Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer 36324
Answer 36324
Uploaded by
Ayush SinghOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer 36324
Answer 36324
Uploaded by
Ayush SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
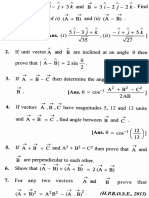
1. A vector A which has magnitude 8.0 is added to a vector B which lies on x-axis.
The sum of these
two vectors lies on y-axis and has a magnitude twice of the magnitude of vector B. The magnitude of
vector B is:
a) 8 ;
b) 1.41*8 ;
c) 8/(5)^1/2 ;
d) 8*(5)^1/2 .
Solution.
As vector B which lies on x-axis, then B (b; 0 ) . The magnitude of vector B is B = b 2 + 0 2 = b .
Assume that A (a1 ; a 2 ) .
The sum of these two vectors is C = A+ B = (a1 ; a 2 ) + (b; 0) = (a1 + b; a 2 ) . This vector lies on y-
axis, so a1 + b = 0 , a1 = b .
The magnitude of vector A is A = a1 + a 2 = ( b ) + a 2 = b 2 + a 2 . According to the
2 2 2 2 2
condition of the problem, A = 8.0 .
The magnitude of vector C is C = 0 2 + a 2 = a 2 . According to the condition of the problem,
2
C = 2 B , so a2 = 2 b .
Summarizing, A = b 2 + (2 b ) = 8.0 ,
8 .0 8 .0
2
b = = .
1+ 2 2
5
8.0
Thus, the magnitude of vector B is B = b = .
5
Answer: C.
You might also like
- Thomas Calculus Early Transcendentals Fifteenth Edition Joel Hass All ChapterDocument67 pagesThomas Calculus Early Transcendentals Fifteenth Edition Joel Hass All Chapterramona.evans546100% (9)
- AMO 2020 Paper and SolutionsDocument33 pagesAMO 2020 Paper and SolutionsAlbertNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 SolnDocument2 pagesTutorial 3 Solnstayhungry0105No ratings yet
- AMM10930Document1 pageAMM10930이건행No ratings yet
- CH - 1 To 15 Upm All SolutionsDocument67 pagesCH - 1 To 15 Upm All SolutionsPratik PandaNo ratings yet
- Methodist Girls' School: Preliminary Examination 2022 Secondary 4Document28 pagesMethodist Girls' School: Preliminary Examination 2022 Secondary 4SADIA RAHMAN ANIMA 22S302No ratings yet
- All India Medical NEET & Engineering JEE Main Entrance Examination (1) Split PDF 1717680211889Document12 pagesAll India Medical NEET & Engineering JEE Main Entrance Examination (1) Split PDF 1717680211889padmajamallikNo ratings yet
- Motion in Plane NEET JEE Practice QuestiosDocument174 pagesMotion in Plane NEET JEE Practice QuestiosjothilakshmiNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem NotesDocument5 pagesPythagorean Theorem NotespeterashNo ratings yet
- 16 VectorsDocument36 pages16 VectorsrupeshNo ratings yet
- Harder 3u Level 1Document14 pagesHarder 3u Level 1greycouncilNo ratings yet
- Endsem Y14Document7 pagesEndsem Y14Midhun MNo ratings yet
- Mathematics SSCII Paper IDocument8 pagesMathematics SSCII Paper IMisbah NaqviNo ratings yet
- HW 5 AnsDocument5 pagesHW 5 AnsAshish BodeleNo ratings yet
- CS 543: Computer Graphics Lecture 3 (Part II) : Points, Scalars and VectorsDocument23 pagesCS 543: Computer Graphics Lecture 3 (Part II) : Points, Scalars and VectorsChi HanaNo ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument3 pagesExerciseAhmet TOLUCNo ratings yet
- Prelim Paper 2 - 2022 - Solution (Comments)Document17 pagesPrelim Paper 2 - 2022 - Solution (Comments)Bryan TangNo ratings yet
- Vector 2021Document13 pagesVector 2021Mayank GoelNo ratings yet
- Section 9.3: The Dot ProductDocument7 pagesSection 9.3: The Dot ProductBakari HamisiNo ratings yet
- Openstax Physics Chapter 1 Lesson 5 5 Products of VectorsDocument15 pagesOpenstax Physics Chapter 1 Lesson 5 5 Products of VectorsWild RiftNo ratings yet
- Groups: Binary OperationsDocument10 pagesGroups: Binary OperationsNilesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Maths Quick Revision NoteDocument12 pagesMaths Quick Revision NoteRohan JeanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - SolutionsDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 - SolutionsTokey LiNo ratings yet
- EC2R Answer KeyDocument3 pagesEC2R Answer Keysrinivasa.reddy1No ratings yet
- Quantitative 07Document30 pagesQuantitative 07zedamtie2015No ratings yet
- The University of British Columbia Assignment Problems and Solutions Summer 2011 Math307Document113 pagesThe University of British Columbia Assignment Problems and Solutions Summer 2011 Math307jeferson.ordonioNo ratings yet
- 7 Coordinate GeometryDocument4 pages7 Coordinate GeometryRoses Are RosieNo ratings yet
- 8.02 Non-Right Triangles - Law of CosinesDocument10 pages8.02 Non-Right Triangles - Law of Cosines정재웅No ratings yet
- EGR2013 Tutorial 8: Z Powers of A Matrix and Matrix Polynomial Z Vector Algebra Z Vector SpacesDocument6 pagesEGR2013 Tutorial 8: Z Powers of A Matrix and Matrix Polynomial Z Vector Algebra Z Vector SpacesKaneki KenNo ratings yet
- VECTORSDocument3 pagesVECTORSPriya MishraNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentvidushi1121No ratings yet
- Vectors and 3D - 29Document24 pagesVectors and 3D - 29rebel rocksNo ratings yet
- Vectors - Part 2: Products: AB ABDocument4 pagesVectors - Part 2: Products: AB ABnisairfanNo ratings yet
- Cbiemapl 02Document14 pagesCbiemapl 02HitanshNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics IIIDocument17 pagesEngineering Mathematics IIIbethuyegoNo ratings yet
- Dot Product and Cross ProductDocument2 pagesDot Product and Cross ProductShahwez AlamNo ratings yet
- Vectors Jeemain - GuruDocument9 pagesVectors Jeemain - Gururohan raj100% (1)
- Algebra Ex AmenDocument6 pagesAlgebra Ex AmencarlaoquendoNo ratings yet
- Vector 2-Triangle Law - ReviewedDocument5 pagesVector 2-Triangle Law - Reviewedarnav BansalNo ratings yet
- 71 VECTOR & 3D PART 4 of 6 PDFDocument18 pages71 VECTOR & 3D PART 4 of 6 PDFwill bellNo ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics University of Illinois at Urbana-ChampaignDocument5 pagesDepartment of Mathematics University of Illinois at Urbana-ChampaignadelNo ratings yet
- 19vectors 3d PDFDocument8 pages19vectors 3d PDFSunita MauryaNo ratings yet
- Vector AnalysisDocument36 pagesVector AnalysisSafdar H. BoukNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 6: 1 θ cos 2 2 θ cos − = α tan 1 α tan 2 α 2 tan − =Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 6: 1 θ cos 2 2 θ cos − = α tan 1 α tan 2 α 2 tan − =楊子慶No ratings yet
- Lec 2 of 5 VectorDocument20 pagesLec 2 of 5 VectorSyakirah MunirNo ratings yet
- MAT285 (Chapter 2)Document24 pagesMAT285 (Chapter 2)ZAIM IMANI ZAWAWINo ratings yet
- SolJul2016B1 PDFDocument1 pageSolJul2016B1 PDFRai CerdanNo ratings yet
- Problema 1.: Opción B Julio 2016Document1 pageProblema 1.: Opción B Julio 2016Rai CerdanNo ratings yet
- CH 9Document3 pagesCH 9nty372001No ratings yet
- Realistic Proof of Square Formula'sDocument3 pagesRealistic Proof of Square Formula'sSaidur Rahman ArifNo ratings yet
- Dad S TheoremDocument17 pagesDad S TheoremyvazzocaanhdvpmlfmNo ratings yet
- Bmo 2024 (Ali Maths)Document8 pagesBmo 2024 (Ali Maths)Rachide DaniNo ratings yet
- MathsB Mats ProbsheetDocument2 pagesMathsB Mats ProbsheetMike AlmutairiNo ratings yet
- HeroDocument4 pagesHeroyoon tim lamNo ratings yet
- Mit18 06scf11 Ses2.5solDocument3 pagesMit18 06scf11 Ses2.5solSarthi GNo ratings yet
- Las Math9 Q4 W6Document7 pagesLas Math9 Q4 W6Maxene Angelie RabanalNo ratings yet
- The Real Number System: Sets of Real Numbers RDocument6 pagesThe Real Number System: Sets of Real Numbers RmohdirhamNo ratings yet
- Math 415. Final Exam. May 6, 2019Document34 pagesMath 415. Final Exam. May 6, 2019Aidi .WafiNo ratings yet
- 0606 s19 QP 12 PDFDocument16 pages0606 s19 QP 12 PDFcalvinNo ratings yet
- MP Exp2Document7 pagesMP Exp2Ayush SinghNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 Problem Definition and EERDocument9 pagesExp 1 Problem Definition and EERAyush SinghNo ratings yet
- App Brewery Cornell Notes TemplateDocument2 pagesApp Brewery Cornell Notes TemplateAyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Document PDF 277Document22 pagesDocument PDF 277Ayush SinghNo ratings yet
- PDF Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument173 pagesPDF Chemical ThermodynamicsAyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Functions: y F y X F XDocument1 pageFunctions: y F y X F XAyush SinghNo ratings yet
- IC Sol W03D1-0Document3 pagesIC Sol W03D1-0Ayush SinghNo ratings yet
- Answer On Question #44294-Physics-Mechanics-Kinematics-DynamicsDocument1 pageAnswer On Question #44294-Physics-Mechanics-Kinematics-DynamicsAyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Application ID: EN17221324 Version No: 2Document1 pageApplication ID: EN17221324 Version No: 2Ayush SinghNo ratings yet