Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Capacitors: D It C VT DT VT I D V I D C C
Capacitors: D It C VT DT VT I D V I D C C
Uploaded by
Karthikrajan SendhilnathanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Capacitors: D It C VT DT VT I D V I D C C
Capacitors: D It C VT DT VT I D V I D C C
Uploaded by
Karthikrajan SendhilnathanCopyright:
Available Formats
Capacitors
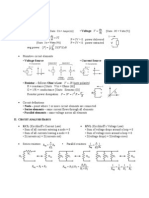
d 1 1
i (t ) = C v ( t ) and v ( t ) = i ( ) d = v ( 0 ) + i ( ) d
t t
dt C C 0
These equations describe an voltage and current that adhere to the passive convention.
All of the currents and voltages are constant in a dc circuit. When the capacitor voltage is
constant, the capacitor current is zero.
Capacitors act like open circuits in dc circuits.
Suppose the capacitor voltage is discontinuous, for example
4.3 t < 2.5
v (t ) =
4.4 t > 2.5
That is, the voltage changes from 4.3 V to 4.4 V abruptly at time t = 2.5 s . At t = 2.5 s , the
derivative of the capacitor voltage is
dv v ( t + t ) v ( t t ) 4.4 4.3
= lim = lim =
d t t 0 ( t + t ) ( t t ) t 0 2 t
Consequently, discontinuous capacitor voltages require infinite capacitor currents. Infinite
currents are physically impossible, so discontinuous capacitor voltages are physically impossible.
In the absence of infinite currents, capacitor voltages must be continuous.
You might also like
- EEEN 201 Lecture Notes-05Document16 pagesEEEN 201 Lecture Notes-05daglarduman510No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes-3Document16 pagesLecture Notes-3ndlovumpendulo281No ratings yet
- Capacitors, Inductors, Sinusoidal Signals and Phasor TransformationDocument38 pagesCapacitors, Inductors, Sinusoidal Signals and Phasor TransformationjunkmailtarsierNo ratings yet
- 5 CLDocument36 pages5 CLMd. Yousuf 2211461642No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Capacitance Inductance - NLHDocument40 pagesChapter 6 - Capacitance Inductance - NLHdyzilos 49No ratings yet
- Eca 1 ProblemsDocument15 pagesEca 1 ProblemsAhmed SohailNo ratings yet
- DC DC Buck ConverterDocument36 pagesDC DC Buck ConverterKunal Kumar GehlotNo ratings yet
- Capacitors Inductor SDocument14 pagesCapacitors Inductor SKhiew HongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part IDocument68 pagesChapter 3 Part IDaniel MengeshaNo ratings yet
- Esc201: Introduction To Electronics: Transient Analysis of Capacitive and Inductive CircuitsDocument30 pagesEsc201: Introduction To Electronics: Transient Analysis of Capacitive and Inductive CircuitsPrakhar chhalotreNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and Inductors (Compatibility Mode)Document23 pagesCapacitors and Inductors (Compatibility Mode)nervin13No ratings yet
- Circuit Types: DC CircuitsDocument6 pagesCircuit Types: DC Circuitsprasad4funNo ratings yet
- EE241: E C I: Lectric IrcuitsDocument64 pagesEE241: E C I: Lectric Ircuitss2-qx (s2.qx)No ratings yet
- Modeling Chapter 1Document18 pagesModeling Chapter 1Dilasha AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and InductorsDocument19 pagesCapacitors and InductorsRizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- MEMS 0031 Electric Circuits: Chapter 7: Lecture 7-1Document30 pagesMEMS 0031 Electric Circuits: Chapter 7: Lecture 7-1Zar KhitabNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and Inductors: Quick ReferenceDocument4 pagesCapacitors and Inductors: Quick ReferenceDildar Khan BhatiNo ratings yet
- Lecture #2 September 5, 2000Document50 pagesLecture #2 September 5, 2000tnamourNo ratings yet
- Esc201t l10 RC RL CircuitsDocument34 pagesEsc201t l10 RC RL CircuitsRachit MahajanNo ratings yet
- 2018-I-Ing Quimica Differential Equation (List-05)Document3 pages2018-I-Ing Quimica Differential Equation (List-05)Bryan MuñozNo ratings yet
- Transient Analysis - First Order CircuitsDocument11 pagesTransient Analysis - First Order CircuitseugeneNo ratings yet
- ES-1 Natural and Forced ResponseDocument39 pagesES-1 Natural and Forced ResponseGanesh DharmireddyNo ratings yet
- Ee2001 (Week3 Week6 Wcy)Document177 pagesEe2001 (Week3 Week6 Wcy)Giang Nguyễn TrườngNo ratings yet
- FourierTechniques in PowerDocument7 pagesFourierTechniques in PowerHassanNo ratings yet
- Lecture14 Wed Oct 11Document3 pagesLecture14 Wed Oct 11Akib ImtihanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document34 pagesLecture 3KISAKYE MOSESNo ratings yet
- Inductance, Capacitance, EtcDocument12 pagesInductance, Capacitance, Etcapi-3803118No ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument2 pagesCapacitorsreekantha reddyNo ratings yet
- EE-211 Linear Circuit Analysis: Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherDocument34 pagesEE-211 Linear Circuit Analysis: Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherHadeedAhmedSherNo ratings yet
- Sect 2 Energy and PowerDocument20 pagesSect 2 Energy and Powerkushil1998No ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Power and Energy: Lecturer: Dr. Vinita Vasudevan Scribe: RSS ChaithanyaDocument3 pagesLecture 4: Power and Energy: Lecturer: Dr. Vinita Vasudevan Scribe: RSS ChaithanyaAniruddha RoyNo ratings yet
- Programa: 1. Introdução Aos Circuitos Eléctricos 2. Grafos e Circuitos Resistivos LinearesDocument25 pagesPrograma: 1. Introdução Aos Circuitos Eléctricos 2. Grafos e Circuitos Resistivos LinearesPedro FernandesNo ratings yet
- Electronics Formulas ECE BOARD EXAMDocument22 pagesElectronics Formulas ECE BOARD EXAMMohammad Rayan Bin EliasNo ratings yet
- Time Domain Response of First Order RL and RC CircuitsDocument21 pagesTime Domain Response of First Order RL and RC CircuitsMOHSINALI MOMINNo ratings yet
- AC Circuit Analysis (Part 1) : EEE 3 Lecture 06Document40 pagesAC Circuit Analysis (Part 1) : EEE 3 Lecture 06No OneNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Lecture-27-21032024Document24 pagesAnalog Electronics Lecture-27-21032024Sayam SanchetiNo ratings yet
- Capacitor and InductorDocument19 pagesCapacitor and Inductorerynnguyen1110No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Capacitors and InductorsDocument46 pagesChapter 6 - Capacitors and InductorsFaizul Haque NiloyNo ratings yet
- CH 09Document66 pagesCH 09Praveen Kumar Kilaparthi0% (1)
- Electronic Curcuit Chapter 4Document49 pagesElectronic Curcuit Chapter 4AbcdNo ratings yet
- PE Boost 5.sqprojDocument4 pagesPE Boost 5.sqprojchandra bhanNo ratings yet
- 6.1 The Capacitor 6.2 The Inductor 6.3 Series - Parallel Combinations of Capacitance and Inductance 6.4 Mutual InductanceDocument28 pages6.1 The Capacitor 6.2 The Inductor 6.3 Series - Parallel Combinations of Capacitance and Inductance 6.4 Mutual Inductancejayant5253No ratings yet
- Source Free CircuitDocument4 pagesSource Free CircuitAhnaf HasanNo ratings yet
- DISU231/EECE231 Basic Circuit Theory Homework 5: Fall Semester 2023Document2 pagesDISU231/EECE231 Basic Circuit Theory Homework 5: Fall Semester 2023이주영No ratings yet
- Lec6 - Mutual InductanceDocument30 pagesLec6 - Mutual InductancePhan Phuong NgocNo ratings yet
- Tutorial QuestionsDocument1 pageTutorial Questionschefrederick01No ratings yet
- Lecture 1003Document4 pagesLecture 1003YocobSamandrewsNo ratings yet
- Transient Response of RL and RC CIRCUITDocument10 pagesTransient Response of RL and RC CIRCUITSajjad AslamNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Energy Storage Element2Document39 pagesWeek 1 - Energy Storage Element2Mcx BarthanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 28 and 29 - Isentropic Flow With Area Change - Handout VersionDocument16 pagesLesson 28 and 29 - Isentropic Flow With Area Change - Handout VersionjacksayshiNo ratings yet
- 6002x Notes ExscapeDocument77 pages6002x Notes ExscapeNVNo ratings yet
- Review of Heat TransferDocument47 pagesReview of Heat TransferNurul HanifahNo ratings yet
- Today:: QT V Itr CDocument8 pagesToday:: QT V Itr CAbdul MuhaiminNo ratings yet
- Chap4-Buck Boost and FlybackDocument29 pagesChap4-Buck Boost and FlybackArchit BaglaNo ratings yet
- E6 SAS 14 Example Sheet 2 SolutionsDocument8 pagesE6 SAS 14 Example Sheet 2 Solutionstamucha.fx.derivNo ratings yet
- Circuit AnalysisDocument15 pagesCircuit AnalysisoffnruninNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Endeavour Automation ProfileDocument15 pagesEndeavour Automation ProfileKarthikrajan SendhilnathanNo ratings yet
- Gate Driver # Input Voltage (MCU) Voltage Across IGBT Input Frequency Input DSO Waveform (MCU) 1 5V 15V 50HzDocument3 pagesGate Driver # Input Voltage (MCU) Voltage Across IGBT Input Frequency Input DSO Waveform (MCU) 1 5V 15V 50HzKarthikrajan SendhilnathanNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security of Smart Grid: Jazeel K T 7821 EDocument32 pagesCyber Security of Smart Grid: Jazeel K T 7821 EKarthikrajan SendhilnathanNo ratings yet
- IgbtDocument9 pagesIgbtKarthikrajan SendhilnathanNo ratings yet
- Rtevents User GuideDocument114 pagesRtevents User GuideKarthikrajan SendhilnathanNo ratings yet
- Print Time:October 02, 2015 18:02:26 Tek Trig'd M Pos: 0sDocument1 pagePrint Time:October 02, 2015 18:02:26 Tek Trig'd M Pos: 0sKarthikrajan SendhilnathanNo ratings yet