Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is An IP Address
What Is An IP Address
Uploaded by
Princess Dahilig0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesAn IP address is a unique identifier used to identify devices on a network. It is composed of 32 binary digits grouped into four octets that can each range from 0 to 255. IP addresses allow devices to connect to each other to transfer files and emails. They are divided into classes and include network and host portions assigned by administrators. The Internet Protocol uses IP addresses to connect devices globally but addresses are running out, necessitating an upgrade to IPv6.
Original Description:
vces
Original Title
Ip Address
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn IP address is a unique identifier used to identify devices on a network. It is composed of 32 binary digits grouped into four octets that can each range from 0 to 255. IP addresses allow devices to connect to each other to transfer files and emails. They are divided into classes and include network and host portions assigned by administrators. The Internet Protocol uses IP addresses to connect devices globally but addresses are running out, necessitating an upgrade to IPv6.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesWhat Is An IP Address
What Is An IP Address
Uploaded by
Princess DahiligAn IP address is a unique identifier used to identify devices on a network. It is composed of 32 binary digits grouped into four octets that can each range from 0 to 255. IP addresses allow devices to connect to each other to transfer files and emails. They are divided into classes and include network and host portions assigned by administrators. The Internet Protocol uses IP addresses to connect devices globally but addresses are running out, necessitating an upgrade to IPv6.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
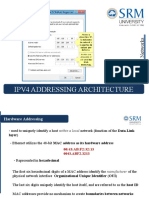
What is an IP address
A way to identify machines on a network
A unique identifier
32 bit binary
Four 8-bit / four octets
Ex: 11100011010100101001101110110001
11100011 - 01010010 - 10011101 - 10110001
E3 - 52 - 9D - B1
IP usage
Used to connect to another computer
Allows transfers of files and e-mail
IP structure
IP addresses consist of four sections
Each section is 8 bits long
Each section can range from 0 to 255
Written, for example, 128.35.0.72
These four sections represent the machine itself and the network it is on
The network portion is assigned.
The host section is determined by the network administrator
5 Classes of IP address A B C D and E
Class A reserved for governments
Class B reserved for medium companies
Class C reserved for small companies
Class D are reserved for multicasting
Class E are reserved for future use
Class A begins 1 to 126
Class B begins 128 to 191
Class C begins 192 to 223
Reserved addresses
Addresses beginning 127 are reserved for loopback and internal testing
xxx.0.0.0 reserved for network address
xxx.255.255.255 reserved for broadcast
IP Addresses
IP addresses are:
Unique
Global and Standardised
Essential
Subnetting - Why?
Division of local networks
Greater number of networks
Simplifies addressing
Subnetting - How
Bits borrowed from host field
Subnetting -Example
130.5.0.0 - Network address
130.5.2.144 - Host address
255.255.255.0 - Subnet Mask
130.5.2.0 - Subnet
The Internet Protocol
Running out!!
Upgraded to IPv6
You might also like
- CSS Ip AddressDocument16 pagesCSS Ip AddressOrlando FelixNo ratings yet
- The Internet Protocol: Eliot Grove Danny Friel Stuart AndersonDocument20 pagesThe Internet Protocol: Eliot Grove Danny Friel Stuart AndersonDlanor AvadecNo ratings yet
- Internet ProtocolDocument20 pagesInternet ProtocolBikila SeketaNo ratings yet
- DannyDocument20 pagesDannyvamc232855No ratings yet
- IPadressDocument20 pagesIPadressapi-3822363No ratings yet
- TCPIP OverviewDocument19 pagesTCPIP Overviewmushtaqnaik123No ratings yet
- The Internet Protocol: Eliot GroveDocument20 pagesThe Internet Protocol: Eliot Groveskill1977No ratings yet
- The Internet Protocol: Eliot GroveDocument20 pagesThe Internet Protocol: Eliot GroveMichael AsanteNo ratings yet
- IPAddressDocument33 pagesIPAddressBrij ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- IP Addressing SchemeDocument18 pagesIP Addressing SchemeRussell OgievaNo ratings yet
- IP Addressing and SubnettingDocument36 pagesIP Addressing and SubnettingRhy Obra100% (2)
- NetworkingDocument100 pagesNetworkingsangamNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Overview of IP Address and SubnettingDocument10 pagesChapter One Overview of IP Address and SubnettingAschalew Getnet MengistuNo ratings yet
- Digital Network - Lecturer2Document68 pagesDigital Network - Lecturer2Jumanne AllyNo ratings yet
- IP AddressingDocument6 pagesIP AddressingLawrence RolluquiNo ratings yet
- Sub NetsDocument60 pagesSub Netsjohn47No ratings yet
- Chn-Unit-5 MaterialDocument21 pagesChn-Unit-5 Materialharshini thagallamudiNo ratings yet
- Ip AddressingDocument16 pagesIp AddressingMay Thin KhineNo ratings yet
- Understanding The TCP/IP Internet LayerDocument31 pagesUnderstanding The TCP/IP Internet LayerQuang Huy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Ip AddressingDocument28 pagesIp AddressingMd AlauddinNo ratings yet
- CCNADocument275 pagesCCNAabhi SinghNo ratings yet
- IP Addressing: Format of An IP AddressDocument8 pagesIP Addressing: Format of An IP AddressLovemore ManyerukeNo ratings yet
- Lab 06Document14 pagesLab 06nomanbsitNo ratings yet
- Computer Network: Ip Addressing & SubnettingDocument28 pagesComputer Network: Ip Addressing & SubnettingM R F FasnaNo ratings yet
- 8 IpDocument94 pages8 IpSaras PantulwarNo ratings yet
- Ipv 4Document32 pagesIpv 4Sudhir Maherwal100% (2)
- Computer Networks - TCMH3722 L3Document66 pagesComputer Networks - TCMH3722 L3Indongo EliaserNo ratings yet
- Network Ip Addresses: Group Id - 11Document2 pagesNetwork Ip Addresses: Group Id - 11PranavSharmaNo ratings yet
- IP AddressDocument20 pagesIP AddressNayr ZdahbNo ratings yet
- AddressingDocument64 pagesAddressingmuhd munzirNo ratings yet
- IP AddressingDocument8 pagesIP AddressingPartha Sarathi NandiNo ratings yet
- Network TheoryDocument25 pagesNetwork TheorySaber ElkassasNo ratings yet
- Internet ProtocolDocument29 pagesInternet ProtocolJulie Ann Gonzales ChentesNo ratings yet
- CCNA Exam NotesDocument26 pagesCCNA Exam NotesDua ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Mcit - Ethio Joint Team Training MaterialDocument56 pagesMcit - Ethio Joint Team Training MaterialMuhammedYeshaw67% (3)
- Ip Addressing & Subnetting: Engr. Carlo Ferdinand C. Calma, CcnaDocument38 pagesIp Addressing & Subnetting: Engr. Carlo Ferdinand C. Calma, CcnaCarloNo ratings yet
- Internet ProtocolsDocument14 pagesInternet ProtocolsMARIO BUENAVENTENo ratings yet
- TCP - IP Internet LayerDocument32 pagesTCP - IP Internet LayerHùng Sinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- IP AddressesDocument14 pagesIP Addresseshadirehman488No ratings yet
- NDC Chapter 1Document10 pagesNDC Chapter 1Miraj SherifNo ratings yet
- Report-IP (原理 实验Document7 pagesReport-IP (原理 实验yāngNo ratings yet
- Lab2 IP Addressing and SubnettingDocument10 pagesLab2 IP Addressing and SubnettingGetachew ShambelNo ratings yet
- TCP IP FundamentalsDocument11 pagesTCP IP FundamentalsMadhav ReddyNo ratings yet
- IP Addressing Lecture AssignmentDocument8 pagesIP Addressing Lecture AssignmentPrinces VillalobosNo ratings yet
- CN Lab 3Document12 pagesCN Lab 3talha khalidNo ratings yet
- CN Unit 2Document49 pagesCN Unit 2Prakhar MishraNo ratings yet
- Internet Working Session IDocument82 pagesInternet Working Session IkevotooNo ratings yet
- TCP - IP Internet LayerDocument32 pagesTCP - IP Internet LayerDonovanNo ratings yet
- 4 Quarter Grade 9 TLE CSS (Computer System Servicing) Internet ProtocolsDocument8 pages4 Quarter Grade 9 TLE CSS (Computer System Servicing) Internet ProtocolsSERVEN GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Ccna 2 Module 4Document6 pagesCcna 2 Module 4shkarkoddl83% (6)
- TVL - CSS12 - Q2 - M4Document10 pagesTVL - CSS12 - Q2 - M4Nuval Jim PatrickNo ratings yet
- Networks Basics: Mentor - Sandeep Kumar by HackittechDocument20 pagesNetworks Basics: Mentor - Sandeep Kumar by HackittechHACKER HACKERNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ip AddressDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Ip AddressMetsi KinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Part 1Document25 pagesChapter 4 Part 1FantaNo ratings yet
- IP AddressingDocument12 pagesIP AddressingDiatomspinalcordNo ratings yet
- Bytes (32 Bits) - These Bytes Are Also Known As Octets.: Classes of IP Addresses, IP Broadcast and IP MulticastDocument10 pagesBytes (32 Bits) - These Bytes Are Also Known As Octets.: Classes of IP Addresses, IP Broadcast and IP MulticastrajNo ratings yet