Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M SC Entrance (Geology) - Panjab University 2013 (Key)
M SC Entrance (Geology) - Panjab University 2013 (Key)
Uploaded by
RavikanthOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
M SC Entrance (Geology) - Panjab University 2013 (Key)
M SC Entrance (Geology) - Panjab University 2013 (Key)
Uploaded by
RavikanthCopyright:
Available Formats
CET (PG)-2013
Question Booklet Series : A/B/C/D Sr. No. :
Important : Please consult your Admit Card / Roll No. Slip before filling your Roll Number on the Test Booklet
and Answer Sheet.
Roll No. In Figures In Words In Words
O.M.R. Answer Sheet Serial No.
Signature of the Candidate :
Subject : M.Sc.(Hons. School/2 Year Course)Geology
Time : 90 minutes Number of Questions : 75 Maximum Marks : 75
DO NOT OPEN THE SEAL ON THE BOOKLET UNTIL ASKED TO DO SO
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Write your Roll No. on the Question Booklet and also on the OMR Answer Sheet in the space provided
and nowhere else.
2. Enter the Subject and Series Code of Question Booklet on the OMR Answer Sheet. Darken the corresponding
bubble with Black Ball Point /Black Gel pen.
3. Do not make any identification mark on the Answer Sheet or Question Booklet.
4. To open the Question Booklet remove the paper seal (s) gently when asked to do so.
5. Please check that this Question Booklet contains 75 questions. In case of any discrepancy, inform the
Assistant Superintendent within 10 minutes of the start of test.
6. Each question has four alternative answers (A, B, C, D) of which only one is correct. For each question,
darken only one bubble (A or B or C or D), whichever you think is the correct answer, on the Answer Sheet
with Black Ball Point / Black Gel pen.
7. If you do not want to answer a question, leave all the bubbles corresponding to that question blank in the
Answer Sheet. No marks will be deducted in such cases.
8. Darken the bubbles in the OMR Answer Sheet according to the Serial No. of the questions given in the
Question Booklet.
9. Negative marking will be adopted for evaluation i.e., 1/4th of the marks of the question will be deducted for each
wrong answer. A wrong answer means incorrect answer or wrong filling of bubble.
10. For calculations, use of simple log tables is permitted. Borrowing of log tables and any other material is not allowed.
11. For rough work only the sheets marked Rough Work at the end of the Question Booklet be used.
12. The Answer Sheet is designed for computer evaluation. Therefore, if you do not follow the instructions
given on the Answer Sheet, it may make evaluation by the computer difficult. Any resultant loss to the
candidate on the above account, i.e., not following the instructions completely, shall be of the
candidate only.
13. After the test, hand over the Question Booklet and the Answer Sheet to the Assistant Superintendent on duty.
14. In no case the Answer Sheet, the Question Booklet, or its part or any material copied/noted from this
Booklet is to be taken out of the examination hall. Any candidate found doing so, would be expelled from
the examination.
15. A candidate who creates disturbance of any kind or changes his/her seat or is found in possession of any
paper possibly of any assistance or found giving or receiving assistance or found using any other unfair
means during the examination will be expelled from the examination by the Centre Superintendent /
Observer whose decision shall be final.
16. Telecommunication equipment such as pager, cellular phone, wireless, scanner, etc., is not
permitted inside the examination hall. Use of calculators is not allowed.
M.Sc. (Hons. School/2 Year Course)Geology/BZL/48987-A 2
M.Sc.(Hons. School/2 Year Course)Geology/A
1. The Moho discontinuity is considered to be a boundary between :
(A) Sial and Sima (B) Crust and mantle
(C) Mantle and Core (D) Inner core and Outer core
2. A Crescentshaped dune with horns pointing downwind is known as :
(A) Barchan (B) Monadnock
(C) Pedestal rock (D) Loess
3. A coral platform connected to the coast is called :
(A) Fringing reef (B) Barrier reef
(C) Atoll (D) Lagoon
4. A pelagic deposit rich in organic material and present in deep ocean zone is :
(A) Ooze (B) Terrigenous deposit
(C) Loess (D) Reef
5. Submerged Valleys having downcutting below the sea level are designated as :
(A) Gorges (B) Antecedent
(C) Fjords (D) Braided
6. The crystal system having three unequal axes at right angles constitutes :
(A) Cubic (B) Hexagonal
(C) Orthorhombic (D) Tetragonal
7. The symmetry of the Tetrahedrite class is :
(A) 6 planes, 7 axes, no centre (B) 3 planes, 7 axes, a centre
(C) 5 planes, 5 axes, no centre (D) 9 planes, 13 axes, no centre
8. A series of faces on a crystal whose intersection lines are mutually parallel to each other
comprises a :
(A) Form (B) Zone
(C) Zone axis (D) Face
9. Which one of the following is known as Brittle mica :
(A) Chlorite (B) Lepidolite
(C) Asbestos (D) Chloritoid
M.Sc. (Hons. School/2 Year Course)Geology/BZL/48987-A 3 [Turn over
10. Chemically the difference between feldspars and feldspathoids is that the former contains
more of :
(A) Na 2O (B) SiO2
(C) K 2O (D) Al2O3
11. The function of polariser in the petrological microscope is to :
(A) Increase the intensity of light (B) Convert the vibration of light in one plane
(C) Enable better focussing (D) Filter the light
12. A metallic mineral shows a greyish black colour, hardness 56, sp. gravity about 5 and
cherry-red streak. The mineral may be identified as :
(A) Pyrrhotite (B) Magnetite
(C) Hematite (D) Galena
13. The mineral allanite belongs to/is a variety of :
(A) Sphene (B) Epidote
(C) Garnet (D) Corundum
14. Jasper is a form of silica which is :
(A) Crystalline (B) Amorphous
(C) Cryptocrystalline (D) Fibrous
15. The diastrophic processes are best explained by :
(A) Intrusion of magma (B) Metamorphism
(C) Plate tectonics (D) Continental drift
16. An acidic magma is one which is saturated with :
(A) Acid vapours (B) Chlorides
(C) Alumina (D) Silica
17. The eutectic proportion for Orthoclase : Quartz pair of minerals is :
(A) 45 : 55 (B) 70 : 30
(C) 42.5 : 57.5 (D) 72.5 : 27.5
18. (C.P : Calcic plagioclase; C.A. P, : Calcalkali plagioclase; A.P : Alkali plagioclase;
A.C.P : AlkaliCalc plagioclase and P.F : potash feldspar)
The sequence of Bowen's continuous reaction series is :
(A) P.F C.A.P AP ACP CP (B) CP ACP CAP PF AP
(C) CAP CP PF AP ACP (D) CP CAP ACP AP PF
M.Sc. (Hons. School/2 Year Course)Geology/BZL/48987-A 4
19. Which of the following is comparatively regional high grade metamorphic rock ?
(A) Marble (B) Schist
(C) Slate (D) Phyllite
20. Manganese ore deposits in India are largely found in :
(A) M.P (B) Rajasthan
(C) Bihar (D) Haryana
21. When groundwater flows from gravel into sand, its rate of flow will :
(A) Decrease (B) Increase
(C) Remain unchanged (D) Difficult to comment
22. A rock containing about 50% pyroxene and 50% olivine may be designated as :
(A) Gabbro (B) Peridotite
(C) Amphibolite (D) Diorite
23. In ocean, the manganese nodules are generally located in the :
(A) Ocean floor (B) Continental shelf
(C) Continental slope (D) Bathyal zone
24. Mark the odd one out :
(A) Iceberg (B) Scree
(C) Marine (D) Cirque
25. A toposheet has a scale of 1 : 50,000. This scale can be stated as :
(A) 1 cm to 1 km (B) 2 cm to 1 km
(C) 3 cm to 1 km (D) 4 cm to 1 km
26. A nonconformity is a kind of unconformity in which the older rock is of :
(A) Metamorphic origin (B) Sedimentary origin
(C) Plutonic origin (D) Volcanic origin
27. The earth was dominated by reptiles during the Mesozoic era which is about ?
(A) 60 170 m.y. back (B) 5000 10,000 y. back
(C) 170 500 m.y. back (D) Over 600 m.y. back
28. Who said : "Present is the key to the past" ?
(A) Sutton (B) Newton
(C) Medlicott (D) Hutton
M.Sc. (Hons. School/2 Year Course)Geology/BZL/48987-A 5 [Turn over
29. Graben structure is related to which river of India ?
(A) Satluj (B) Indus
(C) Narmada (D) Ghaggar
30. The Punjab and Kumaon Himalayas are separated by river :
(A) Satluj (B) Ganges
(C) Indus (D) Chenab
31. Which of the following does not come under the principles of stratigraphy ?
(A) Lithification (B) Lithology
(C) Fossil content (D) Order of superposition
32. In terms of geological time which are in the correct order of longer to shorter duration ?
(A) PeriodEraEpochAge (B) Era EpochAgePeriod
(C) EraPeriodEpochAge (D) EpochAgePeriodEra
33. Kioto Limestone belongs to which geological system ?
(A) Jurassic (B) Permian
(C) Cretaceous (D) Devonian
34. A granite occurring in the Nilgiri massif has distinct character and contains an ortho
pyroxene and is known as :
(A) Singhbhum Granite (B) Charnockite
(C) Closepet Granite (D) Peninsular Gneiss
35. Of the following, which one is considered to be the youngest ?
(A) Erinpura Granite (B) Delhi System
(C) Peninsular Gneiss (D) Closepet Granite
36. Which of the series of the Vindhyan System contains good quality limestone and supports
the cement industry ?
(A) Bhander (B) Rewa
(C) Kaimur (D) Semri
37. The diamond bearing conglomerates separating the rock units in Panna, belong to :
(A) Upper Vindhyans (B) Lower Vindhyans
(C) Cuddapahs (D) Aravallies
38. The Caledonian Orogeny marks the end of :
(A) Cambrian (B) Ordovician
(C) Silurian (D) Devonian
M.Sc. (Hons. School/2 Year Course)Geology/BZL/48987-A 6
39. The term Adamellite is used for a rock containing :
(A) Plagioclase in excess of orthoclase
(B) Plagioclase and orthoclase in equal amounts
(C) Plagioclase is far less than Orthoclase
(D) Plagioclase and felspathoids
40. The range of fine sand is between :
(A) 0.51.00 mm (B) 1.00 2.00 mm
(C) 0.1 0.25 mm (D) 0.01 0.1 mm
41. Rudaceous rocks consist chiefly of :
(A) Clay grade material (B) Gravels to cobbles etc.
(C) Sand grade material (D) Silt grade material
42. Tillite is hardened boulder clay and is indicative of depositional environment of :
(A) Wind (B) river
(C) Glacier (D) Lake
43. The rock consisting of minute spherical or ellipsoidal grains of calcium carbonate is
called :
(A) Oolite (B) Pisolite
(C) Marble (D) Carbonatite
44. The organosedimentary structures may occur in :
(A) Coral reefs (B) Limestones
(C) Radiolarian ooze (D) Coal seams
45. Which one of the following rocks belongs to higher grade of metamorphism ?
(A) Glaucophane schist (B) Sericiteepidote phyllite
(C) Cordierite gneiss (D) Garnetmica schist
46. The contact metamorphism of siliceous limestone may produce :
(A) Wollastonite (B) Dolomite
(C) Muscovite (D) Glauconite
47. The line of maximum curvature in a folded structure is designated as :
(A) Limp (B) Dip
(C) Hinge (D) Axialplane
M.Sc. (Hons. School/2 Year Course)Geology/BZL/48987-A 7 [Turn over
48. Fenestella fossil occurring in Devonian of Spiti is a :
(A) Brachiopod (B) Trilobite
(C) Bryozon (D) Graptolite
49. Spirifer, a brachiopod is characterized by a hinge line which is :
(A) Straight and short (B) Curved and short
(C) Straight and long (D) Curved and long
50. The living representative of brachiopod is :
(A) Productus (B) Lingula
(C) Derbiya (D) Athyris
51. In the twofold classification of Gondwana Group, the upper Gondwana is characterized
by the flora :
(A) Ptilophyllum (B) Glossopteris
(C) Gangamopteris (D) Schizoneura
52. In which one of the following leaf plant fossils, mid sib is present ?
(A) Glossopteris (B) Gangamopteris
(C) Sphenophyllum (D) Schizoneura
53. The classification of Lamellibranchia is based on :
(A) Dentition (B) Umbo
(C) Adductor impression (D) Pallial line
54. The living cephalopoda is :
(A) Baculites (B) Ceratites
(C) Goniatites (D) Nautilus
55. The volcanic equivalent of plutonic rock granodiorite is :
(A) Andesite (B) Phyolite
(C) Trachyte (D) Dacite
56. The increasing grade of metamorphism of shale will give rise to which sequence of
metamorphism rocks ?
(A) Phylliteschistslategneiss (B) Gneissslateschistphyllite
(C) Slateschistphyllitegneiss (D) Slatephylliteschistgneiss
M.Sc. (Hons. School/2 Year Course)Geology/BZL/48987-A 8
57. Which of the following minerals develop under high pressure and low temperature
conditions of metamorphism ?
(A) Tremolite (B) Kyanite
(C) Hornblende (D) Glaucophene
58. The rocks affected by contact metamorphism are termed as :
(A) Hornfels (B) Hornstones
(C) Honestones (D) Mylonites
59. The trilobites are the characteristic fossils of the strata belonging to the :
(A) Palaeozoics (B) Merozoics
(C) Tertiary (D) Quaternaries
60. Which of the following minerals shows resinous lusture :
(A) Satinspar (B) Diamond
(C) Galena (D) Opal
61. The bearing of point B from A is 130. The bearing of A from B will be :
(A) S 50 E (B) S 40 W
(C) N 40 E (D) N 50 W
62. New crust is generated at :
(A) Midoceanic ridge (B) Subduction zone
(C) Island arc (D) Plume
63. Which one of the following has good porosity and is impermeable ?
(A) Sandstone (B) Clay
(C) Granite (D) Conglomerate
64. The net slip of a fault is parallel to the strike of the fault. The fault may be designated
as :
(A) Normal fault (B) Wrench fault
(C) Reverse fault (D) Thrust fault
65. In terms of plate tectonics the Indian plate boundary lies near :
(A) Main Boundary Fault (B) Satluj river
(C) Indus river (D) Main Central Thrust
66. Which of the following gastropods shows sinisteral coiling ?
(A) Bellerophon (B) Conus
(C) Murex (D) Physa
M.Sc. (Hons. School/2 Year Course)Geology/BZL/48987-A 9 [Turn over
67. Ophitic texture is a kind of :
(A) Felsitic texture (B) Granitic texture
(C) Directive texture (D) Poiklitic texture
68. A crystal belonging to holohedral class has one plane of symmetry, one axis of symmetry
and a centre of symmetry, it belongs to :
(A) Isometric system (B) Triclinic system
(C) Tetragonal system (D) Monoclinic system
69. In a biaxial optically positive mineral :
(A) Z forms acute bisectrix (B) X forms acute bisectirx
(C) Optic axial angle large (D) Optic axial angle small
70. Diamond occurs in the rock of :
(A) Hydrothermal origin (B) Magmatic origin
(C) Sedimentary origin (D) Metamorphic origin
71. The mineral used for the manufacture of fireproof cloth, insulators and points :
(A) Barites (B) Gypsum
(C) Fluorspar (D) Asbestos
72. The texture generally observed in lamprophyres is described as :
(A) Hypidiomorphic (B) Panidiomorphic
(C) Allotriomorphic (D) Vitrophyric
73. Which of the following is the ratio of Si : Al in cyclosilicates ?
(A) 1 : 1 (B) 1 : 3
(C) 4 : 11 (D) 2 : 5
74. In which of the following zones of the earth, P and S seismic waves attain maximum
velocities ?
(A) Crust (B) Upper Mantle
(C) Lower Mantle (D) Core
75. Which of the following minerals is the most predominant in syenite ?
(A) Ouartz (B) Nepheline
(C) Plagioclase (D) Alkali Feldspar
M.Sc. (Hons. School/2 Year Course)Geology/BZL/48987-A 10
ROUGH WORK
M.Sc. (Hons. School/2 Year Course)Geology/BZL-48987/A 11
ROUGH WORK
M.Sc. (Hons. School/2 Year Course)Geology/BZL/48987-A 12 36
Panjab University, Chandigarh
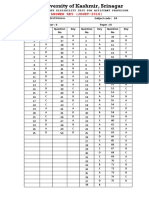
CET(PG)-2013
ANSWERS / KEY
Subject: MSc(HS)(Geology)
Booklet Series Code: A
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
B A A A C C A B D B
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
B C B C C D D D B A
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
A B D B B C A D C A
31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
A C A B A D A C B C
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
B C A B C A C C C B
51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
A A A D D D D A A D
61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70
D A B B C D D D A B
71 72 73 74 75
A B B C D
Note: An 'X' in the key indicates that either the question is ambiguous or it has
printing mistake. All candidates will be given credit for this question.
Page 26
You might also like
- Geography Ss1 3Document9 pagesGeography Ss1 3kolapo feyisetanNo ratings yet
- Earth System History 4th Edition Stanley Test Bank DownloadDocument7 pagesEarth System History 4th Edition Stanley Test Bank DownloadAnthony Turner100% (13)
- Mineralogy MCQs With AnswerDocument11 pagesMineralogy MCQs With Answerkumar Harsh100% (8)
- BAYLOR 7040 166-54238 Rev FDocument68 pagesBAYLOR 7040 166-54238 Rev FPablo Galvez Rodriguez100% (4)
- GG 2005Document21 pagesGG 2005Ratan DasNo ratings yet
- 345 Set-ADocument32 pages345 Set-A82 C SushantNo ratings yet
- GATE 2012 Online Examination GG: Geology and Geophysics: Read The Following Instructions CarefullyDocument18 pagesGATE 2012 Online Examination GG: Geology and Geophysics: Read The Following Instructions Carefullysofeyo8No ratings yet
- GeologyDocument19 pagesGeologySurendran P SurendranNo ratings yet
- GATE 2012 Online Examination GG: Geology and Geophysics: Read The Following Instructions CarefullyDocument18 pagesGATE 2012 Online Examination GG: Geology and Geophysics: Read The Following Instructions CarefullySumit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 609 GeologyDocument27 pages609 GeologySurendran P SurendranNo ratings yet
- GG 2011Document27 pagesGG 2011acNo ratings yet
- Geology Pre 2013Document16 pagesGeology Pre 2013Tech factsNo ratings yet
- Q. 1 - Q. 20 Carry One Mark Each.: GATE Question Papers: Geology and Geophysics 2007 (GG)Document9 pagesQ. 1 - Q. 20 Carry One Mark Each.: GATE Question Papers: Geology and Geophysics 2007 (GG)Lalit JoshiNo ratings yet
- Iit Jam 2021 QPDocument17 pagesIit Jam 2021 QPRomeo Davidson0% (1)
- Geology Question Bank: Answer: DDocument17 pagesGeology Question Bank: Answer: DReham El-sawy100% (1)
- EarthDocument2 pagesEarthStammering MathematicianNo ratings yet
- Neet 19 - Class XiiDocument3 pagesNeet 19 - Class Xiisabatsuhani74No ratings yet
- Class - IX - Chap - Lithosphere - I & IIDocument3 pagesClass - IX - Chap - Lithosphere - I & IIVPNNo ratings yet
- Universe Question Bank (Introduction) : Physics PhysicsDocument2 pagesUniverse Question Bank (Introduction) : Physics Physicsanon_50109362No ratings yet
- KAS Geography Prelims 2010Document16 pagesKAS Geography Prelims 2010mohdahmed12345No ratings yet
- Gate 2015Document16 pagesGate 2015RANGEQUITNo ratings yet
- GATE Geology Paper 2015Document11 pagesGATE Geology Paper 2015Debanga BoruahNo ratings yet
- GATE Geology 2007Document14 pagesGATE Geology 2007Sumit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Class 5 0Document4 pagesClass 5 0Monika SinghalNo ratings yet
- 120 Minutes: Not True of GPS?Document13 pages120 Minutes: Not True of GPS?ditikrishna001No ratings yet
- Crystallography and MineralogyDocument40 pagesCrystallography and MineralogyAmit RajNo ratings yet
- GG: Geology and Geophysics: Duration: Three HoursDocument20 pagesGG: Geology and Geophysics: Duration: Three HoursSumit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- GG 2007Document9 pagesGG 2007Ratan DasNo ratings yet
- Geophysics Test PaperDocument15 pagesGeophysics Test PaperRavi RamineniNo ratings yet
- GEOLVICC21Document5 pagesGEOLVICC21Isaac LalHriat ZauvaNo ratings yet
- Combined Competitive (Preliminary) Examination, 2013: Geography Code No. 09Document16 pagesCombined Competitive (Preliminary) Examination, 2013: Geography Code No. 09Milan TiwariNo ratings yet
- 1584343308IIT JAM GEO QuesDocument15 pages1584343308IIT JAM GEO QuesA common people Residence of JadavpurNo ratings yet
- Mportant Nstructions: Class - 8 (VIII)Document9 pagesMportant Nstructions: Class - 8 (VIII)Mrityunjay SethNo ratings yet
- GG: Geology and Geophysics: ONLINE ExaminationDocument21 pagesGG: Geology and Geophysics: ONLINE ExaminationSumit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CBRT 50 Asst Hydrogeo 20 10 19 FNDocument22 pagesCBRT 50 Asst Hydrogeo 20 10 19 FNdpNo ratings yet
- June 2013 PAPER III RE-EXAMDocument12 pagesJune 2013 PAPER III RE-EXAMRavi DixitNo ratings yet
- Malaysian Earth Science Olympiad - Set 3Document5 pagesMalaysian Earth Science Olympiad - Set 3Lee Sun TaiNo ratings yet
- Earth System History 4th Edition Stanley Test BankDocument8 pagesEarth System History 4th Edition Stanley Test Bankjennifercortezmcnpsjtiek100% (27)
- ? Carl Ritter Hartshorn. HumboldtDocument9 pages? Carl Ritter Hartshorn. HumboldtBindiya Priyadarshani BeheraNo ratings yet
- GATE Geology 2007Document14 pagesGATE Geology 2007saurabh sharmaNo ratings yet
- CN134 Geology For Civil Engineers 1: Semester 2 Examinations June 2014Document8 pagesCN134 Geology For Civil Engineers 1: Semester 2 Examinations June 2014dandewjangerNo ratings yet
- First Quarter ExamDocument3 pagesFirst Quarter ExamJunard AsentistaNo ratings yet
- IESO SubjectDocument17 pagesIESO SubjectCatalin ChirilaNo ratings yet
- Your Name: Please Mark Your AnswersDocument5 pagesYour Name: Please Mark Your AnswersBal KrishnaNo ratings yet
- IIT JAM 2012 Paper GeophysicsDocument63 pagesIIT JAM 2012 Paper GeophysicsacNo ratings yet
- Geology MCQ Test PaperDocument4 pagesGeology MCQ Test PaperWajid HussainNo ratings yet
- SAT Test-03 Class-9th QuestionsDocument4 pagesSAT Test-03 Class-9th Questionsrajeshd231No ratings yet
- AMU Geo PYQ PapersDocument73 pagesAMU Geo PYQ PapersApurva RaiNo ratings yet
- Geology JAM 2018 QP PDFDocument13 pagesGeology JAM 2018 QP PDFH.V. PatilNo ratings yet
- Class 7 2Document4 pagesClass 7 2Afshiya AnjumNo ratings yet
- Ebook SSC CGL Geography Q&A - Last 5 YearsDocument18 pagesEbook SSC CGL Geography Q&A - Last 5 YearsSky DriveNo ratings yet
- NTSE Kerala 2018 Question Paper With Answer Key SATDocument12 pagesNTSE Kerala 2018 Question Paper With Answer Key SATKaviNo ratings yet
- Bansal Classes Class 9 Sample Question PaperDocument8 pagesBansal Classes Class 9 Sample Question PaperJeetu RaoNo ratings yet
- Duration: 2 Hrs. - Maximum Marks: 180 Class - IX (Going To X)Document10 pagesDuration: 2 Hrs. - Maximum Marks: 180 Class - IX (Going To X)Sandeep RevliyaNo ratings yet
- Entrance Test Question Paper Jan 2010Document12 pagesEntrance Test Question Paper Jan 2010Sachin ChakradharNo ratings yet
- M.S 1Document21 pagesM.S 1Sakkeer A VNo ratings yet
- Q. 1 Q. 5 Carry One Mark Each.: GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-8Document21 pagesQ. 1 Q. 5 Carry One Mark Each.: GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-8bijay kanti biswasNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Solid State Gujcet PyqDocument19 pagesCh-1 Solid State Gujcet PyqWhoaretoNo ratings yet
- 1-EDT 01 - Physics and ChemistryDocument7 pages1-EDT 01 - Physics and ChemistryRavikanthNo ratings yet
- Answer Key (Jkset-2016)Document1 pageAnswer Key (Jkset-2016)RavikanthNo ratings yet
- Answer Key (Jkset-2016) : J&K State Eligibility Test ForDocument1 pageAnswer Key (Jkset-2016) : J&K State Eligibility Test ForRavikanthNo ratings yet
- 20 Home ScienceDocument1 page20 Home ScienceRavikanthNo ratings yet
- Answer Key (Jkset-2016)Document1 pageAnswer Key (Jkset-2016)RavikanthNo ratings yet
- Answer Key (Jkset-2016)Document1 pageAnswer Key (Jkset-2016)RavikanthNo ratings yet
- 17 GeographyDocument1 page17 GeographyRavikanthNo ratings yet
- 12 Economics PDFDocument1 page12 Economics PDFRavikanthNo ratings yet
- Answer Key (Jkset-2016)Document1 pageAnswer Key (Jkset-2016)RavikanthNo ratings yet
- Answer Key (Jkset-2016)Document1 pageAnswer Key (Jkset-2016)RavikanthNo ratings yet
- 10 Computer ScienceDocument1 page10 Computer ScienceRavikanthNo ratings yet
- Answer Key (Jkset-2016) : J&K State Eligibility Test For Assistant ProfessorDocument1 pageAnswer Key (Jkset-2016) : J&K State Eligibility Test For Assistant ProfessorRavikanthNo ratings yet
- 3 Life SciencesDocument1 page3 Life SciencesRavikanth100% (1)
- Answer Key (Jkset-2016)Document1 pageAnswer Key (Jkset-2016)RavikanthNo ratings yet
- 4 Mathematical ScienceDocument1 page4 Mathematical ScienceRavikanthNo ratings yet
- Research Process - StepsDocument31 pagesResearch Process - StepsPulkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Memory Addressing and Instruction FormatsDocument9 pagesMemory Addressing and Instruction Formatsrobern ndoloNo ratings yet
- 9 tribologyofGO-UHWMPEDocument10 pages9 tribologyofGO-UHWMPEA P BNo ratings yet
- NXF Perforated Cable Tray en 2017Document65 pagesNXF Perforated Cable Tray en 2017LANKAPALLISURINo ratings yet
- Soal B.ing LM Xii IpaDocument26 pagesSoal B.ing LM Xii IpaGuruh SasmitaNo ratings yet
- M.C.Qs On Indus Valley CivilizationDocument3 pagesM.C.Qs On Indus Valley CivilizationRekha MishraNo ratings yet
- Hi Alex, Do You Have Any More Questions or We Can Close The CSR? Thank You, Best Regards, ViktorDocument13 pagesHi Alex, Do You Have Any More Questions or We Can Close The CSR? Thank You, Best Regards, ViktorMario ParkerNo ratings yet
- Anyone Who Had A Heart - A Case Study in PhysiologyDocument9 pagesAnyone Who Had A Heart - A Case Study in PhysiologyJohnSnow0% (1)
- IT 16 - Neurogenic Bladder - SMDocument31 pagesIT 16 - Neurogenic Bladder - SMRurie Awalia SuhardiNo ratings yet
- TUGAS INDIVIDU - 3-01 - 18 - Manajemen Keuangan - Mind Map CH 15Document1 pageTUGAS INDIVIDU - 3-01 - 18 - Manajemen Keuangan - Mind Map CH 15Ni Made Indah MeliawatiNo ratings yet
- Chap 1-5 NotesDocument14 pagesChap 1-5 NotesBismah SaleemNo ratings yet
- Defining Organisational PoliticsDocument10 pagesDefining Organisational PoliticsAnonymous yy8In96j0rNo ratings yet
- Detergent Flushing of Pre Boiler System-Procedure 250Document11 pagesDetergent Flushing of Pre Boiler System-Procedure 250Sara LopezNo ratings yet
- 1 Esdras (Ezra)Document20 pages1 Esdras (Ezra)Remus CalinaNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance of Developed Materials: Heidee F. Ferrer EddDocument60 pagesQuality Assurance of Developed Materials: Heidee F. Ferrer EddHeart SophieNo ratings yet
- Relate Tables, Graphs, and Equations: BatchesDocument2 pagesRelate Tables, Graphs, and Equations: Batchesahmeeeeeeeeee.expmdNo ratings yet
- Finished Goods Inventories XX Work in Progress XX To Record The Completed JobDocument6 pagesFinished Goods Inventories XX Work in Progress XX To Record The Completed JobClarissa TeodoroNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Teaching English To Tuna Grahita Students: Difficulties and ChallengesDocument75 pagesAn Analysis of Teaching English To Tuna Grahita Students: Difficulties and ChallengesPutri PutriNo ratings yet
- Abortion - A Philosophical Perspective: OpsommingDocument7 pagesAbortion - A Philosophical Perspective: OpsommingGeorge RaresNo ratings yet
- TF2105 Rangkaian Listrik Dan Elektronika: Dr. Suprijanto ST MT, IPM (SP)Document23 pagesTF2105 Rangkaian Listrik Dan Elektronika: Dr. Suprijanto ST MT, IPM (SP)Gilbert SihombingNo ratings yet
- Instructions / Checklist For Filling KYC FormDocument19 pagesInstructions / Checklist For Filling KYC FormPankaj KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Clear Choice: TurbomatrixDocument10 pagesClear Choice: TurbomatrixSaleh HamadanyNo ratings yet
- Assesment BMDocument7 pagesAssesment BMTeja GajjarNo ratings yet
- Numerically Based Analysis of Buried GRPDocument8 pagesNumerically Based Analysis of Buried GRPjeovanNo ratings yet
- System Path VariablesDocument5 pagesSystem Path VariablesUnessNo ratings yet
- LA SpecificationDocument3 pagesLA SpecificationVino VinoNo ratings yet
- Math InterventionDocument6 pagesMath InterventionPAOLO R. ALARDENo ratings yet
- Rt7010 Lighting of Railway Premises PDFDocument17 pagesRt7010 Lighting of Railway Premises PDFCezary P.No ratings yet
- Fernerkundungsbasierte, Automatisierte, Multisensorale Brandflächendetektion Im Kruger National Park, SüdafrikaDocument151 pagesFernerkundungsbasierte, Automatisierte, Multisensorale Brandflächendetektion Im Kruger National Park, SüdafrikawurstomanNo ratings yet