Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Data Structures With C Lab
Data Structures With C Lab
Uploaded by
Sandeep RoyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Data Structures With C Lab
Data Structures With C Lab
Uploaded by
Sandeep RoyCopyright:
Available Formats
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
/*1. Write a C Program to create a sequential file with atleast 5 records, each record having the
structure shown below:
USN - Positive number : Name - 25 Char : Marks1,marks 2,marks 3 are positive Numbers
Write necessary functions
a. To display all the records in the file.
b. To search for a specific record based on the USN. In case the record is not found, suitable
message should be displayed.
Both the options in this case must be demonstrated.*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
typedef struct st
{
int USN,M1,M2,M3;
char Name[25];
}record;
record stu;
void read_data(FILE *fp)
{
printf("\nEnter the USN\t");
scanf("%d",&stu.USN);
printf("Enter the Name\t");
scanf("%s",&stu.Name);
printf("Enter the Marks 1\t");
scanf("%d",&stu.M1);
printf("Enter the Marks 2\t");
scanf("%d",&stu.M2);
printf("Enter the Marks 3\t");
scanf("%d",&stu.M3);
fprintf(fp,"%d\t%s\t%d\t%d\t%d\n",stu.USN,stu.Name,stu.M1,stu.M2,stu.M3);
fclose(fp);
}
void disp_data(record st)
{
printf("%d%18s\t%5d\t%5d\t%5d\n",st.USN,st.Name,st.M1,st.M2,st.M3);
}
void main()
{
FILE *fp;
int i,j,n,ch,key,flag=1,found=0;
clrscr();
printf("\n Enter the Number of students details\t");
scanf("%d",&n);
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 1 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
if(n>0)
fp=fopen("student.dat","w");
printf("\n Enter the students Details\n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("\n Enter the Details of %d Student",i+1);
read_data(fp);
}
fclose(fp);
while(flag)
{
clrscr();
printf("\n1 Add Record\n2 Search\n3 Display all\n4 Exit\n Enter the choice\t");
scanf("%d",&ch);
switch(ch)
{
case 1: fp=fopen("student.dat","a");
read_data(fp);
break;
case 3:
fp=fopen("student.dat","r");
printf("\nUSN\t\tName\tMarks 1\tMarks 2\tMarks
3\n");
while(1)
{
fscanf(fp,"%d%s%d%d
%d",&stu.USN,stu.Name,&stu.M1,&stu.M2,&stu.M3);
if(feof(fp)) break;
disp_data(stu);
}
fclose(fp);
break;
case 2:
fp=fopen("student.dat","r");
printf("\n Enter the USN Number to search\t");
scanf("%d",&key);
while(!feof(fp))
{
fscanf(fp,"%d%s%d%d
%d",&stu.USN,stu.Name,&stu.M1,&stu.M2,&stu.M3);
if(feof(fp)) break;
if(stu.USN==key)
{
printf("\n Record Found\n");
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 2 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
printf("\nUSN\t\tName\tMarks
1\tMarks 2\tMarks 3\n");
disp_data(stu);
found=1;
}
}
fclose(fp);
if(found==0)
{
printf("\nThe record with USN %d is not
found\n",key);
found=0;
}
break;
case 4:
default: flag=0;
}
getch();
}
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 3 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
/*2. Write and demonstrate the following C functions:
a. newStrCpy that does the same job as strcpy
b. newStrCat that does the same job as strcat without using any library functions.*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void newStrCpy(char dest[],char src[])
{
int i;
for(i=0;src[i]!='\0';i++)
dest[i]=src[i];
dest[i]='\0';
}
void newStrCat(char dest[],char src[])
{
int i,j=0;
for(i=0;dest[i]!='\0';i++);
for(j=0;src[j]!='\0';j++)
dest[i+j]=src[j];
dest[i+j]='\0';
}
void main()
{
char s[20],d[40];
clrscr();
printf("Enter the String\t");
scanf("%s",s);
printf("\n newStrCpy( ,%s)",s);
newStrCpy(d,s);
printf(" is %s\n",d);
printf("\nEnter the String for Concatination\t");
scanf("%s",s);
printf("\nnewStrCat(%s,%s) ",d,s);
newStrCat(d,s);
printf(" is %s\n",d);
getch();
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 4 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
/*3. Write a C Program, which accepts the Internet Protocol (IP) address in
decimal dot format (ex. 153.18.8.105) and converts it into 32-bit long
integer (ex. 2568095849) using strtok library function and unions.*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef union ip
{
unsigned long num;
unsigned char ar[3];
}IP;
void main()
{
IP ipaddr;
int i=3,j;
char *ip_add="153.18.8.105";
char *p,*x;
clrscr();
p=strtok(ip_add,".");
ipaddr.ar[i--]=strtol(p,&x,10);
while(p!=NULL)
{
p=strtok(NULL,".");
ipaddr.ar[i--]=strtol(p,&x,10);
}
printf("IP Address in Doted Decimal System\t");
for(j=3;j>=0;j--)
{
if(j!=0)
printf("%d.",ipaddr.ar[j]);
else
printf("%d",ipaddr.ar[j]);
}
printf("\nIP Binary Address %lu",ipaddr.num);
getch();
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 5 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
/*4. Write a C Program to construct a stack of integers and to
perform the following operations on it:
a. Push
b. Pop
c. Display
The program should print appropriate messages for stack overflow,
stack underflow, and stack empty.
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define MAX 5
typedef struct stack
{
int s[10];
int top;
}STACK;
int isfull(int t)
{
return (t==MAX-1);
}
int isempty(int t)
{
return (t==-1);
}
void push(STACK *x,int ele)
{
if(isfull(x->top))
printf("\nStack Full\n");
else
{
x->top++;
x->s[x->top]=ele;
}
}
int pop(STACK *x)
{
int ret=-1;
if(isempty(x->top))
printf("\n Stack is empty\n");
else
{
ret=x->s[x->top];
x->top--;
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 6 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
return ret;
}
void display(STACK x)
{
int i;
if(isempty(x.top))
printf("\n Stack is Empty\n");
else
{
printf ("\n Elements of Stack are\n");
for(i=x.top;i>=0;i--)
printf("%d\t",x.s[i]);
}
}
void main()
{
int ch,ele,flag=1;
STACK a;
a.top=-1;
while(flag)
{
clrscr();
printf("\n 1 Push\n2 Pop\n3 Display\n4 Exit\nEnter the Choice\t");
scanf("%d",&ch);
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
printf("Enter the element to push\t");
scanf("%d",&ele);
push(&a,ele);
break;
case 2:
ele=pop(&a);
if(ele!=-1)
printf("\n Element poped is \t%d",ele);
break;
case 3:
display(a);
break;
case 4:
default: flag=0;
}
getch();
}}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 7 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
/*5. Write a C Program to convert and print a given valid
parenthesized infix arithmetic expression to postfix expression. The
expression consists of single character operands and the binary
operators + (plus), - (minus), * (multiply) and / (divide).*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define MAX 5
typedef struct stack
{
char s[10];
int top;
}STACK;
STACK a;
void push(char ele)
{
a.top++;
a.s[a.top]=ele;
}
char pop()
{
char ret;
ret=a.s[a.top];
a.top--;
return ret;
}
int inper(char x)
{
switch(x)
{
case '+':
case '-': return 1;
case '*':
case '/': return 3;
case '$': return 6;
case ')': return 7;
}
}
int stper(char x)
{
switch(x)
{
case '+':
case '-': return 2;
case '*':
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 8 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
case '/': return 4;
case '$': return 5;
case '(':
case '#': return 0;
}
}
void convert(char infix[],char postfix[])
{
int i,j=0;
char c;
for(i=0;infix[i]!='\0';i++)
{
c=infix[i];
switch(c)
{
case '(':
push(c);
break;
case ')':
while(a.s[a.top]!='(')
postfix[j++]=pop();
pop();
break;
case '+':
case '-':
case '*':
case '/':
case '$':
while(stper(a.s[a.top])>inper(c))
postfix[j++]=pop();
push(c);
break;
default:
postfix[j++]=c;
break;
}
}
while(a.s[a.top]!='#')
postfix[j++]=pop();
postfix[j]='\0';
}
void main()
{
char infix[20],postfix[20];
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 9 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
a.top=-1;
push('#');
clrscr();
printf("Enter the infix Expn\t");
scanf("%s",infix);
convert(infix,postfix);
printf("The postfix expn of %s is %s",infix,postfix);
getch();
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 10 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
/*6. Write a C Program to evaluate a valid suffix/postfix expression using stack. Assume that the
suffix/postfix expression is read as a single line consisting of non-negative single digit operands
and binary arithmetic operators. The arithmetic operators are + (add), - (subtract), * (multiply)
and / (divide).*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<ctype.h>
typedef struct stack
{
double s[10];
int top;
}STACK;
STACK a;
void push(double ele)
{
a.top++;
a.s[a.top]=ele;
}
double pop()
{
double ret;
ret=a.s[a.top];
a.top--;
return ret;
}
double eval(char postfix[])
{
int i;
double x,y;
char c;
for(i=0;postfix[i]!='\0';i++)
{
c=postfix[i];
if(isdigit(c))
push(c-'0');
else
{
x=pop();
y=pop();
switch(c)
{
case '+':push(x+y);
break;
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 11 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
case '-':push(y-x);
break;
case '*':push(x*y);
break;
case '/':push(y/x);
}
}
}
return(pop());
}
void main()
{
char postfix[20];
double res;
clrscr();
printf("Enter the Postfix expn\t");
gets(postfix);
res=eval(postfix);
printf("The Result is %lf",res);
getch();
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 12 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
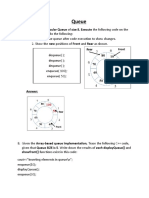
/* 7. Write a C Program to construct a Queue of integers and to perform
the following operations on it:
a. Insert
b. Delete
c. Display
The program should print appropriate messages for Queue overflow,
and Queue empty.*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define MAX 5
typedef struct q
{
int a[10];
int r,f;
}QUEUE;
int isfull(int x)
{
return (x==MAX);
}
int isempty(int x)
{
return (x==-1);
}
void insert(QUEUE *x,int ele)
{
if(isfull(x->r))
printf("\nQueue Full\n");
else
{
x->a[x->r]=ele;
x->r++;
if(x->f==-1)
x->f=0;
}
}
int qdelete(QUEUE *x)
{
int ret=-1;
if(isempty(x->f))
printf("\n Queue is empty\n");
else
{
ret=x->a[x->f];
x->f++;
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 13 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
if(x->f==x->r)
{
x->f=-1;
x->r=0;
}
}
return ret;
}
void display(QUEUE x)
{
int i;
if(isempty(x.f))
printf("\n Stack is Empty\n");
else
{
printf ("\n Elements of Stack are\n");
for(i=x.f;i<x.r;i++)
printf("%d\t",x.a[i]);
}
}
void main()
{
int ch,ele,flag=1;
QUEUE x;
x.f=-1;
x.r=0;
while(flag)
{
clrscr();
printf("\n 1 Insert\n2 Delete\n3 Display\n4 Exit\nEnter the Choice\t");
scanf("%d",&ch);
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
printf("Enter the element to Insert\t");
scanf("%d",&ele);
insert(&x,ele);
break;
case 2:
ele=qdelete(&x);
if(ele!=-1)
printf("\n Element Deleted is \t%d",ele);
break;
case 3:
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 14 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
display(x);
break;
case 4:
default: flag=0;
}
getch();
}
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 15 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
/*8. Write a C Program to simulate the working of a circular
queue of integers using an array.Provide the following operations:
a. Insert
b. Delete
c. Display
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define MAX 5
typedef struct q
{
int a[10];
int r,f;
int count;
}QUEUE;
int isfull(int x)
{
return (x==MAX);
}
int isempty(int x)
{
return (x==0);
}
void insert(QUEUE *x,int ele)
{
if(isfull(x->count))
printf("\nQueue Full\n");
else
{
x->a[x->r]=ele;
x->r=(x->r+1)%MAX;
x->count++;
}
}
int qdelete(QUEUE *x)
{
int ret=-1;
if(isempty(x->count))
printf("\n Queue is empty\n");
else
{
ret=x->a[x->f];
x->f=(x->f+1)%MAX;
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 16 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
x->count--;
}
return ret;
}
void display(QUEUE x)
{
int i,j;
if(isempty(x.count))
printf("\n Stack is Empty\n");
else
{
printf ("\n Elements of Stack are\n");
j=x.f;
for(i=0;i<x.count;i++)
{
printf("%d\t",x.a[j]);
j=(j+1)%MAX;
}
}
}
void main()
{
int ch,ele,flag=1;
QUEUE x;
x.f=0;
x.r=0;
x.count=0;
while(flag)
{
clrscr();
printf("\n1 Insert\n2 Delete\n3 Display\n4 Exit\nEnter the Choice\t");
scanf("%d",&ch);
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
printf("Enter the element to Insert\t");
scanf("%d",&ele);
insert(&x,ele);
break;
case 2:
ele=qdelete(&x);
if(ele!=-1)
printf("\n Element Deleted is \t%d",ele);
break;
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 17 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
case 3:
display(x);
break;
case 4:
default: flag=0;
}
getch();
}
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 18 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
/*9. Write a C Program using dynamic variables and pointers, to construct
a singly linked list consisting of the following information in each node:
student id (integer), student name (character string) and semester (integer).
The operations to be supported are:
a. The insertion operation
i. At the front of a list
ii. At the back of the list
iii. At any position in the list
b. Deleting a node based on student id. If the specified node
is not present in the list an error message should be
displayed. Both the options should be demonstrated.
c. Searching a node based on student id and update the
information content. If the specified node is not present in
the list an error message should be displayed. Both
situations should be displayed.
d. Displaying all the nodes in the list.*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
typedef struct stud
{
int id;
char name[20];
int sem;
}stu;
typedef struct node
{
stu info;
struct node *link;
}N;
stu getdata()
{
stu t;
printf("\nEnter the Student ID\t");
scanf("%d",&t.id);
fflush(stdin);
printf("\nEnter the Student Name\t");
scanf("%s",t.name);
printf("\nEnter the Student Sem\t");
scanf("%d",&t.sem);
return t;
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 19 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
void dispdata(stu x)
{
printf("\n%d\t%s\t%d",x.id,x.name,x.sem);
}
N* getnode(stu x)
{
N *t;
t=(N *) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
t->info=x;
t->link=NULL;
return t;
}
N *finsert(N *f,stu x)
{
N *t=getnode(x);
if(f==NULL)
f=t;
else
{
t->link=f;
f=t;
}
return f;
}
N *einsert(N *f,stu x)
{
N *t,*t1;
t=getnode(x);
if(f==NULL)
f=t;
else
{
t1=f;
while(t1->link!=NULL)
t1=t1->link;
t1->link=t;
}
return f;
}
N *posinsert(N *f,stu x,int pos)
{
int i=1;
N *cur,*t,*prev;
t=getnode(x);
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 20 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
if(f==NULL && pos > 1)
printf("\nInvalid Position\n");
else if(f==NULL && pos==1)
f=t;
else if(f !=NULL && pos == 1)
{
t->link=f;
f=t;
}
else
{
cur=f;
prev=f;
i=1;
while(cur!=NULL && i<=pos-1)
{
prev=cur;
cur=cur->link;
i++;
}
if(cur==NULL)
printf("\nInvalid Position\n");
else
{
t->link=cur;
prev->link=t;
}
}
return f;
}
N *id_delete(N *f,int key)
{
N *cur,*prev;
if(f==NULL)
printf("\nInvalid Key\n");
else if(f->info.id==key)
{
printf("\n Node Deleted\n");
printf("\nID\tName\tSem\n");
dispdata(f->info);
f=f->link;
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 21 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
else
{
cur=f;
prev=f;
while(cur!=NULL && cur->info.id!=key)
{
prev=cur;
cur=cur->link;
}
if(cur==NULL)
printf("\nInvalid ID\n");
else
{
printf("\n Node Deleted\n");
printf("\nID\tName\tSem\n");
dispdata(cur->info);
prev->link=cur->link;
}
}
return f;
}
N *id_update(N *f,int key)
{
N *cur,*prev;
if(f==NULL)
printf("\nInvalid Key\n");
else if(f->info.id==key)
{
printf("New Data\n");
f->info=getdata();
}
else
{
cur=f;
prev=f;
while(cur!=NULL && cur->info.id!=key)
{
prev=cur;
cur=cur->link;
}
if(cur==NULL)
printf("\nInvalid ID\n");
else
{
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 22 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
printf("New Data\n");
cur->info=getdata();
}
}
return f;
}
void display(N *f)
{
N *t=f;
if(f==NULL)
printf(" List is Empty\n");
else
{
printf("\nElement of List is \n");
while(t!=NULL)
{
dispdata(t->info);
t=t->link;
}
}
}
void main()
{
stu x;
N *first=NULL;
int ch,flag=1,pos,id;
while(flag)
{
clrscr();
printf("\n1 Front insert\n2 End Insert\n3 Position Insert\n4 Display\n");
printf("5 ID Delete\n6 Search and Modifiy\n7 Exit\n");
printf("Enter the Choice\t");
scanf("%d",&ch);
switch(ch)
{
case 1: printf("Enter the Student date to Node\n");
x=getdata();
first=finsert(first,x);
break;
case 2: printf("Enter the Student date to Node\n");
x=getdata();
first=einsert(first,x);
break;
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 23 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
case 3:
printf("Enter the Student date to Node\n");
x=getdata();
printf("Enter the Position \t");
scanf("%d",&pos);
first=posinsert(first,x,pos);
break;
case 4: display(first);
break;
case 5:
printf("Enter the ID \t");
scanf("%d",&id);
first=id_delete(first,id);
break;
case 6:
printf("Enter the ID \t");
scanf("%d",&id);
first=id_update(first,id);
break;
case 7:
default: flag=0;
}
getch();
}
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 24 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
/*10. Write a C Program using dynamic variables and pointers to
construct a stack of integers using singly linked list and to
perform the following operations:
a. Push
b. Pop
c. Display
The program should print appropriate messages for stack
overflow and stack empty.
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#define MAX 5
typedef struct node
{
int info;
struct node *link;
}N;
int count=0;
N* getnode(int x)
{
N *t;
t=(N *) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
t->info=x;
t->link=NULL;
return t;
}
N *push(N *f,int x)
{
if(count==MAX)
printf("\n Stack Oveflow");
else
{
N *t=getnode(x);
if(f==NULL)
f=t;
else
{
t->link=f;
f=t;
}
count++;
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 25 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
return f;
}
N *pop(N *f,int &ele)
{
ele =-1;
if(count==0)
printf("\n Stack Empty");
else
{
N *t=f;
ele=f->info;
f=f->link;
free(t);
count--;
}
return f;
}
void display(N *f)
{
N *t=f;
if(f==NULL)
printf(" List is Empty\n");
else
{
printf("\nElement of List is \n");
while(t!=NULL)
{
printf("%d\t",t->info);
t=t->link;
}
}
}
void main()
{
N *first=NULL;
int ch,flag=1,ele;
while(flag)
{
clrscr();
printf("\n1 Push\n2 Pop\n3 Display\n4 Exit\n");
printf("Enter the Choice\t");
scanf("%d",&ch);
switch(ch)
{
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 26 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
case 1: printf("Enter the Info to push\n");
scanf("%d",&ele);
first=push(first,ele);
break;
case 2: first=pop(first,ele);
if(ele!=-1)
printf("\n Element Deleted is %d",ele);
break;
case 3:
display(first);
break;
case 4:
default: flag=0;
}
getch();
}
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 27 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
/*11. Write a C program using dynamic variables and pointers to
construct a queue of integers using singly linked list and to
perform the following operations:
a. Insert
b. Delete
c. Display
The program should print appropriate messages for queue full
and queue empty.
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#define MAX 5
typedef struct node
{
int info;
struct node *link;
}N;
int count=0;
N *front,*rear;
N* getnode(int x)
{
N *t;
t=(N *) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
t->info=x;
t->link=NULL;
return t;
}
void insert(int x)
{
if(count==MAX)
printf("\n Queue Oveflow");
else
{
N *t=getnode(x);
if(rear==NULL)
front=rear=t;
else
{
rear->link=t;
rear=t;
}
count++;
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 28 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
}
}
void Qdelete(int &ele)
{
ele =-1;
if(count==0)
printf("\n Queue Empty");
else
{
N *t=front;
ele=front->info;
front=front->link;
if(front==NULL)
rear=front;
free(t);
count--;
}
}
void display()
{
N *t=front;
if(t==NULL)
printf(" \nQueue is Empty\n");
else
{
printf("\nElement of Queue is \n");
while(t!=NULL)
{
printf("%d\t",t->info);
t=t->link;
}
}
}
void main()
{
front=rear=NULL;
int ch,flag=1,ele;
while(flag)
{
clrscr();
printf("\n1 Insert\n2 Delete\n3 Display\n4 Exit\n");
printf("Enter the Choice\t");
scanf("%d",&ch);
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 29 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
switch(ch)
{
case 1: printf("Enter the Info to Insert\n");
scanf("%d",&ele);
insert(ele);
break;
case 2: Qdelete(ele);
if(ele!=-1)
printf("\n Element Deleted is %d",ele);
break;
case 3:
display();
break;
case 4:
default: flag=0;
}
getch();
}
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 30 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
/*12. Write a C Program to support the following operations on a doubly
linked list where each node consists of integers:
a. Create a doubly linked list by adding each node at the front.
b. Insert a new node to the left of the node whose key value is read
as an input
c. Delete the node of a given data, if it is found, otherwise display
appropriate message.
d. Display the contents of the list.
(Note: Only either (a,b and d) or
(a, c and d) may be asked in the examination)
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<alloc.h>
#include<conio.h>
typedef struct node
{
node *lptr;
int info;
node *rptr;
}N;
N* getnode(int x)
{
N *t;
t=(N *) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
t->info=x;
t->rptr=t->lptr=NULL;
return t;
}
N *finsert(N *f,int x)
{
N *t;
t=getnode(x);
if(f==NULL)
f=t;
else
{
t->rptr=f;
f->lptr=t;
f=t;
}
return f;
}
N *Insert_left(N *f,int x,int key)
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 31 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
{
N *t,*cur;
if(f->info==key)
f=finsert(f,x);
else
{
cur=f;
while(cur!=NULL && cur->info!=key)
cur=cur->rptr;
if(cur==NULL)
printf("\n Invalid Key\n");
else
{
N *t=getnode(x);
t->rptr=cur;
t->lptr=cur->lptr;
cur->lptr=t;
t->lptr->rptr=t;
}
}
return f;
}
N *Delete_key(N *f,int key)
{
N *t,*cur;
if(f->info==key)
{
printf("\n Key Element %d is found and deleted",key);
t=f;
f=f->rptr;
f->lptr=NULL;
free(t);
}
else
{
cur=f;
while(cur!=NULL && cur->info!=key)
cur=cur->rptr;
if(cur==NULL)
printf("\n Key Element %d not found",key);
else
{
printf("\n Key Element %d is found and deleted",key);
cur->lptr->rptr=cur->rptr;
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 32 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
cur->rptr->lptr=cur->lptr;
free(cur);
}
}
return f;
}
void display(N *f)
{
node *t=f;
if(f==NULL)
printf("\nList is empty\n");
else
{
printf("\n Element in the list\n");
while(t!=NULL)
{
printf("%d\t",t->info);
t=t->rptr;
}
}
}
void main()
{
N *first=NULL;
int flag=1,ch,ele,key;
while(flag)
{
clrscr();
printf("\n1 Finsert\n2 Insert Left to Key\n3 Key Delete\n4 Display\n5 Exit\nEnter
the Choice\t");
scanf("%d",&ch);
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
printf("\nEnter the info to insert in the front of the list\t");
scanf("%d",&ele);
first=finsert(first,ele);
break;
case 2:
printf("\nEnter the info and Key\t");
scanf("%d%d",&ele,&key);
first=Insert_left(first,ele,key);
break;
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 33 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
case 3:
printf("\nEnter the Key to delete\t");
scanf("%d",&key);
first=Delete_key(first,key);
break;
case 4:
display(first);
break;
case 5:
default: flag=0;
}
getch();
}
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 34 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
/*13. Write a C Program
a. To construct a binary search tree of integers.
b. To traverse the tree using all the methods i.e., inorder,
preorder and postorder.
c. To display the elements in the tree.
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<alloc.h>
typedef struct node
{
struct node *lptr;
int info;
struct node *rptr;
}N;
N * getnode(int x)
{
N *t=(N *) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
t->info=x;
t->lptr=t->rptr=NULL;
return t;
}
N *insert(N *r,int x)
{
N *p,*q,*t=getnode(x);
if(!r)
r=t;
else
{
p=q=r;
while(q && q->info!=x)
{
p=q;
if(q->info<x)
q=q->rptr;
else
q=q->lptr;
}
if(q->info==x)
printf("\n Duplicat Node\n");
else
{
if(x < p->info)
p->lptr=t;
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 35 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
else
p->rptr=t;
}
}
return r;
}
void inorder(N *r)
{
if(r)
{
inorder(r->lptr);
printf("%d\t",r->info);
inorder(r->rptr);
}
}
void preorder(N *r)
{
if(r)
{
printf("%d\t",r->info);
preorder(r->lptr);
preorder(r->rptr);
}
}
void postorder(N *r)
{
if(r)
{
postorder(r->lptr);
postorder(r->rptr);
printf("%d\t",r->info);
}
}
void display(N *f)
{
printf("\n Inorder\n");
inorder(f);
printf("\n Preorder\n");
preorder(f);
printf("\n Postorder\n");
postorder(f);
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 36 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
void main()
{
N *root=NULL;
int ch,ele,flag=1;
clrscr();
while(flag)
{
printf("Enter The Value of Node\t");
scanf("%d",&ele);
root=insert(root,ele);
printf("Press 1 to Continue");
scanf("%d",&ch);
if(ch!=1)
flag=0;
}
printf("\n Elements of Tree are\n");
display(root);
getch();
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 37 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
/* 14a. Write recursive C Programs for
a. Searching an element on a given list of integers using the
Binary Search method.
b. Solving the Towers of Hanoi problem.*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int bsearch(int a[],int n,int low,int high,int key)
{
int mid=(low+high)/2;
if(low > high)
return -1;
if(a[mid]==key)
return(mid+1);
if(a[mid]<key)
bsearch(a,n,mid+1,high,key);
else
bsearch(a,n,low,mid-1,key);
}
void main()
{
int i,j=0,ele,key,n;
int a[100];
clrscr();
printf("\n Enter the Number of element\t");
scanf("%d",&n) ;
printf("\n Enter %d elements of Array\n",n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
printf("\n Enter the Key to search\t");
scanf("%d",&key);
ele=bsearch(a,n,0,n-1,key);
if(ele==-1)
printf("\n Element is not found\n");
else
printf("\n Element is found at %d\n",ele);
getch();
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 38 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
/* 14 b. Write recursive C Programs for Solving the Towers
of Hanoi problem.*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void tower(int n,char s,char d, char x,int *m)
{
if(n==1)
{
printf("\n Move Disk 1 from %c to %c",s,d);
(*m)++;
}
else
{
tower(n-1,s,x,d,m);
printf("\n Move Disk %d from %c to %c",n,s,d);
(*m)++;
tower(n-1,x,d,s,m);
}
}
void main()
{
int n,m=0;
clrscr();
printf("\Enter the Number of Disks\t");
scanf("%d",&n);
tower(n,'A','B','C',&m);
printf("\n Total Moves %d",m);
getch();
}
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 39 SIRMVIT
Data Structures Laboratory Manual 2010-2011
Department of CSE/ISE Page No 40 SIRMVIT
You might also like
- Chapter 10 SB AnswersDocument18 pagesChapter 10 SB Answersekta sharma0% (1)
- CS1201 Data StructuresDocument4 pagesCS1201 Data StructuressureshNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Lab ManualDocument174 pagesData Structure Lab Manualh_mech100% (1)
- MA60002 Data Structure and Algorithms (Bhakt)Document2 pagesMA60002 Data Structure and Algorithms (Bhakt)Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 Functions and PointersDocument19 pagesMODULE 4 Functions and Pointersmanoj hmNo ratings yet
- CPP Programs ListDocument1 pageCPP Programs ListAshish Rajendra MasihNo ratings yet
- CTS PlacementPaperDocument63 pagesCTS PlacementPaperVivekanandan NarasimmanNo ratings yet
- C Structures and UnionsDocument61 pagesC Structures and UnionsRando BNo ratings yet
- Lab - 1 (Assignment - 1) #PHPDocument1 pageLab - 1 (Assignment - 1) #PHPDipesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ds MaterialDocument61 pagesDs MaterialSai RamNo ratings yet
- 140 Programs in CDocument111 pages140 Programs in CNadar Dinakaran SankaravelNo ratings yet
- Array Java ExerciseDocument5 pagesArray Java ExerciseRiskyana Dewi Intan PNo ratings yet
- Array ProgramsDocument7 pagesArray ProgramsBijay OjhaNo ratings yet
- Structures in CDocument25 pagesStructures in CMonisha CyrilNo ratings yet
- Java Lab Assignment, 2020Document4 pagesJava Lab Assignment, 2020Pritam Basu50% (2)
- Rmkec Meenak Ge8161 PSPP Lab Viva QuestionsDocument3 pagesRmkec Meenak Ge8161 PSPP Lab Viva QuestionsABITHA J UEC19101No ratings yet
- Type C SolutionsDocument12 pagesType C SolutionsHOME WORKNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv: List Python Collections (Arrays) : ExampleDocument49 pagesUnit Iv: List Python Collections (Arrays) : ExampleJeyapalan David PandiyarajNo ratings yet
- Java NotesDocument65 pagesJava NotesDaniel JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Loyola College (Autonomous) Chennai - 600034 Department of Computer Science Question Bank January 2022Document3 pagesLoyola College (Autonomous) Chennai - 600034 Department of Computer Science Question Bank January 2022Prabhu SanminsNo ratings yet
- Javaindex 1Document7 pagesJavaindex 1Sudeep Sharma100% (2)
- C Lab Assignment 1Document10 pagesC Lab Assignment 1api-27455153No ratings yet
- DS LabDocument56 pagesDS LabnaveenhydiNo ratings yet
- C Programming While and Do..Document7 pagesC Programming While and Do..Durga DeviNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument66 pagesFunctionshi_itssandeepNo ratings yet
- Web EngineeringDocument21 pagesWeb EngineeringMohsin GNo ratings yet
- Arrays and StringsDocument56 pagesArrays and StringsAAsfawNo ratings yet
- Functions in C ProgrammingDocument27 pagesFunctions in C ProgrammingBharatraj100% (1)
- C Programming RecursionDocument2 pagesC Programming RecursionslspaNo ratings yet
- Basic C Interview QuestionsDocument14 pagesBasic C Interview Questionsgouri_shanker21No ratings yet
- Topological Sort HomeworkDocument5 pagesTopological Sort Homeworkabhi74No ratings yet
- Computer Network Lab PDFDocument79 pagesComputer Network Lab PDFSAFIKURESHI MONDALNo ratings yet
- C Matrix ProgramsDocument5 pagesC Matrix ProgramsdevfeelNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Viva QuestionsDocument8 pagesData Structures Viva QuestionslokiblazerNo ratings yet
- Java Final Submission (Java Programs)Document51 pagesJava Final Submission (Java Programs)TB50% (2)
- RecursionDocument38 pagesRecursionanjugaduNo ratings yet
- PHP Lab ProgramsDocument3 pagesPHP Lab ProgramsRajiv SivalingamNo ratings yet
- List of Programs For Class XI - 2012Document2 pagesList of Programs For Class XI - 2012Niti Arora80% (5)
- C ProgramsDocument41 pagesC Programspvaibhav0843% (7)
- C Lab - PDFDocument25 pagesC Lab - PDFSubin PS100% (2)
- Node:: Linkedlist LinkedlistDocument3 pagesNode:: Linkedlist Linkedlistchandrasekar ANo ratings yet
- 12 PandasDocument21 pages12 PandasArshpreet Singh100% (1)
- Topological SortingDocument8 pagesTopological SortingGeorge fernandez.INo ratings yet
- Recursion in C: #IncludeDocument2 pagesRecursion in C: #IncludeDr. T. Veeramakali CSE-STAFFNo ratings yet
- Arrays BasicsDocument27 pagesArrays BasicssudhirNo ratings yet
- Trees: 1/34 Data Structures and Algorithms in JavaDocument34 pagesTrees: 1/34 Data Structures and Algorithms in JavaThịnh TrầnNo ratings yet
- 2022 - DS Lab ManualDocument54 pages2022 - DS Lab ManualManu Amba ravikumarNo ratings yet
- Classical IPC ProblemsDocument15 pagesClassical IPC ProblemsFariha Nuzhat MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Dbms Lab ManualDocument51 pagesDbms Lab ManualAngad KamatNo ratings yet
- C Important Questions PDFDocument9 pagesC Important Questions PDFPradeep Kumar Reddy Reddy100% (2)
- List of Java ProgramsDocument37 pagesList of Java ProgramsMartin7_10% (1)
- Visvesvaraya Technological University: Web Technology and Its Applications Practical Assessment (18Cs63)Document20 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University: Web Technology and Its Applications Practical Assessment (18Cs63)hivagsdNo ratings yet
- MCQ DsaDocument2 pagesMCQ Dsaचौधरीखड़कNo ratings yet
- DBMS Manual-1Document39 pagesDBMS Manual-1Divya DharshiniNo ratings yet
- IMPORTANT C PROGRAMS Patterns of Numbers and StarsDocument15 pagesIMPORTANT C PROGRAMS Patterns of Numbers and StarsShubham KashivNo ratings yet
- List of Python ProgramsDocument6 pagesList of Python ProgramsAsad NadeemNo ratings yet
- Dsa - Lab Manual-18csl38Document44 pagesDsa - Lab Manual-18csl38gangad benalNo ratings yet
- CZ1007 Assignment 1Document10 pagesCZ1007 Assignment 1Kenrick_Anggar_6736No ratings yet
- DSLABMANUALDocument35 pagesDSLABMANUALkushalrajur17112004No ratings yet
- DSDocument51 pagesDSjovinmascarenhasNo ratings yet
- DS LabDocument53 pagesDS LabpocalocomocoNo ratings yet
- 2nd SemDocument18 pages2nd SemSuman Raj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Midterm 2018-2019 Semester 2Document5 pagesMidterm 2018-2019 Semester 2Duy TrầnNo ratings yet
- Section 4 Further Problem-Solving and Programming SkillsDocument26 pagesSection 4 Further Problem-Solving and Programming SkillsTrynosNo ratings yet
- SchedulingDocument9 pagesSchedulingVivek SivaramanNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Question BankDocument24 pagesData Structure Question BankRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- DSA ListDocument53 pagesDSA ListRiyaz ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Priority QueueDocument6 pagesPriority Queuesonofgun007No ratings yet
- Data StructureDocument31 pagesData StructureAndrina PraveenNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Lab File BCS 351Document76 pagesData Structure Lab File BCS 351Roasting GamerNo ratings yet
- CS 12 Data Structures (Stack)Document8 pagesCS 12 Data Structures (Stack)HarshNo ratings yet
- Priority QueueDocument4 pagesPriority Queuenupursonkusare27No ratings yet
- Data Structure MCQ QuestionsDocument12 pagesData Structure MCQ QuestionsbhuvneshNo ratings yet
- PythonProjectwith OutputDocument55 pagesPythonProjectwith OutputProbaron BaruahNo ratings yet
- Queues: CS 302 - Data Structures Sections 5.3 and 5.4Document49 pagesQueues: CS 302 - Data Structures Sections 5.3 and 5.4Md. Ridwanul Islam 1812608642No ratings yet
- DSA Interview QuestionsDocument13 pagesDSA Interview QuestionsImran ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document90 pagesAssignment 1Arpit SinghNo ratings yet
- DS FinalRevisionDocument16 pagesDS FinalRevisionOla SamirNo ratings yet
- Data Structure MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) - SanfoundryDocument15 pagesData Structure MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) - SanfoundryEzekiel JamesNo ratings yet
- Stacks, Queues, and Linked ListsDocument15 pagesStacks, Queues, and Linked Listssajith vsNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Lab ManualDocument44 pagesData Structures: Lab ManualTushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Data Structure - PPTDocument26 pagesIntroduction of Data Structure - PPTadhikanshgupta00No ratings yet
- Discrete Event "Hand" Simulation of A GI/GI/1 Queue: Chapter 2 - Fundamental Simulation ConceptsDocument19 pagesDiscrete Event "Hand" Simulation of A GI/GI/1 Queue: Chapter 2 - Fundamental Simulation ConceptsmajidffNo ratings yet
- Data Structure - Programming Language (MCQ) QuestionsDocument5 pagesData Structure - Programming Language (MCQ) QuestionsSantosh BNo ratings yet
- Implementation of A Linked List: AlgorithmDocument91 pagesImplementation of A Linked List: AlgorithmgeethuuuuNo ratings yet
- Data Structure in Hindi PDFDocument85 pagesData Structure in Hindi PDFBijendra Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Assignment 2 Algorithms and Data TypesDocument7 pagesAssignment 2 Algorithms and Data TypesArash SinghNo ratings yet
- All Saints School, Agra: General InstructionsDocument2 pagesAll Saints School, Agra: General InstructionsShesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Erlang Programming RulesDocument21 pagesErlang Programming RulesjoshmuzaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computing II (ITI 1121) Final Examination: SolutionsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Computing II (ITI 1121) Final Examination: SolutionsNatesh KukrejaNo ratings yet