Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 viewsVolume 1
Volume 1
Uploaded by
roxybiscante1. The patient is experiencing acute gastroenteritis, which is an inflammation of the stomach and intestines that causes diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal cramping, and dehydration.
2. The nursing diagnosis is deficient fluid volume related to excessive losses through normal routes due to frequent watery stool.
3. The plan is to monitor the patient's fluid intake and output, maintain adequate hydration through oral and IV fluids, and evaluate if the patient can maintain fluid volume and skin turgor after several days of nursing interventions.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan Diarrhea Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan Diarrhea Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationKrah100% (1)
- Risk NCP - PESCADERO 4CDocument1 pageRisk NCP - PESCADERO 4COrlando VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume (AGEDocument2 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (AGENursesLabs.com83% (6)
- Prado NCPDocument4 pagesPrado NCPalleah pradoNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea (AGE)Document2 pagesDiarrhea (AGE)NursesLabs.com100% (1)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX StoDocument2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX StoBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Short TermDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Short TermLorie May GuillangNo ratings yet
- JVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesJVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitvicenteturasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationpamelaideaNo ratings yet
- Ate Gabs Nyo Pagod NaDocument3 pagesAte Gabs Nyo Pagod NaGabrielle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Salva, R.D NCP & Drug Study (Isph - Gs Pediaward)Document7 pagesSalva, R.D NCP & Drug Study (Isph - Gs Pediaward)Rae Dominick Aquino SalvaNo ratings yet
- NCP Nausea and VomitingDocument4 pagesNCP Nausea and VomitingKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis NCPDocument6 pagesGastroenteritis NCPKaguraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Denise GabatoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: IndependentDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: IndependentgeorgiaNo ratings yet
- NCP 3rd ROTATIONDocument17 pagesNCP 3rd ROTATIONMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- IndependentDocument2 pagesIndependentR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Sto: DX StoDocument2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Sto: DX StoBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX Sto: (Goal Met)Document2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX Sto: (Goal Met)Basema HashhashNo ratings yet
- GASTRITISDocument11 pagesGASTRITIStamannaNo ratings yet
- Final Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesFinal Nursing Care PlanKatherine BellezaNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentOPssslNo ratings yet
- NCP-Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP-Fluid Volume Deficitanon_207994234100% (1)
- ROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPDocument6 pagesROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPkimberly quitonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- KUSAIN - NCP IN NCM 112 RLE ConstipationDocument2 pagesKUSAIN - NCP IN NCM 112 RLE Constipationjay kusainNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument31 pagesNursing Care PlansCyril Jane Caanyagan AcutNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Nausea and VomitDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Nausea and VomitJakeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 2Joanna Marie PacanoNo ratings yet
- NCP Case Analysis GastritisDocument7 pagesNCP Case Analysis GastritisSteffi GolezNo ratings yet
- CS5 (AGE) Acute Gastroenteritis NCPDocument2 pagesCS5 (AGE) Acute Gastroenteritis NCPAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Colle Ofn: Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesColle Ofn: Nursing Care PlanDara Sophia EncarguezNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNursing DiagnosisChe SalveronNo ratings yet
- MS Soapie #1Document2 pagesMS Soapie #1Fatima KateNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Histolytica, ADocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Histolytica, AkristennemarieNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Diarrhea & VomitingDocument4 pagesFluid Volume Deficit R/T Diarrhea & Vomitingjisoo100% (3)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plankeishaaa29100% (6)
- NCP High Risk PregnancyDocument7 pagesNCP High Risk PregnancyRica ParcasioNo ratings yet
- Duty RequirementsDocument13 pagesDuty RequirementsRey Jean GarciaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 1Document3 pagesModule 2 1Lacangan, Thea YvonneNo ratings yet
- Group-5 NCM-107 NCPDocument4 pagesGroup-5 NCM-107 NCPbulok netflakes100% (1)
- Cholera N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesCholera N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Document2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Jesse James Advincula Edjec100% (15)
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPjsksNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationKobe ManuelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Diagnosis Justification: Sodium-132 Mmol/l (Low)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Diagnosis Justification: Sodium-132 Mmol/l (Low)rei_alina75% (4)
- Name: Grace AGE: 28 Gender: Female Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GeneralDocument2 pagesName: Grace AGE: 28 Gender: Female Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GeneralRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Taberna Catherine T - ACUTE GOUTDocument17 pagesTaberna Catherine T - ACUTE GOUTaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosi S Analysis GOAL and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosi S Analysis GOAL and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMark Allison BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis and Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis and Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjay kusainNo ratings yet
- NCP MeningitisDocument2 pagesNCP MeningitisARISNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Subjective: Objective: General Objective: Independent IndependentDocument10 pagesCase Study: Subjective: Objective: General Objective: Independent IndependentChristine EmanNo ratings yet
- NCP - AgeDocument5 pagesNCP - Ageunsp3akabl386% (7)
- Intestinal Ills: Chronic Constipation, Indigestion, Autogenetic Poisons, Diarrhea, Piles, Etc. Also Auto-Infection, Auto-Intoxication, Anemia, Emaciation, Etc. Due to Proctitis and ColitisFrom EverandIntestinal Ills: Chronic Constipation, Indigestion, Autogenetic Poisons, Diarrhea, Piles, Etc. Also Auto-Infection, Auto-Intoxication, Anemia, Emaciation, Etc. Due to Proctitis and ColitisNo ratings yet
- Freedom from Constipation: Natural Remedies for Digestive HealthFrom EverandFreedom from Constipation: Natural Remedies for Digestive HealthNo ratings yet
- Rules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesFrom EverandRules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Short Bowel Syndrome, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Short Bowel Syndrome, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- CPG of PhilhealthDocument31 pagesCPG of PhilhealthMV Davao ToursNo ratings yet
- The Gastrointestinal RADocument3 pagesThe Gastrointestinal RAAisha SaherNo ratings yet
- Phases of Recovery From A Restrictive Eating DisorderDocument7 pagesPhases of Recovery From A Restrictive Eating DisorderAdriana Rangel DueñasNo ratings yet
- Emma ProjectDocument15 pagesEmma ProjectPrecious AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Ritumalta Answers ImciDocument3 pagesRitumalta Answers ImciJess RitumaltaNo ratings yet
- CHN ImciDocument18 pagesCHN Imcij UNo ratings yet
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesAcute Gastroenteritisrobert tucayNo ratings yet
- Duties and Responsibilities of A Midwife in RhuDocument6 pagesDuties and Responsibilities of A Midwife in RhuAlma Potente100% (1)
- tiến trình bài giảng Unit 6 fighting choleraDocument23 pagestiến trình bài giảng Unit 6 fighting cholerayennhi228anneNo ratings yet
- Online Activity 2 BonaguaDocument9 pagesOnline Activity 2 BonaguaJian BonaguaNo ratings yet
- Capstone PharmDocument5 pagesCapstone Pharmmaria60% (5)
- Use of Whey in Controlling Calf DiarrhoeaDocument27 pagesUse of Whey in Controlling Calf DiarrhoeanaturalamirNo ratings yet
- HEALTH-TEACHING-PLAN sUGATON EVALDocument9 pagesHEALTH-TEACHING-PLAN sUGATON EVALPrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument17 pagesDiarrheaAchyut KanungoNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh 2019 MICS Report - EnglishDocument564 pagesBangladesh 2019 MICS Report - EnglishAarajita ParinNo ratings yet
- Bacterial InfectionsDocument416 pagesBacterial Infectionsnihan tanerNo ratings yet
- Copar DocumentationDocument58 pagesCopar DocumentationJessa BorreNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Guide For IMNCI Training of Students-441Document121 pagesTeacher's Guide For IMNCI Training of Students-441National Child Health Resource Centre (NCHRC)No ratings yet
- Group 6 Case Study Pancreatic CancerDocument20 pagesGroup 6 Case Study Pancreatic CancerMarcel TabucolNo ratings yet
- Acute Viral Gastroenteritis in Children in Resource-Rich Countries - Clinical Features and DiagnosisDocument19 pagesAcute Viral Gastroenteritis in Children in Resource-Rich Countries - Clinical Features and DiagnosisNuno AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- E. Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesE. Nursing DiagnosisAle SandraNo ratings yet
- Psidium GuajavaDocument14 pagesPsidium GuajavaAmalia RasyidNo ratings yet
- Amebiasis NCPDocument3 pagesAmebiasis NCPSarah Benjamin0% (1)
- Centre For Community Medicine, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, INDIADocument25 pagesCentre For Community Medicine, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, INDIAKayle PinlacNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Safety, Security and SanitationDocument9 pagesRisk Management Safety, Security and SanitationMaui VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Study: Observational Travelers' DiarrheaDocument5 pagesStudy: Observational Travelers' DiarrheaFathah MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea FlipchartDocument27 pagesDiarrhea FlipchartEliana SochaNo ratings yet
- Mebeverine HydrochloridesDocument4 pagesMebeverine HydrochloridesMpok NoriNo ratings yet
- Diarrhoea in Sheep and GoatsDocument7 pagesDiarrhoea in Sheep and GoatsobertNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Postpartum Stage Mercado Sibal IIIDocument13 pagesModule 8 Postpartum Stage Mercado Sibal IIIFrancisco Sibal IIINo ratings yet
Volume 1
Volume 1
Uploaded by
roxybiscante0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views2 pages1. The patient is experiencing acute gastroenteritis, which is an inflammation of the stomach and intestines that causes diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal cramping, and dehydration.
2. The nursing diagnosis is deficient fluid volume related to excessive losses through normal routes due to frequent watery stool.
3. The plan is to monitor the patient's fluid intake and output, maintain adequate hydration through oral and IV fluids, and evaluate if the patient can maintain fluid volume and skin turgor after several days of nursing interventions.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The patient is experiencing acute gastroenteritis, which is an inflammation of the stomach and intestines that causes diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal cramping, and dehydration.
2. The nursing diagnosis is deficient fluid volume related to excessive losses through normal routes due to frequent watery stool.
3. The plan is to monitor the patient's fluid intake and output, maintain adequate hydration through oral and IV fluids, and evaluate if the patient can maintain fluid volume and skin turgor after several days of nursing interventions.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views2 pagesVolume 1
Volume 1
Uploaded by
roxybiscante1. The patient is experiencing acute gastroenteritis, which is an inflammation of the stomach and intestines that causes diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal cramping, and dehydration.
2. The nursing diagnosis is deficient fluid volume related to excessive losses through normal routes due to frequent watery stool.
3. The plan is to monitor the patient's fluid intake and output, maintain adequate hydration through oral and IV fluids, and evaluate if the patient can maintain fluid volume and skin turgor after several days of nursing interventions.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
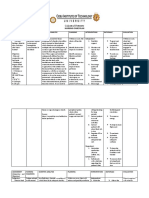
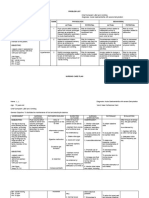
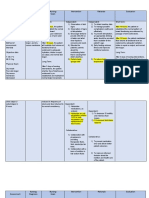
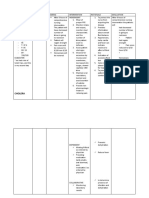
Medical Diagnosis: Acute Gastroenteritis (Adult)
Problem: Deficient Fluid Volume RT Excessive Losses Through Normal Routes
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Explanation
Subjective: (none) Deficient fluid Acute gastroenteritis Short term: 1. Establish rapport 1. To gain patients Short term:
volume RT excessive is an inflammation of After 4 hours of trust
Objective: losses through the stomach and nursing 2. Monitor and After 4 hours of
The patient normal routes AEB intestinal tract that interventions, the record VS 2. To obtain base line nursing interventions,
manifested: frequent passage of primarily affects the patient will report data the patient shall have
passage of loose loose watery stool small bowel. The understanding of 3.Assess patient’s reported
watery stool universal causative factors for condition 3.To be aware of the understanding of
vomiting manifestation of fluid volume deficit patient’s condition causative factors for
abdominal gastroenteritis is Long Term: and feeling fluid volume deficit
cramping diarrhea which After 3 days of
dehydration occurs in varying Nursing 4. Monitor Input & 4. to ensure accurate
nausea intensity, depending Interventions, the Output balance picture of fluid status
fatigue on the organism patient will maintain Long term:
weakness involved and the fluid volume at After 3 days of
health status of the functional level AEB 5. To prevent Nursing
The patient may client. Diarrhea is well hydrated, intake 5. Maintain adequate dehydration & Interventions, the
manifest: defined as an is equal as output, hydration, increase maintain hydration patient shall have
nervousness increase in the and normal skin fluid intake. status. maintained fluid
confusion frequency, volume turgor. 6. To prevent from volume at functional
weight loss and fluid content of 6. Provide frequent dryness level AEB well
decreased skin stool. Rapid oral care hydrated, intake is
turgor propulsion of equal as output, and
decreased urine intestinal contents 7. To deliver fluids normal skin turgor.
output through the small 7. Administer accurately and at
dry mucous bowels may lead to a Intravenous fluids as desired rates.
membrane serious fluid volume prescribed 8. Very young and
fever deficit. [ CITATION extremely elderly
Joy08 \l 1033 ] 8. Determine effects individuals are
of age. quickly affected by
fluid volume deficit
9. Restrict solid food 9. To allow for bowel
intake, as indicated rest and to reduced
This NCP was made with love by NursesLabs.com
(ignore the Monkey)
intestinal workload.
10. Discuss individual 10. To prevent or
risk factors/ potential limit occurrence of
problems and specific fluid deficit.
interventions
This NCP was made with love by NursesLabs.com
(ignore the Monkey)
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan Diarrhea Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan Diarrhea Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationKrah100% (1)
- Risk NCP - PESCADERO 4CDocument1 pageRisk NCP - PESCADERO 4COrlando VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume (AGEDocument2 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (AGENursesLabs.com83% (6)
- Prado NCPDocument4 pagesPrado NCPalleah pradoNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea (AGE)Document2 pagesDiarrhea (AGE)NursesLabs.com100% (1)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX StoDocument2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX StoBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Short TermDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Short TermLorie May GuillangNo ratings yet
- JVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesJVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitvicenteturasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationpamelaideaNo ratings yet
- Ate Gabs Nyo Pagod NaDocument3 pagesAte Gabs Nyo Pagod NaGabrielle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Salva, R.D NCP & Drug Study (Isph - Gs Pediaward)Document7 pagesSalva, R.D NCP & Drug Study (Isph - Gs Pediaward)Rae Dominick Aquino SalvaNo ratings yet
- NCP Nausea and VomitingDocument4 pagesNCP Nausea and VomitingKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis NCPDocument6 pagesGastroenteritis NCPKaguraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Denise GabatoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: IndependentDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: IndependentgeorgiaNo ratings yet
- NCP 3rd ROTATIONDocument17 pagesNCP 3rd ROTATIONMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- IndependentDocument2 pagesIndependentR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Sto: DX StoDocument2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Sto: DX StoBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX Sto: (Goal Met)Document2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX Sto: (Goal Met)Basema HashhashNo ratings yet
- GASTRITISDocument11 pagesGASTRITIStamannaNo ratings yet
- Final Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesFinal Nursing Care PlanKatherine BellezaNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentOPssslNo ratings yet
- NCP-Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP-Fluid Volume Deficitanon_207994234100% (1)
- ROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPDocument6 pagesROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPkimberly quitonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- KUSAIN - NCP IN NCM 112 RLE ConstipationDocument2 pagesKUSAIN - NCP IN NCM 112 RLE Constipationjay kusainNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument31 pagesNursing Care PlansCyril Jane Caanyagan AcutNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Nausea and VomitDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Nausea and VomitJakeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 2Joanna Marie PacanoNo ratings yet
- NCP Case Analysis GastritisDocument7 pagesNCP Case Analysis GastritisSteffi GolezNo ratings yet
- CS5 (AGE) Acute Gastroenteritis NCPDocument2 pagesCS5 (AGE) Acute Gastroenteritis NCPAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Colle Ofn: Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesColle Ofn: Nursing Care PlanDara Sophia EncarguezNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNursing DiagnosisChe SalveronNo ratings yet
- MS Soapie #1Document2 pagesMS Soapie #1Fatima KateNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Histolytica, ADocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Histolytica, AkristennemarieNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Diarrhea & VomitingDocument4 pagesFluid Volume Deficit R/T Diarrhea & Vomitingjisoo100% (3)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plankeishaaa29100% (6)
- NCP High Risk PregnancyDocument7 pagesNCP High Risk PregnancyRica ParcasioNo ratings yet
- Duty RequirementsDocument13 pagesDuty RequirementsRey Jean GarciaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 1Document3 pagesModule 2 1Lacangan, Thea YvonneNo ratings yet
- Group-5 NCM-107 NCPDocument4 pagesGroup-5 NCM-107 NCPbulok netflakes100% (1)
- Cholera N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesCholera N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Document2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Jesse James Advincula Edjec100% (15)
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPjsksNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationKobe ManuelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Diagnosis Justification: Sodium-132 Mmol/l (Low)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Diagnosis Justification: Sodium-132 Mmol/l (Low)rei_alina75% (4)
- Name: Grace AGE: 28 Gender: Female Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GeneralDocument2 pagesName: Grace AGE: 28 Gender: Female Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GeneralRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Taberna Catherine T - ACUTE GOUTDocument17 pagesTaberna Catherine T - ACUTE GOUTaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosi S Analysis GOAL and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosi S Analysis GOAL and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMark Allison BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis and Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis and Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjay kusainNo ratings yet
- NCP MeningitisDocument2 pagesNCP MeningitisARISNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Subjective: Objective: General Objective: Independent IndependentDocument10 pagesCase Study: Subjective: Objective: General Objective: Independent IndependentChristine EmanNo ratings yet
- NCP - AgeDocument5 pagesNCP - Ageunsp3akabl386% (7)
- Intestinal Ills: Chronic Constipation, Indigestion, Autogenetic Poisons, Diarrhea, Piles, Etc. Also Auto-Infection, Auto-Intoxication, Anemia, Emaciation, Etc. Due to Proctitis and ColitisFrom EverandIntestinal Ills: Chronic Constipation, Indigestion, Autogenetic Poisons, Diarrhea, Piles, Etc. Also Auto-Infection, Auto-Intoxication, Anemia, Emaciation, Etc. Due to Proctitis and ColitisNo ratings yet
- Freedom from Constipation: Natural Remedies for Digestive HealthFrom EverandFreedom from Constipation: Natural Remedies for Digestive HealthNo ratings yet
- Rules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesFrom EverandRules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Short Bowel Syndrome, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Short Bowel Syndrome, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- CPG of PhilhealthDocument31 pagesCPG of PhilhealthMV Davao ToursNo ratings yet
- The Gastrointestinal RADocument3 pagesThe Gastrointestinal RAAisha SaherNo ratings yet
- Phases of Recovery From A Restrictive Eating DisorderDocument7 pagesPhases of Recovery From A Restrictive Eating DisorderAdriana Rangel DueñasNo ratings yet
- Emma ProjectDocument15 pagesEmma ProjectPrecious AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Ritumalta Answers ImciDocument3 pagesRitumalta Answers ImciJess RitumaltaNo ratings yet
- CHN ImciDocument18 pagesCHN Imcij UNo ratings yet
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesAcute Gastroenteritisrobert tucayNo ratings yet
- Duties and Responsibilities of A Midwife in RhuDocument6 pagesDuties and Responsibilities of A Midwife in RhuAlma Potente100% (1)
- tiến trình bài giảng Unit 6 fighting choleraDocument23 pagestiến trình bài giảng Unit 6 fighting cholerayennhi228anneNo ratings yet
- Online Activity 2 BonaguaDocument9 pagesOnline Activity 2 BonaguaJian BonaguaNo ratings yet
- Capstone PharmDocument5 pagesCapstone Pharmmaria60% (5)
- Use of Whey in Controlling Calf DiarrhoeaDocument27 pagesUse of Whey in Controlling Calf DiarrhoeanaturalamirNo ratings yet
- HEALTH-TEACHING-PLAN sUGATON EVALDocument9 pagesHEALTH-TEACHING-PLAN sUGATON EVALPrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument17 pagesDiarrheaAchyut KanungoNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh 2019 MICS Report - EnglishDocument564 pagesBangladesh 2019 MICS Report - EnglishAarajita ParinNo ratings yet
- Bacterial InfectionsDocument416 pagesBacterial Infectionsnihan tanerNo ratings yet
- Copar DocumentationDocument58 pagesCopar DocumentationJessa BorreNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Guide For IMNCI Training of Students-441Document121 pagesTeacher's Guide For IMNCI Training of Students-441National Child Health Resource Centre (NCHRC)No ratings yet
- Group 6 Case Study Pancreatic CancerDocument20 pagesGroup 6 Case Study Pancreatic CancerMarcel TabucolNo ratings yet
- Acute Viral Gastroenteritis in Children in Resource-Rich Countries - Clinical Features and DiagnosisDocument19 pagesAcute Viral Gastroenteritis in Children in Resource-Rich Countries - Clinical Features and DiagnosisNuno AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- E. Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesE. Nursing DiagnosisAle SandraNo ratings yet
- Psidium GuajavaDocument14 pagesPsidium GuajavaAmalia RasyidNo ratings yet
- Amebiasis NCPDocument3 pagesAmebiasis NCPSarah Benjamin0% (1)
- Centre For Community Medicine, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, INDIADocument25 pagesCentre For Community Medicine, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, INDIAKayle PinlacNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Safety, Security and SanitationDocument9 pagesRisk Management Safety, Security and SanitationMaui VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Study: Observational Travelers' DiarrheaDocument5 pagesStudy: Observational Travelers' DiarrheaFathah MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea FlipchartDocument27 pagesDiarrhea FlipchartEliana SochaNo ratings yet
- Mebeverine HydrochloridesDocument4 pagesMebeverine HydrochloridesMpok NoriNo ratings yet
- Diarrhoea in Sheep and GoatsDocument7 pagesDiarrhoea in Sheep and GoatsobertNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Postpartum Stage Mercado Sibal IIIDocument13 pagesModule 8 Postpartum Stage Mercado Sibal IIIFrancisco Sibal IIINo ratings yet