Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Clinical Chemistry: NPNs
Clinical Chemistry: NPNs
Uploaded by
Meevie ToledoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Clinical Chemistry: NPNs
Clinical Chemistry: NPNs
Uploaded by
Meevie ToledoCopyright:
Available Formats
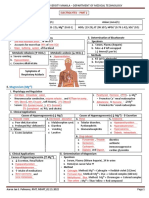
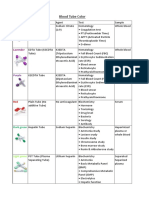
UREA CREATININE CREATINE URIC ACID
Synthesis Protein metabolism Muscle metabolism Arginine, glycine and Purine metabolism
methionine synthesis
Location of synthesis Liver Muscle Liver Liver
Molecular weight 60 Da 113 Da 168 Da
Disease correlation Azotemia Creatinine Muscle disease Uric acid
Uremia or Uremic syndrome Abnormal renal function Muscular dystrophy Gout
Poliomyelitis Increased catabolism of nucleic
Hyperthyroidism acid
Trauma Renal disease
Clinical significance Evaluate renal function Marker for Glomerulus Filtration Diagnosis of muscle Evaluate renal function
Assess hydration status Rate (GFR) disease
Determine nitrogen balance Determine...
Aid in diagnosis of renal disease the sufficiency of kidney function
Verify adequacy of dialysis the severity of kidney damage
Monitor the progression of kidney
disease
Analytic/Lab method 1. Conventional method 1. Jaffe Reaction 1. End point Jaffe method 1. Caraway method (most common)
2. Kinetic/Enzymatic method (most 2. Coupled-enzymatic method 2. Uricase method (more specific)
common)
Creatinase-CK method 3. Couple enzymatic method
3. Chemical method Creatinase-H2O2 method
Isotope dilution mass 3. Reference standard
spectrometry Isotope dilution mass
spectrometry
Specimen requirement Plasma Plasma Heparinised Plasma
Serum Serum Serum
Urine Urine Urine
Interference substances 1. Ammonium ions 1. Ascorbic acid 1. Lipemic specimen
2. Sodium citrate 2. Glucose
3. Sodium fluoride 3. Protein, urea
4. Alpha keto acids/Ketones
5. Cephalosporins, Dopamine,
Lidocaine
6. Hemoglobin & Bilirubin
7. Uric acid
You might also like
- Juju Sundin, Sarah Murdoch-Juju Sundin's Birth Skills - Proven Pain-Management Techniques For Your Labour and Birth PDFDocument287 pagesJuju Sundin, Sarah Murdoch-Juju Sundin's Birth Skills - Proven Pain-Management Techniques For Your Labour and Birth PDFCamila BastosNo ratings yet
- Kettlebell Strength Training AnatomyDocument217 pagesKettlebell Strength Training AnatomyAndreea Slavoaca100% (5)
- Drugs Behavior 7th Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesDrugs Behavior 7th Edition Ebook PDFmaryellen.vansickle498100% (57)
- Function, Structure, Operation of Engine Null (4JK1)Document36 pagesFunction, Structure, Operation of Engine Null (4JK1)jonathan100% (3)
- Nursing Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests DeMYSTiFiedFrom EverandNursing Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests DeMYSTiFiedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Method Statement For Installation of Wiring DevicesDocument6 pagesMethod Statement For Installation of Wiring DevicesMohammed Mujeeb Ali Fathaan100% (2)
- National Health Programmes in IndiaDocument33 pagesNational Health Programmes in IndiaNaveesh Vijay P K100% (3)
- RFT - Theory Notes-: (Important For Practical Also)Document13 pagesRFT - Theory Notes-: (Important For Practical Also)ammuNo ratings yet
- Blood Test Selection GuideDocument5 pagesBlood Test Selection GuideMaxOzNo ratings yet
- Nonprotein Nitrogen CompoundsDocument6 pagesNonprotein Nitrogen CompoundsSheine EspinoNo ratings yet
- เอกหทัย แซ่เตีย MS.C, CDT: Excretory functionDocument29 pagesเอกหทัย แซ่เตีย MS.C, CDT: Excretory functionPakornTongsukNo ratings yet
- Non-Protein Nitrogen Compounds1 (FINALS)Document60 pagesNon-Protein Nitrogen Compounds1 (FINALS)Marydith Ortillo100% (1)
- Clin Path Lab 6 Urinalysis Part 2Document7 pagesClin Path Lab 6 Urinalysis Part 2api-3743217100% (3)
- Main Functions of ProteinDocument3 pagesMain Functions of ProteinsweetwaffleNo ratings yet
- Physio UNI ImpDocument8 pagesPhysio UNI Impiphonekifotos2No ratings yet
- Discussion 1 NPNDocument53 pagesDiscussion 1 NPNFaith TambongNo ratings yet
- Enzymes in Clinical DiagnosisDocument2 pagesEnzymes in Clinical DiagnosisShobe ChuaNo ratings yet
- AminoacidopathiesDocument2 pagesAminoacidopathiesbarbiegahibNo ratings yet
- Ek Ah YG EIA: AlbuminDocument1 pageEk Ah YG EIA: AlbuminRebekah EquizNo ratings yet
- Liver Function: DRS' NotesDocument13 pagesLiver Function: DRS' NotesVijayabaskaran MNo ratings yet
- Liver Function: DRS' NotesDocument13 pagesLiver Function: DRS' NotesVijayabaskaran MNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes BDocument4 pagesElectrolytes BJay AnonuevoNo ratings yet
- NCM116j Reviewer Endocrine UPDATEDDocument14 pagesNCM116j Reviewer Endocrine UPDATEDAliza Abn bklNo ratings yet
- Kidney and Urine Lab ReportDocument11 pagesKidney and Urine Lab ReportYani ManuelNo ratings yet
- New Inborn Error of MetabolismDocument45 pagesNew Inborn Error of Metabolismmannan mangal100% (1)
- Amylase, Lipase, LDH, Trop I (Tabulated)Document9 pagesAmylase, Lipase, LDH, Trop I (Tabulated)maja.amora.swuNo ratings yet
- NPNDocument38 pagesNPNIvan ChuaNo ratings yet
- Non Protein NitrogenousDocument19 pagesNon Protein NitrogenousWina AdrianNo ratings yet
- Renal Function and The Significance of Non-Protein Nitrogen CompoundsDocument12 pagesRenal Function and The Significance of Non-Protein Nitrogen CompoundsSrujana BudheNo ratings yet
- Chemical Examination of Urine: LearningobjectivesDocument38 pagesChemical Examination of Urine: LearningobjectivesWho KnowsNo ratings yet
- Blood TubeDocument3 pagesBlood TubeChhåÿ Föñg IINo ratings yet
- Midterms CC2 - Tabled Pckge InsertsDocument11 pagesMidterms CC2 - Tabled Pckge InsertsrallaysaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2 B Chemical Examination of Urine (Laboratory)Document9 pagesWEEK 2 B Chemical Examination of Urine (Laboratory)Dayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Digestion of Starch by Salivary AmylaseDocument24 pagesDigestion of Starch by Salivary AmylasearunramarNo ratings yet
- Brosul Pelayanan LabDocument2 pagesBrosul Pelayanan Labmuhammad jakariaNo ratings yet
- (CC1) LEC-W12-Nonprotein Nitrogen CompoundsDocument10 pages(CC1) LEC-W12-Nonprotein Nitrogen CompoundsAira UsiNo ratings yet
- MLT All Questions CompiledDocument4 pagesMLT All Questions Compiledfellow80966No ratings yet
- Unit 7 TransDocument5 pagesUnit 7 TransGrace FernandoNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument8 pagesAmino Acids and ProteinsathenasophiaabNo ratings yet
- AUBF LAB - Exams and QuizzesDocument18 pagesAUBF LAB - Exams and QuizzesLUALHATI VILLASNo ratings yet
- Test Blueprint Compre 2024Document2 pagesTest Blueprint Compre 2024Immah PinedaNo ratings yet
- RX 25 Protein MetDocument18 pagesRX 25 Protein Metgiyan77No ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Amino AcidDocument10 pagesLesson 8 - Amino Acidchristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Welcome To TheDocument56 pagesWelcome To ThejaydocNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry - NPNDocument7 pagesClinical Chemistry - NPNCamella Beatrice Lujan ValleNo ratings yet
- Drug Receptor Types: Cut Here Cut HereDocument60 pagesDrug Receptor Types: Cut Here Cut Heredlneisha61100% (13)
- Deficiency Detected by Ureterolithiasis: Partial Adenine PhosphoribosyltransferaseDocument4 pagesDeficiency Detected by Ureterolithiasis: Partial Adenine PhosphoribosyltransferaseMarcelitaTaliaDuwiriNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry PractialDocument170 pagesBiochemistry PractialMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- UrinaryDocument3 pagesUrinaryIYA LABAO100% (1)
- Clinical Microscopy Handouts2016Document23 pagesClinical Microscopy Handouts2016Leila PasigadoNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana Hiperosmolar Hiperglicemic State (SHH)Document13 pagesTatalaksana Hiperosmolar Hiperglicemic State (SHH)Vidya VidyutNo ratings yet
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Dengan Chronic Kidney DiseasesDocument24 pagesAsuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Dengan Chronic Kidney DiseasestidaktahudiriNo ratings yet
- (Netter) Atlas of Human Anatomy. 8° (2023) - 3Document13 pages(Netter) Atlas of Human Anatomy. 8° (2023) - 3ALEXIS SEDERAPNo ratings yet
- BALAJIPPTDocument22 pagesBALAJIPPTapi-3781079No ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary LabsDocument15 pagesHepatobiliary Labslabeeb8No ratings yet
- Report 5-8 in ProviDocument5 pagesReport 5-8 in ProviWilson AgustinNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry LRR InicetDocument290 pagesBiochemistry LRR InicetSendhilNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry Lecture NPNDocument5 pagesClinical Chemistry Lecture NPNmizunoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Urine Screening For Metabolic Disorders: Phenylalanine/Tyrosine Metabolic PathwayDocument1 pageChapter 8 Urine Screening For Metabolic Disorders: Phenylalanine/Tyrosine Metabolic PathwayChynna Izzabelle Alcantara AbellanaNo ratings yet
- To Convert BUN MG/DL To Urea In, BUN Multiplied With 2.14 - To Convert BUN MG/DL To Urea In, BUN Multiplied With 0.36Document6 pagesTo Convert BUN MG/DL To Urea In, BUN Multiplied With 2.14 - To Convert BUN MG/DL To Urea In, BUN Multiplied With 0.36RALPH JAN T. RIONo ratings yet
- Presentation 05 Human Digestion 1Document19 pagesPresentation 05 Human Digestion 1darontolentinoNo ratings yet
- Inborn Error of MetabolismDocument13 pagesInborn Error of MetabolismKuzhandai VeluNo ratings yet
- Non-Protein Nitrogenous Substances: Urea CreatineDocument2 pagesNon-Protein Nitrogenous Substances: Urea CreatineLOU BLESSY CASINONo ratings yet
- Digital Notebook CompilationDocument44 pagesDigital Notebook CompilationReese Alessandra GandulfoNo ratings yet
- Coupled Bioluminescent Assays: Methods, Evaluations, and ApplicationsFrom EverandCoupled Bioluminescent Assays: Methods, Evaluations, and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Receptors in Drug MetabolismFrom EverandNuclear Receptors in Drug MetabolismWen XieNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia TableDocument2 pagesThalassemia TableMeevie ToledoNo ratings yet
- Virology: EnterovirusesDocument40 pagesVirology: EnterovirusesMeevie ToledoNo ratings yet
- Hematology: Hemoglobinopathies TableDocument3 pagesHematology: Hemoglobinopathies TableMeevie Toledo0% (1)
- Mycobacteria To Spirochetes SummaryDocument8 pagesMycobacteria To Spirochetes SummaryMeevie ToledoNo ratings yet
- Community and Public Health PortfolioDocument90 pagesCommunity and Public Health PortfolioMeevie ToledoNo ratings yet
- ME8595 SyllabusDocument1 pageME8595 SyllabusDeepak sakthiNo ratings yet
- Self-Healing DNA Nanostructures - American Chemical SocietyDocument3 pagesSelf-Healing DNA Nanostructures - American Chemical Societydanutzza90No ratings yet
- Folder Clay House DIN A4-KleinDocument20 pagesFolder Clay House DIN A4-KleinoanadraghicescuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Brain in Context of Learning: A Review From Current LiteratureDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Brain in Context of Learning: A Review From Current LiteratureKadek Dwipa DyatmikaNo ratings yet
- WEF New Frontiers of Nutrition 2023Document44 pagesWEF New Frontiers of Nutrition 2023Lorena BelloNo ratings yet
- Soal Uts Kelas 9 MtsDocument5 pagesSoal Uts Kelas 9 Mtsindah sNo ratings yet
- GA CPPU + Fruit + BlueberriesDocument6 pagesGA CPPU + Fruit + BlueberriesAnonymous qWrIJh3No ratings yet
- Wiki Quote CioranDocument31 pagesWiki Quote CioranShaymaa OsamaNo ratings yet
- Mimosa PudicaDocument4 pagesMimosa PudicaIna Guinar100% (1)
- D10T-D11T To Compare PDFDocument44 pagesD10T-D11T To Compare PDFraulipaqNo ratings yet
- Panasonic KX-TG9581 - TG9582 2lineDocument100 pagesPanasonic KX-TG9581 - TG9582 2lineelpirata666No ratings yet
- Tape Mobil JVC.Document16 pagesTape Mobil JVC.EdisonNainggolanNo ratings yet
- 5-x Exam 5-Study Guide-Urinary SystemDocument9 pages5-x Exam 5-Study Guide-Urinary SystemAllison GajadharNo ratings yet
- CV Asep Sifa Algani Terbaru-DikonversiDocument4 pagesCV Asep Sifa Algani Terbaru-DikonversiAziiz ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test Science G7Document6 pagesDiagnostic Test Science G7Atilrep Sailep Tocil100% (1)
- Introduction To Labor Economics: Chapter 2 - The Labor MarketDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Labor Economics: Chapter 2 - The Labor Marketqulb abbasNo ratings yet
- MLSHIS ASSIGNMENT - LESSON 7 LEARNING OUTCOMES ASSESSMENT and LEARNING FEEDBACK DIARYDocument2 pagesMLSHIS ASSIGNMENT - LESSON 7 LEARNING OUTCOMES ASSESSMENT and LEARNING FEEDBACK DIARYLouise Nicole GarciaNo ratings yet
- Senate Hearing, 111TH Congress - Department of Defense Appropriations For Fiscal Year 2010Document610 pagesSenate Hearing, 111TH Congress - Department of Defense Appropriations For Fiscal Year 2010Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Ra-253-Ma DB Us en PDFDocument12 pagesRa-253-Ma DB Us en PDFbadesharamkNo ratings yet
- Research Narrative EssayDocument4 pagesResearch Narrative Essayafhbctdfx100% (2)
- How To Reverse Hearing Loss and TinnitusDocument24 pagesHow To Reverse Hearing Loss and TinnitusMark Sloan100% (4)
- Crystal Field Aspects of Vibrational SpectraDocument10 pagesCrystal Field Aspects of Vibrational SpectraadammplouhNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Strontium Aluminate in Traffic Pain Pavement Markings For Rural and Unilluminated Roads PosterDocument3 pagesEvaluation of Strontium Aluminate in Traffic Pain Pavement Markings For Rural and Unilluminated Roads PosterJansen Paul Sanidad AristaNo ratings yet
- Revision of Essay 3 Sierra LDocument6 pagesRevision of Essay 3 Sierra Lapi-745010852No ratings yet