Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Keeps The Nucleus Together
What Keeps The Nucleus Together
Uploaded by
Anonymous vRpzQ2BLOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Keeps The Nucleus Together
What Keeps The Nucleus Together
Uploaded by
Anonymous vRpzQ2BLCopyright:
Available Formats
What Keeps the Nucleus Together?
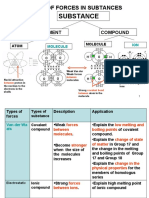
The law of electrostatics says that like charges repel. So, if a nucleus contains two or more
positively charged protons, they should repel each other. But in that case, why doesnt the
nucleus fly apart? The answer to this question involves the four fundamental forces of nature.
We all have a practical familiarity with the first, gravity. Because gravitys attraction depends on
the mass of the objects involved, its effect on the very light protons and neutrons in the nucleus
is too small to measure. The second force, the one in which chemists are most interested, is the
electromagnetic force. Existing both inside and outside the nucleus, it acts between electrically
charged or magnetic objects and is the source of the like charges repel, unlike charges attract
rule.
Both of the other two forces operate only within the nucleus. They are called the strong nuclear
force and theTitle:
Author: WATSON
weak nuclear force. The weak force is
CHEMISTRY
stronger than gravity, but weaker than an
ISBN : _____________200X
electric force; its presence is only apparent in certain forms of radioactivity. The strong nuclear
Figure : 02.07.01UN Serial :__________________
force pulls together protons and neutrons in the nucleus. At very small distances only, such as
those inside the nucleus, this strong force overcomes the electromagnetic force, and prevents the
electrical repulsion of protons from blowing the nucleus apart.
Attractive
force
Not to scale To scale
Gravitational Weak nuclear Strong nuclear Electromagnetic
force force force force
Distance Nucleus Distance
Repulsive
force
Ranges and relative strengths of the four fundamental forces between two protons. The sizes of the colored
areas indicate the relative strengths of the forces. For visibility, those for the gravitational and weak nuclear forces
are greatly exaggerated. Inside the nucleus, the attractive strong nuclear force between protons outweighs the
repulsive electromagnetic force and keeps the nucleus stable. Outside the nucleus, the electromagnetic force is
Note:
stronger and protons repel each other.
1.
LEGEND: Ranges and relative strengths of the four fundamental forces between two protons. The sizes of the colored areas
indicate the relative strengths of the forces. For visibility, those for the gravitational and weak nuclear forces are greatly exaggerated.
Inside the nucleus, the attractive strong nuclear force between protons outweighs the repulsive electromagnetic force and keeps the
nucleus stable. Outside the nucleus, the electromagnetic force is stronger and protons repel each other.
You might also like
- Skills Worksheet: Orbital Motion - Answer KeyDocument4 pagesSkills Worksheet: Orbital Motion - Answer KeyFatma AhliNo ratings yet
- Science Notebook Ch20section2Document7 pagesScience Notebook Ch20section2coleNo ratings yet
- Review of Stereochemical PrinciplesDocument3 pagesReview of Stereochemical PrinciplesAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- Burland, J. B. (1973) - Shaft Friction of Piles in Clay - A Simple Fundamental Approach. Ground Engineering, 6 (3), 30-42Document6 pagesBurland, J. B. (1973) - Shaft Friction of Piles in Clay - A Simple Fundamental Approach. Ground Engineering, 6 (3), 30-42Jennifer Miller100% (1)
- KD 221.1Document2 pagesKD 221.1gabao123No ratings yet
- CamScanner 07-18-2020 20.03.54Document9 pagesCamScanner 07-18-2020 20.03.54Fudhail MaynudeenNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Basic: Forces WhichDocument9 pagesFundamental Basic: Forces WhichFudhail MaynudeenNo ratings yet
- (Left) (Right) : © 1960 Scientific American, IncDocument21 pages(Left) (Right) : © 1960 Scientific American, IncAnshul TeotiaNo ratings yet
- The Four Fundamental Forces of NatureDocument3 pagesThe Four Fundamental Forces of NatureSabyasachi MukharjeeNo ratings yet
- Strong InteractionDocument6 pagesStrong InteractionAkhilesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument40 pagesNuclear PhysicsShakir KhattakNo ratings yet
- Nuclear & Particle Physics-I: Lecture-1 General Properties of NucleiDocument16 pagesNuclear & Particle Physics-I: Lecture-1 General Properties of NucleiAlagh DineshNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Engineering: Aiub Dr. M. Tanseer Ali NPWR Lec 02 /1Document20 pagesNuclear Power Engineering: Aiub Dr. M. Tanseer Ali NPWR Lec 02 /1Naushed NihalNo ratings yet
- MCP 07.14 Nuclear Physics IDocument30 pagesMCP 07.14 Nuclear Physics IHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical: PropertiesDocument7 pagesMechanical: Propertiessandykiller420No ratings yet
- General Physics 2Document3 pagesGeneral Physics 2John Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- PHY102 Lecture Note 2023 - 2024 Session - 085214 - 102031Document7 pagesPHY102 Lecture Note 2023 - 2024 Session - 085214 - 102031Muhammad AbdulazizNo ratings yet
- Assessment in Unit 5Document2 pagesAssessment in Unit 5JunePhil PagadNo ratings yet
- Ion EnergiesDocument39 pagesIon Energiesabashir7852No ratings yet
- Fundamental ForcesDocument3 pagesFundamental ForcesTooba ZahidNo ratings yet
- Jeffrey Pederson - Electric and Magnetic Forces NotesDocument24 pagesJeffrey Pederson - Electric and Magnetic Forces Notesd34dm4nNo ratings yet
- Particle PhysicsDocument101 pagesParticle PhysicsAravindhNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFsam 20 Nuclear-PhysicsDocument2 pages1 PDFsam 20 Nuclear-PhysicsnNo ratings yet
- NucPhys Lect4B2020-1 240305 100151Document16 pagesNucPhys Lect4B2020-1 240305 100151Fara AuliaNo ratings yet
- Type of Forces 1 Notes 2010Document26 pagesType of Forces 1 Notes 2010Mohd Iruan JanalNo ratings yet
- Certain Elements Radiate Particles and Turn Into Other ElementsDocument142 pagesCertain Elements Radiate Particles and Turn Into Other ElementsBoyeth RulidaNo ratings yet
- PPT-Course 1-2-Charge Force Field Gaus PotentialDocument63 pagesPPT-Course 1-2-Charge Force Field Gaus PotentialRaul AtofaneiNo ratings yet
- NucleiDocument1 pageNucleinanditha lejeeshNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ModelDocument11 pagesNuclear Modelzeamayf.biasNo ratings yet
- GP2 Q3W1Document24 pagesGP2 Q3W1DonggadongNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Elctricity & MagnetismDocument33 pagesFundamentals of Elctricity & MagnetismMustafa SHAHZADNo ratings yet
- CP CS24 NuclearPhysicsDocument1 pageCP CS24 NuclearPhysicsSiti Ipah LatipahNo ratings yet
- The Four Fundamental ForcesDocument2 pagesThe Four Fundamental ForcesMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Nuclear ForcesDocument12 pagesChapter 5 Nuclear ForcesKy KetsukiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 21Document10 pagesExperiment 21William RamirezNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Particles, Fundamental Questions: Dean and Professor, Lyman Briggs CollegeDocument25 pagesFundamental Particles, Fundamental Questions: Dean and Professor, Lyman Briggs CollegeAhilya GuptaNo ratings yet
- 5DP Ionisation EnergiesDocument17 pages5DP Ionisation EnergiesVaida MatulevičiūtėNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Forces of NatureDocument1 pageFundamental Forces of NatureBabai GhoshNo ratings yet
- Non Contact ForcesDocument1 pageNon Contact ForcesMareeswari BalasubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Nuclei in One Shot - Class Notes - LEC-6 - PPT-6 - Physics - Nuclei - Vijeta Series - Kshitiz Kanik Sir - RAM NIWASDocument61 pagesNuclei in One Shot - Class Notes - LEC-6 - PPT-6 - Physics - Nuclei - Vijeta Series - Kshitiz Kanik Sir - RAM NIWASprajwal jhaNo ratings yet
- Non Contact ForcesDocument4 pagesNon Contact ForcesMehnaz KhanumNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ForceDocument1 pageNuclear Forceutkarshpathak321No ratings yet
- 2024 - H2 - Forces Notes (Stu)Document28 pages2024 - H2 - Forces Notes (Stu)NieL TianNo ratings yet
- Modern and Nuclear Physics - 2019Document41 pagesModern and Nuclear Physics - 2019Ekwama EwugaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Explanations For TrendsDocument2 pagesDetailed Explanations For TrendsBRITNEY ALEXANDRA VERMINSHUNo ratings yet
- NOTES For 2nd LessonDocument3 pagesNOTES For 2nd LessonYousef ElwakilNo ratings yet
- Lindor Cuffie - Forces HandoutDocument2 pagesLindor Cuffie - Forces HandoutLindor CuffieNo ratings yet
- Models and DecayDocument26 pagesModels and DecaySurjit MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Energy Dependence of Cross SectionsDocument23 pagesEnergy Dependence of Cross SectionsSparsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- PRELIMS - RDT 104 (Technical Factors in Radiology)Document4 pagesPRELIMS - RDT 104 (Technical Factors in Radiology)LoLiTraP KaiNo ratings yet
- NEO JEE 11 P1 PHY H Electric Charges and Fields 09 211Document95 pagesNEO JEE 11 P1 PHY H Electric Charges and Fields 09 211annNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument17 pagesNuclear PhysicsRichard ShinNo ratings yet
- Leptons and Quarks and BosonsDocument6 pagesLeptons and Quarks and BosonsSubhash DhoundiyalNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Some Natural PhenomenaDocument17 pagesClass 8 Some Natural PhenomenaChirag ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ap Chem Unit 1 Review PacketDocument10 pagesAp Chem Unit 1 Review Packetapi-77411869No ratings yet
- Fundamental ForcesDocument14 pagesFundamental ForcesAjay RNo ratings yet
- Resonance Class 9 Ijso Study MaterialDocument127 pagesResonance Class 9 Ijso Study MaterialSarvesh Kumar RaiNo ratings yet
- ForcesessayDocument3 pagesForcesessayapi-331780332No ratings yet
- General Physics IIDocument26 pagesGeneral Physics IIJohn Rudolf CatalanNo ratings yet
- Bonding Forces and EnergiesDocument3 pagesBonding Forces and EnergiesJaden BrownNo ratings yet
- M. Jones, JR.: Organic Chemistry Must Be Read With A Pencil in Your Hand 'Document109 pagesM. Jones, JR.: Organic Chemistry Must Be Read With A Pencil in Your Hand '張湧浩No ratings yet
- 7.3 Forces and Exchange ParticlesDocument1 page7.3 Forces and Exchange ParticlesVyom agarwalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nanoscience - TheoryDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Nanoscience - TheoryAlex QuingaNo ratings yet
- Dec 17 V Sem BSC Hons StatsDocument7 pagesDec 17 V Sem BSC Hons StatsAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- CALCULATED MINIMUM LIQUID FLOWRATES A New Method For Rich-Phase Absorption ColumnsDocument11 pagesCALCULATED MINIMUM LIQUID FLOWRATES A New Method For Rich-Phase Absorption ColumnsharrazyNo ratings yet
- 133 AcylationDocument4 pages133 AcylationAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument334 pagesOrganic ChemistryCristiano Hamdiansyah Sempadian100% (17)
- Bilastine SynthesisDocument3 pagesBilastine SynthesisAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (191: Brunke Et A1. (11) Patent Number: (45) Date of PatentDocument13 pagesUnited States Patent (191: Brunke Et A1. (11) Patent Number: (45) Date of PatentAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes and Questions For The P Block Elements Part DDocument23 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes and Questions For The P Block Elements Part DAnonymous vRpzQ2BL100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry 1Document324 pagesOrganic Chemistry 1Anonymous vRpzQ2BL100% (1)
- Kinetics Mastery AnswersDocument5 pagesKinetics Mastery AnswersAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- C C, C N, C O CouplingDocument67 pagesC C, C N, C O CouplingAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- Reduction-R.o. C. NormanDocument25 pagesReduction-R.o. C. NormanAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- Module2 Reduction PDFDocument55 pagesModule2 Reduction PDFAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- 321L Experimental Section For Lab WriteUPsDocument2 pages321L Experimental Section For Lab WriteUPsAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering-Fluid Mechanics Important MCQDocument32 pagesMechanical Engineering-Fluid Mechanics Important MCQHarshal bansodeNo ratings yet
- Structural Panels in Shear Through-the-Thickness: Standard Test Methods ForDocument10 pagesStructural Panels in Shear Through-the-Thickness: Standard Test Methods ForAnvit GadkarNo ratings yet
- AD 263 - Limitations of Bolt Grades To BS 5950-1 and Eurocode 3Document1 pageAD 263 - Limitations of Bolt Grades To BS 5950-1 and Eurocode 3symon ellimacNo ratings yet
- Crack Propagation in A Stiffener To DeckDocument8 pagesCrack Propagation in A Stiffener To DeckSelim TurkyilmazNo ratings yet
- HEAT CONDUCTION IN A STEAM PIPE Introductory Transport Phenomena-Wiley (2014) - R. Byron Bird Et AlDocument5 pagesHEAT CONDUCTION IN A STEAM PIPE Introductory Transport Phenomena-Wiley (2014) - R. Byron Bird Et AlGael MendozaNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Flexible Multibody Dynamics ConDocument16 pages1 Introduction To Flexible Multibody Dynamics ConMoezNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For First Year First Sem Question Bank For Physics-I Regulation 20913Document21 pagesQuestion Bank For First Year First Sem Question Bank For Physics-I Regulation 20913PRIYA RAJINo ratings yet
- P1.2 Student Practical: Investigating PendulumsDocument6 pagesP1.2 Student Practical: Investigating PendulumsAlenNo ratings yet
- 9A01301 Mechanics of SolidsDocument4 pages9A01301 Mechanics of SolidssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 2010 Physiscs SolutionsDocument21 pages2010 Physiscs Solutionsjoebloggs_com100% (1)
- Concrete CalculationDocument10 pagesConcrete CalculationKaye Ibañez CastilloNo ratings yet
- AAS Perkin AlmerDocument52 pagesAAS Perkin AlmerghincuNo ratings yet
- TMP 439Document3 pagesTMP 439FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Experiment On Heat Transfer Through Fins Having Different NotchesDocument4 pagesExperiment On Heat Transfer Through Fins Having Different NotcheskrantiNo ratings yet
- Creative Mechanism DesignDocument56 pagesCreative Mechanism DesignDibakar SenNo ratings yet
- Ride IndexDocument15 pagesRide IndexPavan GopNo ratings yet
- Baumann Primordial CosmologyDocument77 pagesBaumann Primordial CosmologyLillyOpenMindNo ratings yet
- Failure of Laminated CompositesDocument10 pagesFailure of Laminated CompositesDavid AcostaNo ratings yet
- Study On Heating Process of Ultrasonic Welding For ThermoplasticsDocument18 pagesStudy On Heating Process of Ultrasonic Welding For ThermoplasticsAndrea FrigeniNo ratings yet
- Optimum Redesign of Axial Fan Blade AttachmentDocument15 pagesOptimum Redesign of Axial Fan Blade AttachmentNarayanaNo ratings yet
- Take Home Sept 30 PDFDocument1 pageTake Home Sept 30 PDFHarvey James100% (1)
- Science-9 q4 Week-4 19Document19 pagesScience-9 q4 Week-4 19Dainielle Marie Pascual100% (2)
- Physics PracticalDocument7 pagesPhysics PracticalankurNo ratings yet
- Irc SP.114.2018Document146 pagesIrc SP.114.2018Anonymous YHcvra8Xw6No ratings yet
- 6c - Chapter 8 - Structural Instability - AnnotatedDocument7 pages6c - Chapter 8 - Structural Instability - AnnotatedSalman KhalilNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - II Question Bank PDFDocument11 pagesStrength of Materials - II Question Bank PDFpavanNo ratings yet
- Numericals XIIDocument17 pagesNumericals XIISyed Tanveer100% (1)