Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Full-Bridge Converter: June 27, 2017
Full-Bridge Converter: June 27, 2017
Uploaded by
Shyam ShankarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- IEEE-754 Floating Point Multipler in VerilogDocument8 pagesIEEE-754 Floating Point Multipler in VerilogShyam Shankar55% (11)
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Lect 040Document5 pagesLect 040dheyaaNo ratings yet
- CapasitorDocument22 pagesCapasitorCollin PandieNo ratings yet
- 5 Work and HeatDocument20 pages5 Work and HeatRishabh KaushikNo ratings yet
- IET Power Electronics - 2014 - Ye - Quadratic Boost Converter With Low Buffer Capacitor StressDocument9 pagesIET Power Electronics - 2014 - Ye - Quadratic Boost Converter With Low Buffer Capacitor Stressreza mohajeryNo ratings yet
- Thermo Module 6Document29 pagesThermo Module 6Royce SumagaysayNo ratings yet
- Design Procedure of A Push Pull Current-Fed DC-DCDocument8 pagesDesign Procedure of A Push Pull Current-Fed DC-DCIhya UlumuddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Generation of High VoltageDocument41 pagesChapter 6 Generation of High Voltagevino drenNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and InductorsDocument19 pagesCapacitors and InductorsRizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic I AND IIDocument143 pagesHydraulic I AND IIOthmane BoualamNo ratings yet
- RC Filter Networks Lab Report: 1 TheoryDocument9 pagesRC Filter Networks Lab Report: 1 TheoryOsang Ekeh Bush TitusNo ratings yet
- Handout 10 - Energy BalancesDocument8 pagesHandout 10 - Energy Balancesalexchitongwe48No ratings yet
- Op Amp and Transistor-Based Analog Square Wave Generator DesignDocument10 pagesOp Amp and Transistor-Based Analog Square Wave Generator DesignAto Triyono MetroNo ratings yet
- 12-Refraction MethodDocument15 pages12-Refraction MethodyaredNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Isolated-Output ConvertersDocument46 pagesTopic 6 Isolated-Output Converterscemefi7580No ratings yet
- In This Lecture:: DT Di M DT Di L VDocument5 pagesIn This Lecture:: DT Di M DT Di L VHassan FarssiNo ratings yet
- D.C.-D.C. Conversion (1) : Buck Converter 6.1 Operation: in This LectureDocument4 pagesD.C.-D.C. Conversion (1) : Buck Converter 6.1 Operation: in This LectureHassan FarssiNo ratings yet
- WTD Chapter 3Document64 pagesWTD Chapter 3Mohamed ElgamalNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - AC TO DC CONVERTER (Student Updated)Document60 pagesCHAPTER 2 - AC TO DC CONVERTER (Student Updated)Ct KhatijahNo ratings yet
- 06-DC ChopperDocument26 pages06-DC ChopperTuhin ShahNo ratings yet
- 1 RC CircuitsDocument7 pages1 RC CircuitsMohmed Al NajarNo ratings yet
- Summary Slides Unit 2 Part 2Document9 pagesSummary Slides Unit 2 Part 2ayuuuNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 AC To DC Power ConversionDocument33 pagesTopic 8 AC To DC Power Conversioncemefi7580No ratings yet
- High Voltage Engineering: OvervoltagesDocument24 pagesHigh Voltage Engineering: OvervoltagesrsantanaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1 Chapter 5Document6 pagesThermodynamics 1 Chapter 5Kevin Mark IlaganNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Energi GelombangDocument26 pagesKuliah Energi GelombangTeknik KelautanNo ratings yet
- To Study The Operation of UJT As A Pulse Generation CircuitDocument5 pagesTo Study The Operation of UJT As A Pulse Generation CircuitkashishlalaNo ratings yet
- Fast-Scale Bifurcation in Power-Factor-Correction Buck-Boost Converters and Eects of Incompatible PeriodicitiesDocument14 pagesFast-Scale Bifurcation in Power-Factor-Correction Buck-Boost Converters and Eects of Incompatible PeriodicitieshakikNo ratings yet
- Buck ConvertersDocument15 pagesBuck Convertersחי לוגסיNo ratings yet
- Triangle-Wave Generator (TWG) Outputs Both Triangle and Square Waves. Twgs AreDocument16 pagesTriangle-Wave Generator (TWG) Outputs Both Triangle and Square Waves. Twgs Aremuhaned190No ratings yet
- Partial Discharge Related 6Document5 pagesPartial Discharge Related 6Prasann KatiyarNo ratings yet
- L5 SMPSDocument18 pagesL5 SMPSAyush BhattNo ratings yet
- Resonant ConvertersDocument52 pagesResonant ConvertersKobe YambiNo ratings yet
- DC To DC ConvertersDocument40 pagesDC To DC ConvertersJamir CalNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PDFDocument214 pagesMechanical PDFSangram JadhavNo ratings yet
- Course4 Termo2020Document16 pagesCourse4 Termo2020adrian2r04No ratings yet
- Fardapaper Controller Design For Cuk Converter Using Model Order ReductionDocument5 pagesFardapaper Controller Design For Cuk Converter Using Model Order Reductionmohamed rafeNo ratings yet
- E:To Study The Design of A Transistor Astable MultivibratorDocument4 pagesE:To Study The Design of A Transistor Astable MultivibratorRakibullah SazibNo ratings yet
- P240 EM FormulaeDocument3 pagesP240 EM FormulaeNando HRNo ratings yet
- DATA BOOKLET Electricity and MagnetismDocument62 pagesDATA BOOKLET Electricity and MagnetismPratham AdvaniNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Boost Switching DC-DC Power ConverterDocument44 pagesExperiment 2 Boost Switching DC-DC Power ConverterRAKESH ROSHANNo ratings yet
- PE Lecture - 8 - NDocument26 pagesPE Lecture - 8 - Nahmed el-sayedNo ratings yet
- Capacitance - 18-11-08 (7 LCTR)Document34 pagesCapacitance - 18-11-08 (7 LCTR)vinay singhNo ratings yet
- Capacitance of An Isolated Conductor: Lecture # 1Document33 pagesCapacitance of An Isolated Conductor: Lecture # 1Jigyasu RajputNo ratings yet
- Current MirrorDocument30 pagesCurrent MirrorMeril CyriacNo ratings yet
- Inductive and Magnetic SensorsDocument7 pagesInductive and Magnetic SensorsJefersonNo ratings yet
- Authorized Licensed Use Limited To: Rutgers University. Downloaded On May 17,2021 at 01:24:20 UTC From IEEE Xplore. Restrictions ApplyDocument1 pageAuthorized Licensed Use Limited To: Rutgers University. Downloaded On May 17,2021 at 01:24:20 UTC From IEEE Xplore. Restrictions ApplyElyes MbarekNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Fundamentals of Electric Circuits - S2023 2023-01-13 17 - 23 - 29Document46 pagesChapter 1 - Fundamentals of Electric Circuits - S2023 2023-01-13 17 - 23 - 29SpedNo ratings yet
- SSED - AY2021 S2 Final Review TheoryDocument9 pagesSSED - AY2021 S2 Final Review Theoryttoan2404asdNo ratings yet
- Power AmplifierDocument37 pagesPower AmplifierSristick100% (6)
- Lecture-10: BJT Switching Characteristics, Small Signal ModelDocument13 pagesLecture-10: BJT Switching Characteristics, Small Signal ModelJ JulietNo ratings yet
- EE462L, Spring 2014 DC DC Buck ConverterDocument37 pagesEE462L, Spring 2014 DC DC Buck ConverterprateekNo ratings yet
- Exp 02Document5 pagesExp 02Captain Jack SparrowNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and InductorsDocument19 pagesCapacitors and InductorsAdnan KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture EEE 447 Chap 5 DC DC ConvertersDocument32 pagesLecture EEE 447 Chap 5 DC DC ConverterstasniNo ratings yet
- PST Unit 4Document11 pagesPST Unit 4Karthick Sivakumar ChellamuthuNo ratings yet
- Impulse GenerationDocument14 pagesImpulse GenerationPrasann KatiyarNo ratings yet
- EE309 Notes 07 PDFDocument4 pagesEE309 Notes 07 PDFbals123456100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Rectifier Filter ClipperDocument38 pagesChapter 3 - Rectifier Filter ClipperfaizalabdullahNo ratings yet
- Client Server Programming C CodeDocument9 pagesClient Server Programming C CodeShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 10: Shyam Shankar H R EE15B127 November 9, 2017Document15 pagesAssignment - 10: Shyam Shankar H R EE15B127 November 9, 2017Shyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- QueuingTheory Matlab AssignmentDocument3 pagesQueuingTheory Matlab AssignmentShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7: Ee15B124: H.Sahithya Kavya Ee15B127: Shyam Shankar H R November 6, 2017Document5 pagesAssignment 7: Ee15B124: H.Sahithya Kavya Ee15B127: Shyam Shankar H R November 6, 2017Shyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- PMMC ExperimentDocument2 pagesPMMC ExperimentShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems TutorialDocument2 pagesCommunication Systems TutorialShyam Shankar100% (1)
- Computer Organization Assignment-2: Shyam Shankar H R EE15B127 August 21, 2017Document2 pagesComputer Organization Assignment-2: Shyam Shankar H R EE15B127 August 21, 2017Shyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Communication SystemsDocument1 pageCommunication SystemsShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- What Is Engineering Mechanics ?: Study of The Effect of Forces On A Body at Rest or Uniform MotionDocument15 pagesWhat Is Engineering Mechanics ?: Study of The Effect of Forces On A Body at Rest or Uniform MotionShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Q1. Draw The Timing Diagram For The 8085 Instruction Assigned To Each Student (Refer ToDocument1 pageAssignment 1: Q1. Draw The Timing Diagram For The 8085 Instruction Assigned To Each Student (Refer ToShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Solving Laplace in PythonDocument4 pagesSolving Laplace in PythonShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3: Question (Heuring 2 Ed, 6.29)Document1 pageAssignment 3: Question (Heuring 2 Ed, 6.29)Shyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Discrete Signal ProcessingDocument1 pageDiscrete Signal ProcessingShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Python ProgrammingDocument13 pagesPython ProgrammingShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
Full-Bridge Converter: June 27, 2017
Full-Bridge Converter: June 27, 2017
Uploaded by
Shyam ShankarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Full-Bridge Converter: June 27, 2017
Full-Bridge Converter: June 27, 2017
Uploaded by
Shyam ShankarCopyright:
Available Formats
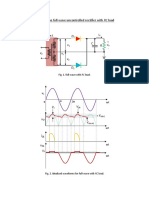
FULL-BRIDGE CONVERTER
June 27, 2017
Abstract
A full bridge is a buck-type converter consisting of a buck regulation stage followed by a full bridge isolation stage. Here, the
transformer is driven symmetrically, such that the net voltage across the windings over two cycles is zero. During the first
switching periood, the switches Q1 and Q4 are closed for time D.Ts . In the next cycle the switches Q2 and Q3 are closed
for the same interval, thus making the net voltage over two cycles = 0. By the principle of volt-second balance the dc load
voltage can be shown to be,
V = nDVg
Block Diagram
Transfer function and Duty cycle
!
1 Vout + Vf
D= Ns
2 Vin . N p
ton
where D is the duty cycle. (D = T )
VQ1 = Vin
Ns
VD1 = 2.Vin . Vf
Np
Advantages of Full bridge topology
1. Could be scaled to higher power levels
Disadvantages of Flyback topology
1. There needs to be a dead time between the ON times, which limits duty cycle.
You might also like
- IEEE-754 Floating Point Multipler in VerilogDocument8 pagesIEEE-754 Floating Point Multipler in VerilogShyam Shankar55% (11)
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Lect 040Document5 pagesLect 040dheyaaNo ratings yet
- CapasitorDocument22 pagesCapasitorCollin PandieNo ratings yet
- 5 Work and HeatDocument20 pages5 Work and HeatRishabh KaushikNo ratings yet
- IET Power Electronics - 2014 - Ye - Quadratic Boost Converter With Low Buffer Capacitor StressDocument9 pagesIET Power Electronics - 2014 - Ye - Quadratic Boost Converter With Low Buffer Capacitor Stressreza mohajeryNo ratings yet
- Thermo Module 6Document29 pagesThermo Module 6Royce SumagaysayNo ratings yet
- Design Procedure of A Push Pull Current-Fed DC-DCDocument8 pagesDesign Procedure of A Push Pull Current-Fed DC-DCIhya UlumuddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Generation of High VoltageDocument41 pagesChapter 6 Generation of High Voltagevino drenNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and InductorsDocument19 pagesCapacitors and InductorsRizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic I AND IIDocument143 pagesHydraulic I AND IIOthmane BoualamNo ratings yet
- RC Filter Networks Lab Report: 1 TheoryDocument9 pagesRC Filter Networks Lab Report: 1 TheoryOsang Ekeh Bush TitusNo ratings yet
- Handout 10 - Energy BalancesDocument8 pagesHandout 10 - Energy Balancesalexchitongwe48No ratings yet
- Op Amp and Transistor-Based Analog Square Wave Generator DesignDocument10 pagesOp Amp and Transistor-Based Analog Square Wave Generator DesignAto Triyono MetroNo ratings yet
- 12-Refraction MethodDocument15 pages12-Refraction MethodyaredNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Isolated-Output ConvertersDocument46 pagesTopic 6 Isolated-Output Converterscemefi7580No ratings yet
- In This Lecture:: DT Di M DT Di L VDocument5 pagesIn This Lecture:: DT Di M DT Di L VHassan FarssiNo ratings yet
- D.C.-D.C. Conversion (1) : Buck Converter 6.1 Operation: in This LectureDocument4 pagesD.C.-D.C. Conversion (1) : Buck Converter 6.1 Operation: in This LectureHassan FarssiNo ratings yet
- WTD Chapter 3Document64 pagesWTD Chapter 3Mohamed ElgamalNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - AC TO DC CONVERTER (Student Updated)Document60 pagesCHAPTER 2 - AC TO DC CONVERTER (Student Updated)Ct KhatijahNo ratings yet
- 06-DC ChopperDocument26 pages06-DC ChopperTuhin ShahNo ratings yet
- 1 RC CircuitsDocument7 pages1 RC CircuitsMohmed Al NajarNo ratings yet
- Summary Slides Unit 2 Part 2Document9 pagesSummary Slides Unit 2 Part 2ayuuuNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 AC To DC Power ConversionDocument33 pagesTopic 8 AC To DC Power Conversioncemefi7580No ratings yet
- High Voltage Engineering: OvervoltagesDocument24 pagesHigh Voltage Engineering: OvervoltagesrsantanaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1 Chapter 5Document6 pagesThermodynamics 1 Chapter 5Kevin Mark IlaganNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Energi GelombangDocument26 pagesKuliah Energi GelombangTeknik KelautanNo ratings yet
- To Study The Operation of UJT As A Pulse Generation CircuitDocument5 pagesTo Study The Operation of UJT As A Pulse Generation CircuitkashishlalaNo ratings yet
- Fast-Scale Bifurcation in Power-Factor-Correction Buck-Boost Converters and Eects of Incompatible PeriodicitiesDocument14 pagesFast-Scale Bifurcation in Power-Factor-Correction Buck-Boost Converters and Eects of Incompatible PeriodicitieshakikNo ratings yet
- Buck ConvertersDocument15 pagesBuck Convertersחי לוגסיNo ratings yet
- Triangle-Wave Generator (TWG) Outputs Both Triangle and Square Waves. Twgs AreDocument16 pagesTriangle-Wave Generator (TWG) Outputs Both Triangle and Square Waves. Twgs Aremuhaned190No ratings yet
- Partial Discharge Related 6Document5 pagesPartial Discharge Related 6Prasann KatiyarNo ratings yet
- L5 SMPSDocument18 pagesL5 SMPSAyush BhattNo ratings yet
- Resonant ConvertersDocument52 pagesResonant ConvertersKobe YambiNo ratings yet
- DC To DC ConvertersDocument40 pagesDC To DC ConvertersJamir CalNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PDFDocument214 pagesMechanical PDFSangram JadhavNo ratings yet
- Course4 Termo2020Document16 pagesCourse4 Termo2020adrian2r04No ratings yet
- Fardapaper Controller Design For Cuk Converter Using Model Order ReductionDocument5 pagesFardapaper Controller Design For Cuk Converter Using Model Order Reductionmohamed rafeNo ratings yet
- E:To Study The Design of A Transistor Astable MultivibratorDocument4 pagesE:To Study The Design of A Transistor Astable MultivibratorRakibullah SazibNo ratings yet
- P240 EM FormulaeDocument3 pagesP240 EM FormulaeNando HRNo ratings yet
- DATA BOOKLET Electricity and MagnetismDocument62 pagesDATA BOOKLET Electricity and MagnetismPratham AdvaniNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Boost Switching DC-DC Power ConverterDocument44 pagesExperiment 2 Boost Switching DC-DC Power ConverterRAKESH ROSHANNo ratings yet
- PE Lecture - 8 - NDocument26 pagesPE Lecture - 8 - Nahmed el-sayedNo ratings yet
- Capacitance - 18-11-08 (7 LCTR)Document34 pagesCapacitance - 18-11-08 (7 LCTR)vinay singhNo ratings yet
- Capacitance of An Isolated Conductor: Lecture # 1Document33 pagesCapacitance of An Isolated Conductor: Lecture # 1Jigyasu RajputNo ratings yet
- Current MirrorDocument30 pagesCurrent MirrorMeril CyriacNo ratings yet
- Inductive and Magnetic SensorsDocument7 pagesInductive and Magnetic SensorsJefersonNo ratings yet
- Authorized Licensed Use Limited To: Rutgers University. Downloaded On May 17,2021 at 01:24:20 UTC From IEEE Xplore. Restrictions ApplyDocument1 pageAuthorized Licensed Use Limited To: Rutgers University. Downloaded On May 17,2021 at 01:24:20 UTC From IEEE Xplore. Restrictions ApplyElyes MbarekNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Fundamentals of Electric Circuits - S2023 2023-01-13 17 - 23 - 29Document46 pagesChapter 1 - Fundamentals of Electric Circuits - S2023 2023-01-13 17 - 23 - 29SpedNo ratings yet
- SSED - AY2021 S2 Final Review TheoryDocument9 pagesSSED - AY2021 S2 Final Review Theoryttoan2404asdNo ratings yet
- Power AmplifierDocument37 pagesPower AmplifierSristick100% (6)
- Lecture-10: BJT Switching Characteristics, Small Signal ModelDocument13 pagesLecture-10: BJT Switching Characteristics, Small Signal ModelJ JulietNo ratings yet
- EE462L, Spring 2014 DC DC Buck ConverterDocument37 pagesEE462L, Spring 2014 DC DC Buck ConverterprateekNo ratings yet
- Exp 02Document5 pagesExp 02Captain Jack SparrowNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and InductorsDocument19 pagesCapacitors and InductorsAdnan KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture EEE 447 Chap 5 DC DC ConvertersDocument32 pagesLecture EEE 447 Chap 5 DC DC ConverterstasniNo ratings yet
- PST Unit 4Document11 pagesPST Unit 4Karthick Sivakumar ChellamuthuNo ratings yet
- Impulse GenerationDocument14 pagesImpulse GenerationPrasann KatiyarNo ratings yet
- EE309 Notes 07 PDFDocument4 pagesEE309 Notes 07 PDFbals123456100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Rectifier Filter ClipperDocument38 pagesChapter 3 - Rectifier Filter ClipperfaizalabdullahNo ratings yet
- Client Server Programming C CodeDocument9 pagesClient Server Programming C CodeShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 10: Shyam Shankar H R EE15B127 November 9, 2017Document15 pagesAssignment - 10: Shyam Shankar H R EE15B127 November 9, 2017Shyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- QueuingTheory Matlab AssignmentDocument3 pagesQueuingTheory Matlab AssignmentShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7: Ee15B124: H.Sahithya Kavya Ee15B127: Shyam Shankar H R November 6, 2017Document5 pagesAssignment 7: Ee15B124: H.Sahithya Kavya Ee15B127: Shyam Shankar H R November 6, 2017Shyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- PMMC ExperimentDocument2 pagesPMMC ExperimentShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems TutorialDocument2 pagesCommunication Systems TutorialShyam Shankar100% (1)
- Computer Organization Assignment-2: Shyam Shankar H R EE15B127 August 21, 2017Document2 pagesComputer Organization Assignment-2: Shyam Shankar H R EE15B127 August 21, 2017Shyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Communication SystemsDocument1 pageCommunication SystemsShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- What Is Engineering Mechanics ?: Study of The Effect of Forces On A Body at Rest or Uniform MotionDocument15 pagesWhat Is Engineering Mechanics ?: Study of The Effect of Forces On A Body at Rest or Uniform MotionShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Q1. Draw The Timing Diagram For The 8085 Instruction Assigned To Each Student (Refer ToDocument1 pageAssignment 1: Q1. Draw The Timing Diagram For The 8085 Instruction Assigned To Each Student (Refer ToShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Solving Laplace in PythonDocument4 pagesSolving Laplace in PythonShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3: Question (Heuring 2 Ed, 6.29)Document1 pageAssignment 3: Question (Heuring 2 Ed, 6.29)Shyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Discrete Signal ProcessingDocument1 pageDiscrete Signal ProcessingShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Python ProgrammingDocument13 pagesPython ProgrammingShyam ShankarNo ratings yet