 2021Document5 pagesABO Discrepancy Assignment Spring 2021Ciarra Asuncion100% (1)
- Example of Completed Blood Safety Indicators FormDocument9 pagesExample of Completed Blood Safety Indicators FormEmhemed Amer TabibNo ratings yet
- (Lesson 6) RBC MorphologyDocument34 pages(Lesson 6) RBC MorphologyYfhps LnmNo ratings yet
- Anemia, Tic, DLC MbbsDocument50 pagesAnemia, Tic, DLC Mbbssharads221004No ratings yet
- Massive Blood Transfusion ProtocolDocument1 pageMassive Blood Transfusion ProtocolTheNurseelleNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of GastroenteritisJun MingNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank 2 PDFDocument5 pagesBlood Bank 2 PDFRajkumar RoderickNo ratings yet
- Emerging and Re-Emerging DiseasesDocument27 pagesEmerging and Re-Emerging Diseasesلؤي فارس100% (1)
- IMH100 4th Handout - ABO Discrepancies and RH Blood TypeDocument4 pagesIMH100 4th Handout - ABO Discrepancies and RH Blood TypenicholeNo ratings yet
- Bio LabbDocument3 pagesBio LabbAnyss Hasni Al-banjariNo ratings yet
- Deterioration of Molasses During Storage - Reasons and ControlDocument4 pagesDeterioration of Molasses During Storage - Reasons and ControlVishnukumarKulkarniNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: Principles and Explorations: Host-Microbe Relationships and Disease ProcessesDocument39 pagesMicrobiology: Principles and Explorations: Host-Microbe Relationships and Disease ProcessesdcitasyariNo ratings yet
- CfuDocument3 pagesCfuHarish KumarNo ratings yet
- 1522-1588 USMLE QuestionsDocument67 pages1522-1588 USMLE QuestionsKiran KrupaNo ratings yet
- ShigellaDocument16 pagesShigellaJay Ann EmanNo ratings yet
- HematDocument3 pagesHematMohit AbhyankarNo ratings yet
- Technical College of Applied Sciences Medical Laboratory Science First Stage - Second Semester Lab Technic ReportDocument9 pagesTechnical College of Applied Sciences Medical Laboratory Science First Stage - Second Semester Lab Technic ReportELYANNo ratings yet
- Consumer Reports Statistics On Hospital Infections in The DC AreaDocument4 pagesConsumer Reports Statistics On Hospital Infections in The DC AreawtopwebNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Blood Group Antibodies: Immunoglobulin Class Remarks Associated With Antigen Frequency (%)Document1 pageCharacteristics of Blood Group Antibodies: Immunoglobulin Class Remarks Associated With Antigen Frequency (%)yepNo ratings yet
- Approach To Gram Stain and Culture Results in The Microbiology LaboratoryDocument8 pagesApproach To Gram Stain and Culture Results in The Microbiology LaboratoryOscar Moisés López SanabioNo ratings yet
- Tle 7 ExamDocument4 pagesTle 7 ExamJoanna Rochelle Patricio Fabicon-Bacnis92% (13)
- AnthraxDocument20 pagesAnthraxanemenyeeNo ratings yet
- Medical Laboratory Sample QuestionsDocument6 pagesMedical Laboratory Sample Questionszopito100% (1)
- PLAUT-VINCENT ANGINA Borrelia Vincenti Tonsillitis PDFDocument2 pagesPLAUT-VINCENT ANGINA Borrelia Vincenti Tonsillitis PDFJosua MakerNo ratings yet
- Boc HemaDocument72 pagesBoc HemaFenyl Isis GuigayomaNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Errors SpreadDocument7 pagesBlood Transfusion Errors SpreadAudreey GwenNo ratings yet
Sket 1
Sket 1
Uploaded by
Xavier Cirer0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesStaphylococcus epidermitis commonly infects prosthetic joints and indwelling catheters by forming biofilms that stick to surfaces and resist antibiotics. It is treated with vancomycin and is part of normal skin flora. Staphylococcus saprophyticus causes urinary tract infections, especially in women, and is novobiocin resistant. Streptococcus pyogenes is the most common cause of pharyngitis and causes toxic shock syndrome. It produces exotoxins and M protein that allow it to evade the immune system and cause post-streptococcal complications. Streptococcus agalactiae commonly causes infections and meningitis in newborns.
Original Description:
docuament
Original Title
sket 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentStaphylococcus epidermitis commonly infects prosthetic joints and indwelling catheters by forming biofilms that stick to surfaces and resist antibiotics. It is treated with vancomycin and is part of normal skin flora. Staphylococcus saprophyticus causes urinary tract infections, especially in women, and is novobiocin resistant. Streptococcus pyogenes is the most common cause of pharyngitis and causes toxic shock syndrome. It produces exotoxins and M protein that allow it to evade the immune system and cause post-streptococcal complications. Streptococcus agalactiae commonly causes infections and meningitis in newborns.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesSket 1
Sket 1
Uploaded by
Xavier CirerStaphylococcus epidermitis commonly infects prosthetic joints and indwelling catheters by forming biofilms that stick to surfaces and resist antibiotics. It is treated with vancomycin and is part of normal skin flora. Staphylococcus saprophyticus causes urinary tract infections, especially in women, and is novobiocin resistant. Streptococcus pyogenes is the most common cause of pharyngitis and causes toxic shock syndrome. It produces exotoxins and M protein that allow it to evade the immune system and cause post-streptococcal complications. Streptococcus agalactiae commonly causes infections and meningitis in newborns.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Staphylococcus Epidermitis:
1. Infects prosthetic joints
2. Infects Indwelling catheters of bladder
3. Most common cause of endocarditis of artificial heart valves
4. Produces biofilms
- Sticks to metal and plastics
- Helps avoid detection
- Resistant to many antibiotics
5. Treatment with vancomycin
6. In skin flora
7. Contaminates blood cultures
8. Novobiocin sensitive
Staphylococcus Saprophyticus
1. Novobiocin resistant
2. Causes infections specially in sexually active females
3. Causes UTI
4. Catalase positive
Both saprophyticus and epidermitis
- 5. Urease positive
- 6. Cogulase negative
Streptococcus Pyogenes (Group A)
1. Encapsulated
- 2. Made of Hyaluronic acid
3. Beta- hemolytic positive
4. Causes Impetigo: also aureus
- Skin infection
- Looks like honey-crust
5. Causes pharyngitis
6. Most common cause of Cellulitis and Erysipelas (more demarcated)
Causes Scarlett fever
- 7. Swelling of tongue
- 8. Pharyngitis
- 9. Wide-spread rash that spares the face
10. Toxic shock syndrome-like
- With super Ab
11. Necrotizing faciitis
- very rapid and serious
Subtypes
- Spe A and C: super antigen ( Scarlett and TSLS)
- 12 Spe B: protease: Nec. fasc
13. M- protein: highly antigenic protein at cell wall
Responsible for RF: type II
- 14. Interferes with opsonization: antiphagocytic
- 15. Mimics myocin (heart): heart valve problems: stenosis
- 16. Occurs only after Pharyngitis
- Jones syndrome
- 17. Joints: polyarthritis
- 18. Heart:
- Valvular damages leading to murmurs
- Myocarditis
- Pericarditis
- 19. Nodules: subcutaneous at forearms, elbows and knees
- 20. Erythema Marginatum
- 21. Sydenham's chorea: involuntary movement of the hands and
face
22. Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis: type III
- Deposition of immune complexes in glomerulus
- 23. Causes edema
- 24. Cola-colored urine
- 25. Occurs after two weeks of infection
- 26 Can occur after Pharyngitis or superficial infection impetigo
- 27. Early diagnostic won't prevent it: need for penicillin
28. Streptolysin-O: lysis RBCs
-29. We generate Ab against it
30. Streptokinase: plasminogen --> plasmin
- Fribrinolytic
31. DNAse
32. Strep pyogenes (Group A) is bacitracin sensitive
- Interferes with cell wall and peptidoglycan synthesis
33. Antistreptolysin o titer for detection
Streptococcus Agalactiae (group B)
1. Causes serious problems in newborns
2. Hippurate positive
3. Polysaccharide capsule
4. CAMP positive
- 11. Arrowhead zone hemolysis
5. Increased zone hemolysis when plated with Staph Aureus
6. Beta hemolysis positive
7. Bacitracin resistant
8. Nr 1 cause of meningitis in neonates
9. Causes Neonatal sepsis
10. Also causes pneumonia
12. Neonates get infected by Group B in delivery
13. Culture at 35 weeks of pregnancy
14. To avoid baby infection
- Intrapartum penicillin
Staphylococcus aureus 16. Most common cause
1. Violet: gram + of osteomyelitis
2. Catalase: + 17. Scalded Skin syndrome: skin
3. Coagulase: + peals of
4. Beta hemolysis: + - By protease
5. Ferments mannitol: yellow 18. Toxic Shock Syndrome
6. Protein A - Acts as super antigen
- Binds FC region of Ab to avoid 19. Food poisoning
complement activation - preformed toxins
7. Colonizes nares of nose - Rapid: 1-8 h
8. Causes Pneumonia - 20. From meat and cream-
- 9. Patchy infiltrate on X-ray base food
- 10. Post-viral bacterial pneumonia 21. MRSA: Methylin Resistant St
11. Most common cause of septic - 22. By modifying its penicillin
arthritis binding proteins (PBP)
12. They causes abscesses 22. Treatment by Vancomycin
13. Acute bacterial endocarditis - 23. Or Nafcillin
- Rapid onset
- 14. In IV drug users
- 15. Usually at tricuspid valve
You might also like
- AABB Technical Manual 20th EditionDocument841 pagesAABB Technical Manual 20th Editionparag f80% (5)
- Method CMMEFDocument13 pagesMethod CMMEFAlexiel Nguyen0% (1)
- BLOOD TRANSFUSION NotesDocument7 pagesBLOOD TRANSFUSION NotesErl D. MelitanteNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Bacteria ChartDocument1 pageGram Positive Bacteria ChartAngelina IafanoNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The Skin and Eyes (Microbiology Chapter 21)Document82 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The Skin and Eyes (Microbiology Chapter 21)Katrina Isabel100% (1)
- BacteriologyDocument36 pagesBacteriologyMuhammad Furqaan Bari100% (1)
- Hematology NCLEX MCQDocument24 pagesHematology NCLEX MCQKo Ye100% (2)
- Sket 2Document6 pagesSket 2Xavier CirerNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology Edited 1Document65 pagesBacteriology Edited 1Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sketchy WordDocument9 pagesSketchy WordPäw Yusoph100% (1)
- Medical BacteriologyDocument108 pagesMedical BacteriologyTamarah YassinNo ratings yet
- Neisseria: Family Neisseriaceae With Four GeneraDocument26 pagesNeisseria: Family Neisseriaceae With Four GeneraAmit Mansukh MistryNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Diseases - TreatmentDocument7 pagesBacterial Diseases - Treatmentyasaira707No ratings yet
- LP Bacteria ChartDocument21 pagesLP Bacteria ChartTaman HoangNo ratings yet
- Microbiology - Bacteria Summary (Updated)Document26 pagesMicrobiology - Bacteria Summary (Updated)moZZeltovNo ratings yet
- Foundations in Microbiology: The Cocci of Medical Importance TalaroDocument71 pagesFoundations in Microbiology: The Cocci of Medical Importance TalaroOdurNo ratings yet
- 1 Gram Positive Bacterial InfectionDocument87 pages1 Gram Positive Bacterial InfectionCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Pyogenic CocciDocument4 pagesPyogenic CocciIvy LarrazabalNo ratings yet
- Neisseria, Diph, AnthraxDocument53 pagesNeisseria, Diph, AnthraxAyat MostafaNo ratings yet
- 1 Staph, Strep, NeisseriaDocument79 pages1 Staph, Strep, NeisseriaMj BrionesNo ratings yet
- Finasls 1 Staph Strep PDFDocument50 pagesFinasls 1 Staph Strep PDFFrancis ValdezNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus 1Document8 pagesStaphylococcus 1JohnWangerNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System, Mycobacteria MayDocument26 pagesRespiratory System, Mycobacteria MayMøhammed Amer KamelNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Aureus Infiection Thang 1 2007Document44 pagesStaphylococcus Aureus Infiection Thang 1 2007Nguyễn Tấn BìnhNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive CocciDocument55 pagesGram Positive CocciAyat MostafaNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases Affecting NVSDocument42 pagesInfectious Diseases Affecting NVSFATIMA LAVADIANo ratings yet
- Gram Pozitive CocciDocument47 pagesGram Pozitive CocciJedjdjdjdjdhjdNo ratings yet
- T'S Complied Ndbe Questions 2013-2015: FungiDocument34 pagesT'S Complied Ndbe Questions 2013-2015: FungiSheila JuddNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 BacteriologyDocument51 pagesUnit 4 BacteriologySharmila LamisharNo ratings yet
- Boards II Pages 1 121Document120 pagesBoards II Pages 1 121karate.b97No ratings yet
- Tangy Cleaned Up 2015Document41 pagesTangy Cleaned Up 2015Pass Boards100% (10)
- 760 Staphylococcus PPT UG LectureDocument47 pages760 Staphylococcus PPT UG Lectureridwan.biotekNo ratings yet
- ACE Edit 1 - 2Document142 pagesACE Edit 1 - 2Carly DyaNo ratings yet
- Unknown 10Document8 pagesUnknown 10Heran TeferiNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Chart FINALDocument27 pagesBacteria Chart FINALSteelers86100% (1)
- Diseases of The Skin and Eyes Wounds and BitesDocument22 pagesDiseases of The Skin and Eyes Wounds and BitesAmir IejieNo ratings yet
- Pathogenic Gram Negative CocciiDocument31 pagesPathogenic Gram Negative Cocciitemesgensemahegn55No ratings yet
- Gram Positive CocciDocument21 pagesGram Positive CocciRedelle Mae Nini100% (2)
- Bacterial Infections of The Skin, Soft TissuesDocument27 pagesBacterial Infections of The Skin, Soft TissuesSHIHAB UDDIN KAZI100% (1)
- Foundations in Microbiology: TalaroDocument71 pagesFoundations in Microbiology: Talaromertx013No ratings yet
- Coagulase +ve Coagulase - VeDocument41 pagesCoagulase +ve Coagulase - Veshrutik91No ratings yet
- Soal UasDocument10 pagesSoal UasDila ZeinNo ratings yet
- Microbiology TablesDocument19 pagesMicrobiology TablesRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- INFECTIONS Staphylococcal InfectionsDocument48 pagesINFECTIONS Staphylococcal InfectionsDr.P.NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Staph and Strep Skin InfectonsDocument60 pagesStaph and Strep Skin InfectonsteenaNo ratings yet
- StaphylococcusDocument39 pagesStaphylococcusAmmarNo ratings yet
- Infections of The SkinlllDocument7 pagesInfections of The SkinlllDanessa AlavataNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Study GuideDocument6 pagesChapter 21 Study GuideJaneNo ratings yet
- Skin and Soft-Tissue Infections: ImpetigoDocument26 pagesSkin and Soft-Tissue Infections: ImpetigoDr. Rizwanuddin QaziNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The Different Organ System SKINDocument102 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The Different Organ System SKINBea Bianca CruzNo ratings yet
- CB Part 3Document76 pagesCB Part 3Mohammad MambuayNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of Respiratory System AO Rev3Document40 pagesMicrobial Diseases of Respiratory System AO Rev3rahafahmed20043No ratings yet
- Acs Skabies InternationalDocument3 pagesAcs Skabies InternationalChandra AnggaraNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus: Medical Faculty - Hang Tuah UniversityDocument25 pagesStaphylococcus: Medical Faculty - Hang Tuah UniversityFranciska MawuntuNo ratings yet
- Perinatal Infection - Infeksi NeonatusDocument51 pagesPerinatal Infection - Infeksi NeonatusRiska PriyaniNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Summary DocumentDocument7 pagesMicrobiology Summary DocumentKNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci StaphylococciDocument41 pagesGram Positive Cocci StaphylococciZainab ElgehaniNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The Skin & EyesDocument52 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The Skin & EyesAna100% (3)
- 476 - MCB 201Document7 pages476 - MCB 201sonidave06No ratings yet
- Lecture-6 - Gram-Positive Cocci: Assist - Prof.Dr. Hiba Jasim HamzaDocument19 pagesLecture-6 - Gram-Positive Cocci: Assist - Prof.Dr. Hiba Jasim Hamzahussein.al-bohaija.nurs1765No ratings yet
- Pathologic andDocument6 pagesPathologic andAisha DoreenNo ratings yet
- 911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!From Everand911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- COVID 1984: The Pandemic, The Great Reset and the New World Order: A comprehensive and evidence-based investigation of the Covid-19 crisis, including data, facts, backgrounds, forecasts and solutionsFrom EverandCOVID 1984: The Pandemic, The Great Reset and the New World Order: A comprehensive and evidence-based investigation of the Covid-19 crisis, including data, facts, backgrounds, forecasts and solutionsNo ratings yet
- ABO Discrepancy Assignment Spring 2021Document5 pagesABO Discrepancy Assignment Spring 2021Ciarra Asuncion100% (1)
- Example of Completed Blood Safety Indicators FormDocument9 pagesExample of Completed Blood Safety Indicators FormEmhemed Amer TabibNo ratings yet
- (Lesson 6) RBC MorphologyDocument34 pages(Lesson 6) RBC MorphologyYfhps LnmNo ratings yet
- Anemia, Tic, DLC MbbsDocument50 pagesAnemia, Tic, DLC Mbbssharads221004No ratings yet
- Massive Blood Transfusion ProtocolDocument1 pageMassive Blood Transfusion ProtocolTheNurseelleNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of GastroenteritisJun MingNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank 2 PDFDocument5 pagesBlood Bank 2 PDFRajkumar RoderickNo ratings yet
- Emerging and Re-Emerging DiseasesDocument27 pagesEmerging and Re-Emerging Diseasesلؤي فارس100% (1)
- IMH100 4th Handout - ABO Discrepancies and RH Blood TypeDocument4 pagesIMH100 4th Handout - ABO Discrepancies and RH Blood TypenicholeNo ratings yet
- Bio LabbDocument3 pagesBio LabbAnyss Hasni Al-banjariNo ratings yet
- Deterioration of Molasses During Storage - Reasons and ControlDocument4 pagesDeterioration of Molasses During Storage - Reasons and ControlVishnukumarKulkarniNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: Principles and Explorations: Host-Microbe Relationships and Disease ProcessesDocument39 pagesMicrobiology: Principles and Explorations: Host-Microbe Relationships and Disease ProcessesdcitasyariNo ratings yet
- CfuDocument3 pagesCfuHarish KumarNo ratings yet
- 1522-1588 USMLE QuestionsDocument67 pages1522-1588 USMLE QuestionsKiran KrupaNo ratings yet
- ShigellaDocument16 pagesShigellaJay Ann EmanNo ratings yet
- HematDocument3 pagesHematMohit AbhyankarNo ratings yet
- Technical College of Applied Sciences Medical Laboratory Science First Stage - Second Semester Lab Technic ReportDocument9 pagesTechnical College of Applied Sciences Medical Laboratory Science First Stage - Second Semester Lab Technic ReportELYANNo ratings yet
- Consumer Reports Statistics On Hospital Infections in The DC AreaDocument4 pagesConsumer Reports Statistics On Hospital Infections in The DC AreawtopwebNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Blood Group Antibodies: Immunoglobulin Class Remarks Associated With Antigen Frequency (%)Document1 pageCharacteristics of Blood Group Antibodies: Immunoglobulin Class Remarks Associated With Antigen Frequency (%)yepNo ratings yet
- Approach To Gram Stain and Culture Results in The Microbiology LaboratoryDocument8 pagesApproach To Gram Stain and Culture Results in The Microbiology LaboratoryOscar Moisés López SanabioNo ratings yet
- Tle 7 ExamDocument4 pagesTle 7 ExamJoanna Rochelle Patricio Fabicon-Bacnis92% (13)
- AnthraxDocument20 pagesAnthraxanemenyeeNo ratings yet
- Medical Laboratory Sample QuestionsDocument6 pagesMedical Laboratory Sample Questionszopito100% (1)
- PLAUT-VINCENT ANGINA Borrelia Vincenti Tonsillitis PDFDocument2 pagesPLAUT-VINCENT ANGINA Borrelia Vincenti Tonsillitis PDFJosua MakerNo ratings yet
- Boc HemaDocument72 pagesBoc HemaFenyl Isis GuigayomaNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Errors SpreadDocument7 pagesBlood Transfusion Errors SpreadAudreey GwenNo ratings yet