Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Theme Topic / Textbook Chapter Sub-Topic / Textbook Section Title No. Section No
Theme Topic / Textbook Chapter Sub-Topic / Textbook Section Title No. Section No
Uploaded by
Regie Sacil EspiñaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Theme Topic / Textbook Chapter Sub-Topic / Textbook Section Title No. Section No
Theme Topic / Textbook Chapter Sub-Topic / Textbook Section Title No. Section No
Uploaded by
Regie Sacil EspiñaCopyright:
Available Formats
Universal Curriculum Physics GCE 'O' Level Science
Chapter Section
Theme Topic / Textbook Chapter Sub-Topic / Textbook Section Title
No. No.
General Physics 1 Measurement 1.4 Measurement of Time On what does the period of a ball pendulum depend?
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.1 Distance and Displacement Displacement and distance
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.1 Distance and Displacement Position
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.2 Speed, Velocity and Acceleration Position, speed and time
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.2 Speed, Velocity and Acceleration Average and instantaneous speed
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.2 Speed, Velocity and Acceleration Velocity is a vector
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.2 Speed, Velocity and Acceleration Uniformly accelerating motion
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.2 Speed, Velocity and Acceleration Acceleration
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.2 Speed, Velocity and Acceleration Acceleration and speed increment
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.3 Graphs of Motion Position time graph
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.3 Graphs of Motion Speed and a graph
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.3 Graphs of Motion Speed time graph for uniform acceleration
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.3 Graphs of Motion Speed time graph for non-uniform acceleration
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.3 Graphs of Motion Acceleration and the graph of speed
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.3 Graphs of Motion How to derive acceleration from the graph v(t)
The relationship between the inclination of the graph of speed and
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.3 Graphs of Motion
acceleration
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.3 Graphs of Motion Calculation of distance in uniformly accelerating motion
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.3 Graphs of Motion How to calculate distance when the graph of the speed is given
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.3(extension) Graphs of Motion How to plot one graph given another
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.4 Acceleration due to Gravity What type of motion is it?
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.4 Acceleration due to Gravity Change in velocity
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.4 Acceleration due to Gravity Distance
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.4 Acceleration due to Gravity An upward vertical projection and free fall
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.4 Acceleration due to Gravity Free fall in a vacuum
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.4(OPTIONAL) Acceleration due to Gravity Air resistance (drag)
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.4(OPTIONAL) Acceleration due to Gravity Relationship between air resistance and speed
General Physics 2 Kinematics 2.4(extension) Acceleration due to Gravity Free fall on the Moon
General Physics 3 Forces 3.1 Forces Force what is it?
General Physics 3 Forces 3.1(extension) Forces Large and small forces
General Physics 3 Forces 3.1 Forces Types of forces
General Physics 3 Forces 3.2 Vector Diagrams Graphical representation of forces
General Physics 3 Forces 3.2 Vector Diagrams Resultant force
General Physics 3 Forces 3.2 Vector Diagrams Addition of forces by means of a parallelogram
General Physics 3 Forces 3.2 Vector Diagrams Addition of forces by means of a triangle
General Physics 3 Forces 3.3 Forces and Motion Effects of the application of force
General Physics 3 Forces 3.3 Forces and Motion What is force needed for?
General Physics 3 Forces 3.3 Forces and Motion Newton's First Law of Motion
General Physics 3 Forces 3.3 Forces and Motion Newton's Second Law of Motion
General Physics 3 Forces 3.3 Forces and Motion Force as a product of mass and acceleration
General Physics 3 Forces 3.3 Forces and Motion The resultant force
General Physics 3 Forces 3.3(OPTIONAL) Forces and Motion Two forces: action and reaction
2014 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd
Universal Curriculum Physics GCE 'O' Level Science
General Physics 3 Forces 3.3(OPTIONAL) Forces and Motion Forces of action and reaction act in opposite directions
General Physics 3 Forces 3.3(OPTIONAL) Forces and Motion The same magnitude
General Physics 3 Forces 3.3(OPTIONAL) Forces and Motion Forces affect different bodies
General Physics 3 Forces 3.3(OPTIONAL) Forces and Motion The Third Law of Motion
General Physics 3 Forces 3.3(OPTIONAL) Forces and Motion Walking and rolling
General Physics 3 Forces 3.4 Friction and Its Effects The effects of friction
General Physics 3 Pressure 3.6 Pressure The effects of the force of a load
General Physics 3 Pressure 3.6 Pressure Definition of pressure
General Physics 3 Pressure 3.6 Pressure Changes in area
General Physics 4 Weight, Mass and Density 4.1 Mass and Weight Weight versus mass
General Physics 4 Weight, Mass and Density 4.1 Mass and Weight Mass and weight of a body
General Physics 4 Weight, Mass and Density 4.1 Mass and Weight Weight and mass
General Physics 4 Weight, Mass and Density 4.1 Mass and Weight A balance as a type of force gauge
General Physics 4 Weight, Mass and Density 4.2 Inertia The Inertia Principle
General Physics 4 Weight, Mass and Density 4.3 Density Definition of density
General Physics 4 Weight, Mass and Density 4.3 Density How to determine the density of a solid
General Physics 4 Weight, Mass and Density 4.3 Density Why objects float or sink
General Physics 4 Weight, Mass and Density 4.3(extension) Density The density of a liquid
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.1 Moments Forces and rotation
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.1 Moments The magnitude of the moment of a force
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.1 Moments The moment of a force (including direction)
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.2 Principle of Moments A see-saw
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.2 Principle of Moments Equilibrium of moments
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.2 Principle of Moments A motionless solid
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.2 Principle of Moments Weighing scales
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.2 Principle of Moments Workers holding a beam
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.2(extension) Principle of Moments Levers
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.2 Principle of Moments Long arm, small force
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.3 Centre of Gravity A broom
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.3 Centre of Gravity A figure
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.3 Centre of Gravity Equilibrium of forces and moments of forces
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.4 Stability Types of equilibrium
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.4 Stability Solids in equilibrium
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.4 Stability Equilibrium
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.4 Stability When will it topple?
General Physics 5 Turning Effect of Forces 5.4 Stability Which car to choose?
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1 Energy Gravitational potential energy
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1 Energy Potential energy and the centre of gravity
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1 Energy Transformations and transfer of energy
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1 Energy Energy and movement
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1 Energy Formula for kinetic energy
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1 Energy Kinetic energy and potential energy
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1 Energy Kinetic energy and elastic potential energy
2014 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd
Universal Curriculum Physics GCE 'O' Level Science
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1 Energy Mechanical energy
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1 Energy Principle of conservation of mechanical energy
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1 Energy Energy of a pendulum ball
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1 Energy Jumps on the Moon
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1 Energy A pendulum activity
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1 Energy Shooting with a catapult activity
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1 Energy The Law of Conservation of Energy
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1 Energy Energy losses
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1(OPTIONAL) Energy The efficiency of a motor
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.1(OPTIONAL) Energy The efficiency of the energy conversion process
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.2 Work Force and displacement
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.2 Work Units of work
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.2 Work How to calculate work
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.2 Work When is 'work' not work
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.2 Work Work done to lift a body
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.3 Power Rate at which work is done
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.3 Power Units of power
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.3(extension) Power Power in nature and technology
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.3 Power Power and work of a man activity
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.3(extension) Power Power as a product of force and velocity
General Physics 6 Energy, Work and Power 6.3 Power Power and efficiency
Thermal Physics 7 Kinetic Model of Matter 7.1 The States of Matter Matter
Thermal Physics 7 Kinetic Model of Matter 7.2(extension) The Kinetic Model of Matter Gases
Thermal Physics 7 Kinetic Model of Matter 7.2(extension) The Kinetic Model of Matter Liquids
Thermal Physics 7 Kinetic Model of Matter 7.2 The Kinetic Model of Matter Solids
Thermal Physics 7 Kinetic Model of Matter 7.2(extension) The Kinetic Model of Matter Diffusion
Thermal Physics 8 Transfer of Thermal Energy 8.2 Conduction Microscopic view of conduction
Thermal Physics 8 Transfer of Thermal Energy 8.2 Conduction The heating of a body
Thermal Physics 8 Transfer of Thermal Energy 8.3 Convection Heat exchange by convection in gases
Thermal Physics 8 Transfer of Thermal Energy 8.4 Radiation Radiation
Thermal Physics 8 Transfer of Thermal Energy 8.5 Applications of Thermal Energy Transfer Applications of convection
Thermal Physics 8 Transfer of Thermal Energy 8.5 Applications of Thermal Energy Transfer The phenomenon of radiation
Thermal Physics 8 Transfer of Thermal Energy 8.5 Applications of Thermal Energy Transfer How to decrease losses
Thermal Physics 9 Thermal Properties of Matter 9.1 Heat Capacity and Specific Heat Capacity Internal energy
Thermal Physics 9 Thermal Properties of Matter 9.1 Heat Capacity and Specific Heat Capacity Internal energy and temperature
Thermal Physics 9 Thermal Properties of Matter 9.2 Melting and Solidification Melting and freezing
Thermal Physics 9 Thermal Properties of Matter 9.3 Boiling and Condensation Evaporation, condensation, and boiling
Thermal Physics 9 Thermal Properties of Matter 9.3 Boiling and Condensation The boiling point
Thermal Physics 9 Thermal Properties of Matter 9.3 Boiling and Condensation Changes in temperature during heating
Thermal Physics 9 Thermal Properties of Matter 9.4 Evaporation The rate of evaporation
Thermal Physics 9 Thermal Properties of Matter 9.4 Evaporation Flow of heat
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.1 Reflection of Light A ray of light
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.1 Reflection of Light The Law of Reflection
2014 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd
Universal Curriculum Physics GCE 'O' Level Science
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.1 Reflection of Light Virtual image
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.1 Reflection of Light A mirror
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.1(extension) Reflection of Light Reflectors
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.2 Refraction of Light Light refraction
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.2 Refraction of Light What affects refraction?
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.2 Refraction of Light The refractive index
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.3 Total Internal Reflection Critical angle
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.3 Total Internal Reflection Total internal reflection
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.3 Total Internal Reflection A prism
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.3 Total Internal Reflection Binoculars
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.4 Refraction by Thin Lenses Converging and diverging lenses
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.5 Ray Diagrams for Thin Converging Lenses Images in lenses
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.5 Ray Diagrams for Thin Converging Lenses Converging lens, x > 2f
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.5 Ray Diagrams for Thin Converging Lenses Converging lens, f < x < 2f
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.5 Ray Diagrams for Thin Converging Lenses Converging lens, x < f
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.5 Ray Diagrams for Thin Converging Lenses A magnifying glass
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.5 Ray Diagrams for Thin Converging Lenses A photographic camera
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.5 Ray Diagrams for Thin Converging Lenses Sight defects
Light, Waves and Sound 10 Light 10.5 Ray Diagrams for Thin Converging Lenses Glasses
Light, Waves and Sound 11 Waves 11.1 Introducing Waves Wave pulse and a mechanical wave
Light, Waves and Sound 11 Waves 11.1 Introducing Waves Transfer of energy by waves
Light, Waves and Sound 11 Waves 11.1 Introducing Waves Transverse and longitudinal waves
Light, Waves and Sound 11 Waves 11.2 Properties of Wave Motion The wavelength and the velocity of wave propagation
Light, Waves and Sound 11 Waves 11.2(extension) Properties of Wave Motion On what does wave refraction depend?
Light, Waves and Sound 12 Electromagnetic Waves 12.1 Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic waves
Light, Waves and Sound 12 Electromagnetic Waves 12.1(extension) Electromagnetic Waves Light as an electromagnetic wave
Light, Waves and Sound 12 Electromagnetic Waves 12.1(extension) Electromagnetic Waves Parameters of an electromagnetic wave
Light, Waves and Sound 12 Electromagnetic Waves 12.1 Electromagnetic Waves The division of electromagnetic waves
Light, Waves and Sound 12 Electromagnetic Waves 12.2 Applications and Effects of Electromagnetic Waves Radio waves
Light, Waves and Sound 12 Electromagnetic Waves 12.2 Applications and Effects of Electromagnetic Waves Microwaves
Light, Waves and Sound 12 Electromagnetic Waves 12.2(extension) Applications and Effects of Electromagnetic Waves Infrared
Light, Waves and Sound 12 Electromagnetic Waves 12.2(extension) Applications and Effects of Electromagnetic Waves Light
Light, Waves and Sound 12 Electromagnetic Waves 12.2(extension) Applications and Effects of Electromagnetic Waves Ultraviolet
Light, Waves and Sound 12 Electromagnetic Waves 12.2(extension) Applications and Effects of Electromagnetic Waves X-ray radiation
Light, Waves and Sound 12 Electromagnetic Waves 12.2(extension) Applications and Effects of Electromagnetic Waves Gamma radiation
Light, Waves and Sound 12 Electromagnetic Waves 12.2 Applications and Effects of Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic radiation summary
Light, Waves and Sound 12 Electromagnetic Waves 12.2(extension) Applications and Effects of Electromagnetic Waves Greenhouse effect
Light, Waves and Sound 12 Electromagnetic Waves 12.2(OPTIONAL) Applications and Effects of Electromagnetic Waves Ionizing radiation
Light, Waves and Sound 13 Sound 13.1 What is Sound? Sound
Light, Waves and Sound 13 Sound 13.2 Transmission of Sound Propagation of sound
Light, Waves and Sound 13 Sound 13.2 Transmission of Sound Wavelength
Light, Waves and Sound 13 Sound 13.3 Reflection of Sound Echo
Light, Waves and Sound 13 Sound 13.3 Reflection of Sound Echolocation
2014 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd
Universal Curriculum Physics GCE 'O' Level Science
Light, Waves and Sound 13 Sound 13.1(extension) Ultrasound Audibility range
Light, Waves and Sound 13 Sound 13.4 Pitch and Loudness The amplitude and the frequency of sound
Light, Waves and Sound 13 Sound 13.4 Pitch and Loudness The timbre
Electricity and Magnetism 14 Static Electricity 14.1 Electrostatics Positive and negative electricity
Electricity and Magnetism 14 Static Electricity 14.1 Electrostatics Protons and electrons
Electricity and Magnetism 14 Static Electricity 14.1(extension) Electrostatics The principle of conservation of charge
Electricity and Magnetism 14 Static Electricity 14.1 Electrostatics Electric charges
Electricity and Magnetism 14 Static Electricity 14.2 Electric Field Electric field
Electricity and Magnetism 14 Static Electricity 14.2 Electric Field Electric field of a system of point charges
Electricity and Magnetism 15 Current Electricity 15.1 Electric Current An electric circuit
Electricity and Magnetism 15 Current Electricity 15.1 Electric Current A close look at current
Electricity and Magnetism 15 Current Electricity 15.1 Electric Current Current
Electricity and Magnetism 15 Current Electricity 15.2 Electromotive Force and Potential Difference Electromotive force
Electricity and Magnetism 15 Current Electricity 15.2(OPTIONAL) Electromotive Force and Potential Difference How to connect cells
Electricity and Magnetism 15 Current Electricity 15.3 Resistance How resistance affects the way in which a conductor works
Electricity and Magnetism 15 Current Electricity 15.3 Resistance Electrical resistance
Electricity and Magnetism 15 Current Electricity 15.3 Resistance Resistors with variable resistance
Electricity and Magnetism 15 Current Electricity 15.3(OPTIONAL) Resistance Ohm's Law
Electricity and Magnetism 15 Current Electricity 15.3(OPTIONAL) Resistance The resistance of a light bulb filament
Electricity and Magnetism 15 Current Electricity 15.3(OPTIONAL) Resistance The relationship between resistance and temperature
Electricity and Magnetism 15 Current Electricity 15.3(OPTIONAL) Resistance A semiconductor diode
Electricity and Magnetism 15 Current Electricity 15.3(OPTIONAL) Resistance Diode testing
Electricity and Magnetism 15 Current Electricity 15.4 Resistivity The resistance of a conductor depends on its dimensions
Electricity and Magnetism 16 D.C. Circuits 16.1 Series Circuits Connection in series
Electricity and Magnetism 16 D.C. Circuits 16.1 Series Circuits Replacement resistance connection in series
Electricity and Magnetism 16 D.C. Circuits 16.2 Parallel Circuits Connection in parallel
Electricity and Magnetism 16 D.C. Circuits 16.2 Parallel Circuits Replacement resistance connection in parallel
Electricity and Magnetism 16 D.C. Circuits 16.2 Parallel Circuits Connection in parallel
Electricity and Magnetism 17 Practical Electricity 17.2 Measuring Electrical Energy The work done by an electric current
Electricity and Magnetism 17 Practical Electricity 17.2 Measuring Electrical Energy The power of an electric current
Electricity and Magnetism 17 Practical Electricity 17.2 Measuring Electrical Energy How much does it cost to watch television?
Electricity and Magnetism 17 Practical Electricity 17.2 Measuring Electrical Energy How much can you save by using an energy-saving light bulb?
Electricity and Magnetism 17 Practical Electricity 17.3 Dangers of Electricity Overload and short-circuit
Electricity and Magnetism 17 Practical Electricity 17.4 Safety Features in Home Circuitries Household mains
Electricity and Magnetism 17 Practical Electricity 17.4 Safety Features in Home Circuitries What type of connection is it?
Electricity and Magnetism 17 Practical Electricity 17.4 Safety Features in Home Circuitries The properties of a connection in parallel
Electricity and Magnetism 17 Practical Electricity 17.4 Safety Features in Home Circuitries Circuit breakers
Electricity and Magnetism 17 Practical Electricity 17.4 Safety Features in Home Circuitries Modern electric mains systems
Electricity and Magnetism 17 Practical Electricity 17.4 Safety Features in Home Circuitries Conductors
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Magnetism 18.1 Magnets and Magnetic Materials Magnets
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Magnetism 18.1 Magnets and Magnetic Materials Magnetic poles
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Magnetism 18.1 Magnets and Magnetic Materials A magnet
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Magnetism 18.3 Magnetisation and Demagnetisation Ferromagnets
2014 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd
Universal Curriculum Physics GCE 'O' Level Science
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Magnetism 18.3 Magnetisation and Demagnetisation Magnetisation
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Magnetism 18.4 Magnetic Fields Magnetic field
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Magnetism 18.4 Magnetic Fields The Earth's magnetic field
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Electromagnetism 18.6 Magnetic Effect of a Current A magnetic needle in the vicinity of a conductor
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Electromagnetism 18.6 Magnetic Effect of a Current The magnetic field around a conductor
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Electromagnetism 18.6 Magnetic Effect of a Current The magnetic field of a loop
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Electromagnetism 18.6 Magnetic Effect of a Current The magnetic field of a coil
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Electromagnetism 18.6 Magnetic Effect of a Current The electromagnet
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Electromagnetism 18.6 Magnetic Effect of a Current Electromagnets
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Electromagnetism 18.7 The Motor Effect - Force due to Magnetic Fields Electromagnetic force
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Electromagnetism 18.7 The Motor Effect - Force due to Magnetic Fields Left-hand rule
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Electromagnetism 18.7 The Motor Effect - Force due to Magnetic Fields Magnetic field and an electric charge
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Electromagnetism 18.7(OPTIONAL) The Motor Effect - Force due to Magnetic Fields Interaction between conductors
Turning Effect on a Current-carrying Coil in a
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Electromagnetism 18.8 The forces that turn the frame
Magnetic Field
Turning Effect on a Current-carrying Coil in a
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Electromagnetism 18.8(OPTIONAL) The rotation of the frame
Magnetic Field
Turning Effect on a Current-carrying Coil in a
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Electromagnetism 18.8(OPTIONAL) A commutator
Magnetic Field
Turning Effect on a Current-carrying Coil in a
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Electromagnetism 18.8(OPTIONAL) Brushes and commutator
Magnetic Field
Turning Effect on a Current-carrying Coil in a
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Electromagnetism 18.8(OPTIONAL) A rotor
Magnetic Field
Turning Effect on a Current-carrying Coil in a
Electricity and Magnetism 18 Electromagnetism 18.8(OPTIONAL) More frames
Magnetic Field
2014 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd
You might also like
- Ebook PDF Conceptual Physical Science 6th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Conceptual Physical Science 6th Edition PDFamy.martin707100% (42)
- BGN 273 Assignment Thermal ComfortDocument3 pagesBGN 273 Assignment Thermal ComfortAkalily Sofiena0% (1)
- Engineering Mechanics 1Document109 pagesEngineering Mechanics 1Adnan KhanNo ratings yet
- 50 Questions To Ask A FranchisorDocument3 pages50 Questions To Ask A FranchisorRegie Sacil EspiñaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document4 pagesChapter 5Aadar NNo ratings yet
- Debre Markos University: College of Natural and Computational Science Department of PhysicsDocument4 pagesDebre Markos University: College of Natural and Computational Science Department of PhysicsYesgat enawgawNo ratings yet
- List of Topics and Subtopics in PHYSICS FORM 4Document10 pagesList of Topics and Subtopics in PHYSICS FORM 4nurafinahanani8No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Basic Physics: Compiled By: Chibuikem N. OkekeDocument12 pagesLecture Notes On Basic Physics: Compiled By: Chibuikem N. OkekeCHIBUIKEM OKEKEOGUEGBENo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics II (Dynamics) CourseoutlineDocument3 pagesEngineering Mechanics II (Dynamics) Courseoutlineashenafihenok400No ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To KinDinDocument27 pages1.1 Introduction To KinDinRio AlifNo ratings yet
- Delhi Institute of Technology, Management and Research, FBDDocument4 pagesDelhi Institute of Technology, Management and Research, FBDDildar Khan BhatiNo ratings yet
- Title of Kinematics - 001Document1 pageTitle of Kinematics - 001Siddharth JainNo ratings yet
- Perancangan Mengajar: Dynamics & MechanismDocument5 pagesPerancangan Mengajar: Dynamics & MechanismHui ShanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Physical WorldDocument15 pagesUnit 1 Physical WorldRavindra MnNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Lecture NotesDocument28 pagesDynamics Lecture NotesThanh ChươngNo ratings yet
- Learning Standard ListDocument2 pagesLearning Standard Listyang jihwonNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Syllabus 23-24Document9 pagesIGCSE Physics Syllabus 23-24rmsschool978No ratings yet
- 1st PUC - Physics Mid TermDocument2 pages1st PUC - Physics Mid TermSankirth PNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS 2021-2022: Standard: 11 Subject: PhysicsDocument8 pagesSYLLABUS 2021-2022: Standard: 11 Subject: Physicschandran chandranNo ratings yet
- Fall 2020-Mechanics and WavesDocument7 pagesFall 2020-Mechanics and WavesJAVED AKHTAR REG.2020 UET NFC FD ELECT 76.No ratings yet
- JEE Class Companion Physics: Module-2Document7 pagesJEE Class Companion Physics: Module-2neoisonlyoneNo ratings yet
- JEE Class Companion Physics: Module-2Document167 pagesJEE Class Companion Physics: Module-2The Indian100% (1)
- Mathemetical Physics Class NotesDocument218 pagesMathemetical Physics Class NotesSwashy Yadav50% (2)
- Applied Mech SyllabusDocument5 pagesApplied Mech SyllabusAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - UPM 2022-23 - Upto Ch-7Document1 pageLesson Plan - UPM 2022-23 - Upto Ch-7Aryan AnsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Basic of StaticsDocument42 pagesChapter 1 Basic of StaticsHabtie WalleNo ratings yet
- Mid Year Exam (May 2017) Exam Scope: Form 4 (Chapter 1 Till 3)Document1 pageMid Year Exam (May 2017) Exam Scope: Form 4 (Chapter 1 Till 3)ShidevNo ratings yet
- Course Introduction: Far Western University Bachelor of Engineering (Civil) Course of Study 2071Document3 pagesCourse Introduction: Far Western University Bachelor of Engineering (Civil) Course of Study 2071सचिन खड्काNo ratings yet
- LECTURE Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument22 pagesLECTURE Statics of Rigid BodiesRey Ar OrionNo ratings yet
- Dynamics: BDA 20303 SEMESTER 1 SESSION 2017/2018 By: Khairulnizam NgadimonDocument22 pagesDynamics: BDA 20303 SEMESTER 1 SESSION 2017/2018 By: Khairulnizam NgadimonShaktivell LetchumananNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document22 pagesCH 01yarendogan360No ratings yet
- Classical Mechanics - B P CowanDocument121 pagesClassical Mechanics - B P CowanAGNo ratings yet
- Mechanics and Heat Course Out LineDocument3 pagesMechanics and Heat Course Out Linerzzzumoh207No ratings yet
- 111 (B) 06 FM TheMomentumEquationDocument77 pages111 (B) 06 FM TheMomentumEquation宋 珉No ratings yet
- A2 Physics Revision GuideDocument78 pagesA2 Physics Revision GuideThomas Roe100% (3)
- PhysicsDocument3 pagesPhysicsAlexis Narcelles SiaNo ratings yet
- 02 MechanicsDocument42 pages02 MechanicsLuis CottosNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering: Lecture 6 - Introduction To: Dynamics & Kinematics - Newton's LawDocument14 pagesMechanical Engineering: Lecture 6 - Introduction To: Dynamics & Kinematics - Newton's LawTrinito GomesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Mechanical Engineering and Force VectorDocument32 pagesUnit 1 Mechanical Engineering and Force VectorNÏALNo ratings yet
- 1introduction To DynamicsDocument32 pages1introduction To DynamicsRheineNo ratings yet
- Remedial CourseOutlineDocument2 pagesRemedial CourseOutlineefokimemNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Physics Course Outline For Term 1Document1 pageGrade 9 Physics Course Outline For Term 1Keol AkumaNo ratings yet
- Ebook Classical and Analytical Mechanics Theory Applied Examples and Practice 1St Edition Poznyak Alexander S Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesEbook Classical and Analytical Mechanics Theory Applied Examples and Practice 1St Edition Poznyak Alexander S Online PDF All Chapterdaniel.lackey655100% (10)
- Lecture Mechanics For Engineering StaticDocument83 pagesLecture Mechanics For Engineering StaticAli AlaamiryNo ratings yet
- Physics COLDocument2 pagesPhysics COLHanan FuadNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Miko Anderson P. YjaresDocument50 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodies: Miko Anderson P. YjaresAlvin RazoNo ratings yet
- Course Contents:: 302101 0 Introductory Physics 1 eDocument2 pagesCourse Contents:: 302101 0 Introductory Physics 1 emamoun mufarraqNo ratings yet
- HSSRPTR +1 Physics Notes KamilDocument104 pagesHSSRPTR +1 Physics Notes KamilAswithNo ratings yet
- 01/23/21 Chapter 1 General Principles 1Document40 pages01/23/21 Chapter 1 General Principles 1arindamckbt100% (1)
- Syllabus For PhysicsDocument20 pagesSyllabus For Physicsshamimshafeb2005No ratings yet
- Notes CH - 13Document22 pagesNotes CH - 13Nuruddin ShaariNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibration 3Document12 pagesMechanical Vibration 3Abednego SiagianNo ratings yet
- Engineering-Mechanics Notes PDFDocument100 pagesEngineering-Mechanics Notes PDFMahesh RamtekeNo ratings yet
- 2 Motion Along A Straight LineDocument80 pages2 Motion Along A Straight LineDaniel Ramsés Barrientos HernándezNo ratings yet
- Newtonian PhysicsDocument290 pagesNewtonian PhysicsNikunj100% (1)
- Phys 1011 Course Outlune 2016 NewDocument5 pagesPhys 1011 Course Outlune 2016 Newfikru065No ratings yet
- 1201 SyllabusDocument1 page1201 Syllabusmzbreezy808No ratings yet
- Long Short DefDocument4 pagesLong Short Defملک آصفNo ratings yet
- Motion - Part 1: General Awareness: PhysicsDocument4 pagesMotion - Part 1: General Awareness: PhysicsPavan TejaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1Document13 pagesLesson 1.1Crisostomo IbarraNo ratings yet
- Bhavikatti Engineering Mechanics SampleDocument11 pagesBhavikatti Engineering Mechanics SamplehakeemniyasNo ratings yet
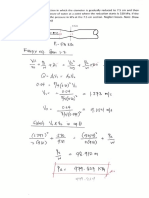
- Practical 2: Investigating The Universe - Gravity: T, Depends On The Length of The String and The GDocument3 pagesPractical 2: Investigating The Universe - Gravity: T, Depends On The Length of The String and The GRegie Sacil EspiñaNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision For o Level PhysicsDocument28 pagesQuick Revision For o Level PhysicsRegie Sacil EspiñaNo ratings yet
- Building A Simple MotorDocument5 pagesBuilding A Simple MotorRegie Sacil EspiñaNo ratings yet
- Sec. 4 Physics Final Exam Sec. 4 Physics Final Exam: Topics To Review: Topics To ReviewDocument1 pageSec. 4 Physics Final Exam Sec. 4 Physics Final Exam: Topics To Review: Topics To ReviewRegie Sacil EspiñaNo ratings yet
- Teachers Guide Lower Secondary Science PDFDocument141 pagesTeachers Guide Lower Secondary Science PDFRegie Sacil Espiña33% (3)
- DPS Worksheet C01 (Teacher)Document5 pagesDPS Worksheet C01 (Teacher)Regie Sacil EspiñaNo ratings yet
- RIS Scheme of Work Science Grade 6 (Stage 7) .v1Document44 pagesRIS Scheme of Work Science Grade 6 (Stage 7) .v1Regie Sacil EspiñaNo ratings yet
- UC Phys SG Synopsis ListingDocument38 pagesUC Phys SG Synopsis ListingRegie Sacil EspiñaNo ratings yet
- Forces in Action: Work Done and Energy TransferDocument1 pageForces in Action: Work Done and Energy TransferRegie Sacil EspiñaNo ratings yet
- Forces in Action: Work Done and Energy TransferDocument1 pageForces in Action: Work Done and Energy TransferRegie Sacil EspiñaNo ratings yet
- HydrodynamicDocument2 pagesHydrodynamicjulesjusayanNo ratings yet
- FBARDocument7 pagesFBARprabu1928No ratings yet
- 2Document2 pages2peach5No ratings yet
- LMR Final Physics 3.30 - RemovedDocument13 pagesLMR Final Physics 3.30 - RemovedEco DudeNo ratings yet
- Quantum PhysicsDocument3 pagesQuantum Physicsaashhs kechuoNo ratings yet
- Sistemas de GeneracionDocument9 pagesSistemas de GeneracionNestor ReyesNo ratings yet
- 15 - Wave MotionDocument40 pages15 - Wave MotionDeepakGuptaNo ratings yet
- General Familiarity With Other NDT Methods Module 1Document4 pagesGeneral Familiarity With Other NDT Methods Module 1wefewNo ratings yet
- Determining Specular Radiant Flux DistributionsDocument34 pagesDetermining Specular Radiant Flux DistributionsdomingocattoniNo ratings yet
- Falkner-Skan Boundary LayerDocument3 pagesFalkner-Skan Boundary Layerengineer bilalNo ratings yet
- QM Internal ExamDocument4 pagesQM Internal Exammadhutrivikram100% (2)
- S R, H B T: Olar Adiation EAT Alance AND EmperatureDocument9 pagesS R, H B T: Olar Adiation EAT Alance AND EmperatureLaila KhattakNo ratings yet
- Structural Dynamics - ESA 322 Lecture 2Document36 pagesStructural Dynamics - ESA 322 Lecture 2Purawin Subramaniam0% (1)
- Lecture Notes and Solved Examples (Unit-II-Part-Two)Document9 pagesLecture Notes and Solved Examples (Unit-II-Part-Two)Dame AyaneNo ratings yet
- Exam Chapter Wave and Vibration (A)Document2 pagesExam Chapter Wave and Vibration (A)Senny Ummu AlMuharrom100% (1)
- CE 137 - C - Final Exam Answers PDFDocument9 pagesCE 137 - C - Final Exam Answers PDFMarsolito PuaNo ratings yet
- EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 3 Waveguide/Fiber ModesDocument27 pagesEE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 3 Waveguide/Fiber Modeshema_swizNo ratings yet
- MEM311 Manual 09192014Document77 pagesMEM311 Manual 09192014Sam Yang SunNo ratings yet
- 2 Rad S: Applied ForceDocument2 pages2 Rad S: Applied Forcehehe ambosNo ratings yet
- 3 Laws of Motion Lesson Plan - KODIGODocument5 pages3 Laws of Motion Lesson Plan - KODIGODaniel LorioNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula SheetDocument4 pagesPhysics Formula SheetS S AcharyaNo ratings yet
- q8 Weather and ClimateDocument29 pagesq8 Weather and ClimateTrixie Mendoza SalvacionNo ratings yet
- Final TestDocument10 pagesFinal TestIndah KurniasihNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear VibrationDocument25 pagesNonlinear VibrationMohdQasimNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument17 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectBharath P JayanNo ratings yet
- Telescope Book HistoryDocument24 pagesTelescope Book HistoryMd Chand AsiqueNo ratings yet
- The Character of High-Frequency Strong Ground MotionDocument25 pagesThe Character of High-Frequency Strong Ground MotionJoel D. CruzNo ratings yet
- Method of Statement For RadiationDocument4 pagesMethod of Statement For RadiationFiras AlbaweiNo ratings yet