Professional Documents
Culture Documents
I Important Rem Nders: A Due To On A
I Important Rem Nders: A Due To On A
Uploaded by
JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflow0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesThe document provides an overview of key concepts from a physics lecture on Newton's Three Laws, including reminders about an upcoming problem set and exam. It also lists important forces to consider like gravity, tension, and normal forces. Tips are provided for problem solving like drawing free-body diagrams and using component analysis carefully. Students are encouraged to think critically about the objects forces act on and which can only be determined using F=ma.
Original Description:
lec9
Original Title
lec9
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides an overview of key concepts from a physics lecture on Newton's Three Laws, including reminders about an upcoming problem set and exam. It also lists important forces to consider like gravity, tension, and normal forces. Tips are provided for problem solving like drawing free-body diagrams and using component analysis carefully. Students are encouraged to think critically about the objects forces act on and which can only be determined using F=ma.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesI Important Rem Nders: A Due To On A
I Important Rem Nders: A Due To On A
Uploaded by
JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowThe document provides an overview of key concepts from a physics lecture on Newton's Three Laws, including reminders about an upcoming problem set and exam. It also lists important forces to consider like gravity, tension, and normal forces. Tips are provided for problem solving like drawing free-body diagrams and using component analysis carefully. Students are encouraged to think critically about the objects forces act on and which can only be determined using F=ma.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Last Lecture Important Reminders
Newtons Three Laws
Today Pset # 3 due Friday at 10am.
More discussion Exam #1 average = 64.
Lots of examples Final class grade will be on a curve.
Important Concepts We dont give letter grade equivalents on individual
Think carefully about what object each force acts on exams. General guidance is:
Think carefully about which forces have well defined >80 is good, <60 is not good, <45 is poor
values and which one you need to calculate from F=ma
If you want to discuss your exam or general class
Think carefully about the acceleration performance, contact me or your recitation
instructor during office hours or by appointment.
Newtons Three Laws Inertial Reference Frames
1) If v is constant, then F must be zero and if F=0,
then v must be constant. These principles only apply for observers who are
! ! not accelerating, a so-called inertial frame
2) ! F = ma There are philosophical objections to this concept
3) Force due to object A on object B is always exactly since its hard to precisely define an inertial frame
equal in magnitude and always exactly opposite in except as one where Newtons Laws are valid
direction to the force due to object B on object A.
Alternative formulations are beyond the scope of
Some Advice this course, you dont need to worry about it
Your instincts are often wrong. Be careful!
! !
! F = ma is your friend. Trust what it tells you.
Forces you know about (so far)
Problem Solving Tool:(Revised)Free-Body Checklist
Draw a clear diagram of (each) object
Gravity near Earths surface: |F|=Mg, points down Think carefully about all of the forces on (each) object
String tension: Can
! be given explicitly or implicitly or Think carefully about the angles of the forces
!
found from ! F = ma Chose an axis, put it on your drawing
One example: String breaks if tension is larger than XX. Think carefully about the acceleration and put what you
Externa!l forces: Can be given explicitly or found know on your drawing
!
from ! F = ma Calculate components: ! Fx = max ! Fy = may ...
! !
Normal force: Almost always found from ! F = ma Solve
An Old Friend: Component Checklist Summary
! ! ! ! ! !
! F = ma ! F = ma ! = ma
F
Loop through vectors, is there a component?
Action-reaction pairs are an important concept in
Is there an angle factor solving problems but need to be considered very
Is it sine or cosine? carefully, especially the fact that the two forces in the
pair act on different objects
Is it positive or negative?
Think carefully about which forces
! can almost always
!
only be determined using ! F = ma
Typical examples are the normal force and string tension
You might also like
- Construx 6460 - Lunar Command Station Instruction SheetDocument8 pagesConstrux 6460 - Lunar Command Station Instruction SheetPaul Kostrzewa100% (2)
- Strength of Materials (S.O.M.) Model Question Paper (Q.P.) SolutionDocument16 pagesStrength of Materials (S.O.M.) Model Question Paper (Q.P.) SolutionProf. P. H. Jain93% (14)
- 12 Tribes Volume 2Document539 pages12 Tribes Volume 2Mariana100% (4)
- The University of Sanbra Guide To Intelligent Life - The NazrenDocument5 pagesThe University of Sanbra Guide To Intelligent Life - The NazrenSW-FanNo ratings yet
- Sit Anywhere. Assigned Seats Will Start This Friday. Pset#1 Due Here Tomorrow at Start of Class. Last LectureDocument1 pageSit Anywhere. Assigned Seats Will Start This Friday. Pset#1 Due Here Tomorrow at Start of Class. Last LectureJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- I Important Rem Nders: ! !K ! ! ! F K L ! LDocument1 pageI Important Rem Nders: ! !K ! ! ! F K L ! LJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Important Reminders Properties of Friction - Direction: ! M!a ! M!a ! M!aDocument1 pageImportant Reminders Properties of Friction - Direction: ! M!a ! M!a ! M!aJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- SOM - FE - Sem 2 - 2023-24Document25 pagesSOM - FE - Sem 2 - 2023-24ROHIT D MANGALEKARNo ratings yet
- Ap C Imp NotesDocument3 pagesAp C Imp Notesmahsan abbasNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Equilibrium of A ParticleDocument5 pagesCH 3 Equilibrium of A ParticleSteven ColeyNo ratings yet
- Mechyr1 Chapter 10::: Forces and MotionDocument31 pagesMechyr1 Chapter 10::: Forces and MotionAgrata PouloseNo ratings yet
- Clas 10Document7 pagesClas 10Kim Yessamin MadarcosNo ratings yet
- 0107 Lecture Notes - AP Physics 1 Review of Dynamics - Docx Page 1 of 1Document1 page0107 Lecture Notes - AP Physics 1 Review of Dynamics - Docx Page 1 of 1Goodman HereNo ratings yet
- UEME1263 - Topic 1 - Uniaxial Stress and StrainDocument104 pagesUEME1263 - Topic 1 - Uniaxial Stress and StrainKiritoNo ratings yet
- Free Body Diagrams - Essential PhysicsDocument37 pagesFree Body Diagrams - Essential PhysicsHendra du NantNo ratings yet
- Calculating The Truss Member ForcesDocument31 pagesCalculating The Truss Member ForcesGiuseppe Di GrandeNo ratings yet
- 160 Lab 13 ExampleDocument13 pages160 Lab 13 Examplemoven gastonNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Sub Chapter NotesDocument2 pages2.2 Sub Chapter NotesMe, Myself and INo ratings yet
- Lesson 1part 2Document8 pagesLesson 1part 2kareemaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Laws of Motion Notes Manoj SirDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Laws of Motion Notes Manoj SirSTUDY WITH MADHAVNo ratings yet
- Lect18 PDFDocument6 pagesLect18 PDFAthul VincentNo ratings yet
- 10 1425 Web Lec 24 MoreStaticsDocument13 pages10 1425 Web Lec 24 MoreStaticsAK CreationNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesDocument14 pagesCH 5 Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesSteven ColeyNo ratings yet
- The Method of JointsDocument4 pagesThe Method of JointssesostrisserbiusNo ratings yet
- Chap13mech PDFDocument34 pagesChap13mech PDFPower FullNo ratings yet
- Point-Wise Convergence and Uniform ConvergenceDocument3 pagesPoint-Wise Convergence and Uniform ConvergenceHưng PhạmNo ratings yet
- Forces With BlanksDocument6 pagesForces With BlanksHyun Gu KangNo ratings yet
- Mechyr1 Chapter 10::: Forces and MotionDocument23 pagesMechyr1 Chapter 10::: Forces and MotionfarismohNo ratings yet
- Word 2Document6 pagesWord 2aadityaray2004No ratings yet
- Mechyr1 Chapter 10::: Forces and MotionDocument23 pagesMechyr1 Chapter 10::: Forces and MotionDiyaNo ratings yet
- Physics Forces PDFDocument5 pagesPhysics Forces PDFObed Alonso LlagunoNo ratings yet
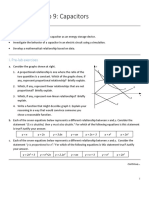
- Physics 229 Lab 9: Capacitors: GoalsDocument6 pagesPhysics 229 Lab 9: Capacitors: GoalsThomas PanNo ratings yet
- Physics 229 Lab 9: Capacitors: GoalsDocument6 pagesPhysics 229 Lab 9: Capacitors: GoalsThomas PanNo ratings yet
- Lec3 Oct11 2022 RandomForest NaiveBayesDocument33 pagesLec3 Oct11 2022 RandomForest NaiveBayesasasdNo ratings yet
- Lecture03 Force Stress 2023Document33 pagesLecture03 Force Stress 2023Nastassja BiccardNo ratings yet
- Numbers For LifeDocument62 pagesNumbers For Lifedavidmajutla87No ratings yet
- 1 1Document2 pages1 1Turuncu Adam0% (1)
- The Bare Essentials: Week 1Document5 pagesThe Bare Essentials: Week 1LexNo ratings yet
- MomentsDocument38 pagesMomentsaslaym607No ratings yet
- 10 1425 Web Lec 23 StaticsDocument20 pages10 1425 Web Lec 23 Staticspidor5281No ratings yet
- 05 - Lecture-1 PDFDocument21 pages05 - Lecture-1 PDFrenz pepaNo ratings yet
- Angle of Depression LP (Thesis)Document6 pagesAngle of Depression LP (Thesis)Balbuena, Maria Adela EduarteNo ratings yet
- Christ The King College-San Fernando City, La Union Inc.: Quarter 2 Module 3Document5 pagesChrist The King College-San Fernando City, La Union Inc.: Quarter 2 Module 3Jose LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Statistics Homework Sample Problems With SolutionsDocument7 pagesStatistics Homework Sample Problems With SolutionsHebrew JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Physics For Engineers Lesson 1 VectorsDocument21 pagesPhysics For Engineers Lesson 1 VectorsJohn Aiven EyayaNo ratings yet
- GenMathQ1W5 SLMDocument14 pagesGenMathQ1W5 SLMgabosara298No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Science 10Document4 pagesLesson Plan For Science 10Aster May CatulongNo ratings yet
- Week2-Mechanical PropertiesDocument34 pagesWeek2-Mechanical PropertiesMuhammad AzeemNo ratings yet
- PHASM/G442 Particle Physics Dr. Ryan Nichol Prof. Ruben SaakyanDocument35 pagesPHASM/G442 Particle Physics Dr. Ryan Nichol Prof. Ruben SaakyanRoy VeseyNo ratings yet
- HowScienceWorks GraphsDocument30 pagesHowScienceWorks GraphsJatin MistryNo ratings yet
- BlankChapter1 IntrotoCalculusDocument17 pagesBlankChapter1 IntrotoCalculusShama ANo ratings yet
- Solving Problems Involving Sets Using Venn DiagramDocument12 pagesSolving Problems Involving Sets Using Venn DiagramVanessa Pangan KellerNo ratings yet
- Math MidtermsDocument2 pagesMath MidtermsAngelNo ratings yet
- Physics Lec 24 MoreStaticsDocument11 pagesPhysics Lec 24 MoreStaticsAnthony Wijaya, S.Pd., M.Si.No ratings yet
- STUDENT MODULE 4 finalGENPHY1 PDFDocument6 pagesSTUDENT MODULE 4 finalGENPHY1 PDFKimberly LopezNo ratings yet
- 03 Random - Variables - SLIDEDocument20 pages03 Random - Variables - SLIDEari rahadyanNo ratings yet
- Feynman Diagrams: Particle and Nuclear PhysicsDocument20 pagesFeynman Diagrams: Particle and Nuclear PhysicsHaibin SuNo ratings yet
- 02 Chapter 6Document55 pages02 Chapter 6Abdul Rafay Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis Using SasDocument46 pagesStatistical Analysis Using Saskabelo MotsepeNo ratings yet
- Vectors Live Class-3 Teacher NotesDocument29 pagesVectors Live Class-3 Teacher Notescaptain FURYNo ratings yet
- Important Reminders Problem-Solving Strategy 4-StepsDocument5 pagesImportant Reminders Problem-Solving Strategy 4-StepsJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Happy Holidays! Happy New Year! Welcome Back! Important Reminders Complete Description of MotionDocument2 pagesHappy Holidays! Happy New Year! Welcome Back! Important Reminders Complete Description of MotionJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Prs 01 09 06solDocument1 pagePrs 01 09 06solJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Important Reminders Complete Description of Motion: " # ! " !! !R " !F ! R F Sin (#)Document2 pagesImportant Reminders Complete Description of Motion: " # ! " !! !R " !F ! R F Sin (#)JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Lec 31Document1 pageLec 31JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- I Important Rem Nders: Energy and Momentum of RotationDocument1 pageI Important Rem Nders: Energy and Momentum of RotationJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- I Important Rem Nders: G NM KGDocument1 pageI Important Rem Nders: G NM KGJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Prs 11 01 05solDocument1 pagePrs 11 01 05solJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Lec 29Document1 pageLec 29JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- I Important Rem Nders: Note Distinction Between Mass and WeightDocument2 pagesI Important Rem Nders: Note Distinction Between Mass and WeightJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- I Important Rem Nders: 0 V Cos (!) !G V Sin (")Document2 pagesI Important Rem Nders: 0 V Cos (!) !G V Sin (")JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Lec 20Document1 pageLec 20JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Lec 30Document2 pagesLec 30JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Lec 12Document1 pageLec 12JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Lec 13Document1 pageLec 13JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- ) Important Reminders Blast From The Past (Early Exam ReviewDocument2 pages) Important Reminders Blast From The Past (Early Exam ReviewJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Prs 11 01 05sol PDFDocument1 pagePrs 11 01 05sol PDFJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Sit Anywhere. Assigned Seats Will Start This Friday. Pset#1 Due Here Tomorrow at Start of Class. Last LectureDocument1 pageSit Anywhere. Assigned Seats Will Start This Friday. Pset#1 Due Here Tomorrow at Start of Class. Last LectureJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- ! V + V + V ! A + A + A: Important Reminders Kinematics: Description of MotionDocument2 pages! V + V + V ! A + A + A: Important Reminders Kinematics: Description of MotionJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Prs 11 03 05solDocument1 pagePrs 11 03 05solJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Moves Down The Incline. Which of The Does Not Move at All. Which of TheDocument2 pagesMoves Down The Incline. Which of The Does Not Move at All. Which of TheJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Prs 11 08 05solDocument3 pagesPrs 11 08 05solJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Block A Collides With Block B. After The Collisions The Two Blocks Stick Together. Which of The Following Is True?Document2 pagesBlock A Collides With Block B. After The Collisions The Two Blocks Stick Together. Which of The Following Is True?JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- I Important Rem Nders: Constant Velocity Is OK, Accelerated Observer Is NotDocument2 pagesI Important Rem Nders: Constant Velocity Is OK, Accelerated Observer Is NotJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Prs 11 29 05solDocument1 pagePrs 11 29 05solJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Prs 11 17 05solDocument1 pagePrs 11 17 05solJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Displacement Versus Distance Velocity and Acceleration: Velocity Equal To Zero?Document2 pagesDisplacement Versus Distance Velocity and Acceleration: Velocity Equal To Zero?JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document2 pagesLec 2JoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Prs 11 22 05solDocument3 pagesPrs 11 22 05solJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- Doppler EffectDocument8 pagesDoppler EffectkrawczybNo ratings yet
- Satellite CommunicationsDocument28 pagesSatellite CommunicationsDarren Jeff Manuel MicumaoNo ratings yet
- "Moondust" (Sci-Fi Horror Graphic Novel)Document28 pages"Moondust" (Sci-Fi Horror Graphic Novel)Nick KoriaginNo ratings yet
- Microwave Remote SensingDocument13 pagesMicrowave Remote SensingAkash BadoniNo ratings yet
- Sung To The Tune of O Christmas TreeDocument2 pagesSung To The Tune of O Christmas TreeinstcrisNo ratings yet
- Dane Rudhyar - Astrology PsychoanalyzedDocument8 pagesDane Rudhyar - Astrology PsychoanalyzedcalfamonicaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 ElsDocument44 pagesLesson 2 ElsJhellee AquinoNo ratings yet
- Chaos Compendium pt02Document67 pagesChaos Compendium pt02kabniel100% (1)
- Teading Comprehension TestDocument2 pagesTeading Comprehension TestmarbadanNo ratings yet
- Divisional Chart-IDocument1 pageDivisional Chart-Iabhisek1987No ratings yet
- Part of Fortune in 4th HouseDocument4 pagesPart of Fortune in 4th HousetratakNo ratings yet
- Twilight Imperium 3 Living Rulebook v1.3Document72 pagesTwilight Imperium 3 Living Rulebook v1.3ZucNo ratings yet
- Bnotes PDFDocument62 pagesBnotes PDFGlory GloryNo ratings yet
- XPS (X Ray Photoemission Spectroscopy) /ESCA (Electron Spectroscopy For Chemical Analysis)Document46 pagesXPS (X Ray Photoemission Spectroscopy) /ESCA (Electron Spectroscopy For Chemical Analysis)Serdar ArıcanNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Fluorescence - C MillerDocument24 pagesX-Ray Fluorescence - C MillerRodrigo AndradeNo ratings yet
- IAO For People in A Hurry - Chooi Je QinDocument6 pagesIAO For People in A Hurry - Chooi Je QinSudip RokayaNo ratings yet
- Teenage Sigma Space Racers by Keren Obara PDFDocument31 pagesTeenage Sigma Space Racers by Keren Obara PDFobarakerenNo ratings yet
- Ometric Optics (139-156)Document18 pagesOmetric Optics (139-156)Saraswathi PuppalaNo ratings yet
- Kira GonDocument1 pageKira Gonp_haganNo ratings yet
- Hip Parch Us Was Called The Father of TrigonometryDocument3 pagesHip Parch Us Was Called The Father of TrigonometryChristian Miguel EgnoraNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 3Document9 pagesPractice Test 3Anonymous jxeb81uI0% (1)
- Amazing Space Facts For KidsDocument8 pagesAmazing Space Facts For KidsJeff DoeNo ratings yet
- SUNlite5 1Document36 pagesSUNlite5 1charlesfortNo ratings yet
- Natal Chart (Data Sheets) : Jul - Day 2454076.917420 TT, T 65.1 SecDocument2 pagesNatal Chart (Data Sheets) : Jul - Day 2454076.917420 TT, T 65.1 SecelifNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 11Document18 pagesPhysics Chapter 11cryptachrisNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Unt2 Lesson3lDocument6 pagesActivity 3 Unt2 Lesson3lGerald PiolNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Examples 2Document6 pagesAir Pollution Examples 2rohit agrawalNo ratings yet