Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsThe Volume of Gases
The Volume of Gases
Uploaded by
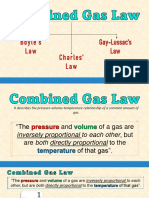
RishikeshThe document discusses the ideal gas law and its relationships between temperature, pressure, volume, and mass of gases. It explains that according to Boyle's law, the product of pressure and volume is constant at constant temperature. Charles' law states the ratio of volume to temperature is constant at constant pressure. Combining these laws, the document derives the ideal gas law that the product of pressure, volume, and temperature divided by the number of moles of gas is a constant value known as R.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Properties of GasesDocument26 pagesThe Properties of GasesHitesh Swami100% (1)
- The Ideal - Gas Equation of StateDocument13 pagesThe Ideal - Gas Equation of StateAudu SanusiNo ratings yet
- ME 161: Introduction To Mechanical Engineering: Asif KabirDocument21 pagesME 161: Introduction To Mechanical Engineering: Asif KabirMohammad Asif KabirNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument15 pagesStates of MatterShaku JoshiNo ratings yet
- GasesDocument16 pagesGasesAnas MohamedNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Pressure: Chapter 5: GasesDocument4 pages5.1 Pressure: Chapter 5: GasesSam ChungNo ratings yet
- Kinetic TheoryDocument44 pagesKinetic TheoryMEGHA100% (3)
- Boyle's LawDocument2 pagesBoyle's Lawjerieljade.talabonNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Heat: 3. Changes of State 4. GaslawsDocument15 pagesTemperature and Heat: 3. Changes of State 4. GaslawsAndré OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Combined Avogadro's and Ideal Gas LawsDocument39 pagesCombined Avogadro's and Ideal Gas LawsKiceNo ratings yet
- CHM131 - Chapter 6 - The Gaseous StateDocument37 pagesCHM131 - Chapter 6 - The Gaseous StateNotes NotesNo ratings yet
- Week 3 PPT AD CHEMDocument8 pagesWeek 3 PPT AD CHEMSophia Ysabelle EstradaNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas LawDocument5 pagesIdeal Gas LawChristian Alic KelleyNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas EquationDocument20 pagesIdeal Gas EquationsamNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 IdealgaslawDocument45 pagesChapter3 Idealgaslaw翁绍棠No ratings yet
- Physics Week 20 Reading Assignment - Theodore KimDocument6 pagesPhysics Week 20 Reading Assignment - Theodore KimTheodore KimNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Xi Term 2 All ChaptersDocument60 pagesChemistry Xi Term 2 All ChaptersKalpesh BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Gay LUSSACSDocument2 pagesGay LUSSACSNoean LargoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Gas Laws ExercisesDocument6 pagesChemistry Gas Laws Exercisesjag1231No ratings yet
- Ideal Gases LectureDocument6 pagesIdeal Gases LectureRica ChavezNo ratings yet
- Buenasher Learning Academy Inc.: Robert Boyle (1627-1691)Document5 pagesBuenasher Learning Academy Inc.: Robert Boyle (1627-1691)Maam Elle CruzNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasesDocument12 pagesIdeal GasesSavva LazarevNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law: Volume and Pressure: Temperature Must Be Expressed On The Absolute Temperature or Kelvin ScaleDocument4 pagesBoyle's Law: Volume and Pressure: Temperature Must Be Expressed On The Absolute Temperature or Kelvin ScaleChris Heydenrych100% (1)
- Gas Laws - Wikipedia PDFDocument17 pagesGas Laws - Wikipedia PDFEmegu MosesNo ratings yet
- 10 GasesDocument7 pages10 GasesKkkNo ratings yet
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET-CHEM 1 q1 Week 4Document8 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET-CHEM 1 q1 Week 4Jhude JosephNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law: Important: Charles's Law Only Works When The Pressure Is ConstantDocument3 pagesBoyle's Law: Important: Charles's Law Only Works When The Pressure Is ConstantYlla GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document47 pagesChapter 19maxim santos100% (1)
- Measurement 16Document16 pagesMeasurement 16Gaurav ShekharNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Gas Metering: by SNGPL-Metering DepartmentDocument15 pagesPresentation On Gas Metering: by SNGPL-Metering DepartmentbrianNo ratings yet
- The Equation Shows That, As Volume Increases, The Pressure of The Gas Decreases in Proportion, and Vice VersaDocument1 pageThe Equation Shows That, As Volume Increases, The Pressure of The Gas Decreases in Proportion, and Vice VersaEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document17 pagesUnit 2Saravana HamsaveniNo ratings yet
- Basic Rules and Laws of Science For Food TechnologyDocument22 pagesBasic Rules and Laws of Science For Food TechnologypokhralikanchhaNo ratings yet
- School of Physics and Astronomy Junior Honours Thermodynamics GJA 2013-2014Document4 pagesSchool of Physics and Astronomy Junior Honours Thermodynamics GJA 2013-2014Babu AravindNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document51 pagesScience 10Jimin ParkNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory and Gas Laws HandoutDocument4 pagesKinetic Theory and Gas Laws HandoutTamikaNo ratings yet
- GasesDocument23 pagesGasesbatazaiNo ratings yet
- State of MatterDocument52 pagesState of MatterAditi MahajanNo ratings yet
- Theory 4.1 Experiment of Boyle's Law: Constant PV P ConstantDocument3 pagesTheory 4.1 Experiment of Boyle's Law: Constant PV P ConstantAuzaNo ratings yet
- Gaseous State NovelDocument101 pagesGaseous State Novelkrishna gautamNo ratings yet
- Mechnotes: Unit - 1 ObjectiveDocument25 pagesMechnotes: Unit - 1 ObjectiveKaran SelvaNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws:: P V K VDocument18 pagesGas Laws:: P V K VFarah Zu'biNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gases: By: Alocitta .A /01 Aulia Shalmaa P.R /05 Rizandi Arya P / 20 Mariera Anisa /26 M. Iqbal H /27Document11 pagesIdeal Gases: By: Alocitta .A /01 Aulia Shalmaa P.R /05 Rizandi Arya P / 20 Mariera Anisa /26 M. Iqbal H /27Alocitta AnindyanariNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3 - Properties of Perfect GasDocument8 pagesLecture-3 - Properties of Perfect Gas292301238No ratings yet
- The Equation of State For A Perfect Gas: A. Boyle'S LawDocument9 pagesThe Equation of State For A Perfect Gas: A. Boyle'S LawCzarina Jane PeregrinNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document26 pagesUnit 1firehywotNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 The Gas LawsDocument7 pagesLecture 2 The Gas LawsScrappy WellNo ratings yet
- The Gas Laws: Cortez Vince Robert Linghon QuishaDocument10 pagesThe Gas Laws: Cortez Vince Robert Linghon QuishaZ ACERNo ratings yet
- G484 Module 3 4.3.4 Ideal GasesDocument10 pagesG484 Module 3 4.3.4 Ideal GasesIgnatius AgustaNo ratings yet
- Physical Behavior of Gases: Kinetic TheoryDocument12 pagesPhysical Behavior of Gases: Kinetic TheoryPAUL KOLERENo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Pressure, Volume, and Hot AirDocument22 pagesGas Laws: Pressure, Volume, and Hot AirIrwan M. IskoberNo ratings yet
- History of Gas LawDocument10 pagesHistory of Gas Lawsunshine sunooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document46 pagesChapter 10Parth GandhiNo ratings yet
- Meterological ParametersDocument47 pagesMeterological ParametersRDWSD SedamNo ratings yet
- Order 1771128Document4 pagesOrder 1771128Nahshon M. ObiriNo ratings yet
- Victorio Oriel - Ideal Gas Law and Molar Mass EquationDocument5 pagesVictorio Oriel - Ideal Gas Law and Molar Mass Equationapi-233267698No ratings yet
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Machine Learning Prof. Anirban Santara Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Machine Learning Prof. Anirban Santara Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurRishikeshNo ratings yet
- Granular Flows: Persented By: HETRAM (2014CH10100)Document16 pagesGranular Flows: Persented By: HETRAM (2014CH10100)RishikeshNo ratings yet
- Startup@Iit DelhiDocument1 pageStartup@Iit DelhiRishikeshNo ratings yet
- Membrane TechnologyDocument1 pageMembrane TechnologyRishikeshNo ratings yet
- CRE Assignment - 1Document3 pagesCRE Assignment - 1Rishikesh100% (1)
- Rajasthan Board of Secondary Education, Ajmer: Result: Senior Secondary (Science) Examination, 2016Document1 pageRajasthan Board of Secondary Education, Ajmer: Result: Senior Secondary (Science) Examination, 2016RishikeshNo ratings yet
- 8 PDFDocument1 page8 PDFRishikeshNo ratings yet
- Paper Waste WaterDocument7 pagesPaper Waste WaterRishikeshNo ratings yet
- Liquid Extraction From RetentateDocument1 pageLiquid Extraction From RetentateRishikeshNo ratings yet
The Volume of Gases
The Volume of Gases
Uploaded by
Rishikesh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageThe document discusses the ideal gas law and its relationships between temperature, pressure, volume, and mass of gases. It explains that according to Boyle's law, the product of pressure and volume is constant at constant temperature. Charles' law states the ratio of volume to temperature is constant at constant pressure. Combining these laws, the document derives the ideal gas law that the product of pressure, volume, and temperature divided by the number of moles of gas is a constant value known as R.
Original Description:
Gases
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the ideal gas law and its relationships between temperature, pressure, volume, and mass of gases. It explains that according to Boyle's law, the product of pressure and volume is constant at constant temperature. Charles' law states the ratio of volume to temperature is constant at constant pressure. Combining these laws, the document derives the ideal gas law that the product of pressure, volume, and temperature divided by the number of moles of gas is a constant value known as R.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageThe Volume of Gases
The Volume of Gases
Uploaded by
RishikeshThe document discusses the ideal gas law and its relationships between temperature, pressure, volume, and mass of gases. It explains that according to Boyle's law, the product of pressure and volume is constant at constant temperature. Charles' law states the ratio of volume to temperature is constant at constant pressure. Combining these laws, the document derives the ideal gas law that the product of pressure, volume, and temperature divided by the number of moles of gas is a constant value known as R.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
The volume of gases can be measured easily.
Hence, the composition of
gases can be expressed in
terms of volume per cent. If parameters, such as temperature and pressure of
the gas are known, then
the density of the gas can be calculated. This, in turn, gives the mass of the
gas. While dealing with
substances existing in the gaseous state, the relationship among the
temperature, pressure, mass and
volume must be known.
2.9.1 Ideal Gas Law
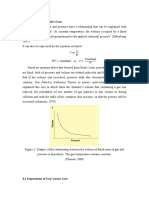
According to Boyles law, for a given mass of an ideal gas, the product of the
pressure and volume is
constant at a constant temperature, i.e.
P V = Constant(2.16)
where
P = Absolute pressure (N/m
2
)
V = Volume occupied by the gas (m
3
)
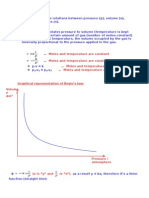
According to Charles law, for a given mass of an ideal gas, the ratio of the
volume to temperature is
constant at a given pressure, i.e.
= Constant(2.17)
where
V = Volume occupied by the gas (m
T = Absolute temperature (K)
Combining Eqs. (2.16) and (2.17), we get
3
)
= Constant(2.18)
The constant is designated by the symbol R, known as univ
You might also like
- The Properties of GasesDocument26 pagesThe Properties of GasesHitesh Swami100% (1)
- The Ideal - Gas Equation of StateDocument13 pagesThe Ideal - Gas Equation of StateAudu SanusiNo ratings yet
- ME 161: Introduction To Mechanical Engineering: Asif KabirDocument21 pagesME 161: Introduction To Mechanical Engineering: Asif KabirMohammad Asif KabirNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument15 pagesStates of MatterShaku JoshiNo ratings yet
- GasesDocument16 pagesGasesAnas MohamedNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Pressure: Chapter 5: GasesDocument4 pages5.1 Pressure: Chapter 5: GasesSam ChungNo ratings yet
- Kinetic TheoryDocument44 pagesKinetic TheoryMEGHA100% (3)
- Boyle's LawDocument2 pagesBoyle's Lawjerieljade.talabonNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Heat: 3. Changes of State 4. GaslawsDocument15 pagesTemperature and Heat: 3. Changes of State 4. GaslawsAndré OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Combined Avogadro's and Ideal Gas LawsDocument39 pagesCombined Avogadro's and Ideal Gas LawsKiceNo ratings yet
- CHM131 - Chapter 6 - The Gaseous StateDocument37 pagesCHM131 - Chapter 6 - The Gaseous StateNotes NotesNo ratings yet
- Week 3 PPT AD CHEMDocument8 pagesWeek 3 PPT AD CHEMSophia Ysabelle EstradaNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas LawDocument5 pagesIdeal Gas LawChristian Alic KelleyNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas EquationDocument20 pagesIdeal Gas EquationsamNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 IdealgaslawDocument45 pagesChapter3 Idealgaslaw翁绍棠No ratings yet
- Physics Week 20 Reading Assignment - Theodore KimDocument6 pagesPhysics Week 20 Reading Assignment - Theodore KimTheodore KimNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Xi Term 2 All ChaptersDocument60 pagesChemistry Xi Term 2 All ChaptersKalpesh BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Gay LUSSACSDocument2 pagesGay LUSSACSNoean LargoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Gas Laws ExercisesDocument6 pagesChemistry Gas Laws Exercisesjag1231No ratings yet
- Ideal Gases LectureDocument6 pagesIdeal Gases LectureRica ChavezNo ratings yet
- Buenasher Learning Academy Inc.: Robert Boyle (1627-1691)Document5 pagesBuenasher Learning Academy Inc.: Robert Boyle (1627-1691)Maam Elle CruzNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasesDocument12 pagesIdeal GasesSavva LazarevNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law: Volume and Pressure: Temperature Must Be Expressed On The Absolute Temperature or Kelvin ScaleDocument4 pagesBoyle's Law: Volume and Pressure: Temperature Must Be Expressed On The Absolute Temperature or Kelvin ScaleChris Heydenrych100% (1)
- Gas Laws - Wikipedia PDFDocument17 pagesGas Laws - Wikipedia PDFEmegu MosesNo ratings yet
- 10 GasesDocument7 pages10 GasesKkkNo ratings yet
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET-CHEM 1 q1 Week 4Document8 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET-CHEM 1 q1 Week 4Jhude JosephNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law: Important: Charles's Law Only Works When The Pressure Is ConstantDocument3 pagesBoyle's Law: Important: Charles's Law Only Works When The Pressure Is ConstantYlla GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document47 pagesChapter 19maxim santos100% (1)
- Measurement 16Document16 pagesMeasurement 16Gaurav ShekharNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Gas Metering: by SNGPL-Metering DepartmentDocument15 pagesPresentation On Gas Metering: by SNGPL-Metering DepartmentbrianNo ratings yet
- The Equation Shows That, As Volume Increases, The Pressure of The Gas Decreases in Proportion, and Vice VersaDocument1 pageThe Equation Shows That, As Volume Increases, The Pressure of The Gas Decreases in Proportion, and Vice VersaEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document17 pagesUnit 2Saravana HamsaveniNo ratings yet
- Basic Rules and Laws of Science For Food TechnologyDocument22 pagesBasic Rules and Laws of Science For Food TechnologypokhralikanchhaNo ratings yet
- School of Physics and Astronomy Junior Honours Thermodynamics GJA 2013-2014Document4 pagesSchool of Physics and Astronomy Junior Honours Thermodynamics GJA 2013-2014Babu AravindNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document51 pagesScience 10Jimin ParkNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory and Gas Laws HandoutDocument4 pagesKinetic Theory and Gas Laws HandoutTamikaNo ratings yet
- GasesDocument23 pagesGasesbatazaiNo ratings yet
- State of MatterDocument52 pagesState of MatterAditi MahajanNo ratings yet
- Theory 4.1 Experiment of Boyle's Law: Constant PV P ConstantDocument3 pagesTheory 4.1 Experiment of Boyle's Law: Constant PV P ConstantAuzaNo ratings yet
- Gaseous State NovelDocument101 pagesGaseous State Novelkrishna gautamNo ratings yet
- Mechnotes: Unit - 1 ObjectiveDocument25 pagesMechnotes: Unit - 1 ObjectiveKaran SelvaNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws:: P V K VDocument18 pagesGas Laws:: P V K VFarah Zu'biNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gases: By: Alocitta .A /01 Aulia Shalmaa P.R /05 Rizandi Arya P / 20 Mariera Anisa /26 M. Iqbal H /27Document11 pagesIdeal Gases: By: Alocitta .A /01 Aulia Shalmaa P.R /05 Rizandi Arya P / 20 Mariera Anisa /26 M. Iqbal H /27Alocitta AnindyanariNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3 - Properties of Perfect GasDocument8 pagesLecture-3 - Properties of Perfect Gas292301238No ratings yet
- The Equation of State For A Perfect Gas: A. Boyle'S LawDocument9 pagesThe Equation of State For A Perfect Gas: A. Boyle'S LawCzarina Jane PeregrinNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document26 pagesUnit 1firehywotNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 The Gas LawsDocument7 pagesLecture 2 The Gas LawsScrappy WellNo ratings yet
- The Gas Laws: Cortez Vince Robert Linghon QuishaDocument10 pagesThe Gas Laws: Cortez Vince Robert Linghon QuishaZ ACERNo ratings yet
- G484 Module 3 4.3.4 Ideal GasesDocument10 pagesG484 Module 3 4.3.4 Ideal GasesIgnatius AgustaNo ratings yet
- Physical Behavior of Gases: Kinetic TheoryDocument12 pagesPhysical Behavior of Gases: Kinetic TheoryPAUL KOLERENo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Pressure, Volume, and Hot AirDocument22 pagesGas Laws: Pressure, Volume, and Hot AirIrwan M. IskoberNo ratings yet
- History of Gas LawDocument10 pagesHistory of Gas Lawsunshine sunooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document46 pagesChapter 10Parth GandhiNo ratings yet
- Meterological ParametersDocument47 pagesMeterological ParametersRDWSD SedamNo ratings yet
- Order 1771128Document4 pagesOrder 1771128Nahshon M. ObiriNo ratings yet
- Victorio Oriel - Ideal Gas Law and Molar Mass EquationDocument5 pagesVictorio Oriel - Ideal Gas Law and Molar Mass Equationapi-233267698No ratings yet
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Machine Learning Prof. Anirban Santara Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Machine Learning Prof. Anirban Santara Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurRishikeshNo ratings yet
- Granular Flows: Persented By: HETRAM (2014CH10100)Document16 pagesGranular Flows: Persented By: HETRAM (2014CH10100)RishikeshNo ratings yet
- Startup@Iit DelhiDocument1 pageStartup@Iit DelhiRishikeshNo ratings yet
- Membrane TechnologyDocument1 pageMembrane TechnologyRishikeshNo ratings yet
- CRE Assignment - 1Document3 pagesCRE Assignment - 1Rishikesh100% (1)
- Rajasthan Board of Secondary Education, Ajmer: Result: Senior Secondary (Science) Examination, 2016Document1 pageRajasthan Board of Secondary Education, Ajmer: Result: Senior Secondary (Science) Examination, 2016RishikeshNo ratings yet
- 8 PDFDocument1 page8 PDFRishikeshNo ratings yet
- Paper Waste WaterDocument7 pagesPaper Waste WaterRishikeshNo ratings yet
- Liquid Extraction From RetentateDocument1 pageLiquid Extraction From RetentateRishikeshNo ratings yet