Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problems On Ducts 7oct
Problems On Ducts 7oct
Uploaded by
Akash Chandra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
97 views2 pagesThis document contains 3 problems related to air flow in duct systems. Problem 1 involves calculating velocities and pressure losses in a branching duct system. Problem 2 involves pressure losses through a reducer connecting two circular ducts. Problem 3 involves calculating the required static pressure at the start of a duct system involving changes in diameter and discharging to atmosphere.
Original Description:
Problems on Duct
Original Title
Problems on Ducts 7Oct
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains 3 problems related to air flow in duct systems. Problem 1 involves calculating velocities and pressure losses in a branching duct system. Problem 2 involves pressure losses through a reducer connecting two circular ducts. Problem 3 involves calculating the required static pressure at the start of a duct system involving changes in diameter and discharging to atmosphere.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
97 views2 pagesProblems On Ducts 7oct
Problems On Ducts 7oct
Uploaded by
Akash ChandraThis document contains 3 problems related to air flow in duct systems. Problem 1 involves calculating velocities and pressure losses in a branching duct system. Problem 2 involves pressure losses through a reducer connecting two circular ducts. Problem 3 involves calculating the required static pressure at the start of a duct system involving changes in diameter and discharging to atmosphere.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
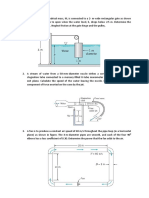
1.
The main air supply duct of an air-conditioning
system is 800 mm 600 mm in cross-section,
and carries 300 m3/min of standard air. It
branches in to two ducts of cross-section 600
mm 500 mm and 600 mm 400 mm. If the
mean velocity in the larger branch is 480 m/min,
find
i. mean velocity in the main duct and the
smaller branch
ii. mean velocity pressure in each duct in
mm of water.
2. A circular duct of 100 mm diameter converges
gradually to a 75 mm duct, as shown. The static
pressure just upstream of the reducer is 30 mm
of water and the velocity is 450 m/min. The loss
of pressure in the reducer is 0.1 of the velocity
head in the duct downstream of the reducer.
Calculate the total pressures upstream and
downstream of the reducer. Also determine the
pressure indicated by a U-tube water manometer
connected differentially to pressure tappings
upstream and downstream of the reducer.
3. The duct shown in the figure is supplied with air
at a velocity of 600 m/min in section AB, which is
0.6 m in diameter and 45 m in length.
The duct CD is 1.2 m in diameter and 150 m in
length and duct EF is 0.45 m in diameter and 15 m
in length. It discharges freely to atmosphere at F.
The loss in the expander BC is 0.5 times the velocity
pressure in duct AB and the loss in the reducer DE
is 0.2 times the velocity pressure in the duct EF.
Using the expression
0.263 V 1.85
pf
D1.27
where pf is the pressure loss due to friction in mm of
water per 100 m length of the duct, V is the duct
velocity in m/s and D is the diameter of the duct in
m, find the static pressure required at point A.
You might also like
- College of Engineering, Computer Studies and Architecture: Problem Sets in Hydraulics (HYDL01E)Document8 pagesCollege of Engineering, Computer Studies and Architecture: Problem Sets in Hydraulics (HYDL01E)Ria LauronNo ratings yet
- ATME4224 Tutorial 1Document2 pagesATME4224 Tutorial 1Pung Kang QinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 7Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 7AmyRapaNo ratings yet
- NHP Price Catalogue NZ PDFDocument873 pagesNHP Price Catalogue NZ PDFAkash Chandra100% (2)
- A Laminar Flow Is Taking Place in A Pipe of Diameter 200 MMDocument9 pagesA Laminar Flow Is Taking Place in A Pipe of Diameter 200 MMANBU RAJ ANo ratings yet
- 14 MarksDocument4 pages14 MarksmohanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Set 3 of CE (ES) 401 2023Document7 pagesAssignment Set 3 of CE (ES) 401 2023Kausik BeraNo ratings yet
- Bao HydrauDocument32 pagesBao HydrauNguyễn Tiến NghĩaNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii FLUID DYNAMICS: Surface and Body Forces, Concepts of Fluid System andDocument23 pagesUnit-Iii FLUID DYNAMICS: Surface and Body Forces, Concepts of Fluid System andyrajesh1050% (2)
- Plate 2 1Document2 pagesPlate 2 1Jersey PerlasNo ratings yet
- Soal Tugas BernoulliDocument7 pagesSoal Tugas BernoulliAnnisaNurulFadilahNo ratings yet
- 9A01304 Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pages9A01304 Fluid MechanicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- HW Hydraulics (setII) Ch3Document4 pagesHW Hydraulics (setII) Ch3Zairah Francisco100% (1)
- HW Hydraulics (SetII) Ch3Document4 pagesHW Hydraulics (SetII) Ch3Zairah FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pagesFluid MechanicsTemesgen DemessieNo ratings yet
- Tutorial DuctDocument2 pagesTutorial DuctSodha PujanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Set 2 of CE (ES) 401 2023Document7 pagesAssignment Set 2 of CE (ES) 401 2023Kausik BeraNo ratings yet
- Ge 13Document1 pageGe 13Hasib SaripadaNo ratings yet
- ECW 231 Tutorial and Answers Continuity and Energy Eqn and Their Applications - Sept19Document8 pagesECW 231 Tutorial and Answers Continuity and Energy Eqn and Their Applications - Sept19hairinnisaNo ratings yet
- B Tech Mechanical QuestionsDocument11 pagesB Tech Mechanical QuestionsAnkita VermaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids and Fluids (MEE1032) : U y /3+2x-x y V Xy - 2y-X /3Document1 pageMechanics of Solids and Fluids (MEE1032) : U y /3+2x-x y V Xy - 2y-X /3AllNo ratings yet
- Water QuestionsDocument1 pageWater QuestionshhhhNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Flow and Hydraulics Part 2Document16 pagesFundamentals of Flow and Hydraulics Part 2John CastilloNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fluids Nov / Dec 2013 Important Questions Unit - IDocument5 pagesMechanics of Fluids Nov / Dec 2013 Important Questions Unit - IjvinothupendraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document2 pagesTutorial 4gokul virat0% (1)
- 9A01304 Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pages9A01304 Fluid MechanicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- MTO - PROBLEM - SHEETS - 2and 3Document5 pagesMTO - PROBLEM - SHEETS - 2and 3MOHIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument5 pagesHydraulicsMark Daryl Lopez Billedo100% (1)
- Soal Tambah Nilai Mekflu1 - QuestionsDocument2 pagesSoal Tambah Nilai Mekflu1 - QuestionsAnonymous gJAiNqqe29No ratings yet
- FM Assignment 2Document8 pagesFM Assignment 2jayakumarNo ratings yet
- Sheet (1) Fluid Mechanics 2Document6 pagesSheet (1) Fluid Mechanics 2drawanyNo ratings yet
- Q Assignment 2Document3 pagesQ Assignment 2Vikneswaran NathanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Bernoulli Equation Part 2Document2 pagesTutorial Bernoulli Equation Part 2Muhamad Hazim ZaabaNo ratings yet
- PipeFlow PracticeProblemsDocument23 pagesPipeFlow PracticeProblemsFawaz PartoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 QuestionsDocument2 pagesTutorial 4 QuestionsJiNx AngNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Question BankDocument8 pagesFluid Mechanics and Machinery Question BankGnana Subramanian ArumugamNo ratings yet
- BernaulliDocument6 pagesBernaulliCamille SemillaNo ratings yet
- Advance Fluid Mechanics TurorialDocument2 pagesAdvance Fluid Mechanics Turorialpinakramanuj11150% (2)
- Assignment 4 MEC 207Document7 pagesAssignment 4 MEC 207Praveen SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aalim Muhammed Salegh College of Engineering Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument6 pagesAalim Muhammed Salegh College of Engineering Department of Mechanical EngineeringMaran ElangovanNo ratings yet
- Unit: V-Flow Through PipesDocument28 pagesUnit: V-Flow Through PipesEyob AdNo ratings yet
- VL2017185001350 DaDocument2 pagesVL2017185001350 DaHarsh SoniNo ratings yet
- ES 65 Drill 2Document2 pagesES 65 Drill 2edmark icalina100% (1)
- Hvac Ducting SystemsDocument8 pagesHvac Ducting SystemsPandaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Questions FMDocument2 pagesUnit 2 Questions FMrajasekarNo ratings yet
- Sent Tutorial 5 Prob OnlyDocument2 pagesSent Tutorial 5 Prob OnlyYu LoengNo ratings yet
- Review Chem Eng3 Flow of Fluids PDFDocument4 pagesReview Chem Eng3 Flow of Fluids PDFOwenPonceUmacobNo ratings yet
- FluidDocument1 pageFluidMahmoud Abo ElhamdNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Fluid Mechanics Ii - 030410041152 - 1Document11 pagesQuestion Bank For Fluid Mechanics Ii - 030410041152 - 1Bharath Waj100% (1)
- Mech 422 Problem Sets Fluid MachineriesDocument7 pagesMech 422 Problem Sets Fluid MachineriesMarvin LabajoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics, Lec (Pce 13 - M) : Bernoulli'S Energy TheoremDocument4 pagesHydraulics, Lec (Pce 13 - M) : Bernoulli'S Energy TheoremJersey PerlasNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Part 2 Ready To Print CE PaperDocument15 pagesProblem Set Part 2 Ready To Print CE PaperJeffward Jaguio0% (1)
- Past ExamDocument16 pagesPast ExamAlex ChungNo ratings yet
- Test On Fluid MechanicsDocument11 pagesTest On Fluid MechanicsJonathan GreenNo ratings yet
- Prob Set 1Document2 pagesProb Set 1ChristianNo ratings yet
- Assignments HydraulicsDocument3 pagesAssignments Hydraulicsjayadevakodi100% (1)
- Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandElectricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Creta GLDocument1 pageHyundai Creta GLAkash ChandraNo ratings yet
- MacEwans Dinflow Instructions 2019Document10 pagesMacEwans Dinflow Instructions 2019Akash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Output Ratings Ratings and Performance Data: 65.0 kVA 52.0 KW 72.0 kVA 57.6 KWDocument4 pagesOutput Ratings Ratings and Performance Data: 65.0 kVA 52.0 KW 72.0 kVA 57.6 KWAkash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Solar Water Pumping Guidelines V1Document68 pagesSolar Water Pumping Guidelines V1Akash Chandra100% (1)
- List of Generator PartsDocument1 pageList of Generator PartsAkash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Sewer GEMSDocument260 pagesSewer GEMSAkash Chandra100% (1)
- Mm392 Lab 3 - Scheduling: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesMm392 Lab 3 - Scheduling: ObjectivesAkash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Schneider CatalogueDocument190 pagesSchneider CatalogueAkash ChandraNo ratings yet
- IWE Report Template Updated May 2008Document9 pagesIWE Report Template Updated May 2008Akash ChandraNo ratings yet
- STRC201 Sdof JMWB PDFDocument99 pagesSTRC201 Sdof JMWB PDFAkash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Tidal PowerDocument26 pagesTidal PowerAkash ChandraNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal NotesDocument56 pagesSheet Metal NotesAkash Chandra100% (1)
- PMP Marking Rubric For EEDocument2 pagesPMP Marking Rubric For EEAkash ChandraNo ratings yet
- CV Template Finance Bank TellerDocument2 pagesCV Template Finance Bank TellerWemmy TakaNo ratings yet
- Plastics QDocument1 pagePlastics QAkash ChandraNo ratings yet