Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M6u5 Parent Letter
M6u5 Parent Letter
Uploaded by
api-366304862Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
M6u5 Parent Letter
M6u5 Parent Letter
Uploaded by
api-366304862Copyright:
Available Formats
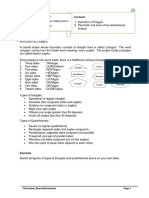
Math 6 Unit 5
Area and Volume
Volume 1 Issue 5
References Dear Parents
Helpful Links: In this unit students will learn about finding the area of polygons, the surface area of prisms and
www.khanacademy.org/ pyramids, and the volume of prisms with fractional edges.
math/basic-geo/basic-
geo-volume-surface-
area/basic-geo-
Concepts Students will Use and Understand
volume/v/volume-of-a- The area of irregular and regular polygons can be found by decomposing the polygon into
rectangular-prism-with- rectangles, triangles and other shapes.
fractional-cubes
Manipulatives and the construction of nets may be used in computing the surface area of
www.onlinemathlearning rectangular and triangular prisms, and volume of right rectangular prism.
.com/prism-surface- Formulas may be used to compute the areas of polygons, surface areas of rectangular and
area.html triangular prisms, and volumes of right rectangular prisms.
Appropriate units of measure should be used when computing the area (square units) of
www.geogebra.org/en/u
pload/files/english/Victor polygons, and surface area (square units) and volume of prisms (cubic units).
ia/TriangleArea.html Views of rectangular and triangular prisms may be interpreted and sketched to provide a 2-
dimensional representation of a three dimensional figure.
www.ixl.com/math/gra Fractional edge lengths are equivalent to the dimensions of solid figures
de-6/volume-and- The volume of a solid figure is the number of same sized cubes filling the space so that there are
surface-area
no gaps and overlaps.
http://www.learner.or
g/interactives/geometr Vocabulary
y/3d_prisms.html Area: The number of square units it takes to completely fill a space or surface.
Bases of a Prism: The two faces formed by congruent polygons that lie in parallel planes, all of the other
Georgia Math faces being parallelograms.
Textbook Connection: Cubic Units: Volume of the solids is measured in Cubic Units.
Edge: The intersection of a pair of faces in a three-dimensional figure.
Ch. 8: Lessons 1-5 Equilateral Triangle: A triangle which has all three of its sides equal in length.
Ch. 9: Lessons 1-5 Face: One of the polygons that makes up a polyhedron.
Fractional edge length: The length of each edge of the cube is a fraction.
Textbook Online: Isosceles Triangle: A triangle which has two of its sides equal in length.
Georgia Math Kite: A quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of equal adjacent sides.
http://connected.mcgr A kite-shaped figure.
aw- Lateral Faces: In a prism, a face that is not a base of the figure.
hill.com/connected/log Net: A two-dimensional figure that, when folded, forms the surfaces of a three-dimensional object.
in.do Parallelogram: A quadrilateral with both pairs of opposite sides parallel.
Polygon: A number of coplanar line segments, each connected end to end to form a closed shape. A
regular polygon has all sides equal and all interior angles equal. An irregular polygon sides are not all the
same length nor does the interior angles have the same measure.
Polyhedron: A 3-dimensional figure that has polygons as faces.
Prism: A polyhedron with two parallel and congruent faces, called bases, and all other faces that are
parallelograms.
Quadrilaterals: Four coplanar line segments linked end to end to create a closed figure.
A 4-sided polygon.
Rectangle: A 4-sided polygon where all interior angles are 90.
Rectangular prism: A solid (3-dimensional) object which has six faces that are rectangles.
Rhombus: A quadrilateral with all four sides equal in length.
Right Triangle: A triangle where one of its interior angles is a right angle (90 degrees).
Right rectangular prism: In a right prism, the lateral faces are each perpendicular to the bases.
Scalene Triangle: A triangle where all three sides are different in length.
Square: A quadrilateral that has four right angles and four equal sides.
Surface area: The total area of the 2-dimensional surfaces that make up a 3-dimensional object.
Trapezoid: A quadrilateral which has one pair of parallel sides.
Triangles: A closed figure consisting of three line segments linked end-to-end.
A 3-sided polygon
Triangular prism: A prism whose bases are triangles. A solid (3-dimensional object what has five faces:
three rectangles and two bases.
Vertices: The common endpoint of two or more rays or line segments
Volume: The amount of space occupied by an object.
Volume of a Prism: The area of a base times the height. The number of cubic units to fill a prism.
Try http://intermath.coe.uga.edu/dictnary/homepg.asp or http://www.amathsdictionaryforkids.com/ for
further examples.
Formulas Example 1 Example 2
What is the area of this triangle? What is the area of this flower garden?
Area
8 ft
28 cm
Parallelogram 8 cm
A = bh 16 cm
9 ft
Triangle
A = bh 13 ft
24 cm
Volume Example 3 Example 4
The net of a square pyramid is shown below.
Rectangular Prism
5 in
V = lwh
2 in
V = Bh
8 in
1 in
1 in
What is the volume of the rectangular prism? What is the surface area of the pyramid?
Key
Example 1 Example 2
A = bh A = bh A = bh 22.5
A=bh A=bh A=bh + 72.0
A = 24 8 A=95 A=98 94.5
A = 192 A = 45 A = 72
A = 96 A = 22.5 The area of the
The area of the triangle is 96 cm2. garden is 94.5 ft2.
Example 3 Example 4
V = lwh A = b2 A = bh 80
V = l w h A=bb A=bh + 64
V = 1 1 2 A=88 A=85 144
V = 1 2 A = 64 A = 40
V = 3 in3 A = 20 The surface area of
20 4 = 80 the pyramid is 144 in2.
You might also like
- 7.5.1 - Surface Area of A Prism and CylinderDocument5 pages7.5.1 - Surface Area of A Prism and CylinderGaran WisemanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - QuadrilateralsDocument29 pagesLecture 4 - QuadrilateralsSandra Enn BahintingNo ratings yet
- Geometry EOC Review PacketDocument39 pagesGeometry EOC Review PacketVale MejiaNo ratings yet
- Rumus PrimoidalDocument7 pagesRumus PrimoidaltsipilNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument9 pagesMathematicsRachel AmairaNo ratings yet
- Math Cartoon AnimationDocument3 pagesMath Cartoon Animationapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Geo Performance Task s2 1Document6 pagesGeo Performance Task s2 1api-553676905No ratings yet
- Mathematics Note For Grade 10Document8 pagesMathematics Note For Grade 10darseziyad34No ratings yet
- Mensuration: Basic Concepts and Important Formulas Equilateral TriangleDocument5 pagesMensuration: Basic Concepts and Important Formulas Equilateral TriangleSrinu MaddikuntlaNo ratings yet
- Geometry: B. Solid/Space Geometry 1. Position of Lines in SpaceDocument9 pagesGeometry: B. Solid/Space Geometry 1. Position of Lines in SpaceBagas FajriansyahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part 1Document16 pagesChapter 3 Part 1KokieNo ratings yet
- A About Area and PerimeterDocument11 pagesA About Area and PerimeterAmiel ColanoNo ratings yet
- Four-Side Plane FiguresDocument26 pagesFour-Side Plane FiguresFajrin Maulana Kingwijati100% (1)
- Quadrilaterals Digital TextDocument14 pagesQuadrilaterals Digital TextAmruthaNo ratings yet
- Plane Figures: Group 1Document49 pagesPlane Figures: Group 1Danielle Kate MadridNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Math Vocabulary (Gr. 8)Document3 pagesChapter 11 Math Vocabulary (Gr. 8)moona imranNo ratings yet
- Ge 4 ModuleDocument33 pagesGe 4 ModuleRenvil Igpas MompilNo ratings yet
- Heep 206Document42 pagesHeep 206Bodhisatya BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- The Volume,, of A Cube Is Determined by The Following FormulaDocument12 pagesThe Volume,, of A Cube Is Determined by The Following FormulaMolla DerbewNo ratings yet
- Nets - Volume - Surface Area of Prisms PDFDocument9 pagesNets - Volume - Surface Area of Prisms PDFTaseen TanvirNo ratings yet
- Visualizing Solid Shapes PDFDocument42 pagesVisualizing Solid Shapes PDFAshishNo ratings yet
- Geraldine Ramos - MIDTERMDocument10 pagesGeraldine Ramos - MIDTERMGeraldine RamosNo ratings yet
- Plane Figure and Their Properties A. Plane Figure Definition of Plane FigureDocument5 pagesPlane Figure and Their Properties A. Plane Figure Definition of Plane FigureKasmawati FatirNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry PrismsDocument17 pagesAnalytic Geometry PrismsCarl Kristopher Pelonia100% (1)
- Final Math PortfolioDocument32 pagesFinal Math Portfolioapi-311730016No ratings yet
- Ch8 Quadrilaterals Chapter NotesDocument5 pagesCh8 Quadrilaterals Chapter NotesMohanNayakNo ratings yet
- GEE 9 - Chapter 4 - Plane FiguresDocument23 pagesGEE 9 - Chapter 4 - Plane FiguresPREFIX THAT IS LONG - Lester LoutteNo ratings yet
- Measurement Notes For Grade 10 MathematicsDocument14 pagesMeasurement Notes For Grade 10 MathematicsBanekeNo ratings yet
- Airline Tickets: Unit SquareDocument1 pageAirline Tickets: Unit SquareCarol LizardoNo ratings yet
- Quadrilateral 2024 (1)Document41 pagesQuadrilateral 2024 (1)Yonela MquqwanaNo ratings yet
- Ariel Li Basic GeometryDocument5 pagesAriel Li Basic GeometryOmkar MandalNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3.2-MOM-1H_3.Document62 pagesChapter-3.2-MOM-1H_3.lamerez.j2004No ratings yet
- Math 5-Plane and Solid Geometry-Research - Bsed 2d-EscañoDocument35 pagesMath 5-Plane and Solid Geometry-Research - Bsed 2d-EscañoJulie Anne Ponteres EscañoNo ratings yet
- A QuadrilateralDocument64 pagesA QuadrilateralRed Dela Cruz100% (1)
- 8.1 Three-Dimensional Figures: ObjectivesDocument18 pages8.1 Three-Dimensional Figures: Objectiveszakaria shineeNo ratings yet
- 6 2 Unit 5 VocabDocument2 pages6 2 Unit 5 Vocabapi-260971765No ratings yet
- Descriptive Geometry II: Oct. 23/ 2021 Muhammed ADocument32 pagesDescriptive Geometry II: Oct. 23/ 2021 Muhammed AHULE ADDIS ENTERTAINMENTNo ratings yet
- Lesson On Solid MensurationDocument18 pagesLesson On Solid MensurationKelly Lulu100% (1)
- Chapter 3.1 Basic Concepts of SolidsDocument7 pagesChapter 3.1 Basic Concepts of SolidsSanchez Jhundell R. - BSME 2ENo ratings yet
- Area and PerimetreDocument28 pagesArea and PerimetreИакс ВбдубакировNo ratings yet
- w11 HDTBasMathDocument3 pagesw11 HDTBasMathKhaeroni KhaeroniNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration PDFDocument25 pagesSolid Mensuration PDFHEIDI ROSE MENDOZANo ratings yet
- MTG Handout Session9Document5 pagesMTG Handout Session9Kenzo Rafael ManaloNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment English For Basics Mathematics Solid/ Space GeometryDocument7 pagesIndividual Assignment English For Basics Mathematics Solid/ Space GeometryNadya Zahwa LuthainNo ratings yet
- 3 6webDocument18 pages3 6webJohn Nikko NicolasNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 2Document62 pagesChapter-3 2AleahNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Parallelograms and Their Properties: Lesson 1Document31 pagesKinds of Parallelograms and Their Properties: Lesson 1Ivy Mae CagandeNo ratings yet
- Cynthia Medina Salas: 25 203 Leonel CantúDocument6 pagesCynthia Medina Salas: 25 203 Leonel CantúCHOINo ratings yet
- Surface Area and VolumeDocument27 pagesSurface Area and VolumeRiNo ratings yet
- POLYGONSDocument45 pagesPOLYGONSBlessa Mae100% (1)
- ArMath1 - Presentation3Document31 pagesArMath1 - Presentation3Jayson RamirezNo ratings yet
- Triangle Square: Heptagon OctagonDocument54 pagesTriangle Square: Heptagon OctagonJyotsna Rawal100% (1)
- Module 3 - Unit 2Document16 pagesModule 3 - Unit 2ntulagan05No ratings yet
- Geometry!!!Document19 pagesGeometry!!!Jane AnonasNo ratings yet
- Measurement - Solid FiguresDocument44 pagesMeasurement - Solid FiguresFREDERICK FUENTESNo ratings yet
- SurfaceAreaandVolume TEXTDocument26 pagesSurfaceAreaandVolume TEXTprabsahiNo ratings yet
- Volume FormulaDocument5 pagesVolume FormulachesteruytiepoNo ratings yet
- Types Formulas Parts Special Polygons Names: What Is A Polygon?Document4 pagesTypes Formulas Parts Special Polygons Names: What Is A Polygon?Johnel AgueloNo ratings yet
- Area Formulas: Gemonrty FormulaDocument12 pagesArea Formulas: Gemonrty FormulaPankaj Jirafe100% (1)
- How To Find Area of A ParallelogramDocument5 pagesHow To Find Area of A Parallelogramapi-126876773No ratings yet
- 1.Pbk Nets and Surface Areas Yr8Document14 pages1.Pbk Nets and Surface Areas Yr8ChristineNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Three-Dimensional Figures with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Three-Dimensional Figures with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Ordered Pairs Worksheet and ActivityDocument2 pagesOrdered Pairs Worksheet and Activityapi-366304862No ratings yet
- 6th Grade Choice Board 4-17Document1 page6th Grade Choice Board 4-17api-366304862No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Study GuideDocument2 pagesUnit 2 Study Guideapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Unit 6 Study Guide Answer KeyDocument4 pagesUnit 6 Study Guide Answer Keyapi-366304862100% (1)
- 1106 Am Office LensDocument1 page1106 Am Office Lensapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Mathematicians Research ProjectDocument3 pagesMathematicians Research Projectapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Study Guide Answer KeyDocument6 pagesUnit 5 Study Guide Answer Keyapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Teacher For A DayDocument2 pagesTeacher For A Dayapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Lsga Math Mock Milestone Student VersionDocument36 pagesLsga Math Mock Milestone Student Versionapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Sqs Student WorksheetDocument2 pagesSqs Student Worksheetapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Name - Date - Per - Measures of Variation WorksheetDocument1 pageName - Date - Per - Measures of Variation Worksheetapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Box and Whisker PlotsDocument20 pagesBox and Whisker Plotsapi-366304862No ratings yet
- CCGPS Math 6 Grade Unit 5 Study Guide - Area & Volume FormulasDocument6 pagesCCGPS Math 6 Grade Unit 5 Study Guide - Area & Volume Formulasapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Study Guide Answer KeyDocument6 pagesUnit 5 Study Guide Answer Keyapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Mathematical Association of America The American Mathematical MonthlyDocument3 pagesMathematical Association of America The American Mathematical MonthlyAllanNo ratings yet
- hw3 SolDocument4 pageshw3 Solkalaputra100% (1)
- Visualising Solid Shapes: Unit 6 Unit 6 Unit 6 Unit 6 Unit 6Document42 pagesVisualising Solid Shapes: Unit 6 Unit 6 Unit 6 Unit 6 Unit 6AjiteshPaddaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Class Viii PDFDocument13 pagesMathematics Class Viii PDFKhushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- A Process of Testing Mathematics - Level 4.1 - 2020 3rd and 4th Edition Answer KeyDocument11 pagesA Process of Testing Mathematics - Level 4.1 - 2020 3rd and 4th Edition Answer KeyKishaNo ratings yet
- Prueba de Admisión - Grado Primero.Document3 pagesPrueba de Admisión - Grado Primero.Gabriela Vilegas DiazNo ratings yet
- 2D and 3D ShapesDocument3 pages2D and 3D ShapesvirusNo ratings yet
- 12-2 Surface Areas of Prisms and Cylinders PDFDocument24 pages12-2 Surface Areas of Prisms and Cylinders PDFMuneeza Hashmi100% (1)
- Circles Are Drawn With Four Vertices As The CenterDocument5 pagesCircles Are Drawn With Four Vertices As The CenterAyushNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Integers, Powers and Roots: AnswersDocument37 pagesChapter 1 Integers, Powers and Roots: AnswersMoaaz MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Viviani's Theorem - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesViviani's Theorem - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediarenzenzo92No ratings yet
- Projection of LineDocument3 pagesProjection of LineSuyog ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Numeracy REVISION Booklet 3Document19 pagesNumeracy REVISION Booklet 3evans munakuNo ratings yet
- Leonardo Da Vinci's PolyhedraDocument10 pagesLeonardo Da Vinci's Polyhedraguitarist^_^No ratings yet
- The E Tutor - Similarities of TrianglesDocument22 pagesThe E Tutor - Similarities of Trianglesinfo5963No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Faces: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument16 pagesChapter 8 Faces: Multiple Choice QuestionsLilianLeeNo ratings yet
- Edulabz: InternationalDocument6 pagesEdulabz: InternationalrajikrajanNo ratings yet
- Revised-Ssm-Class Viii MathematicsDocument91 pagesRevised-Ssm-Class Viii MathematicsKPOP IS LIFENo ratings yet
- Michel Deza, Serguei Shpectorov and Mathieu Dutour-Sikiric - Wythoff Construction and l1 - EmbeddingDocument53 pagesMichel Deza, Serguei Shpectorov and Mathieu Dutour-Sikiric - Wythoff Construction and l1 - EmbeddingFlaoeramNo ratings yet
- Area of A TriangleDocument10 pagesArea of A TriangleAyeola RobertsonNo ratings yet
- Visualizes, Names and Describes Polygons With 5 of More SidesDocument20 pagesVisualizes, Names and Describes Polygons With 5 of More SidesDANNAH MARIE ANDANo ratings yet
- Solid Object: Ce 102: Civil Engineering Drawing IDocument27 pagesSolid Object: Ce 102: Civil Engineering Drawing INazmul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Prmo - Rmo l8 (Geometry l1)Document44 pagesPrmo - Rmo l8 (Geometry l1)ankit satpati0% (1)
- Triangle MixreviewtrianglesumDocument4 pagesTriangle Mixreviewtrianglesumapi-3270415240% (1)
- NSM 8 CB Ch09Document29 pagesNSM 8 CB Ch09Lino100% (2)
- Quadrilateral: Kite: A Quadrilateral in Which Two Disjoint Pairs ofDocument3 pagesQuadrilateral: Kite: A Quadrilateral in Which Two Disjoint Pairs ofmichaelllaNo ratings yet
- Extra Practice Sample AnswersDocument1 pageExtra Practice Sample Answersalcilene almeidaNo ratings yet
- QA - Session 12 - Mensuration - Final - 2019Document3 pagesQA - Session 12 - Mensuration - Final - 2019Ashwini JadhavNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q3 - W2Document10 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q3 - W2Lei DollosaNo ratings yet