Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chem12 55
Chem12 55
Uploaded by
MuhammadCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 5 - Pogil Kinetic MolecularDocument3 pages5 - Pogil Kinetic Molecular776pmsfq2f100% (2)
- Test Bank For Introductory Chemistry, 2e Kevin Revell Test BankDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Introductory Chemistry, 2e Kevin Revell Test BankNail BaskoNo ratings yet
- SCH4U - Unit 1 - Version C PDFDocument64 pagesSCH4U - Unit 1 - Version C PDFAbdul Mujeeb100% (1)
- 7.1.2 - Spectra - QUESTIONSDocument3 pages7.1.2 - Spectra - QUESTIONSmalihaNo ratings yet
- Types of Bonds WorksheetDocument3 pagesTypes of Bonds WorksheetKenji Munsuro100% (2)
- Types of Bonds WorksheetDocument3 pagesTypes of Bonds WorksheetKenji Munsuro100% (2)
- Chapter 9 Test Chemical ReactionsDocument8 pagesChapter 9 Test Chemical Reactionskarthickumarag100% (1)
- Atomic - Structure of The Periodic Table WorksheetDocument1 pageAtomic - Structure of The Periodic Table WorksheetEdison Alfonso SturgessNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Chapter 6 ReviewDocument8 pagesChemical Bonding: Chapter 6 ReviewCabdicasiis Maxamuud GuuleedNo ratings yet
- Atoms and The Periodic Table Study Guide AnswersDocument10 pagesAtoms and The Periodic Table Study Guide Answersapi-267855902100% (1)
- CovalentBondsSE PDFDocument4 pagesCovalentBondsSE PDFAmaan Allana0% (2)
- UNIT TEST-Pathogens and DiseaseDocument15 pagesUNIT TEST-Pathogens and DiseaseElizabeth McallisterNo ratings yet
- Atomic History Worksheet Answer KeyDocument1 pageAtomic History Worksheet Answer KeyRhuvy Ramos0% (1)
- Chapter 5 InorgDocument29 pagesChapter 5 InorgMauritiusFeliciano100% (2)
- I B Chem 1 Pract Test BondingDocument7 pagesI B Chem 1 Pract Test BondingMuy TamNo ratings yet
- What Is A Mole SummativeDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Mole Summativeapi-291560513No ratings yet
- ANSWERS - Review The AtomDocument5 pagesANSWERS - Review The AtomDayana MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Study GuideDocument2 pagesChapter One Study GuideLaurie Gardner100% (1)
- Dot Structures Practice PacketDocument6 pagesDot Structures Practice Packetgoogley71No ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet: Matter #1Document6 pagesChemistry Worksheet: Matter #1Anisah MahmudahNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Worksheet 1: Significant Figures and Dimensional AnalysisDocument17 pagesIB Chemistry Worksheet 1: Significant Figures and Dimensional AnalysisFinn Bruchet100% (1)
- Atomic Structure: Chapter Test BDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure: Chapter Test BTeegin HackerNo ratings yet
- Questions On Periodic TableDocument5 pagesQuestions On Periodic TableTarek FaramawyNo ratings yet
- Ionic Covalent Bonds PractDocument2 pagesIonic Covalent Bonds PractRina NoviantiNo ratings yet
- Molecular PolarityDocument4 pagesMolecular PolarityTea RadicNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Chemical EquationsDocument6 pagesStudent Exploration: Chemical EquationsAndreNo ratings yet
- Ionic Packet For Lab Chem 2010 2011Document16 pagesIonic Packet For Lab Chem 2010 2011Victor BritoNo ratings yet
- Properties of Covalent CompoundsDocument2 pagesProperties of Covalent CompoundsManP13No ratings yet
- CH 12 Study GuideDocument4 pagesCH 12 Study Guideapi-342334216100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding and StructureDocument34 pagesChemical Bonding and StructureLaraStrbacNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Solutes Solvents Solubility Solutions VCBCCTDocument17 pagesChemistry Solutes Solvents Solubility Solutions VCBCCTDIONYSUS100% (1)
- Bonding TestDocument4 pagesBonding TestTon Nette FoyoNo ratings yet
- snc2D - Practice ExamDocument5 pagessnc2D - Practice Examganjaman2009-emailNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes - Molecular & Ionic Compound Structure & PropertiesDocument18 pagesUnit 2 Notes - Molecular & Ionic Compound Structure & PropertiesDragonbariumNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reactions Powerpoint PresentationDocument6 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions Powerpoint Presentationapi-1991761550% (6)
- Worksheet 3 (Partial Pressures)Document2 pagesWorksheet 3 (Partial Pressures)Jose Ruben SortoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chemistry of Life Review PacketDocument7 pagesUnit 2 Chemistry of Life Review PacketShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- Bohr Model and Electron ConfigurationDocument33 pagesBohr Model and Electron ConfigurationLiviaAsriNo ratings yet
- CMC Chapter 11Document58 pagesCMC Chapter 11Marah Omar50% (2)
- Ionic Bonding Worksheet: Name: - Period: - DateDocument2 pagesIonic Bonding Worksheet: Name: - Period: - DateAly MohamedNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reactions Close Reading PDFDocument4 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions Close Reading PDFStefanie CorcoranNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Document4 pagesChemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Lama DebanaNo ratings yet
- HL Topic 7 17 EquilibriumDocument9 pagesHL Topic 7 17 EquilibriumDavid DancerNo ratings yet
- 2019 Lesson 12 Empirical and Molecular FormulasDocument42 pages2019 Lesson 12 Empirical and Molecular FormulasMinenhle Mnikathi100% (1)
- Upper Final-Practice Questions - April 2023 Ans KeyDocument14 pagesUpper Final-Practice Questions - April 2023 Ans KeyVi NgôNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy Changes and Hess CyclesDocument17 pagesEnthalpy Changes and Hess CyclesMoon KimNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 ChemicChemical Kinetics and Equilibriumal Kinetics and Equilibrium Notes (Answers)Document22 pagesUnit 5 ChemicChemical Kinetics and Equilibriumal Kinetics and Equilibrium Notes (Answers)Muhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Note01-10 StudentDocument28 pagesAcid Base Note01-10 Studentc_66hsia7505No ratings yet
- Act Biology QuestionsDocument9 pagesAct Biology Questionsmohamed mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Bonding PowerpointDocument14 pagesBonding Powerpointᴍɪᴋᴋɪᴋᴀᴢᴇ100% (2)
- IB Sample TestDocument31 pagesIB Sample TeststonedinoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Atomic Structure, STD 8thDocument3 pagesWorksheet On Atomic Structure, STD 8thArshad KhanNo ratings yet
- (2.1) E, C, & M (Without Answer)Document2 pages(2.1) E, C, & M (Without Answer)Rose Ann Saldivia AgramonNo ratings yet
- Kamar McFarlane - Mole Conversion WorksheetDocument3 pagesKamar McFarlane - Mole Conversion WorksheetKamar McfarlaneNo ratings yet
- SNR Chemistry 19 Formula Data BookDocument17 pagesSNR Chemistry 19 Formula Data Bookapi-125934329No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Review QuestionsDocument11 pagesAtomic Structure Review Questionsoc100% (1)
- Separation HW BOOK PDFDocument9 pagesSeparation HW BOOK PDFAngela KocevskaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Study GuideDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Study GuideportbluepicklesNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarterly Test in g9 ScienceDocument5 pages2nd Quarterly Test in g9 ScienceLIWLIWA SUGUITAN100% (1)
- Quarterly Test in g9 Science 2nd GradingDocument4 pagesQuarterly Test in g9 Science 2nd GradingPedro GenosasNo ratings yet
- 2nd Mastery Test ChemistryDocument3 pages2nd Mastery Test Chemistrystephenibahan330No ratings yet
- Quiz - Bonding A KEYDocument3 pagesQuiz - Bonding A KEYManongdo AllanNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction Worksheet: Name: . DateDocument4 pagesAsexual Reproduction Worksheet: Name: . DateMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Cells Worksheet: Name: . DateDocument5 pagesCells Worksheet: Name: . DateMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Grade 8Document1 pageWorksheet Grade 8MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Do Not Allow "Gravity". N MG: G GravitationalDocument7 pagesDo Not Allow "Gravity". N MG: G GravitationalMuhammadNo ratings yet
- ThermalDocument9 pagesThermalMuhammadNo ratings yet
- P1 HomeworkDocument5 pagesP1 HomeworkMuhammad0% (1)
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument2 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: Holt PhysicsDocument8 pagesAnswer Key: Holt PhysicsMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For The IB MYP 4&5: by Concept: Unit PlannerDocument11 pagesChemistry For The IB MYP 4&5: by Concept: Unit PlannerMuhammad80% (5)
- 0972 w19 GT PDFDocument1 page0972 w19 GT PDFMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Vibrations and Waves: Additional Practice ADocument4 pagesVibrations and Waves: Additional Practice AMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Quiz Grade 10 OctoberDocument2 pagesQuiz Grade 10 OctoberMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Measures of Simple Harmonic Motion: Term Example S UnitDocument1 pageMeasures of Simple Harmonic Motion: Term Example S UnitMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Teacher Notes and Answers 11 Vibrations and WavesDocument3 pagesTeacher Notes and Answers 11 Vibrations and WavesMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Of Water (HDocument7 pagesOf Water (HMuhammadNo ratings yet
- S 2 in One Orbital P 6 in Three Orbital D 10 in Five Orbital F 14 in Seven OrbitalDocument6 pagesS 2 in One Orbital P 6 in Three Orbital D 10 in Five Orbital F 14 in Seven OrbitalMuhammadNo ratings yet
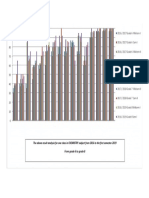
- The Above Result Analysis For One Class in CHEMISTRY Subject From 2016 To The First Semester 2019 From Grade 6 To Grade 8Document1 pageThe Above Result Analysis For One Class in CHEMISTRY Subject From 2016 To The First Semester 2019 From Grade 6 To Grade 8MuhammadNo ratings yet
- The Activation Energy of The Forward Reaction Is Shown by A. B. C. D. EDocument7 pagesThe Activation Energy of The Forward Reaction Is Shown by A. B. C. D. EMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Ag + C H ODocument9 pagesAg + C H OMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Chemical Periodicity (REVISED)Document3 pagesChemical Periodicity (REVISED)Annie Valerie OgedeNo ratings yet
- Recycling of PTFEDocument36 pagesRecycling of PTFEyatheendravarmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryDelosreyes ChildrenNo ratings yet
- Title of Assignment: Water PropertiesDocument10 pagesTitle of Assignment: Water PropertiesAriful IslamNo ratings yet
- (2nd) Learning Plan Sci 9Document18 pages(2nd) Learning Plan Sci 9Ven AnosNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences Table of Specifications NCBTS-BASED For LETDocument7 pagesPhysical Sciences Table of Specifications NCBTS-BASED For LETAnabelle MaumayNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding Comics GuidelinesDocument1 pageIonic and Covalent Bonding Comics GuidelinesArch Broqueza33% (3)
- FIRST MODULE ON PHYSICAL SCIENCE 2021 GRADE 11 For PrintingDocument33 pagesFIRST MODULE ON PHYSICAL SCIENCE 2021 GRADE 11 For PrintingTaruk OcumenNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Science 9Document3 pagesSummative Test Science 9Karl Frenz Otida100% (2)
- LS ST 103: General Chemistry 1: Radungo@tsu - Edu.phDocument4 pagesLS ST 103: General Chemistry 1: Radungo@tsu - Edu.phJerald LavariasNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 SolutionsDocument10 pagesExam 2 SolutionsHayden KelehanNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Chemical Bonding ICSE Solutions Class 10 ChemistryDocument18 pagesCH 2 Chemical Bonding ICSE Solutions Class 10 ChemistrylionelkenethNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes 2023 Separate Part 2Document170 pagesChemistry Notes 2023 Separate Part 2antonettemosweu211No ratings yet
- Xe F5 XF6 Complexes Engl 2005Document12 pagesXe F5 XF6 Complexes Engl 2005رضا جویاNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Chapter 1Document8 pagesAnswer Key Chapter 1ankit492No ratings yet
- Chemistry3 96) PDocument43 pagesChemistry3 96) PShlok ParekhNo ratings yet
- Pchem10e Solutions Ch10 AtkinsonDocument32 pagesPchem10e Solutions Ch10 Atkinson동글No ratings yet
- Chemistry A LevelDocument104 pagesChemistry A Levelrockykj100% (1)
- BiologyDocument313 pagesBiologysatya194289% (9)
- Chemical Bonding ProjectDocument2 pagesChemical Bonding ProjectTokimemoto Lustre Reid0% (1)
- Notes On Molecular Orbital CalculationDocument170 pagesNotes On Molecular Orbital CalculationFreeWill100% (1)
- Fall 2021 Department of Chemistry and Earth Sciences Arts and Sciences 3Document9 pagesFall 2021 Department of Chemistry and Earth Sciences Arts and Sciences 3DABAB DABABNo ratings yet
- X New Ionization and BondingDocument12 pagesX New Ionization and BondingkrisnuNo ratings yet
- 5070 w19 Ms 21Document10 pages5070 w19 Ms 21heerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Chemistry of Engineering MaterialsDocument36 pagesChapter 5 Chemistry of Engineering Materialsksm rachasNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Module 1Document38 pagesUnit 1 Module 1Pearl NecoleNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions D AN BLOCKDocument11 pagesMultiple Choice Questions D AN BLOCKMahrishiShukla100% (1)
Chem12 55
Chem12 55
Uploaded by
MuhammadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chem12 55
Chem12 55
Uploaded by
MuhammadCopyright:
Available Formats
Name Date Class
COVALENT BONDING
Chapter Test A
A. Matching
Match each description in Column B with the correct term in Column A. Write the letter of the correct description on
the line.
Column A Column B
1. coordinate covalent bond a. shows the kinds and numbers present in a molecule of a
compound
2. nonpolar covalent bond b. chemical formula that shows the arrangement of atoms in
molecules and polyatomic ions
3. hydrogen bond c. a covalent bond between two atoms of different electronegativities
in which the bonding electrons are not shared equally
4. double covalent bond d. interaction caused by the motion of electrons
5. dispersion force e. a covalent bond formed by the equal sharing of bonding electrons
by two atoms
6. molecular formula f. a covalent bond involving two pairs of electrons; each atom
donates one pair of electrons to the bond
7. structural formula g. a covalent bond in which three pairs of electrons are shared by
two bonded atoms
8. polar bond h. substance in which all of the atoms are covalently bonded to each
other
9. triple covalent bond i. a covalent bond between two atoms in which the shared electron
pair comes from only one of the atoms
10. network solid j. force that occurs when a hydrogen atom that is covalently bonded
to a very electronegative atom is also weakly bonded to an
unshared pair of electrons in the same or a nearby molecule
196 Core Teaching Resources
Name Date Class
B. Multiple Choice
Choose the best answer and write its letter on the line.
11. Which of these elements does not exist as a diatomic molecule?
a. I c. H
b. F d. He
12. Which one of the following compounds is not covalent?
a. SCl2 c. HCl
b. KCl d. S2Cl2
13. How many valence electrons does an atom of any halogen have?
a. 1 c. 4
b. 2 d. 7
14. A diatomic molecule with a triple covalent bond is
a. N2. c. H2.
b. Br2. d. O2.
15. A molecule of nitrous oxide, N2O, contains all of the following except
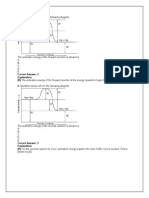
a. a coordinate covalent bond. c. a double bond.
b. a triple bond. d. nonbonding pairs of electrons.
16. If a bonding pair of electrons is unequally shared between two atoms, the bond is
a. ionic. c. coordinate covalent.
b. nonpolar covalent. d. polar covalent.
17. What is the electron dot structure for water?
a. c.
b. d.
18. Which of the following compounds is not ionic?
a. NaI c. CO2
b. CaCl2 d. Na2O
19. A covalent bond forms
a. when an element becomes a noble gas.
b. when atoms share electrons.
c. between metals and nonmetals.
d. when electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
20. What is the electron dot structure for the polyatomic ion OH?
a. c.
b. d.
21. Which of these compounds would not have covalent bonds?
a. NO2 c. N2O4
b. K2O d. H2O2
Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding 197
Name Date Class
22. A molecule with a single covalent bond is
a. CO2. c. NO.
b. F2. d. N2.
23. Chlorine is a gas, bromine is a liquid, and iodine is a solid because of differences in the strength of their
a. hydrogen bonds. c. dipole interactions.
b. dispersion forces. d. polar bonds.
24. When H+ forms a bond with H2O to form hydronium ion, H3O+, this bond is called a coordinate covalent
bond because
a. both bonding electrons come from the oxygen atom.
b. it is an especially strong bond.
c. the electrons are equally shared.
d. the oxygen no longer has eight electrons surrounding it.
25. Which of the following molecules has one lone pair of electrons?
a. CH4 c. H2O
b. HCl d. NH3
26. Which of the following is the weakest?
a. hydrogen bond c. dipole interaction
b. polar covalent bond d. ionic bond
27. The carbon tetrachloride molecule is
a. four-cornered. c. tetrahedral.
b. square. d. pyramidal.
C. Questions
Answer the following questions in the space provided.
28. Draw structural formulas for the following substances.
a. Br2
b. N2
c. CO
29. State whether the following compounds contain polar covalent bonds, nonpolar covalent bonds, or ionic bonds. (You
may refer to the table of electronegativities on the top of the next page.)
a. KF
b. SO2
c. NO2
d. HBr
198 Core Teaching Resources
Name Date Class
30. The following covalent molecules have only single covalent bonds. Draw an electron dot structure for each one.
a. HBr c. PCl3
b. H2O2
D. Essay
31. Describe a network solid and give two examples.
E. Additional Questions and Problems
Answer the following in the space provided. Show your work.
32. Calculate the total energy needed to dissociate all the bonds in one mole of ethyl alcohol, C 2H5OH. (Assume that the
total energy is the sum of the individual bond dissociation energies.) The structural formula of ethyl alcohol is
H H
H C C H
H O H
Bond Energy (kJ/mol)
HH 435
CH 393
CO 356
OH 464
CC 347
Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding 199
Name Date Class
33. With the aid of a diagram, describe how the overlap of one 2p orbital from each of two atoms forms a sigma bond,
but the overlap of the remaining two 2p orbitals from each atom forms pi bonds.
34. Indicate the hybrid orbitals used by each carbon atom in the following compound. The carbons are numbered for
easy reference.
H H
1 2 3 4 5
H C C C C C H
H O H
35. Draw electron dot structures for PCl5 and SF6. (Hint: These compounds are exceptions to the octet rule.)
200 Core Teaching Resources
You might also like
- 5 - Pogil Kinetic MolecularDocument3 pages5 - Pogil Kinetic Molecular776pmsfq2f100% (2)
- Test Bank For Introductory Chemistry, 2e Kevin Revell Test BankDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Introductory Chemistry, 2e Kevin Revell Test BankNail BaskoNo ratings yet
- SCH4U - Unit 1 - Version C PDFDocument64 pagesSCH4U - Unit 1 - Version C PDFAbdul Mujeeb100% (1)
- 7.1.2 - Spectra - QUESTIONSDocument3 pages7.1.2 - Spectra - QUESTIONSmalihaNo ratings yet
- Types of Bonds WorksheetDocument3 pagesTypes of Bonds WorksheetKenji Munsuro100% (2)
- Types of Bonds WorksheetDocument3 pagesTypes of Bonds WorksheetKenji Munsuro100% (2)
- Chapter 9 Test Chemical ReactionsDocument8 pagesChapter 9 Test Chemical Reactionskarthickumarag100% (1)
- Atomic - Structure of The Periodic Table WorksheetDocument1 pageAtomic - Structure of The Periodic Table WorksheetEdison Alfonso SturgessNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Chapter 6 ReviewDocument8 pagesChemical Bonding: Chapter 6 ReviewCabdicasiis Maxamuud GuuleedNo ratings yet
- Atoms and The Periodic Table Study Guide AnswersDocument10 pagesAtoms and The Periodic Table Study Guide Answersapi-267855902100% (1)
- CovalentBondsSE PDFDocument4 pagesCovalentBondsSE PDFAmaan Allana0% (2)
- UNIT TEST-Pathogens and DiseaseDocument15 pagesUNIT TEST-Pathogens and DiseaseElizabeth McallisterNo ratings yet
- Atomic History Worksheet Answer KeyDocument1 pageAtomic History Worksheet Answer KeyRhuvy Ramos0% (1)
- Chapter 5 InorgDocument29 pagesChapter 5 InorgMauritiusFeliciano100% (2)
- I B Chem 1 Pract Test BondingDocument7 pagesI B Chem 1 Pract Test BondingMuy TamNo ratings yet
- What Is A Mole SummativeDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Mole Summativeapi-291560513No ratings yet
- ANSWERS - Review The AtomDocument5 pagesANSWERS - Review The AtomDayana MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Study GuideDocument2 pagesChapter One Study GuideLaurie Gardner100% (1)
- Dot Structures Practice PacketDocument6 pagesDot Structures Practice Packetgoogley71No ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet: Matter #1Document6 pagesChemistry Worksheet: Matter #1Anisah MahmudahNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Worksheet 1: Significant Figures and Dimensional AnalysisDocument17 pagesIB Chemistry Worksheet 1: Significant Figures and Dimensional AnalysisFinn Bruchet100% (1)
- Atomic Structure: Chapter Test BDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure: Chapter Test BTeegin HackerNo ratings yet
- Questions On Periodic TableDocument5 pagesQuestions On Periodic TableTarek FaramawyNo ratings yet
- Ionic Covalent Bonds PractDocument2 pagesIonic Covalent Bonds PractRina NoviantiNo ratings yet
- Molecular PolarityDocument4 pagesMolecular PolarityTea RadicNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Chemical EquationsDocument6 pagesStudent Exploration: Chemical EquationsAndreNo ratings yet
- Ionic Packet For Lab Chem 2010 2011Document16 pagesIonic Packet For Lab Chem 2010 2011Victor BritoNo ratings yet
- Properties of Covalent CompoundsDocument2 pagesProperties of Covalent CompoundsManP13No ratings yet
- CH 12 Study GuideDocument4 pagesCH 12 Study Guideapi-342334216100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding and StructureDocument34 pagesChemical Bonding and StructureLaraStrbacNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Solutes Solvents Solubility Solutions VCBCCTDocument17 pagesChemistry Solutes Solvents Solubility Solutions VCBCCTDIONYSUS100% (1)
- Bonding TestDocument4 pagesBonding TestTon Nette FoyoNo ratings yet
- snc2D - Practice ExamDocument5 pagessnc2D - Practice Examganjaman2009-emailNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes - Molecular & Ionic Compound Structure & PropertiesDocument18 pagesUnit 2 Notes - Molecular & Ionic Compound Structure & PropertiesDragonbariumNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reactions Powerpoint PresentationDocument6 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions Powerpoint Presentationapi-1991761550% (6)
- Worksheet 3 (Partial Pressures)Document2 pagesWorksheet 3 (Partial Pressures)Jose Ruben SortoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chemistry of Life Review PacketDocument7 pagesUnit 2 Chemistry of Life Review PacketShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- Bohr Model and Electron ConfigurationDocument33 pagesBohr Model and Electron ConfigurationLiviaAsriNo ratings yet
- CMC Chapter 11Document58 pagesCMC Chapter 11Marah Omar50% (2)
- Ionic Bonding Worksheet: Name: - Period: - DateDocument2 pagesIonic Bonding Worksheet: Name: - Period: - DateAly MohamedNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reactions Close Reading PDFDocument4 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions Close Reading PDFStefanie CorcoranNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Document4 pagesChemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Lama DebanaNo ratings yet
- HL Topic 7 17 EquilibriumDocument9 pagesHL Topic 7 17 EquilibriumDavid DancerNo ratings yet
- 2019 Lesson 12 Empirical and Molecular FormulasDocument42 pages2019 Lesson 12 Empirical and Molecular FormulasMinenhle Mnikathi100% (1)
- Upper Final-Practice Questions - April 2023 Ans KeyDocument14 pagesUpper Final-Practice Questions - April 2023 Ans KeyVi NgôNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy Changes and Hess CyclesDocument17 pagesEnthalpy Changes and Hess CyclesMoon KimNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 ChemicChemical Kinetics and Equilibriumal Kinetics and Equilibrium Notes (Answers)Document22 pagesUnit 5 ChemicChemical Kinetics and Equilibriumal Kinetics and Equilibrium Notes (Answers)Muhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Note01-10 StudentDocument28 pagesAcid Base Note01-10 Studentc_66hsia7505No ratings yet
- Act Biology QuestionsDocument9 pagesAct Biology Questionsmohamed mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Bonding PowerpointDocument14 pagesBonding Powerpointᴍɪᴋᴋɪᴋᴀᴢᴇ100% (2)
- IB Sample TestDocument31 pagesIB Sample TeststonedinoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Atomic Structure, STD 8thDocument3 pagesWorksheet On Atomic Structure, STD 8thArshad KhanNo ratings yet
- (2.1) E, C, & M (Without Answer)Document2 pages(2.1) E, C, & M (Without Answer)Rose Ann Saldivia AgramonNo ratings yet
- Kamar McFarlane - Mole Conversion WorksheetDocument3 pagesKamar McFarlane - Mole Conversion WorksheetKamar McfarlaneNo ratings yet
- SNR Chemistry 19 Formula Data BookDocument17 pagesSNR Chemistry 19 Formula Data Bookapi-125934329No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Review QuestionsDocument11 pagesAtomic Structure Review Questionsoc100% (1)
- Separation HW BOOK PDFDocument9 pagesSeparation HW BOOK PDFAngela KocevskaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Study GuideDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Study GuideportbluepicklesNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarterly Test in g9 ScienceDocument5 pages2nd Quarterly Test in g9 ScienceLIWLIWA SUGUITAN100% (1)
- Quarterly Test in g9 Science 2nd GradingDocument4 pagesQuarterly Test in g9 Science 2nd GradingPedro GenosasNo ratings yet
- 2nd Mastery Test ChemistryDocument3 pages2nd Mastery Test Chemistrystephenibahan330No ratings yet
- Quiz - Bonding A KEYDocument3 pagesQuiz - Bonding A KEYManongdo AllanNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction Worksheet: Name: . DateDocument4 pagesAsexual Reproduction Worksheet: Name: . DateMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Cells Worksheet: Name: . DateDocument5 pagesCells Worksheet: Name: . DateMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Grade 8Document1 pageWorksheet Grade 8MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Do Not Allow "Gravity". N MG: G GravitationalDocument7 pagesDo Not Allow "Gravity". N MG: G GravitationalMuhammadNo ratings yet
- ThermalDocument9 pagesThermalMuhammadNo ratings yet
- P1 HomeworkDocument5 pagesP1 HomeworkMuhammad0% (1)
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument2 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: Holt PhysicsDocument8 pagesAnswer Key: Holt PhysicsMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For The IB MYP 4&5: by Concept: Unit PlannerDocument11 pagesChemistry For The IB MYP 4&5: by Concept: Unit PlannerMuhammad80% (5)
- 0972 w19 GT PDFDocument1 page0972 w19 GT PDFMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Vibrations and Waves: Additional Practice ADocument4 pagesVibrations and Waves: Additional Practice AMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Quiz Grade 10 OctoberDocument2 pagesQuiz Grade 10 OctoberMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Measures of Simple Harmonic Motion: Term Example S UnitDocument1 pageMeasures of Simple Harmonic Motion: Term Example S UnitMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Teacher Notes and Answers 11 Vibrations and WavesDocument3 pagesTeacher Notes and Answers 11 Vibrations and WavesMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Of Water (HDocument7 pagesOf Water (HMuhammadNo ratings yet
- S 2 in One Orbital P 6 in Three Orbital D 10 in Five Orbital F 14 in Seven OrbitalDocument6 pagesS 2 in One Orbital P 6 in Three Orbital D 10 in Five Orbital F 14 in Seven OrbitalMuhammadNo ratings yet
- The Above Result Analysis For One Class in CHEMISTRY Subject From 2016 To The First Semester 2019 From Grade 6 To Grade 8Document1 pageThe Above Result Analysis For One Class in CHEMISTRY Subject From 2016 To The First Semester 2019 From Grade 6 To Grade 8MuhammadNo ratings yet
- The Activation Energy of The Forward Reaction Is Shown by A. B. C. D. EDocument7 pagesThe Activation Energy of The Forward Reaction Is Shown by A. B. C. D. EMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Ag + C H ODocument9 pagesAg + C H OMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Chemical Periodicity (REVISED)Document3 pagesChemical Periodicity (REVISED)Annie Valerie OgedeNo ratings yet
- Recycling of PTFEDocument36 pagesRecycling of PTFEyatheendravarmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryDelosreyes ChildrenNo ratings yet
- Title of Assignment: Water PropertiesDocument10 pagesTitle of Assignment: Water PropertiesAriful IslamNo ratings yet
- (2nd) Learning Plan Sci 9Document18 pages(2nd) Learning Plan Sci 9Ven AnosNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences Table of Specifications NCBTS-BASED For LETDocument7 pagesPhysical Sciences Table of Specifications NCBTS-BASED For LETAnabelle MaumayNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding Comics GuidelinesDocument1 pageIonic and Covalent Bonding Comics GuidelinesArch Broqueza33% (3)
- FIRST MODULE ON PHYSICAL SCIENCE 2021 GRADE 11 For PrintingDocument33 pagesFIRST MODULE ON PHYSICAL SCIENCE 2021 GRADE 11 For PrintingTaruk OcumenNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Science 9Document3 pagesSummative Test Science 9Karl Frenz Otida100% (2)
- LS ST 103: General Chemistry 1: Radungo@tsu - Edu.phDocument4 pagesLS ST 103: General Chemistry 1: Radungo@tsu - Edu.phJerald LavariasNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 SolutionsDocument10 pagesExam 2 SolutionsHayden KelehanNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Chemical Bonding ICSE Solutions Class 10 ChemistryDocument18 pagesCH 2 Chemical Bonding ICSE Solutions Class 10 ChemistrylionelkenethNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes 2023 Separate Part 2Document170 pagesChemistry Notes 2023 Separate Part 2antonettemosweu211No ratings yet
- Xe F5 XF6 Complexes Engl 2005Document12 pagesXe F5 XF6 Complexes Engl 2005رضا جویاNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Chapter 1Document8 pagesAnswer Key Chapter 1ankit492No ratings yet
- Chemistry3 96) PDocument43 pagesChemistry3 96) PShlok ParekhNo ratings yet
- Pchem10e Solutions Ch10 AtkinsonDocument32 pagesPchem10e Solutions Ch10 Atkinson동글No ratings yet
- Chemistry A LevelDocument104 pagesChemistry A Levelrockykj100% (1)
- BiologyDocument313 pagesBiologysatya194289% (9)
- Chemical Bonding ProjectDocument2 pagesChemical Bonding ProjectTokimemoto Lustre Reid0% (1)
- Notes On Molecular Orbital CalculationDocument170 pagesNotes On Molecular Orbital CalculationFreeWill100% (1)
- Fall 2021 Department of Chemistry and Earth Sciences Arts and Sciences 3Document9 pagesFall 2021 Department of Chemistry and Earth Sciences Arts and Sciences 3DABAB DABABNo ratings yet
- X New Ionization and BondingDocument12 pagesX New Ionization and BondingkrisnuNo ratings yet
- 5070 w19 Ms 21Document10 pages5070 w19 Ms 21heerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Chemistry of Engineering MaterialsDocument36 pagesChapter 5 Chemistry of Engineering Materialsksm rachasNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Module 1Document38 pagesUnit 1 Module 1Pearl NecoleNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions D AN BLOCKDocument11 pagesMultiple Choice Questions D AN BLOCKMahrishiShukla100% (1)