Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laboratory Exercise - Respiratory System
Laboratory Exercise - Respiratory System
Uploaded by
John Henry G. Gabriel IVCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory Exercise - Respiratory System
Laboratory Exercise - Respiratory System
Uploaded by
John Henry G. Gabriel IVCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercise No.
12 Respiratory System
Learning objectives
1. Recognize major parts of the respiratory track: trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, terminal
bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles, alveolar duct, and alveoli.
2. Understand the blood-air interface in the alveolus and know the function of the type 1 and 2
pneumocyte and alveolar macrophage.
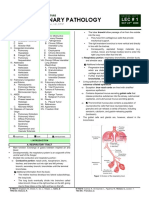
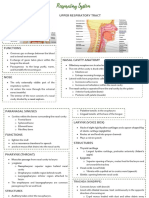
The respiratory system functions in the exchange of gases between the external and internal
environments. Major parts of the system include the nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and
pulmonary alveoli. Some regions of the respiratory system are specialized for conduction of
gases and other areas of the system function primarily in the exchange of gases. In both regions
mechanisms exist to filter the gases. The function of each part of the respiratory system is
reflected in the structure of its wall: the type of epithelium and its apical modifications,
intraepithelial and subepithelial glands, cartilaginous rings and plates, smooth muscle and elastic
tissue, and the relationship of capillary endothelium to alveolar epithelium.
Segment Characteristics
Conducting
Cartilage rings, pseudostratified ciliated epithelium with
Trachea
goblet cells, glands in submucosa
Plates of cartilage, smooth muscle, pseudostratified
Bronchi ciliated
epithelium with goblet cells, glands may be present
larger bronchioles Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium with goblet cells
smaller bronchioles Simple columnar or cuboidal, ciliated epithelium
Simple cuboidal ciliated epithelium with nonciliated
terminal bronchioles
Clara cells
Respiratory
Alveoli form outpocketings from walls of bronchiole,
Respiratory bronchioles
smooth muscle in nonrespiratory portions of walls
initial segment Both ciliated and Clara cells
distal segment Clara cells predominate
Squamous epithelium (type I pneumocytes), surfactant
Alveolar ducts and alveoli
cells (type II pneumocytes), macrophages
Specimen in focus: Trachea, Bronchi, Lungs
Illustrate the following histological features of the Respiratory System:
Answer the following questions:
1. Which cell is a also called a septal cell?
a. Clara cell b. Type I pneumocyte c. Type II pneumocyte d. Dust cell e. Brush cell
2. Which cell is a respiratory macrophage?
a. Kupffer cells b. Histiocyte c. Dust cell d. Langerhans cell e. Microglia
3. Which cell is a type of neuron?
a. Basal cells b. Brush cells c. Olfactory cells d. Sustentacular cells e. All of the above
4. What cell types are found in the respiratory mucosa?
a. Ciliated cells b. Goblet cells c. Basal cells d. Brush cells e. All of the above
5. What type of tissue makes up the epiglottis?
a. Compact bone b. Spongy bone c. Hyaline cartilage d. Fibrocartilage e. Elastic cartilage
6. What is the smallest airspace of the respiratory tree?
a. Alveolar duct b. Alveoli c. Alveolar sac d. Respiratory bronchiole e. Terminal bronchiole
7. What type of epithelium lines the trachea?
a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple cuboidal epithelium
c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Stratified squamous epithelium e. Pseudostratified epithelium
8. Which structure is part of the conducting portion of the airway?
a. Bronchi b. Alveolar ducts c. Alveoli d. Alveolar sacs e. Respiratory bronchioles
9. What type of epithelium lines the vestibule?
a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Simple columnar epithelium
c. Stratified squamous epithelium d. Ciliated pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells
e. Transitional epithelium
10. Which cartilage of the larynx is made of hyaline cartilage?
a. Thyroid cartilage b. Cricoid cartilage c. Arytenoid cartilage d. Corniculate cartilage
e. All of the above
11. Which cartilage of the larynx is made of elastic cartilage?
a. Thyroid cartilage b. Cricoid cartilage c. Arytenoid cartilage d. Epiglottis e. Corniculate
cartilage
12. Which cell is rarely found in the alveolus?
a. Clara cell b. Type I pneumocyte c. Type II pneumocyte d. Dust cell e. Brush cell
13. What are the alveolar pores called?
a. Pores of Luschka b. Pores of Descemet c. Pores of Mall d. Pores of Kohn e. Pores of Disse
14. What is the first portion of the respiratory tree where gas exchange can occur?
a. Alveolar duct
b. Alveoli
c. Alveolar sac
d. Respiratory bronchiole
e. Terminal bronchiole
15. Which cell is a squamous pulmonary epithelial cell?
a. Clara cell
b. Type I pneumocyte
c. Type II pneumocyte
d. Dust cell
e. Brush cell
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Practise Questions Keith & Moore 5th Edition - Should ReadDocument113 pagesPractise Questions Keith & Moore 5th Edition - Should ReadAmirsalar Eslami83% (6)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Respiratory System: D) Dullness With A Tympanic ShadeDocument31 pagesRespiratory System: D) Dullness With A Tympanic Shademohammad farooque razaaNo ratings yet
- Bronchial ObstructionDocument137 pagesBronchial ObstructionGrajdianu Natalia100% (1)
- Laboratory Exercise - LymphaticsDocument5 pagesLaboratory Exercise - LymphaticsJohn Henry G. Gabriel IVNo ratings yet
- Granular CastDocument2 pagesGranular CastJohn Henry G. Gabriel IVNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise - MuscleDocument3 pagesLaboratory Exercise - MuscleJohn Henry G. Gabriel IVNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Lesson 2Document4 pagesParasitology Lesson 2John Henry G. Gabriel IVNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 4688Document2 pagesRepublic Act 4688John Henry G. Gabriel IVNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 7719 - National Blood Services Act of 1994: by AziramDocument8 pagesRepublic Act 7719 - National Blood Services Act of 1994: by AziramJohn Henry G. Gabriel IVNo ratings yet
- Definition of TermsDocument29 pagesDefinition of TermsJohn Henry G. Gabriel IV100% (6)
- Parasitology-Definition of TermsDocument4 pagesParasitology-Definition of TermsJohn Henry G. Gabriel IVNo ratings yet
- BLOOD SPECIMEN CollectionDocument12 pagesBLOOD SPECIMEN CollectionJohn Henry G. Gabriel IV100% (11)
- The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen PreparationDocument50 pagesThe Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen PreparationJohn Henry G. Gabriel IVNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis Element Inorganic Compound Functional Group Organic CompoundDocument8 pagesQualitative Analysis Element Inorganic Compound Functional Group Organic CompoundJohn Henry G. Gabriel IVNo ratings yet
- Ch15 Lecture PPT ADocument17 pagesCh15 Lecture PPT AEulanda DelenNo ratings yet
- DEEPAK SIR ANATOMY FinalDocument98 pagesDEEPAK SIR ANATOMY FinalPrabin DharalaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2 All in OneDocument102 pagesAnatomy 2 All in OneDragoiu AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Prometric MCQs (Blank)Document55 pagesPrometric MCQs (Blank)irnumambreen15No ratings yet
- Question Bank Class Vii (Science) Chapter-1 Nutrition in PlantsDocument34 pagesQuestion Bank Class Vii (Science) Chapter-1 Nutrition in Plantssivsyadav50% (2)
- Pulmonary Pathology: Maria Sarah L. Lenon, MD, DPSPDocument32 pagesPulmonary Pathology: Maria Sarah L. Lenon, MD, DPSPKATREEYA ELEONOR LIMSINo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical (MS) Lecture Respiratory System: Alteration in OxygenationDocument44 pagesMedical Surgical (MS) Lecture Respiratory System: Alteration in OxygenationYman Gio BumanglagNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesThe Respiratory Systempaulo_camuaNo ratings yet
- DLP (Boyle's Law)Document6 pagesDLP (Boyle's Law)Lern JergiNo ratings yet
- Iaslc 8th Posters 24x36 2018 Final Version 1Document1 pageIaslc 8th Posters 24x36 2018 Final Version 1Faskanita NadapdapNo ratings yet
- Histology: Ust Faculty of Medicine and Surgery Class of 2016Document14 pagesHistology: Ust Faculty of Medicine and Surgery Class of 2016Ashley Beatriz PascualNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examinations by DR - Shamol MMCDocument1,174 pagesClinical Examinations by DR - Shamol MMCsadiaafrin66523No ratings yet
- 15 Signs in Thoracic Imaging.20Document15 pages15 Signs in Thoracic Imaging.20Don Kihot100% (1)
- Module # 3 Physiological Changes in Aging Affecting Various SystemsDocument30 pagesModule # 3 Physiological Changes in Aging Affecting Various SystemsJann ericka JaoNo ratings yet
- Sputum Analysis and BalDocument41 pagesSputum Analysis and BalClaire GonoNo ratings yet
- Overview of Thoracic Radiology: Paul M. Rist, DVM, Dipl. ACVRDocument55 pagesOverview of Thoracic Radiology: Paul M. Rist, DVM, Dipl. ACVRNeny ChalondokterNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Urine and Other Body Fluids - , RMT Sputum & Bronchoalveolar Lavage (Bal)Document11 pagesAnalysis of Urine and Other Body Fluids - , RMT Sputum & Bronchoalveolar Lavage (Bal)jeffreyNo ratings yet
- Sputum, Sweat, Gastric FluidDocument8 pagesSputum, Sweat, Gastric FluidLuci Kuro Neko100% (1)
- ?1 - Chest X-Ray Interpretation - A Structured Approach - Radiology - OSCEDocument14 pages?1 - Chest X-Ray Interpretation - A Structured Approach - Radiology - OSCEVerónicaNo ratings yet
- Postmortem Distribution 1Document10 pagesPostmortem Distribution 1Zeba NiazNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System ReviewerDocument7 pagesRespiratory System ReviewerVictoria Ellex TiomicoNo ratings yet
- Stridor, Aspiration, and Cough in ChildrenDocument41 pagesStridor, Aspiration, and Cough in ChildrenArif Rahman DmNo ratings yet
- Sci 9 LM DRAFT 3.31.2014Document394 pagesSci 9 LM DRAFT 3.31.2014URBIZTONDO, GIAN CARLO M.No ratings yet
- 1-крок-1-ЛС-KROK 2007-2017-English-HistolohyDocument26 pages1-крок-1-ЛС-KROK 2007-2017-English-HistolohyAbhani MøhitNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1 - Respiration (Notes)Document4 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 1 - Respiration (Notes)Autumn JJ40% (5)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Impaired Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Impaired Breathing PatternChie Hyun-AeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsDocument25 pagesRespiratory System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsMourian Aman100% (1)