Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chamber's Journal January 06 PDF
Chamber's Journal January 06 PDF
Uploaded by
Manisha SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- TR - CM - Configuration Document TemplateDocument44 pagesTR - CM - Configuration Document TemplateHrushikesh Vishnu Shrotriya95% (39)
- Prudential Norms For Non-Banking Financial (Non-Deposit Accepting or Holding) CompaniesDocument6 pagesPrudential Norms For Non-Banking Financial (Non-Deposit Accepting or Holding) CompaniesGreeshma Babu ShylajaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Npa of Public Sector Banks in India: Sulagna Das, AbhijitduttaDocument9 pagesA Study On Npa of Public Sector Banks in India: Sulagna Das, AbhijitduttaSunil Kumar PalikelaNo ratings yet
- Income Recognition, Asset Classification and Provisioning Norms For The Urban Cooperat Ive BanksDocument10 pagesIncome Recognition, Asset Classification and Provisioning Norms For The Urban Cooperat Ive Banksramsundar_99No ratings yet
- Banking Accounts: by Prof. Maheshwari Vijay KumarDocument7 pagesBanking Accounts: by Prof. Maheshwari Vijay KumarOmpriya AcharyaNo ratings yet
- 2 Statement of Financial PositionDocument7 pages2 Statement of Financial Positionreagan blaireNo ratings yet
- Debt RestructuringDocument5 pagesDebt RestructuringVinay TripathiNo ratings yet
- Hemant Vijay Pandya: Non-Banking Financial Company An OverviewDocument32 pagesHemant Vijay Pandya: Non-Banking Financial Company An OverviewHashmi SutariyaNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet)Document12 pages3.3 Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet)Brier Jaspin AguirreNo ratings yet
- Advanced Auditing and Professional Ethics 1688653213Document28 pagesAdvanced Auditing and Professional Ethics 1688653213mdasifraza3196No ratings yet
- Irac NormsDocument9 pagesIrac NormsAtul ThakurNo ratings yet
- Irac Norms: Bank Branch AuditDocument45 pagesIrac Norms: Bank Branch AuditjamilsbmmNo ratings yet
- 08 MF NBFC - UnlockedDocument23 pages08 MF NBFC - UnlockedBittu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Accountancy XII Exam Handbook For 2024 ExamDocument88 pagesAccountancy XII Exam Handbook For 2024 ExamHari prakarsh Nimi100% (1)
- WA0004. - RemovedDocument76 pagesWA0004. - Removedsushil.saliyan1003No ratings yet
- Indofood CBP Sukses Makmur TBK Statement of Financial PositionDocument4 pagesIndofood CBP Sukses Makmur TBK Statement of Financial Positionmuhamad khadiqNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements of Banking Companies: © The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaDocument44 pagesFinancial Statements of Banking Companies: © The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaHarikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Model NFS - Full PFRS (2022) - Nonlending and NonfinancingDocument35 pagesModel NFS - Full PFRS (2022) - Nonlending and NonfinancingJoel RazNo ratings yet
- Non-Performing Assets (NPA) : Asset Classification, Income Recognition and Provisioning NormsDocument52 pagesNon-Performing Assets (NPA) : Asset Classification, Income Recognition and Provisioning Normspriyankaarora9010No ratings yet
- Prudential Norms ExplanationDocument4 pagesPrudential Norms ExplanationSneha ChavanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Auditing & Professional Ethics: Master MindsDocument17 pagesAdvanced Auditing & Professional Ethics: Master MindsMaroju RajithaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Npas: A NPA Is A Loan or An Advance WhereDocument58 pagesDefinition of Npas: A NPA Is A Loan or An Advance WhereAnnu BallanNo ratings yet
- Credit Audit - Positive Score Areas in Pre Sanction - Tips On Value Statements in Credit Auditable Accounts Upto Rs 50 CRDocument73 pagesCredit Audit - Positive Score Areas in Pre Sanction - Tips On Value Statements in Credit Auditable Accounts Upto Rs 50 CRHaRa TNo ratings yet
- Caballero Ba53 Chap 2Document32 pagesCaballero Ba53 Chap 2Drew BooNo ratings yet
- Recovery Policy - 2012Document23 pagesRecovery Policy - 2012Dhawan SandeepNo ratings yet
- Goal - A Process of Continuous Improvement - Eliyahu Goldratt (Qwerty80)Document43 pagesGoal - A Process of Continuous Improvement - Eliyahu Goldratt (Qwerty80)Girish GaykawadNo ratings yet
- Chapter1: Introduction: Nonperforming Asset in BankDocument35 pagesChapter1: Introduction: Nonperforming Asset in BankMaridasrajanNo ratings yet
- Section 4 IDocument22 pagesSection 4 ISatish Ranjan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Unveiling Valuation Challenges: in Reporting of Nav by Aifs Under Sebi (Alternative Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012Document12 pagesUnveiling Valuation Challenges: in Reporting of Nav by Aifs Under Sebi (Alternative Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012Sourabh GargNo ratings yet
- Ind AS 7 PDFDocument23 pagesInd AS 7 PDFnavinsurana1987No ratings yet
- Money and BankingDocument10 pagesMoney and BankingSahil ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Audit of AdvancesDocument29 pagesAudit of AdvancesHemanshu SolankiNo ratings yet
- Npa in SbiDocument96 pagesNpa in SbiApoorva M V100% (2)
- Non-Banking Financial CompaniesDocument49 pagesNon-Banking Financial CompaniesAdison Growar SatyeNo ratings yet
- NBFC Project Report by MS. Sonia JariaDocument34 pagesNBFC Project Report by MS. Sonia JariaSonia SoniNo ratings yet
- A Study On NPA of Public Sector Banks in India: January 2014Document10 pagesA Study On NPA of Public Sector Banks in India: January 2014rajesh nimodiaNo ratings yet
- Final DT 100 Important Questions Final Audit Practice Questions Financial Reporting Conceptual NotesDocument14 pagesFinal DT 100 Important Questions Final Audit Practice Questions Financial Reporting Conceptual NotesDheeraj TurpunatiNo ratings yet
- KPMG Flash News Draft Guidelines For Core Investment CompaniesDocument5 pagesKPMG Flash News Draft Guidelines For Core Investment CompaniesmurthyeNo ratings yet
- Resource Planning PolicyDocument3 pagesResource Planning Policymadhvi GajjarNo ratings yet
- 17 SMIC ECNs Info Memo 071620 FilingDocument185 pages17 SMIC ECNs Info Memo 071620 FilingAira Mae CabiyaanNo ratings yet
- Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFC)Document25 pagesNon-Banking Financial Companies (NBFC)nikita kothari18No ratings yet
- Ca Final NBFCDocument5 pagesCa Final NBFCDeepak DhondiyalNo ratings yet
- UBL AnalysisDocument19 pagesUBL Analysismuhammad akramNo ratings yet
- Emperical ProjectDocument11 pagesEmperical ProjectSajal ChakarvartyNo ratings yet
- Financial Staements Duly Authenticated As Per Section 134 (Including Boards Report, Auditors Report and Other Documents) - 29102023Document28 pagesFinancial Staements Duly Authenticated As Per Section 134 (Including Boards Report, Auditors Report and Other Documents) - 29102023mnbvcxzqwerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Accounting and Reporting of Financial InstrumentsDocument24 pagesChapter 6 Accounting and Reporting of Financial InstrumentsMahendra Kumar B RNo ratings yet
- Audit of NBFCDocument17 pagesAudit of NBFCSriramNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Non Performing Assets (NPA) On Punjab National BankDocument14 pagesAn Analysis of Non Performing Assets (NPA) On Punjab National BankRajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Deck IX - Chapter 10Document17 pagesDeck IX - Chapter 10Kannan MeiyurNo ratings yet
- IRAC Norms 1Document27 pagesIRAC Norms 1sailuteluguNo ratings yet
- Model NFS - Full PFRS (2022) - LENDING AND FINANCINGDocument39 pagesModel NFS - Full PFRS (2022) - LENDING AND FINANCINGJoel RazNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument4 pagesFrequently Asked QuestionspradeepNo ratings yet
- Pas 1Document58 pagesPas 1Reggie Pernites Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- IFRS Study Notes - Day 1Document76 pagesIFRS Study Notes - Day 1Obisike EmeziNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document16 pagesUnit 2Sharine ReyesNo ratings yet
- SIDBI CSAS-Scheme DetailsDocument4 pagesSIDBI CSAS-Scheme DetailsPRIYAM VAGHASIYANo ratings yet
- Independent Auditor's Report: Corporate Board and Management Reports Financial StatementsDocument81 pagesIndependent Auditor's Report: Corporate Board and Management Reports Financial Statements198 Murzello MignonneNo ratings yet
- What Are We Going To Cover?Document7 pagesWhat Are We Going To Cover?Hemant KhemaniNo ratings yet
- Accounting Policies - Study Group 4IDocument24 pagesAccounting Policies - Study Group 4ISatish Ranjan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Impact of Bank'S Npa On Economic Health of IndiaDocument7 pagesImpact of Bank'S Npa On Economic Health of IndiaShrutiNo ratings yet
- Rpi 0415Document41 pagesRpi 0415Manisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Ethical Leadership: The Need For A New Approach in Retail: Pallavi PandeyDocument9 pagesEthical Leadership: The Need For A New Approach in Retail: Pallavi PandeyManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Abusive Supervision in Work Organizations Review SDocument258 pagesAbusive Supervision in Work Organizations Review SManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Authentic Leadership Trust and Work EngagementDocument7 pagesAuthentic Leadership Trust and Work EngagementManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- MBA Syllabus 2017Document58 pagesMBA Syllabus 2017Manisha SinghNo ratings yet
- EndnoteDocument4 pagesEndnoteManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- International HR ManagementDocument9 pagesInternational HR ManagementManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Management of Leadership Style: An Approach To Organizational Performance and Effectiveness in NigeriaDocument13 pagesManagement of Leadership Style: An Approach To Organizational Performance and Effectiveness in NigeriaManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 10 TB Working Capital ManagementDocument22 pagesCH 10 TB Working Capital ManagementFran PranNo ratings yet
- BP 68 - Corporation CodeDocument25 pagesBP 68 - Corporation CodeJacinto Jr JameroNo ratings yet
- E Payment I.T On Salary Mo April-19Document12 pagesE Payment I.T On Salary Mo April-19HussainMohammadUmarNo ratings yet
- IFMR FImpact Investment Fund BrochureDocument2 pagesIFMR FImpact Investment Fund BrochureNirav ShahNo ratings yet
- Inox India LimitedDocument8 pagesInox India Limitedsociety0294No ratings yet
- Kahit Nalugi Yung Kumpanya, Secured Pa Rin Yung Pinautang Mo Na Babalik Sayo Plus Yung Mga InterestDocument14 pagesKahit Nalugi Yung Kumpanya, Secured Pa Rin Yung Pinautang Mo Na Babalik Sayo Plus Yung Mga InterestMc Reidgard RomblonNo ratings yet
- Mutual FundsDocument43 pagesMutual FundsPrakhar TrivediNo ratings yet
- Indian Stock MarketDocument71 pagesIndian Stock MarketNeha Thakur100% (1)
- Interim Order in The Matter of Progress Cultivation Limited.Document12 pagesInterim Order in The Matter of Progress Cultivation Limited.Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- Fiim S01Document47 pagesFiim S01Firaol DelesaNo ratings yet
- Part II Semester IVDocument38 pagesPart II Semester IVRamyaNo ratings yet
- Law 430 - Banking LawsDocument8 pagesLaw 430 - Banking Lawstomoyo tvNo ratings yet
- Financial SystemDocument36 pagesFinancial SystemSrikanth BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Trust Deed: Instructions For Preparation of Endowment Fund DocumentDocument18 pagesTrust Deed: Instructions For Preparation of Endowment Fund DocumentHenan Educational ServicesNo ratings yet
- Baviera V PaglinawanDocument3 pagesBaviera V PaglinawanLoveAnneNo ratings yet
- DessertationDocument53 pagesDessertationitsmeadi100% (1)
- Revise Old Corp CodeDocument76 pagesRevise Old Corp CodeElvie Jaim Cuizon ValienteNo ratings yet
- Robinhood Response To Feb 2 LetterDocument195 pagesRobinhood Response To Feb 2 LetterFOX BusinessNo ratings yet
- Capital Market - Study NotesDocument25 pagesCapital Market - Study Notessivaji naikNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of Policy For Engagement of Recovery AgenciesDocument17 pagesSalient Features of Policy For Engagement of Recovery Agenciesashaorissa1997No ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument8 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentApril ManaloNo ratings yet
- Project ReportpdfDocument80 pagesProject ReportpdfsunnyjatNo ratings yet
- An Assignment of Stock Exchange & Portfolio Management: Topic: - International Bond MarketDocument18 pagesAn Assignment of Stock Exchange & Portfolio Management: Topic: - International Bond MarketashishNo ratings yet
- Role of Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument15 pagesRole of Financial Markets and Institutionsনাহিদ উকিল জুয়েলNo ratings yet
- Stock PurchaseDocument3 pagesStock PurchaseWalter BoninNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 KEYDocument43 pagesChapter 3 KEYpthieuanh123No ratings yet
- Nism Questions-26 GDocument14 pagesNism Questions-26 GabhishekNo ratings yet
- Icici Bank Loans PDFDocument3 pagesIcici Bank Loans PDFRagothaman RNo ratings yet
Chamber's Journal January 06 PDF
Chamber's Journal January 06 PDF
Uploaded by
Manisha SinghOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chamber's Journal January 06 PDF
Chamber's Journal January 06 PDF
Uploaded by
Manisha SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
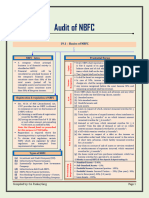
Special Story nBFC
CA Bhavesh Vora
Prudential Norms for Non-banking Financial
(Non-Deposit Accepting or Holding) Companies
Background 22, 2007 supersede Non-Banking Financial
Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), Companies Prudential Norms (Reserve Bank)
forms an integral part of Indian inancial system, Directions, 1998 contained in Notification
providing various financial services. In recent No. DFC. 119/DG(SPT)/98 dated January
times, activities of NBFCs have undergone 31, 1998.
variety of changes through inancial innovation.
NBFC initially gets incorporated under Indian RBI has recently announced draft guidelines
Companies Act, 1956 and later on obtains in respect of NBFC sector which also includes
Certificate of Incorporation from RBI. As aspects relating to various prudential norms.
compared to Banks, replace with such companies The same is being covered in separate article,
have greater lexibility and can undertake higher and hence this article is based on extant
risks and tailor make the services to suit the regulations pertaining to prudential norms for
requirements of clients. At present, NBFCs in NBFCs.
India has become prominent in wide range
of services such as Bill discounting, factoring, This article covers some of the important
investment activities, hire-purchase finance, provisions stipulated under the prudential
lease inance, loans, loans against securities, loan norms-
against gold, precious metals, etc. With increase
in activities, it is also important to regulate I. Accounting guidelines
and effectively monitor the functioning of such
NBFCs. The RBI, having considered necessary in II. Asset Classification and provisioning
the public interest and being satisied that for the requirements for standard and Non-
purpose of enabling them to regulate the credit Performing assets
system to advantage of the country, has laid
down the prudential norms. III. Disclosure in Balance sheet
The prudential norms directions were issued IV. Accounting year to be followed
by RBI u/s 45JA of the Reserve Bank of India
Act, 1934. The directions issued in 2007 vide V. Concentration of credit/investments
Notification No. DNBS.192/ DG (VL)-2007
and DNBS.193/ DG (VL)-2007 dated February VI. Other Compliance Aspects
SS-III-13 The Chamber's Journal January 2013
299
Prudential norms for non-banking Financial (non-deposit accepting or Holding) companies
I. Accounting Guidelines current or long term at the time of making
Some of the Accounting related aspects includes each investment. There can be no inter-class
Income Recognition criteria, Accounting of transfer of investments on ad hoc basis later
Investments, asset classiication and provisioning on. Inter class transfer should be done at the
requirements. beginning of half year and with the approval of
the board. The directions also speciies various
RBI has prescribed that Income recognition should valuation guidelines in respect of quoted and
be based on recognised accounting principles, unquoted current investments leaving the Long
however Accounting Standards and Guidance term Investments to be valued as per ICAI
Notes from ICAI will be followed as far as Accounting Standards.
they are not inconsistent with any of the RBI
directions. It requires quoted current investments to be
grouped into speciied categories and valuation
Income like interest /discount /any other of each category to be done at aggregate
charges on NPAs shall be recognised only cost or aggregate market value whichever is
when actually realised, RBI also requires that lower. Depreciation should be provided and
income recognised before asset becoming NPA appreciation (if any) should be ignored category-
should be reversed in the financial year in wise and not scrip-wise.
which such asset becomes NPA. The directions
requires NBFCs to recognise income from Unquoted equity shares in the nature of current
dividends on shares of corporate bodies and investments shall be valued at cost or break-up
units of mutual funds on cash basis, unless the value, whichever is lower. RBI has prescribed
company has declared the dividend in AGM that fair value for the break-up value of the
and right of the company to receive the same shares may be replaced, if considered necessary.
has been established, in such cases, it can be Where the balance sheet of the investee company
recognized on accrual basis. Income from bonds is not available for two years, such shares shall
and debentures of corporate bodies and from be valued at one rupee only.
government securities/bonds may be taken
Breakup value means the equity capital and
into account on accrual basis provided it is
reserves as reduced by intangible assets and
paid regularly and is not in arrears. Income
revaluation reserves, divided by the number of
on securities of corporate bodies or public
equity shares of the investee company.
sector undertakings may be taken into account
on accrual basis provided the payment of
interest and repayment of the security has been II. Asset classification and
guaranteed by Central Government. provisioning requirements
The following categories are defined in
accounting of investments the regulations mainly based on period of
Investing is one of the core activities of NBFCs, outstanding of the interest and principal.
hence RBI requires the Board of Directors to
(i) Standard assets;
Frame investment policy of the company and
implement the same. The policy should include (ii) Sub-standard assets;
criteria laid down by the board for classiication
of investments into long-term and short term. (iii) Doubtful assets; and
The investments need to be classified into (iv) Loss assets
The Chamber's Journal January 2013 SS-III-14
:30
Special Story nBFC
Broad Provisioning Requirements are depicted in the table below.
assets Explanation period provision on provision on Security
loan Balance
Standard Standard asset means the asset in respect It is regular asset 0.25% of all
Assets of which, no default in repayment of and does not standard
principal or payment of interest is orm part of NPA assets
perceived and which does not disclose
any problem nor carry more than normal
risk attached to the business
NPA An asset, in respect of which, interest/ 6 months
installment/reimbursement has remained
overdue for a period of six months or more
Sub- Asset classiied as NPA for a period not Non-performing 10% of the No speciic provisions
standard exceeding 18 months; assets for a outstanding regarding security
assets Asset where terms of agreement regarding period of 18 amount
interest/principal were renegotiated or months or
rescheduled or restructured after commen- Renegotiated
cement of operations, until the expiry of loans up to one
one year of satisfactory performance under year of satisactory
the renegotiated or rescheduled or performance of
restructured terms new terms.
Doubtful Doubtful asset means: Remains sub 100% over To the extent of loan
assets (a) a term loan, or standard asset realisable which is covered by value
(b) a lease asset, or for period of value of of realizable securities, the
(c) a hire purchase asset, or 18 months and Securities following provisioning is
(d) any other asset, above required based on the
which remains a sub-standard asset for a period the asset (the
period exceeding 18 months underlying loan) has been
considered doubtful
Up to - one year 20%
One - three years 30%
More than three years
50%
Loss As identiied by Company, Auditor or RBI Period not 100% write
assets (Period is not speciied) or Potential threat speciied off in the
of Non Recoverability due to erosion in the books
value of securities or non-availability of
security or any fraudulent act or omission
on the part of the borrower.
The class of assets referred to above shall not be upgraded merely as a result of rescheduling/
renegotiation/restructuring, unless it satisies the conditions required for the upgradation. The
condition is that the assets should show satisfactory performance under the restructured and/or
rescheduled and/or renegotiated terms at least for a year.
SS-III-15 The Chamber's Journal January 2013
319
Prudential norms for non-banking Financial (non-deposit accepting or Holding) companies
III. Disclosure in the balance sheet Maturity pattern of assets and liabilities."
The directions specify certain disclosure The formats for the above disclosures are also
requirements in the balance sheet. Disclosure of speciied by RBI.
provisions created without netting them from
the income or against the value of assets. The IV. Accounting Year to be followed
provisions shall be distinctly indicated under Every non-banking financial company shall
separate heads of account as (i) Provisions for prepare its balance sheet and profit and loss
bad and doubtful debts; and (ii) Provisions for account as on March 31 every year. Prior
depreciation in investments. Provisions shall not approval of RBI is needed, before approaching
be appropriated from the general provisions and Registrar of Companies, if the company wants
loss reserves held. Provisions shall be debited to extend the date as per provisions of the
to the profit and loss account. The excess of Companies Act, 1956. In case extension is
provisions, if any, held under the heads general granted, the company has to file proforma
provisions and loss reserves may be written balance sheet and the statutory returns
back without making adjustment against the pertaining to March 31.
provisions.
The balance sheet needs to be inalised within a
Every non-banking financial company shall period of three months from the date to which
append a schedule to its balance sheet and give it pertains.
the particulars as set out in format provided in
the prudential norms. V. Concentration of credit/
The following disclosure requirements are investment
applicable only to systemically important (Asset Systemically important non-deposit taking non-
Size more than ` 100 crores) non-deposit taking banking inancial company cannot invest and/
non-banking inancial company - or lend to a single borrower/investee or single
Capital to Risk Assets Ratio (CRAR) group of borrowers/investee beyond speciied
Exposure to real estate sector, both direct limits laid down by RBI. The limits are given as
and indirect; and a percentage of its owned funds.
To limits on lending limits on investment Combined limits on
in shares lending & investment
Single borrower/party 15% of owned funds 15% of owned funds 25% of owned funds
Single group of borrowers/parties 25% of owned funds 25% of owned funds 40% of owned funds
Infrastructure
Loan/Investment
Single Borrower Additional 5% Additional 5% Additional 5%
Single Group of Borrowers
(Only if the additional loan/ Additional 10% Additional 10% Additional 10%
investment is infrastructure
Loan/investment)
For Infrastructure Finance 25% of Owned funds 30% of Owned funds
Company
Single Borrower
Single Group of Borrowers 40% of Owned funds 50% of Owned funds
The Chamber's Journal January 2013 SS-III-16
:32
Special Story nBFC
Provided that the ceiling on the investment December 30 of that year. Such certiicate shall
in shares of another company shall not be also indicate the asset / income pattern of the
applicable to a systemically important non- non-banking financial company for making
deposit taking non-banking inancial company in it eligible for classification as Asset Finance
respect of investment in the equity capital of an Company, Investment Company or Loan
insurance company up to the extent speciically Company.
permitted, in writing, by the Reserve Bank of
India. (b) Information in regard to change of
Asset Finance Company may in exceptional address, directors, auditors, etc. to be
circumstances, exceed the above ceilings submitted
on credit / investment concentration to a Communicate within one month from the
single party or a single group of parties by 5 per occurrence of any change in the postal address,
cent of its owned fund, with the approval of its telephone number/s and fax number/s of the
Board. registered/corporate office, the names and
residential addresses of the directors of the
Any systemically important non-deposit taking company, the names and the oficial designations
non-banking financial company not accessing of its principal officers, the names and office
public funds, either directly or indirectly, and address of the auditors of the company, and the
not issuing guarantees (which may require specimen signatures of the oficers authorised to
access to public funds when the guarantees sign on behalf of the company
devolve) may make an application to the
Bank for an appropriate alteration in the above (c) loans against non-banking financial
limits. companys own shares prohibited
Explanation : "Public funds" for the purpose of No non-banking financial company shall lend
the proviso shall include funds raised either against its own shares.
directly or indirectly through public deposits,
Commercial Papers, debentures, inter-corporate (d) loans against security of single product -
deposits and bank inance. Gold jewellery
NBFCs cannot lend against collateral of gold
The NBFCs also need to formulate policy in jewellery in excess of 60 per cent of its value and
respect of exposures to a single party / a single all NBFCs shall disclose in their balance sheet
group of parties. the percentage of such loans (gold loans) to their
total assets.
VI. Other Compliances NBFCs cannot grant any advance against bullion
(a) Submission of a certiicate from Statutory / primary gold and gold coins. NBFCs primarily
auditor to the Bank engaged in lending against gold jewellery (such
Every non-banking financial company shall loans comprising 50 percent or more of their
submit a Certiicate from its Statutory Auditor inancial assets) shall maintain a minimum Tier
that it is engaged in the business of non-banking l capital of 12 per cent by April 1, 2014.
financial institution along with the asset /
income pattern, requiring it to hold a Certiicate (e) NBFCs not to be partners in partnership
of Registration under Section 45-IA of the RBI irms
Act. The same needs to be submitted within No NBFC shall contribute to the capital of a
one month from the date of finalisation of the partnership firm or become a partner of such
balance sheet and in any case not later than irm.
SS-III-17 The Chamber's Journal January 2013
339
Prudential norms for non-banking Financial (non-deposit accepting or Holding) companies
(f) Demand or call loans less than fifteen per cent of its aggregate risk
In case the NBFC provides Demand Loan or weighted assets on balance sheet and of risk
call loans (a type of loan where both the parties adjusted value of off-balance sheet items.
are free to call back or pay back loan as per
their will, subject to agreement of the loan The total of Tier II capital, at any point of time,
and minimum notice period decided in the shall not exceed one hundred per cent of Tier I
agreement) Board of Directors need to Frame capital.
policy for granting call/demand loans and Calculation of Tier I, Tier II and Risk weighted
implement the policy to stipulate various aspects assets has been specified in the regulations,
as specified in the prudential norms such as Risk Weights for various on balance sheet
Rate of Interest, Cutoff date for review of the items and off balance sheet items also have been
loans, period of the loan, reasons if no interest is speciied.
stipulated or when moratorium is granted.
Exemptions
(g) Constitution of audit Committee by non- The Reserve Bank of India may, if it considers it
banking inancial companies necessary for avoiding any hardship or for any
NBFC with assets of ` 50 crore and above as per other just and suficient reason, grant extension
its last audited balance sheet shall constitute an of time to comply with or exempt any non-
Audit Committee, consisting of not less than banking financial company or class of non-
three members of its Board of Directors. banking inancial companies, from all or any of
Audit Committee as required under Section the provisions of these directions either generally
292A of the Companies Act, 1956 shall be the or for any specified period, subject to such
Audit Committee for the purposes of this conditions as the Reserve Bank of India may
paragraph and it will have same powers, impose.
functions and duties as laid down in section As mentioned in the opening part of this article
292A of the Companies Act, 1956. that RBI has proposed substantial changes
in regulations pertaining to aspects such as
(h) Requirement as to capital adequacy `registration conditions, continuity, disclosure
Every systemically important NBFC shall requirements and functioning of NBFCs, one will
maintain minimum capital ratio consisting of have to apply the relevant part of the guidelines
Tier I and Tier II capital which shall not be once enacted.
2
The world is a beautiful book,
but of little use to him who cannot read it.
Goldoni
The remedy for wrongs is to forget them.
Syrus
The Chamber's Journal January 2013 SS-III-18
:34
You might also like
- TR - CM - Configuration Document TemplateDocument44 pagesTR - CM - Configuration Document TemplateHrushikesh Vishnu Shrotriya95% (39)
- Prudential Norms For Non-Banking Financial (Non-Deposit Accepting or Holding) CompaniesDocument6 pagesPrudential Norms For Non-Banking Financial (Non-Deposit Accepting or Holding) CompaniesGreeshma Babu ShylajaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Npa of Public Sector Banks in India: Sulagna Das, AbhijitduttaDocument9 pagesA Study On Npa of Public Sector Banks in India: Sulagna Das, AbhijitduttaSunil Kumar PalikelaNo ratings yet
- Income Recognition, Asset Classification and Provisioning Norms For The Urban Cooperat Ive BanksDocument10 pagesIncome Recognition, Asset Classification and Provisioning Norms For The Urban Cooperat Ive Banksramsundar_99No ratings yet
- Banking Accounts: by Prof. Maheshwari Vijay KumarDocument7 pagesBanking Accounts: by Prof. Maheshwari Vijay KumarOmpriya AcharyaNo ratings yet
- 2 Statement of Financial PositionDocument7 pages2 Statement of Financial Positionreagan blaireNo ratings yet
- Debt RestructuringDocument5 pagesDebt RestructuringVinay TripathiNo ratings yet
- Hemant Vijay Pandya: Non-Banking Financial Company An OverviewDocument32 pagesHemant Vijay Pandya: Non-Banking Financial Company An OverviewHashmi SutariyaNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet)Document12 pages3.3 Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet)Brier Jaspin AguirreNo ratings yet
- Advanced Auditing and Professional Ethics 1688653213Document28 pagesAdvanced Auditing and Professional Ethics 1688653213mdasifraza3196No ratings yet
- Irac NormsDocument9 pagesIrac NormsAtul ThakurNo ratings yet
- Irac Norms: Bank Branch AuditDocument45 pagesIrac Norms: Bank Branch AuditjamilsbmmNo ratings yet
- 08 MF NBFC - UnlockedDocument23 pages08 MF NBFC - UnlockedBittu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Accountancy XII Exam Handbook For 2024 ExamDocument88 pagesAccountancy XII Exam Handbook For 2024 ExamHari prakarsh Nimi100% (1)
- WA0004. - RemovedDocument76 pagesWA0004. - Removedsushil.saliyan1003No ratings yet
- Indofood CBP Sukses Makmur TBK Statement of Financial PositionDocument4 pagesIndofood CBP Sukses Makmur TBK Statement of Financial Positionmuhamad khadiqNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements of Banking Companies: © The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaDocument44 pagesFinancial Statements of Banking Companies: © The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaHarikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Model NFS - Full PFRS (2022) - Nonlending and NonfinancingDocument35 pagesModel NFS - Full PFRS (2022) - Nonlending and NonfinancingJoel RazNo ratings yet
- Non-Performing Assets (NPA) : Asset Classification, Income Recognition and Provisioning NormsDocument52 pagesNon-Performing Assets (NPA) : Asset Classification, Income Recognition and Provisioning Normspriyankaarora9010No ratings yet
- Prudential Norms ExplanationDocument4 pagesPrudential Norms ExplanationSneha ChavanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Auditing & Professional Ethics: Master MindsDocument17 pagesAdvanced Auditing & Professional Ethics: Master MindsMaroju RajithaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Npas: A NPA Is A Loan or An Advance WhereDocument58 pagesDefinition of Npas: A NPA Is A Loan or An Advance WhereAnnu BallanNo ratings yet
- Credit Audit - Positive Score Areas in Pre Sanction - Tips On Value Statements in Credit Auditable Accounts Upto Rs 50 CRDocument73 pagesCredit Audit - Positive Score Areas in Pre Sanction - Tips On Value Statements in Credit Auditable Accounts Upto Rs 50 CRHaRa TNo ratings yet
- Caballero Ba53 Chap 2Document32 pagesCaballero Ba53 Chap 2Drew BooNo ratings yet
- Recovery Policy - 2012Document23 pagesRecovery Policy - 2012Dhawan SandeepNo ratings yet
- Goal - A Process of Continuous Improvement - Eliyahu Goldratt (Qwerty80)Document43 pagesGoal - A Process of Continuous Improvement - Eliyahu Goldratt (Qwerty80)Girish GaykawadNo ratings yet
- Chapter1: Introduction: Nonperforming Asset in BankDocument35 pagesChapter1: Introduction: Nonperforming Asset in BankMaridasrajanNo ratings yet
- Section 4 IDocument22 pagesSection 4 ISatish Ranjan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Unveiling Valuation Challenges: in Reporting of Nav by Aifs Under Sebi (Alternative Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012Document12 pagesUnveiling Valuation Challenges: in Reporting of Nav by Aifs Under Sebi (Alternative Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012Sourabh GargNo ratings yet
- Ind AS 7 PDFDocument23 pagesInd AS 7 PDFnavinsurana1987No ratings yet
- Money and BankingDocument10 pagesMoney and BankingSahil ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Audit of AdvancesDocument29 pagesAudit of AdvancesHemanshu SolankiNo ratings yet
- Npa in SbiDocument96 pagesNpa in SbiApoorva M V100% (2)
- Non-Banking Financial CompaniesDocument49 pagesNon-Banking Financial CompaniesAdison Growar SatyeNo ratings yet
- NBFC Project Report by MS. Sonia JariaDocument34 pagesNBFC Project Report by MS. Sonia JariaSonia SoniNo ratings yet
- A Study On NPA of Public Sector Banks in India: January 2014Document10 pagesA Study On NPA of Public Sector Banks in India: January 2014rajesh nimodiaNo ratings yet
- Final DT 100 Important Questions Final Audit Practice Questions Financial Reporting Conceptual NotesDocument14 pagesFinal DT 100 Important Questions Final Audit Practice Questions Financial Reporting Conceptual NotesDheeraj TurpunatiNo ratings yet
- KPMG Flash News Draft Guidelines For Core Investment CompaniesDocument5 pagesKPMG Flash News Draft Guidelines For Core Investment CompaniesmurthyeNo ratings yet
- Resource Planning PolicyDocument3 pagesResource Planning Policymadhvi GajjarNo ratings yet
- 17 SMIC ECNs Info Memo 071620 FilingDocument185 pages17 SMIC ECNs Info Memo 071620 FilingAira Mae CabiyaanNo ratings yet
- Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFC)Document25 pagesNon-Banking Financial Companies (NBFC)nikita kothari18No ratings yet
- Ca Final NBFCDocument5 pagesCa Final NBFCDeepak DhondiyalNo ratings yet
- UBL AnalysisDocument19 pagesUBL Analysismuhammad akramNo ratings yet
- Emperical ProjectDocument11 pagesEmperical ProjectSajal ChakarvartyNo ratings yet
- Financial Staements Duly Authenticated As Per Section 134 (Including Boards Report, Auditors Report and Other Documents) - 29102023Document28 pagesFinancial Staements Duly Authenticated As Per Section 134 (Including Boards Report, Auditors Report and Other Documents) - 29102023mnbvcxzqwerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Accounting and Reporting of Financial InstrumentsDocument24 pagesChapter 6 Accounting and Reporting of Financial InstrumentsMahendra Kumar B RNo ratings yet
- Audit of NBFCDocument17 pagesAudit of NBFCSriramNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Non Performing Assets (NPA) On Punjab National BankDocument14 pagesAn Analysis of Non Performing Assets (NPA) On Punjab National BankRajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Deck IX - Chapter 10Document17 pagesDeck IX - Chapter 10Kannan MeiyurNo ratings yet
- IRAC Norms 1Document27 pagesIRAC Norms 1sailuteluguNo ratings yet
- Model NFS - Full PFRS (2022) - LENDING AND FINANCINGDocument39 pagesModel NFS - Full PFRS (2022) - LENDING AND FINANCINGJoel RazNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument4 pagesFrequently Asked QuestionspradeepNo ratings yet
- Pas 1Document58 pagesPas 1Reggie Pernites Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- IFRS Study Notes - Day 1Document76 pagesIFRS Study Notes - Day 1Obisike EmeziNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document16 pagesUnit 2Sharine ReyesNo ratings yet
- SIDBI CSAS-Scheme DetailsDocument4 pagesSIDBI CSAS-Scheme DetailsPRIYAM VAGHASIYANo ratings yet
- Independent Auditor's Report: Corporate Board and Management Reports Financial StatementsDocument81 pagesIndependent Auditor's Report: Corporate Board and Management Reports Financial Statements198 Murzello MignonneNo ratings yet
- What Are We Going To Cover?Document7 pagesWhat Are We Going To Cover?Hemant KhemaniNo ratings yet
- Accounting Policies - Study Group 4IDocument24 pagesAccounting Policies - Study Group 4ISatish Ranjan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Impact of Bank'S Npa On Economic Health of IndiaDocument7 pagesImpact of Bank'S Npa On Economic Health of IndiaShrutiNo ratings yet
- Rpi 0415Document41 pagesRpi 0415Manisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Ethical Leadership: The Need For A New Approach in Retail: Pallavi PandeyDocument9 pagesEthical Leadership: The Need For A New Approach in Retail: Pallavi PandeyManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Abusive Supervision in Work Organizations Review SDocument258 pagesAbusive Supervision in Work Organizations Review SManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Authentic Leadership Trust and Work EngagementDocument7 pagesAuthentic Leadership Trust and Work EngagementManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- MBA Syllabus 2017Document58 pagesMBA Syllabus 2017Manisha SinghNo ratings yet
- EndnoteDocument4 pagesEndnoteManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- International HR ManagementDocument9 pagesInternational HR ManagementManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Management of Leadership Style: An Approach To Organizational Performance and Effectiveness in NigeriaDocument13 pagesManagement of Leadership Style: An Approach To Organizational Performance and Effectiveness in NigeriaManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 10 TB Working Capital ManagementDocument22 pagesCH 10 TB Working Capital ManagementFran PranNo ratings yet
- BP 68 - Corporation CodeDocument25 pagesBP 68 - Corporation CodeJacinto Jr JameroNo ratings yet
- E Payment I.T On Salary Mo April-19Document12 pagesE Payment I.T On Salary Mo April-19HussainMohammadUmarNo ratings yet
- IFMR FImpact Investment Fund BrochureDocument2 pagesIFMR FImpact Investment Fund BrochureNirav ShahNo ratings yet
- Inox India LimitedDocument8 pagesInox India Limitedsociety0294No ratings yet
- Kahit Nalugi Yung Kumpanya, Secured Pa Rin Yung Pinautang Mo Na Babalik Sayo Plus Yung Mga InterestDocument14 pagesKahit Nalugi Yung Kumpanya, Secured Pa Rin Yung Pinautang Mo Na Babalik Sayo Plus Yung Mga InterestMc Reidgard RomblonNo ratings yet
- Mutual FundsDocument43 pagesMutual FundsPrakhar TrivediNo ratings yet
- Indian Stock MarketDocument71 pagesIndian Stock MarketNeha Thakur100% (1)
- Interim Order in The Matter of Progress Cultivation Limited.Document12 pagesInterim Order in The Matter of Progress Cultivation Limited.Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- Fiim S01Document47 pagesFiim S01Firaol DelesaNo ratings yet
- Part II Semester IVDocument38 pagesPart II Semester IVRamyaNo ratings yet
- Law 430 - Banking LawsDocument8 pagesLaw 430 - Banking Lawstomoyo tvNo ratings yet
- Financial SystemDocument36 pagesFinancial SystemSrikanth BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Trust Deed: Instructions For Preparation of Endowment Fund DocumentDocument18 pagesTrust Deed: Instructions For Preparation of Endowment Fund DocumentHenan Educational ServicesNo ratings yet
- Baviera V PaglinawanDocument3 pagesBaviera V PaglinawanLoveAnneNo ratings yet
- DessertationDocument53 pagesDessertationitsmeadi100% (1)
- Revise Old Corp CodeDocument76 pagesRevise Old Corp CodeElvie Jaim Cuizon ValienteNo ratings yet
- Robinhood Response To Feb 2 LetterDocument195 pagesRobinhood Response To Feb 2 LetterFOX BusinessNo ratings yet
- Capital Market - Study NotesDocument25 pagesCapital Market - Study Notessivaji naikNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of Policy For Engagement of Recovery AgenciesDocument17 pagesSalient Features of Policy For Engagement of Recovery Agenciesashaorissa1997No ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument8 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentApril ManaloNo ratings yet
- Project ReportpdfDocument80 pagesProject ReportpdfsunnyjatNo ratings yet
- An Assignment of Stock Exchange & Portfolio Management: Topic: - International Bond MarketDocument18 pagesAn Assignment of Stock Exchange & Portfolio Management: Topic: - International Bond MarketashishNo ratings yet
- Role of Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument15 pagesRole of Financial Markets and Institutionsনাহিদ উকিল জুয়েলNo ratings yet
- Stock PurchaseDocument3 pagesStock PurchaseWalter BoninNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 KEYDocument43 pagesChapter 3 KEYpthieuanh123No ratings yet
- Nism Questions-26 GDocument14 pagesNism Questions-26 GabhishekNo ratings yet
- Icici Bank Loans PDFDocument3 pagesIcici Bank Loans PDFRagothaman RNo ratings yet