Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microbiome Poster Final
Microbiome Poster Final
Uploaded by
api-284935948Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- NRDD The Landscape For Lipid Nanoparticle Based Genomic Medicines PDFDocument4 pagesNRDD The Landscape For Lipid Nanoparticle Based Genomic Medicines PDFru ruNo ratings yet
- 2020-Review-Population Genetics in The Human MicrobiomeDocument15 pages2020-Review-Population Genetics in The Human MicrobiomeCristian Felipe Sandoval QuiñonezNo ratings yet
- 10 17129@botsci 1902Document11 pages10 17129@botsci 1902Noe Essono KolloNo ratings yet
- Microbial Fingerprinting - A Current Vogue in Microbial ForensicsDocument6 pagesMicrobial Fingerprinting - A Current Vogue in Microbial ForensicsAlifah Evi ScaniaNo ratings yet
- A Review of Bioinformatics Tools For Bio-Prospecting From Metagenomic Sequence DataDocument10 pagesA Review of Bioinformatics Tools For Bio-Prospecting From Metagenomic Sequence DataramadattaNo ratings yet
- Shotgun Metagenomics Methods GuideDocument14 pagesShotgun Metagenomics Methods GuideStefanoNo ratings yet
- BauermeisterDocument37 pagesBauermeisterenaNo ratings yet
- Draft Poster For PSBMBDocument1 pageDraft Poster For PSBMBceejhaybiochemNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microbiology and Identification of Microbial Species - EditedDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Microbiology and Identification of Microbial Species - EditedValentine CheptumNo ratings yet
- Journal of Ethnopharmacology: Contents Lists Available atDocument10 pagesJournal of Ethnopharmacology: Contents Lists Available atJoseph BossaNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Antimicrobial ResistanceDocument25 pagesInvestigation of Antimicrobial Resistancemenacerhadil9No ratings yet
- MetagenomicsDocument1 pageMetagenomicsKate Nicole BerdinNo ratings yet
- Microbiome Derived Metabolome As A PotenDocument3 pagesMicrobiome Derived Metabolome As A PotenJULIETANo ratings yet
- 4.the Commensal Microbiome Is Associated With anti-PD-1 Efficacy in Metastatic Melanoma PatientsDocument6 pages4.the Commensal Microbiome Is Associated With anti-PD-1 Efficacy in Metastatic Melanoma Patientszhe zhNo ratings yet
- Ramadan 4Document7 pagesRamadan 4aldimugniNo ratings yet
- Bioinformation: Phylogenetic Analysis of Chloroplast Matk Gene From Zingiberaceae For Plant Dna BarcodingDocument4 pagesBioinformation: Phylogenetic Analysis of Chloroplast Matk Gene From Zingiberaceae For Plant Dna BarcodingFairus ZainNo ratings yet
- Usp 1116 em For Aseptic ProcessingDocument11 pagesUsp 1116 em For Aseptic ProcessingKraken Ur100% (1)
- LeptospirosisDocument1 pageLeptospirosisQonita Prasta AgustiaNo ratings yet
- Infrared Spectroscopy in Microbiology: Dieter NaumannDocument31 pagesInfrared Spectroscopy in Microbiology: Dieter NaumannDAVID ROSAS VARANo ratings yet
- Isolation and Partial Characterization of Pigment-Like Antibiotics Produced by A New Strain of Streptosporangium Isolated From An Algerian SoilDocument10 pagesIsolation and Partial Characterization of Pigment-Like Antibiotics Produced by A New Strain of Streptosporangium Isolated From An Algerian SoilM xNo ratings yet
- Minireview: Sami Aito Eishi Keda Iroshi Zura Iwamu InamisawaDocument13 pagesMinireview: Sami Aito Eishi Keda Iroshi Zura Iwamu InamisawaBekele OljiraNo ratings yet
- Dentification of Dermatophytes by Sequence Analysis of The rRNA Gene Internal Transcribed Spacer RegionsDocument9 pagesDentification of Dermatophytes by Sequence Analysis of The rRNA Gene Internal Transcribed Spacer RegionsRobertus RonnyNo ratings yet
- Salonenetal DNAextractionJMM2010 PDFDocument8 pagesSalonenetal DNAextractionJMM2010 PDFumiNo ratings yet
- Candida AlbicansDocument9 pagesCandida Albicansa6924593No ratings yet
- Humanure PortugueseDocument23 pagesHumanure PortuguesepatmesquitaNo ratings yet
- NRG 3182Document11 pagesNRG 3182sznistvanNo ratings yet
- A Review of Methods and Databases For MetagenomicDocument15 pagesA Review of Methods and Databases For MetagenomicVictor WolleckNo ratings yet
- Jurnal BiokimiaDocument9 pagesJurnal BiokimiaSri NingsihNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S104453232300026X MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S104453232300026X MainSami FauzanNo ratings yet
- The Human Microbiome at The Interface of Health and Disease PDFDocument11 pagesThe Human Microbiome at The Interface of Health and Disease PDFabcder1234No ratings yet
- Bacterial GenomicsDocument4 pagesBacterial GenomicsTigray OutlookNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diversity & Met A GenomesDocument49 pagesMicrobial Diversity & Met A GenomesNikhil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Review: P.C. Barko, M.A. Mcmichael, K.S. Swanson, and D.A. WilliamsDocument17 pagesReview: P.C. Barko, M.A. Mcmichael, K.S. Swanson, and D.A. WilliamsAngélicaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Characterization of Cultivated and Wild Genotypes of Punica Granatum L. (Pomegranate) by Using SSR MarkerDocument9 pagesMolecular Characterization of Cultivated and Wild Genotypes of Punica Granatum L. (Pomegranate) by Using SSR MarkerSSR-IIJLS JournalNo ratings yet
- Kenyan Traditional Medicine Exploring Solutions To The Modern Antibacterial Crises Through Natural Products ChemistryDocument8 pagesKenyan Traditional Medicine Exploring Solutions To The Modern Antibacterial Crises Through Natural Products ChemistryHerald Scholarly Open AccessNo ratings yet
- Mirnas in Tuberculosis: New Avenues For Diagnosis and Host-Directed TherapyDocument14 pagesMirnas in Tuberculosis: New Avenues For Diagnosis and Host-Directed Therapypriyanka05guhaNo ratings yet
- Array of Hope: Expression Profiling Identifies Disease Biomarkers and MechanismDocument8 pagesArray of Hope: Expression Profiling Identifies Disease Biomarkers and MechanismSuri VijayNo ratings yet
- Functional Diversity of Microbial Ecologies Estimated From Ancient Human Coprolites and Dental CalculusDocument13 pagesFunctional Diversity of Microbial Ecologies Estimated From Ancient Human Coprolites and Dental CalculusVasillis MamosNo ratings yet
- JC-22 04 29Document18 pagesJC-22 04 29litianhui333No ratings yet
- Aem 02764-08Document8 pagesAem 02764-08Alex Cristian IonutNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering of Meiosis Related Genes For Crop Improvement in CerealsDocument8 pagesGenetic Engineering of Meiosis Related Genes For Crop Improvement in CerealsTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- MODELO Journal of Pharmacy and PharmacologyDocument4 pagesMODELO Journal of Pharmacy and PharmacologyjnfjjuniorNo ratings yet
- The Bright Side of Microbial Dark Matter: Lessons Learned From The Uncultivated MajorityDocument10 pagesThe Bright Side of Microbial Dark Matter: Lessons Learned From The Uncultivated MajoritySixto Gutiérrez SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Biolreprod0031 PDFDocument8 pagesBiolreprod0031 PDFStephany L JonathanNo ratings yet
- Review 1Document9 pagesReview 1Nilab FanaeNo ratings yet
- anjum-et-al-2017-molecular-methods-for-detection-of-antimicrobial-resistanceDocument17 pagesanjum-et-al-2017-molecular-methods-for-detection-of-antimicrobial-resistanceJunior MbatepNo ratings yet
- Clinical Metagenomics: Microbial GenomicsDocument15 pagesClinical Metagenomics: Microbial GenomicsebrarNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Multiplication of Eucalyptus Hybrid Via: Temporary Immersion Bioreactor: Culture Media and Cytokinin EffectsDocument8 pagesIn Vitro Multiplication of Eucalyptus Hybrid Via: Temporary Immersion Bioreactor: Culture Media and Cytokinin EffectsFenny OctavianiNo ratings yet
- Hypnosis & DNA Microarrays 2008Document7 pagesHypnosis & DNA Microarrays 2008malwinatmdNo ratings yet
- Collective Antibiotic Resistance: Mechanisms and ImplicationsDocument7 pagesCollective Antibiotic Resistance: Mechanisms and ImplicationsWilfrido Jose Barrios AgamezNo ratings yet
- A New View of The Tree of Life PDFDocument6 pagesA New View of The Tree of Life PDFBelénAlvarezVargasNo ratings yet
- 2 - Landoni - APPS - 2020Document6 pages2 - Landoni - APPS - 2020Rocío GRNo ratings yet
- Quantifying Bias Introduced by Sample Collection in Relative and Absolute Microbiome MeasurementsDocument17 pagesQuantifying Bias Introduced by Sample Collection in Relative and Absolute Microbiome MeasurementsscribdNo ratings yet
- 15310-Article Text-49579-3-10-20201231Document15 pages15310-Article Text-49579-3-10-20201231sakarobytujuh7CRNo ratings yet
- Bellis Kullman. 2000. Application of Flow Cytometry For Measurement of Nuclear DNA Content in Fungi.Document16 pagesBellis Kullman. 2000. Application of Flow Cytometry For Measurement of Nuclear DNA Content in Fungi.Bellis KullmanNo ratings yet
- High Definition For Systems Biology of Microbial Commun - 2016 - Current OpinionDocument8 pagesHigh Definition For Systems Biology of Microbial Commun - 2016 - Current OpinionLuis GómezNo ratings yet
- Genotyping of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isolates From A Low-Endemic Setting in Northwestern State of Paraná in Southern BrazilDocument7 pagesGenotyping of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isolates From A Low-Endemic Setting in Northwestern State of Paraná in Southern BrazilimneoNo ratings yet
- Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Effects of Mercury in House Fly Musca Diptera MuscidaeDocument8 pagesCytotoxic and Genotoxic Effects of Mercury in House Fly Musca Diptera MuscidaeJhon BarrosNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Protection ArticleDocument10 pagesAntibiotic Protection ArticleYogi Raja BiswaNo ratings yet
- Preliminaries: What Is Life?Document8 pagesPreliminaries: What Is Life?Fadhili DungaNo ratings yet
- Magic School BusDocument4 pagesMagic School Busapi-314049675No ratings yet
- Malignant Myopericytoma: Report of A New Case and Review of The LiteratureDocument6 pagesMalignant Myopericytoma: Report of A New Case and Review of The LiteratureRachel AutranNo ratings yet
- PDF Fundamental Approaches To Screen Abnormalities in Drosophila Monalisa Mishra Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Fundamental Approaches To Screen Abnormalities in Drosophila Monalisa Mishra Ebook Full Chapterminnie.medel445100% (2)
- Jay Tugend - Mitosis Performance TaskDocument4 pagesJay Tugend - Mitosis Performance Taskapi-673971695No ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Biomolecules PDFDocument23 pagesStructures and Functions of Biomolecules PDFMark Bryan TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Peroxisome Diversity and EvolutionDocument10 pagesPeroxisome Diversity and EvolutionPaulius SungailaNo ratings yet
- Quipper Nucleic AcidDocument38 pagesQuipper Nucleic AcidRhearose AlcariaNo ratings yet
- Almustaqbal University Collage Department Semester Exam./ 1 Attempt Sample: Subject: Human Biology Code: Max. Time: 2 H. Class: First DateDocument3 pagesAlmustaqbal University Collage Department Semester Exam./ 1 Attempt Sample: Subject: Human Biology Code: Max. Time: 2 H. Class: First DateZainab HasanNo ratings yet
- Translational Autoimmunity Volume 3 Autoimmune Disease Associated With Different Clinical Features Nima Rezaei Ebook Full ChapterDocument51 pagesTranslational Autoimmunity Volume 3 Autoimmune Disease Associated With Different Clinical Features Nima Rezaei Ebook Full Chaptertamera.stone860100% (5)
- Mass Spectrometry Based Metabolomics A Guide For Annotation, Quantification and Best ReportingDocument10 pagesMass Spectrometry Based Metabolomics A Guide For Annotation, Quantification and Best ReportingsridharNo ratings yet
- Fcimb 10 00079Document11 pagesFcimb 10 00079MateoNo ratings yet
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Ed Booksmedicos - Org (0076-0116) PDFDocument41 pagesLehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Ed Booksmedicos - Org (0076-0116) PDFNancy Flores SanchezNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Answer Key WebDocument2 pagesQuiz 1 Answer Key WebErik WellsNo ratings yet
- 202incoperation of Nitrogen Into Amino Acids PDFDocument38 pages202incoperation of Nitrogen Into Amino Acids PDFnyasha chinyangaNo ratings yet
- Lijeesh Kumar Puthiya Purayil - 1001693261Document1 pageLijeesh Kumar Puthiya Purayil - 1001693261Mithun KumarNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics For Bs BiologyDocument6 pagesThesis Topics For Bs BiologyBuyCollegePapersOnlineHuntsville100% (2)
- Sts Quiz Reviewer 1Document11 pagesSts Quiz Reviewer 1理论No ratings yet
- Butterfly Effect ThesisDocument5 pagesButterfly Effect Thesisirywesief100% (2)
- The Way Back To Biological Beekeeping Dee LusbyDocument336 pagesThe Way Back To Biological Beekeeping Dee Lusbyluis pita sierraNo ratings yet
- Ch14 3Document4 pagesCh14 3hervatt50% (2)
- 7761 - Criopreservacion de Semen de Pardo e Indio de Leon en Su Area de OrigenDocument7 pages7761 - Criopreservacion de Semen de Pardo e Indio de Leon en Su Area de OrigenCarlos lazoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Sars-Cov-2 (RDRP Gene)Document1 pageLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Sars-Cov-2 (RDRP Gene)srinathNo ratings yet
- Research Skills. Case Study. Rosalind Franklin DNADocument2 pagesResearch Skills. Case Study. Rosalind Franklin DNAChym LimeNo ratings yet
- Epigenetic ModificationsDocument1 pageEpigenetic ModificationsFerny PintoNo ratings yet
- Caenorhabditis Elegans A Pluricellular Model - 2010 - Biochimica Et BiophysicaDocument9 pagesCaenorhabditis Elegans A Pluricellular Model - 2010 - Biochimica Et BiophysicaDesmond BohamNo ratings yet
- WEEK4 ModuleLec&LabDocument13 pagesWEEK4 ModuleLec&LabMaricris GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Primer Design For PCR AssignmentDocument5 pagesPrimer Design For PCR Assignmentshalinianandhkumar100% (1)
- 6882 Agric. 2019 Paper 2 MSDocument5 pages6882 Agric. 2019 Paper 2 MSsibongisenistewartNo ratings yet
- SPSR 2021 CompressedDocument109 pagesSPSR 2021 CompressedYouTube YouTube vancedNo ratings yet
Microbiome Poster Final
Microbiome Poster Final
Uploaded by
api-284935948Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Microbiome Poster Final
Microbiome Poster Final
Uploaded by
api-284935948Copyright:
Available Formats
Insights
into the impact of geography and genetics on the pecan
microbiome
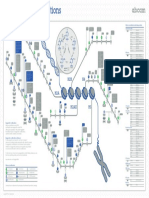
Deborah K. Ray, J. Nick Fisk, Kimberly Cervantes, Esteban Molina, Jaya R. Soneji, Jennifer J. Randall.
Department of Entomology, Plant Pathology, and Weed Science, New Mexico State University, Las Cruces, NM 88003. Email: jrandall@nmsu.edu
ABSTRACT MATERIALS & METHODS CONTINUED
Carya illinoinensis, commonly known as pecan, is native to many Microbiome Analysis
Fig.3 Relative Abundance of
Fig.3 Relative Abundance of
regions across North America and has a lifespan that can extend over Quality control, chimera filtering, clustering, and analysis of the sequencing results was Microbial Genera
Microbial Genera
100 years. This long life span and broad center of origin, along with performed with mothur v.1.39.0. For operational taxonomic unit (OTU) clustering and
cross-pollination, results in genotype-specific differences in the identification, the full SILVA bacterial database (accessed January 2017) was used as
microbiome of this native nut tree. Recent innovations in technology reference. Conservative recommendations put forth by Schloss et. al (2009) for analysis
used to assess microbiome interactions have made it possible for us to of Illumina MiSeq data (accounting for the longer 2X250 read length) were followed.
gain insight into the microbial communities associated with pecan. In a Additional statistics and visualizations were performed using the program language and
previous experiment, we explored the nature of microbial software R.
communities of pecans through culturing and sequencing the
microorganisms present in tissue culture and greenhouse propagated Diversity of Microbial Populations
trees. The diversity of our findings led us to conduct further research
Methylobacterium
on the microbiomes of micropropagated pecans. In an attempt to
Western Genotype
identify the microorganisms present in unique pecan genotypes, total
DNA was isolated and enriched using the NEB Next Microbiome
Enrichment kit. Our samples included two genotypes and two
antibiotic treatments, with a control sample for each genotype. This
enriched DNA underwent Next Generation Sequencing to elucidate
no Methylobacterium
microbial populations present. Microbiome analysis revealed diverse
communities of microorganisms in both genotypes, which were
significantly impacted by antibiotic treatments.
MATERIALS & METHODS Fig. 4 Cluster Dendrogram
Fig.4 Cluster Dendrogramof Population
of
Plant Material and Treatments
Plant material was taken from six micropropagated pecan trees (Fig.
Similarity (OTU Level=0.03)
Population Similarity (OTU Level=0.03)
Methylobacterium
Riverside Genotype
1), three each from a Western genotype from Arizona and a Riverside S6
genotype from New Mexico. One sample per genotype was used as a S5
control and received no antibiotic treatment. The remaining two S3
samples from each genotype received antibiotic treatments, one at a S2
high level and one at a low level. Tissues were ground using liquid S1
no Methylobacterium
nitrogen in a mortar and pestle. Samples were then stored in a -20C
S4
freezer to avoid degradation until further processing.
Fig.3 and
Fig.3 4 S1-S3
and are are
4 S1-S3 a Western genotype
a Western and S4-S6
genotype and are a Riverside
S4-S6 genotype.
are a Riverside
DNA extraction S1genotype.
and S4 wereS1theand
controls
S4 with
wereno antibiotic treatment.
the controls with S2noandantibiotic
S5 had low
DNA was extracted using Qiagen DNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen, levels of antibiotic
treatment. S2 andtreatment.
S5 had lowS3levels
and of
S6antibiotic
had hightreatment.
levels of antibiotic
S3 and
Germany) and stored in a -20C freezer to preserve the DNA. treatment.
S6 had high levels of antibiotic treatment.
Microbiome Enrichment kit Fig.2 The most abundant genera (threshold=0.03) per sample as a proportion of total abundance in that
The genomic DNA was utilized for microbe enrichment using a NEB sample. Other refers to the cumulative total of all other genera. S1-S3 are a Western genotype and CONCLUSIONS
Next Microbiome DNA Enrichment Kit to identify microbial S4-S6 are a Riversisde genotype. S1 and S4 were the controls with no antibiotic treatment. S2 and S5 Antibiotic treatments led to shifts in microbiome compositions
populations. The DNA was then sent for next generation sequencing had low levels of antibiotic treatment. S3 and S6 had high levels of antibiotic treatment. and an overall decrease in microbial diversity. It is unknown what
using services provided by the University of Minnesota. influence this will have in a field environment.
RESULTS Methylobacterium is a keystone feature of the microbiome of
Plant Material Microbiome sequence analysis indicated that different microbial populations were these genotypes.
present in all six samples (Fig. 2). Next, we are comparing microbiomes from pecan trees of the
The most abundant microbe identified in four out of six samples was same variety in different geographical locations as well as
Methylobacterium. In two samples, S5 and S6, Cryobacterium was most abundant different varieties in the same location.
(Fig. 2). S5 and S6 are both a Riverside genotype and both received antibiotic
treatment. REFERENCES
High antibiotic treatments resulted in a loss of alpha diversity, meaning that it Schloss, P.D., et al., Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent,
decreased the total number of microbial species present (Fig. 3). community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial
communities. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2009. 75(23):7537-41
The microbial populations in all of our Western genotype samples were similar in
control group and both low and high antibiotic treatments(Fig. 4).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The microbial populations in both antibiotic treated Riverside genotype samples were The authors would like to thank NEB for providing us with the NEB Next
Fig.1 (A) Micropropagated pecan trees. (B) Transfers of micropropagated similar, while the control sample without antibiotic treatment had a highly unique Microbiome DNA Enrichment Kit. The authors would like to thank the New
pecan trees to greenhouse under controlled environment. microbial community (Fig. 4). Mexico State University Experimental Station for their support.
You might also like
- NRDD The Landscape For Lipid Nanoparticle Based Genomic Medicines PDFDocument4 pagesNRDD The Landscape For Lipid Nanoparticle Based Genomic Medicines PDFru ruNo ratings yet
- 2020-Review-Population Genetics in The Human MicrobiomeDocument15 pages2020-Review-Population Genetics in The Human MicrobiomeCristian Felipe Sandoval QuiñonezNo ratings yet
- 10 17129@botsci 1902Document11 pages10 17129@botsci 1902Noe Essono KolloNo ratings yet
- Microbial Fingerprinting - A Current Vogue in Microbial ForensicsDocument6 pagesMicrobial Fingerprinting - A Current Vogue in Microbial ForensicsAlifah Evi ScaniaNo ratings yet
- A Review of Bioinformatics Tools For Bio-Prospecting From Metagenomic Sequence DataDocument10 pagesA Review of Bioinformatics Tools For Bio-Prospecting From Metagenomic Sequence DataramadattaNo ratings yet
- Shotgun Metagenomics Methods GuideDocument14 pagesShotgun Metagenomics Methods GuideStefanoNo ratings yet
- BauermeisterDocument37 pagesBauermeisterenaNo ratings yet
- Draft Poster For PSBMBDocument1 pageDraft Poster For PSBMBceejhaybiochemNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microbiology and Identification of Microbial Species - EditedDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Microbiology and Identification of Microbial Species - EditedValentine CheptumNo ratings yet
- Journal of Ethnopharmacology: Contents Lists Available atDocument10 pagesJournal of Ethnopharmacology: Contents Lists Available atJoseph BossaNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Antimicrobial ResistanceDocument25 pagesInvestigation of Antimicrobial Resistancemenacerhadil9No ratings yet
- MetagenomicsDocument1 pageMetagenomicsKate Nicole BerdinNo ratings yet
- Microbiome Derived Metabolome As A PotenDocument3 pagesMicrobiome Derived Metabolome As A PotenJULIETANo ratings yet
- 4.the Commensal Microbiome Is Associated With anti-PD-1 Efficacy in Metastatic Melanoma PatientsDocument6 pages4.the Commensal Microbiome Is Associated With anti-PD-1 Efficacy in Metastatic Melanoma Patientszhe zhNo ratings yet
- Ramadan 4Document7 pagesRamadan 4aldimugniNo ratings yet
- Bioinformation: Phylogenetic Analysis of Chloroplast Matk Gene From Zingiberaceae For Plant Dna BarcodingDocument4 pagesBioinformation: Phylogenetic Analysis of Chloroplast Matk Gene From Zingiberaceae For Plant Dna BarcodingFairus ZainNo ratings yet
- Usp 1116 em For Aseptic ProcessingDocument11 pagesUsp 1116 em For Aseptic ProcessingKraken Ur100% (1)
- LeptospirosisDocument1 pageLeptospirosisQonita Prasta AgustiaNo ratings yet
- Infrared Spectroscopy in Microbiology: Dieter NaumannDocument31 pagesInfrared Spectroscopy in Microbiology: Dieter NaumannDAVID ROSAS VARANo ratings yet
- Isolation and Partial Characterization of Pigment-Like Antibiotics Produced by A New Strain of Streptosporangium Isolated From An Algerian SoilDocument10 pagesIsolation and Partial Characterization of Pigment-Like Antibiotics Produced by A New Strain of Streptosporangium Isolated From An Algerian SoilM xNo ratings yet
- Minireview: Sami Aito Eishi Keda Iroshi Zura Iwamu InamisawaDocument13 pagesMinireview: Sami Aito Eishi Keda Iroshi Zura Iwamu InamisawaBekele OljiraNo ratings yet
- Dentification of Dermatophytes by Sequence Analysis of The rRNA Gene Internal Transcribed Spacer RegionsDocument9 pagesDentification of Dermatophytes by Sequence Analysis of The rRNA Gene Internal Transcribed Spacer RegionsRobertus RonnyNo ratings yet
- Salonenetal DNAextractionJMM2010 PDFDocument8 pagesSalonenetal DNAextractionJMM2010 PDFumiNo ratings yet
- Candida AlbicansDocument9 pagesCandida Albicansa6924593No ratings yet
- Humanure PortugueseDocument23 pagesHumanure PortuguesepatmesquitaNo ratings yet
- NRG 3182Document11 pagesNRG 3182sznistvanNo ratings yet
- A Review of Methods and Databases For MetagenomicDocument15 pagesA Review of Methods and Databases For MetagenomicVictor WolleckNo ratings yet
- Jurnal BiokimiaDocument9 pagesJurnal BiokimiaSri NingsihNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S104453232300026X MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S104453232300026X MainSami FauzanNo ratings yet
- The Human Microbiome at The Interface of Health and Disease PDFDocument11 pagesThe Human Microbiome at The Interface of Health and Disease PDFabcder1234No ratings yet
- Bacterial GenomicsDocument4 pagesBacterial GenomicsTigray OutlookNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diversity & Met A GenomesDocument49 pagesMicrobial Diversity & Met A GenomesNikhil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Review: P.C. Barko, M.A. Mcmichael, K.S. Swanson, and D.A. WilliamsDocument17 pagesReview: P.C. Barko, M.A. Mcmichael, K.S. Swanson, and D.A. WilliamsAngélicaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Characterization of Cultivated and Wild Genotypes of Punica Granatum L. (Pomegranate) by Using SSR MarkerDocument9 pagesMolecular Characterization of Cultivated and Wild Genotypes of Punica Granatum L. (Pomegranate) by Using SSR MarkerSSR-IIJLS JournalNo ratings yet
- Kenyan Traditional Medicine Exploring Solutions To The Modern Antibacterial Crises Through Natural Products ChemistryDocument8 pagesKenyan Traditional Medicine Exploring Solutions To The Modern Antibacterial Crises Through Natural Products ChemistryHerald Scholarly Open AccessNo ratings yet
- Mirnas in Tuberculosis: New Avenues For Diagnosis and Host-Directed TherapyDocument14 pagesMirnas in Tuberculosis: New Avenues For Diagnosis and Host-Directed Therapypriyanka05guhaNo ratings yet
- Array of Hope: Expression Profiling Identifies Disease Biomarkers and MechanismDocument8 pagesArray of Hope: Expression Profiling Identifies Disease Biomarkers and MechanismSuri VijayNo ratings yet
- Functional Diversity of Microbial Ecologies Estimated From Ancient Human Coprolites and Dental CalculusDocument13 pagesFunctional Diversity of Microbial Ecologies Estimated From Ancient Human Coprolites and Dental CalculusVasillis MamosNo ratings yet
- JC-22 04 29Document18 pagesJC-22 04 29litianhui333No ratings yet
- Aem 02764-08Document8 pagesAem 02764-08Alex Cristian IonutNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering of Meiosis Related Genes For Crop Improvement in CerealsDocument8 pagesGenetic Engineering of Meiosis Related Genes For Crop Improvement in CerealsTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- MODELO Journal of Pharmacy and PharmacologyDocument4 pagesMODELO Journal of Pharmacy and PharmacologyjnfjjuniorNo ratings yet
- The Bright Side of Microbial Dark Matter: Lessons Learned From The Uncultivated MajorityDocument10 pagesThe Bright Side of Microbial Dark Matter: Lessons Learned From The Uncultivated MajoritySixto Gutiérrez SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Biolreprod0031 PDFDocument8 pagesBiolreprod0031 PDFStephany L JonathanNo ratings yet
- Review 1Document9 pagesReview 1Nilab FanaeNo ratings yet
- anjum-et-al-2017-molecular-methods-for-detection-of-antimicrobial-resistanceDocument17 pagesanjum-et-al-2017-molecular-methods-for-detection-of-antimicrobial-resistanceJunior MbatepNo ratings yet
- Clinical Metagenomics: Microbial GenomicsDocument15 pagesClinical Metagenomics: Microbial GenomicsebrarNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Multiplication of Eucalyptus Hybrid Via: Temporary Immersion Bioreactor: Culture Media and Cytokinin EffectsDocument8 pagesIn Vitro Multiplication of Eucalyptus Hybrid Via: Temporary Immersion Bioreactor: Culture Media and Cytokinin EffectsFenny OctavianiNo ratings yet
- Hypnosis & DNA Microarrays 2008Document7 pagesHypnosis & DNA Microarrays 2008malwinatmdNo ratings yet
- Collective Antibiotic Resistance: Mechanisms and ImplicationsDocument7 pagesCollective Antibiotic Resistance: Mechanisms and ImplicationsWilfrido Jose Barrios AgamezNo ratings yet
- A New View of The Tree of Life PDFDocument6 pagesA New View of The Tree of Life PDFBelénAlvarezVargasNo ratings yet
- 2 - Landoni - APPS - 2020Document6 pages2 - Landoni - APPS - 2020Rocío GRNo ratings yet
- Quantifying Bias Introduced by Sample Collection in Relative and Absolute Microbiome MeasurementsDocument17 pagesQuantifying Bias Introduced by Sample Collection in Relative and Absolute Microbiome MeasurementsscribdNo ratings yet
- 15310-Article Text-49579-3-10-20201231Document15 pages15310-Article Text-49579-3-10-20201231sakarobytujuh7CRNo ratings yet
- Bellis Kullman. 2000. Application of Flow Cytometry For Measurement of Nuclear DNA Content in Fungi.Document16 pagesBellis Kullman. 2000. Application of Flow Cytometry For Measurement of Nuclear DNA Content in Fungi.Bellis KullmanNo ratings yet
- High Definition For Systems Biology of Microbial Commun - 2016 - Current OpinionDocument8 pagesHigh Definition For Systems Biology of Microbial Commun - 2016 - Current OpinionLuis GómezNo ratings yet
- Genotyping of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isolates From A Low-Endemic Setting in Northwestern State of Paraná in Southern BrazilDocument7 pagesGenotyping of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isolates From A Low-Endemic Setting in Northwestern State of Paraná in Southern BrazilimneoNo ratings yet
- Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Effects of Mercury in House Fly Musca Diptera MuscidaeDocument8 pagesCytotoxic and Genotoxic Effects of Mercury in House Fly Musca Diptera MuscidaeJhon BarrosNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Protection ArticleDocument10 pagesAntibiotic Protection ArticleYogi Raja BiswaNo ratings yet
- Preliminaries: What Is Life?Document8 pagesPreliminaries: What Is Life?Fadhili DungaNo ratings yet
- Magic School BusDocument4 pagesMagic School Busapi-314049675No ratings yet
- Malignant Myopericytoma: Report of A New Case and Review of The LiteratureDocument6 pagesMalignant Myopericytoma: Report of A New Case and Review of The LiteratureRachel AutranNo ratings yet
- PDF Fundamental Approaches To Screen Abnormalities in Drosophila Monalisa Mishra Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Fundamental Approaches To Screen Abnormalities in Drosophila Monalisa Mishra Ebook Full Chapterminnie.medel445100% (2)
- Jay Tugend - Mitosis Performance TaskDocument4 pagesJay Tugend - Mitosis Performance Taskapi-673971695No ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Biomolecules PDFDocument23 pagesStructures and Functions of Biomolecules PDFMark Bryan TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Peroxisome Diversity and EvolutionDocument10 pagesPeroxisome Diversity and EvolutionPaulius SungailaNo ratings yet
- Quipper Nucleic AcidDocument38 pagesQuipper Nucleic AcidRhearose AlcariaNo ratings yet
- Almustaqbal University Collage Department Semester Exam./ 1 Attempt Sample: Subject: Human Biology Code: Max. Time: 2 H. Class: First DateDocument3 pagesAlmustaqbal University Collage Department Semester Exam./ 1 Attempt Sample: Subject: Human Biology Code: Max. Time: 2 H. Class: First DateZainab HasanNo ratings yet
- Translational Autoimmunity Volume 3 Autoimmune Disease Associated With Different Clinical Features Nima Rezaei Ebook Full ChapterDocument51 pagesTranslational Autoimmunity Volume 3 Autoimmune Disease Associated With Different Clinical Features Nima Rezaei Ebook Full Chaptertamera.stone860100% (5)
- Mass Spectrometry Based Metabolomics A Guide For Annotation, Quantification and Best ReportingDocument10 pagesMass Spectrometry Based Metabolomics A Guide For Annotation, Quantification and Best ReportingsridharNo ratings yet
- Fcimb 10 00079Document11 pagesFcimb 10 00079MateoNo ratings yet
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Ed Booksmedicos - Org (0076-0116) PDFDocument41 pagesLehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Ed Booksmedicos - Org (0076-0116) PDFNancy Flores SanchezNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Answer Key WebDocument2 pagesQuiz 1 Answer Key WebErik WellsNo ratings yet
- 202incoperation of Nitrogen Into Amino Acids PDFDocument38 pages202incoperation of Nitrogen Into Amino Acids PDFnyasha chinyangaNo ratings yet
- Lijeesh Kumar Puthiya Purayil - 1001693261Document1 pageLijeesh Kumar Puthiya Purayil - 1001693261Mithun KumarNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics For Bs BiologyDocument6 pagesThesis Topics For Bs BiologyBuyCollegePapersOnlineHuntsville100% (2)
- Sts Quiz Reviewer 1Document11 pagesSts Quiz Reviewer 1理论No ratings yet
- Butterfly Effect ThesisDocument5 pagesButterfly Effect Thesisirywesief100% (2)
- The Way Back To Biological Beekeeping Dee LusbyDocument336 pagesThe Way Back To Biological Beekeeping Dee Lusbyluis pita sierraNo ratings yet
- Ch14 3Document4 pagesCh14 3hervatt50% (2)
- 7761 - Criopreservacion de Semen de Pardo e Indio de Leon en Su Area de OrigenDocument7 pages7761 - Criopreservacion de Semen de Pardo e Indio de Leon en Su Area de OrigenCarlos lazoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Sars-Cov-2 (RDRP Gene)Document1 pageLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Sars-Cov-2 (RDRP Gene)srinathNo ratings yet
- Research Skills. Case Study. Rosalind Franklin DNADocument2 pagesResearch Skills. Case Study. Rosalind Franklin DNAChym LimeNo ratings yet
- Epigenetic ModificationsDocument1 pageEpigenetic ModificationsFerny PintoNo ratings yet
- Caenorhabditis Elegans A Pluricellular Model - 2010 - Biochimica Et BiophysicaDocument9 pagesCaenorhabditis Elegans A Pluricellular Model - 2010 - Biochimica Et BiophysicaDesmond BohamNo ratings yet
- WEEK4 ModuleLec&LabDocument13 pagesWEEK4 ModuleLec&LabMaricris GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Primer Design For PCR AssignmentDocument5 pagesPrimer Design For PCR Assignmentshalinianandhkumar100% (1)
- 6882 Agric. 2019 Paper 2 MSDocument5 pages6882 Agric. 2019 Paper 2 MSsibongisenistewartNo ratings yet
- SPSR 2021 CompressedDocument109 pagesSPSR 2021 CompressedYouTube YouTube vancedNo ratings yet