Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Signal Conditioning RTD
Signal Conditioning RTD
Uploaded by
Ashwini KushwahaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Signal Conditioning RTD
Signal Conditioning RTD
Uploaded by
Ashwini KushwahaCopyright:
Available Formats
Home Download Slot Booking Feedback.
Contact us Login Custom Search Search
. you are here->home->electrical engineering->electronic instrumentation laboratory->signal conditioning circuit for rtd (resistance temperature detector) .
.
Signal Conditioning Circuit for RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) .
. .....
Introduction Theory Procedure Simulator Self Evaluation Reference Feedback
..... .....
Theory of RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector)
An RTD (resistance temperature detector) is a temperature detector based upon a variation in
electric resistance. The commonest metal for this application is platinum. RTDs rely on the positive
temperature coefficient for a conductors resistance. In a conductor the number of electrons available to
conduct electricity does not significantly change with temperature. But when the temperature increases, the
vibration of atoms around their equilibrium positions increase in amplitude. This result in a greater
dispersion of electrons, which reduces their average speed. Hence, the resistance increases when the
temperature rises.
The relationship between temperature and resistance of RTD is given by-
where,
is resistance at
is resistance at 0oC, and is temperature coefficient of resistance. represents the change
in resistance per degree centigrade change in temperature. For example, Pt100 is platinum RTD with
resistance of 100 at 0oC. For platinum = 0.00385 and at 100 oC, Pt100 will have a resistance of
Measurement of RTD with Wheatstone-Bridge Circuit
Mostly RTD instruments used Wheatstone bridge circuit for measurement purpose. Bridge contains
RTD at one arm and other remaining three arms connected with standard resistances. Bridge is generally a
resistance measuring device which converts the resistance of RTD into electrical signal.
Here the as mention above the equation (1) may be written as
For given values of and , and and hence measuring the (With the help of
Wheatstone bridge circuit) change in temperature can be found out.
As shown in the fig. below
To measure the out-put voltage of signal conditioning circuit for RTD, following equations
are required-
is the resistance of platinum, is the resistance at 0 oC, is the temperature coefficient of
platinum wire and is the temperature.
2. Bridge output
Here is the resistance of platinum wire and are the standard resistances and
E is the input voltage applied to the bridge.
3. Differential amplifier output
where A is voltage gain of a differential amplifier.
Cite this Simulator:
iitg.vlab.co.in,. (2012). Signal Conditioning Circuit for RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector). Retrieved 8 September
2017, from iitg.vlab.co.in/?sub=61&brch=174&sim=1035&cnt=1
Copyright @ 2017 Under the NME ICT initiative of MHRD (Licensing Terms)
Powered by AmritaVirtual Lab Collaborative Platform [ Ver 00.11. ]
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5824)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
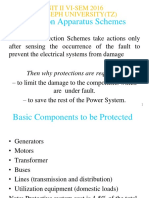
- Protection Apparatus Schemes: Unit Ii Vi-Sem 2016 St. Joseph University (TZ)Document55 pagesProtection Apparatus Schemes: Unit Ii Vi-Sem 2016 St. Joseph University (TZ)Ashwini Kushwaha100% (1)
- Stabilization of The Electromechanical Oscillations of Synchronous GeneratorDocument11 pagesStabilization of The Electromechanical Oscillations of Synchronous GeneratorAshwini KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Tata Zest Osb-Final - 1Document166 pagesTata Zest Osb-Final - 1Ashwini KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Certificate Human and GeographyDocument197 pagesCertificate Human and GeographywasimhassanNo ratings yet
- THE RISE AND FALL OF INDIAN ENVIRONMENTALISM, Hindustan Times - Welcome To Ramachandra GuhaDocument3 pagesTHE RISE AND FALL OF INDIAN ENVIRONMENTALISM, Hindustan Times - Welcome To Ramachandra GuhaAshwini KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Scan 0005Document6 pagesScan 0005Ashwini KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Nicholas HenryDocument11 pagesNicholas HenryAshwini KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Ug1119 Vivado Creating Packaging Ip TutorialDocument71 pagesUg1119 Vivado Creating Packaging Ip TutorialJim JimNo ratings yet
- En 50397-2 P2Document42 pagesEn 50397-2 P2HopNo ratings yet
- Experiment: To Determine The Reaction of Simply Supported Beam External LoadedDocument11 pagesExperiment: To Determine The Reaction of Simply Supported Beam External LoadedHamza RajputNo ratings yet
- Footstep Power Generation Using Piezoelectric SensorDocument6 pagesFootstep Power Generation Using Piezoelectric SensorJeet DattaNo ratings yet
- Basic Theories of PaDocument25 pagesBasic Theories of Panaja firdausNo ratings yet
- EuphemismsDocument2 pagesEuphemismssifo nebbarNo ratings yet
- Mid - I - Quiz - Question Bank - P&S - Ar-20Document4 pagesMid - I - Quiz - Question Bank - P&S - Ar-20AMBATI TARUNNo ratings yet
- EEET2485 - Research Methods Project Proposal SubmissionDocument4 pagesEEET2485 - Research Methods Project Proposal SubmissionNguyễn Văn TổngNo ratings yet
- CE311 - Homework 4 - SolutionDocument11 pagesCE311 - Homework 4 - SolutionSilvanir TioeNo ratings yet
- Simatic st80 STPC Chap02 English 2013Document138 pagesSimatic st80 STPC Chap02 English 2013Eduardo Bueno LemesNo ratings yet
- Netflix Analysis Report (2105878 - Bibhudutta Swain)Document19 pagesNetflix Analysis Report (2105878 - Bibhudutta Swain)Bibhudutta SwainNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity of Soil: 7.0 SyllabusDocument37 pagesBearing Capacity of Soil: 7.0 Syllabustejani yakshu100% (1)
- Intro Mass SpecDocument2 pagesIntro Mass SpecHuy Đặng Anh0% (1)
- PlanningDocument1 pagePlanningBrody ChanNo ratings yet
- Inferential Statistical Decision Making TreesDocument2 pagesInferential Statistical Decision Making TreesLeana Polston-MurdochNo ratings yet
- B. Sc. Environmental Science Sem 1Document4 pagesB. Sc. Environmental Science Sem 1Uzeir SelotNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Linear ModelingDocument20 pagesWorksheet - Linear Modelingmathsman9No ratings yet
- Operations Research: Chapter 3 (I)Document39 pagesOperations Research: Chapter 3 (I)Ashish BanstolaNo ratings yet
- Major06 QP DLP NEET2019 (Pmtcorner - In) PDFDocument40 pagesMajor06 QP DLP NEET2019 (Pmtcorner - In) PDFMegha HazarikaNo ratings yet
- ch.2 Electric Potential and Capacitor - NotesDocument10 pagesch.2 Electric Potential and Capacitor - Notesnandank44373No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesVien YaelNo ratings yet
- Curriculum VitÆ Nom Et Prénom: Bachari Khaldoun Date EtDocument5 pagesCurriculum VitÆ Nom Et Prénom: Bachari Khaldoun Date EtThe-ScribderNo ratings yet
- 2022 Mathematical Methods Examination Paper 2Document33 pages2022 Mathematical Methods Examination Paper 2fefdesasdfaNo ratings yet
- SCORING The Analytical Exposition TextDocument3 pagesSCORING The Analytical Exposition TextRica SugandiNo ratings yet
- Developing The Internal Audit Strategic Plan: - Practice GuideDocument20 pagesDeveloping The Internal Audit Strategic Plan: - Practice GuideMike NicolasNo ratings yet
- Interreg Danube Implementation ManualDocument84 pagesInterreg Danube Implementation ManualMadalina SbarceaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 3 - CE 315 Numericals Moduleset BDocument7 pagesWeek 2 3 - CE 315 Numericals Moduleset BGrant Jomar SiadorNo ratings yet
- CSEC Mathematics Specimen 2008 P2 SolutionsDocument15 pagesCSEC Mathematics Specimen 2008 P2 Solutionszarzsultan12No ratings yet
- 2% L-Leucin 3% PEG 6000Document10 pages2% L-Leucin 3% PEG 6000Con Sóng Âm ThầmNo ratings yet
- Donnie Darko Explanation of What, How and WhyDocument3 pagesDonnie Darko Explanation of What, How and WhyAuric GoldfingerNo ratings yet