Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kicap Law
Kicap Law
Uploaded by
WM Hazwan W Mustapa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views1 pageThis document uses Kirchoff's laws to solve a circuit with three branches and two nodes. It sets up two equations using Kirchoff's current law at each node. It then derives two more equations using Kirchoff's voltage law around the two loops. Solving the resulting system of equations yields a current of -0.143 Amps for I1 and 0.429 Amps for I2. Therefore, the current in resistor R3 is 0.286 Amps.
Original Description:
a
Original Title
kicap law
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document uses Kirchoff's laws to solve a circuit with three branches and two nodes. It sets up two equations using Kirchoff's current law at each node. It then derives two more equations using Kirchoff's voltage law around the two loops. Solving the resulting system of equations yields a current of -0.143 Amps for I1 and 0.429 Amps for I2. Therefore, the current in resistor R3 is 0.286 Amps.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views1 pageKicap Law
Kicap Law
Uploaded by
WM Hazwan W MustapaThis document uses Kirchoff's laws to solve a circuit with three branches and two nodes. It sets up two equations using Kirchoff's current law at each node. It then derives two more equations using Kirchoff's voltage law around the two loops. Solving the resulting system of equations yields a current of -0.143 Amps for I1 and 0.429 Amps for I2. Therefore, the current in resistor R3 is 0.286 Amps.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
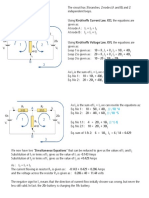
Kirchoffs Circuit Law Example No1
Find the current flowing in the 40 Resistor, R3
The circuit has 3 branches, 2 nodes (A and B) and 2 independent loops.
Using Kirchoffs Current Law, KCL the equations are given as;
At node A : I1 + I2 = I3
At node B : I3 = I1 + I2
Using Kirchoffs Voltage Law, KVL the equations are given as;
Loop 1 is given as : 10 = R1 x I1 + R3 x I3 = 10I1 + 40I3
Loop 2 is given as : 20 = R2 x I2 + R3 x I3 = 20I2 + 40I3
Loop 3 is given as : 10 - 20 = 10I1 - 20I2
As I3 is the sum of I1 + I2 we can rewrite the equations as;
Eq. No 1 : 10 = 10I1 + 40(I1 + I2) = 50I1 + 40I2
Eq. No 2 : 20 = 20I2 + 40(I1 + I2) = 40I1 + 60I2
We now have two Simultaneous Equations that can be reduced to give us the values of I1 and I2
Substitution of I1 in terms of I2 gives us the value of I1 as -0.143 Amps
Substitution of I2 in terms of I1 gives us the value of I2 as +0.429 Amps
As : I3 = I1 + I2
The current flowing in resistor R3 is given as : -0.143 + 0.429 = 0.286 Amps
and the voltage across the resistor R3 is given as : 0.286 x 40 = 11.44 volts
The negative sign for I1 means that the direction of current flow initially chosen was wrong, but never
the less still valid. In fact, the 20v battery is charging the 10v battery.
You might also like
- Kirchhoffs Law Problems and SolutionsDocument3 pagesKirchhoffs Law Problems and SolutionsSpencer HayesNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff's Laws ExampleDocument2 pagesKirchhoff's Laws ExampleAyyub AchilevNo ratings yet
- Application of KCL and KVL-1Document2 pagesApplication of KCL and KVL-1Vinayak Saini100% (1)
- Kirchoffs Circuit Laws: Presentation by Donald Gunn Beng (Hons), MietDocument19 pagesKirchoffs Circuit Laws: Presentation by Donald Gunn Beng (Hons), MietGrimmo1979No ratings yet
- KCL KVL NumericalsDocument10 pagesKCL KVL NumericalsDharam BassiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 (Topic 1-Kirchhoff's Laws Method)Document5 pagesModule 2 (Topic 1-Kirchhoff's Laws Method)KIN RED CUERDONo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff's Current Law ExampleDocument2 pagesKirchhoff's Current Law Examplehsejmal12345No ratings yet
- 5 Kirchhoff's LawsDocument13 pages5 Kirchhoff's LawsMohamed AhmedNo ratings yet
- ECA Lab ManualDocument49 pagesECA Lab Manualgecsiwan70No ratings yet
- Kirchoff's LawsDocument38 pagesKirchoff's LawsSam Denielle Tugaoen100% (1)
- Thevenin's Theorem: SolutionDocument30 pagesThevenin's Theorem: SolutionRaghupatiNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms: 1. Node 2. Junction 3. Branch 4. Loop 5. Mesh 6. Voltage DropDocument26 pagesDefinition of Terms: 1. Node 2. Junction 3. Branch 4. Loop 5. Mesh 6. Voltage DropYuan MoralesNo ratings yet
- DC Circuit AnalysisDocument17 pagesDC Circuit AnalysisShizu SeijuroNo ratings yet
- TR RL Hukum Ohm Dan Hukum KirchhoffDocument10 pagesTR RL Hukum Ohm Dan Hukum KirchhoffPasmayana Sinaga09No ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits and Kirchhoff's RulesDocument6 pagesElectrical Circuits and Kirchhoff's RulesKaye RamosNo ratings yet
- Electrical TechnologyDocument55 pagesElectrical TechnologyRajeev Ranjan Pushp50% (2)
- Simple Circuits and Kirchoffs LawsDocument24 pagesSimple Circuits and Kirchoffs LawsJoseMiguelDomingo100% (1)
- Superposition Theorem ExperimentDocument6 pagesSuperposition Theorem ExperimentKamal karolyaNo ratings yet
- Kirchoffs Circuit LawsDocument3 pagesKirchoffs Circuit Lawsceller101No ratings yet
- Kirchhoff LawDocument16 pagesKirchhoff LawJan Ashley LapuzNo ratings yet
- Direct Current Circuit AnalysisDocument58 pagesDirect Current Circuit AnalysisLutfi LatifNo ratings yet
- Application of Linear Algebra in Electrical CircuitDocument16 pagesApplication of Linear Algebra in Electrical CircuitkhairunnisalazimNo ratings yet
- Shreyas Patil KVL ExpDocument27 pagesShreyas Patil KVL Expshreyas patilNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Worksheet in General Physics 2 Kirchhoff'S Rules I. Introductory ConceptDocument7 pagesLearning Activity Worksheet in General Physics 2 Kirchhoff'S Rules I. Introductory ConceptDino Manuel E. PrestadoNo ratings yet
- E4821 Analisis LitarDocument14 pagesE4821 Analisis LitarEyfa NordinNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 8 Kirchhoffs LawDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 8 Kirchhoffs LawChristian EspanolNo ratings yet
- Bee Lab ManualDocument43 pagesBee Lab ManualShivansh SahuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7-Kirchhoffs LawDocument8 pagesLesson 7-Kirchhoffs LawKhim PingolNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 NotesDocument90 pagesUnit-1 NotesSujit KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Circuit TheoryDocument34 pages1 Circuit TheoryLove StrikeNo ratings yet
- 1 Circuit TheoryDocument34 pages1 Circuit TheoryFaris Abd HalimNo ratings yet
- Kirchof LawsDocument33 pagesKirchof LawsZain SaleemNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document39 pagesChap 2miyuruNo ratings yet
- CHP 1: Circuit TheoryDocument42 pagesCHP 1: Circuit TheoryjojoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 (Equivalent Resistance)Document113 pagesChapter 02 (Equivalent Resistance)Mahra AlaliNo ratings yet
- Hukum KirchoffDocument15 pagesHukum KirchoffarifNo ratings yet
- Handouts For Module 1.2 - EE211Document4 pagesHandouts For Module 1.2 - EE211Chrisser Van BaetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 ReportDocument9 pagesChapter 18 ReportNayLinNo ratings yet
- Direct Current (DC) CircuitsDocument11 pagesDirect Current (DC) CircuitsLim JiaShinNo ratings yet
- Simple Circuits and Kirchoffs LawsDocument35 pagesSimple Circuits and Kirchoffs LawsChristianNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Kirchhoff's Laws WorksheetDocument4 pages5.2 Kirchhoff's Laws Worksheet윤영석No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Circuits AnalysisDocument4 pagesLesson 3 Circuits AnalysisrainaNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Kirchoff's Laws Worksheet: Kirchhoff's Current LawDocument4 pages5.2 Kirchoff's Laws Worksheet: Kirchhoff's Current LawAltheo MateoNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff LawDocument42 pagesKirchhoff LawChris Osea AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics PPT Lesson 5 ParallelDocument31 pagesBasic Electronics PPT Lesson 5 ParallelStacie DDDNo ratings yet
- 107 Network TheoremDocument16 pages107 Network TheoremHamnah HosanyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 08Document29 pagesLecture 08amitNo ratings yet
- DC CircuitsDocument14 pagesDC CircuitsDaveNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff's LawsDocument11 pagesKirchhoff's LawsImus CaviteNo ratings yet
- Network Theory EC201 NoteDocument70 pagesNetwork Theory EC201 NotevpzfarisNo ratings yet
- PHY 214aDocument9 pagesPHY 214aonyedikachukwurNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)Document6 pagesKirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)JulesNo ratings yet
- KVLDocument5 pagesKVLAliNo ratings yet
- Melbourne School of Engineering ELEN30009 Electrical Network Analysis & Design Semester 1, 2017Document34 pagesMelbourne School of Engineering ELEN30009 Electrical Network Analysis & Design Semester 1, 2017RogerNo ratings yet
- RC RL PDFDocument4 pagesRC RL PDFVivek SarafNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 PDFDocument20 pagesChapter1 PDFWM Hazwan W MustapaNo ratings yet
- Eqt 271Document13 pagesEqt 271WM Hazwan W MustapaNo ratings yet
- Politeknik Sultan Haji Ahmad Shah: AS101/Quiz2/Jun11Document2 pagesPoliteknik Sultan Haji Ahmad Shah: AS101/Quiz2/Jun11WM Hazwan W MustapaNo ratings yet
- Communicationskillsppt Compatibility ModeDocument24 pagesCommunicationskillsppt Compatibility ModeWM Hazwan W MustapaNo ratings yet