Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fundamentals of Power Systems: P VI Cos
Fundamentals of Power Systems: P VI Cos
Uploaded by
ragupaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fundamentals of Power Systems: P VI Cos
Fundamentals of Power Systems: P VI Cos
Uploaded by
ragupaCopyright:
Available Formats
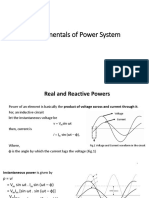
FUNDAMENTALS OF POWER SYSTEMS 3
The value of p is positive when both v and i are either positive or negative and represents
the rate at which the energy is being consumed by the load. In this case the current flows in
the direction of voltage drop. On the other hand power is negative when the current flows in
the direction of voltage rise which means that the energy is being transferred from the load
into the network to which it is connected. If the circuit is purely reactive the voltage and
current will be 90 out of phase and hence the power will have equal positive and negative half
cycles and the average value will be zero. From equation (1.2) the power pulsates around the
average power at double the supply frequency.
p
v
i
IVIIII cos f
Fig. 1.1 Voltage, current and power in single phase circuit.
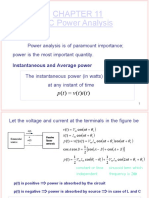
Equation (1.2) can be rewritten as
p = VI cos (1 cos 2t) VI sin sin 2t (1.3)
I II
We have decomposed the instantaneous power into two components (Fig. 1.2).
II
p = VI cos f
VI sin f
Fig. 1.2 Active, reactive and total power in a single phase circuit.
(i) The component P marked I pulsates around the same average power VI cos but
never goes negative as the factor (1 cos 2t) can at the most become zero but it will never go
negative. We define this average power as the real power P which physically means the useful
power being transmitted.
You might also like
- Voltage ControlDocument25 pagesVoltage Controlbenson215100% (2)
- Components of Electric Power SystemsDocument21 pagesComponents of Electric Power SystemskpchakralaNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Analysis - I Unit - 2: Power Factor & Its SignificanceDocument3 pagesElectric Circuit Analysis - I Unit - 2: Power Factor & Its Significancemeeravali_snNo ratings yet
- RK Kanodia NetworksDocument961 pagesRK Kanodia NetworksSahil SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Power Systems PDFDocument13 pagesFundamentals of Power Systems PDFSurender ReddyNo ratings yet
- Boylistad Power ACDocument37 pagesBoylistad Power ACAgung Al-JabbarNo ratings yet
- cCh11 - AC Power AnalysisDocument23 pagescCh11 - AC Power Analysis鄭又嘉No ratings yet
- Reactive Power1Document8 pagesReactive Power1Tulika BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- AC Power and The Power TriangleDocument7 pagesAC Power and The Power TriangleMohammed Shujath aliNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Utility Interactions and Harmonic Mitigation 2023Document18 pagesLec 2 Utility Interactions and Harmonic Mitigation 2023sachith wijesooriyaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Concepts and Network Simplification TechniquesDocument110 pagesCircuit Concepts and Network Simplification TechniquesJpricarioNo ratings yet
- 18EE32 - Mr. Nagaraj EEEDocument538 pages18EE32 - Mr. Nagaraj EEERosa ChambiNo ratings yet
- EE3726 - Chapter 11 - AC Power AnalysisDocument17 pagesEE3726 - Chapter 11 - AC Power AnalysisTrần Minh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - Unit-2Document142 pagesUnit-1 - Unit-2yvkrishnareddyNo ratings yet
- Circuit Concepts and Network Simplification Techniques 15EC34 PDFDocument535 pagesCircuit Concepts and Network Simplification Techniques 15EC34 PDFShreekar Halvi100% (2)
- Electrical Ciruit Analysis PDFDocument582 pagesElectrical Ciruit Analysis PDFMohammed SabeelNo ratings yet
- Module 1-Nas PDFDocument110 pagesModule 1-Nas PDFadilNo ratings yet
- Week 1 2Document37 pagesWeek 1 2basit qureshiNo ratings yet
- Topic Refresher:: The Power TriangleDocument1 pageTopic Refresher:: The Power Triangleradhikadikshit9No ratings yet
- Fundamentals PQ Per Unit 2022Document33 pagesFundamentals PQ Per Unit 2022Shahwar AliaNo ratings yet
- EEEB113 Circuit Analysis I: Basic ConceptsDocument41 pagesEEEB113 Circuit Analysis I: Basic ConceptsGabriel Carl AlpuertoNo ratings yet
- Teza Fizika II Vjeshte 2020Document1 pageTeza Fizika II Vjeshte 2020Mateo HysaNo ratings yet
- 17S2 EE3010 PPT Lecture6-ElectromagnetismDocument22 pages17S2 EE3010 PPT Lecture6-Electromagnetismming yangNo ratings yet
- Circuit Concepts and Network Simplification TechniquesDocument110 pagesCircuit Concepts and Network Simplification TechniquesshrishaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity: Q Δ t Δ Q Δ I Document34 pagesCurrent Electricity: Q Δ t Δ Q Δ I Nil KamalNo ratings yet
- Exp. 2 Transformer Load TestDocument4 pagesExp. 2 Transformer Load TestAbdelrahman MuadiNo ratings yet
- Fig 2.1 Three Leg Topology of Shunt Active Power FilterDocument19 pagesFig 2.1 Three Leg Topology of Shunt Active Power FiltersivaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 AC Power PDFDocument64 pagesChapter 3 AC Power PDFVievie Le BluewberrietrufflesNo ratings yet
- Phys 230 Winter 2010 - Chapter 23Document32 pagesPhys 230 Winter 2010 - Chapter 23almaty138gymNo ratings yet
- The Method of Detecting Asynchronous Power Swing Based On The Variation of Active PowerDocument6 pagesThe Method of Detecting Asynchronous Power Swing Based On The Variation of Active PowerFelix GamarraNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectificationDocument3 pagesHalf Wave RectificationMohammad alhaboob2030No ratings yet
- 2 B PV Cell 2Document12 pages2 B PV Cell 2Tahsin IbtidaNo ratings yet
- BEEE Unit 1 Part 2Document11 pagesBEEE Unit 1 Part 2balasubramanyam200517No ratings yet
- 1 Basic Principles: 1.1 Power in Single-Phase AC CircuitsDocument9 pages1 Basic Principles: 1.1 Power in Single-Phase AC CircuitsDharamNo ratings yet
- 0a - Reading Assignment 1Document3 pages0a - Reading Assignment 1Ebad SajjadNo ratings yet
- Osram Led Power Factor GuideDocument7 pagesOsram Led Power Factor GuidevfrwasteNo ratings yet
- AC Power AnalysisDocument62 pagesAC Power AnalysisKornkanok PMNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Force: F EubDocument18 pagesElectromagnetic Force: F Eubpoonam guptaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document6 pagesLab Report 1Shaheer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance PDFDocument20 pagesElectrostatic Potential and Capacitance PDFAman JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 6 EDocument33 pagesLecture - 6 ETung HoNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis 2 Laboratory Experiment 1: Power Factor CorrectionDocument13 pagesCircuit Analysis 2 Laboratory Experiment 1: Power Factor CorrectionZulqarnain KhanNo ratings yet
- ESS - Calculation For Capacitive Power Requirement For Achieving Targeted Power FactorDocument3 pagesESS - Calculation For Capacitive Power Requirement For Achieving Targeted Power FactorPrasad GoreNo ratings yet
- Ece 10Document32 pagesEce 10nachiketaanand20No ratings yet
- EE301 Lesson 25 AC Power and PWR TriangleDocument27 pagesEE301 Lesson 25 AC Power and PWR TriangleAli AkbarNo ratings yet
- Power Quality Measurement Under Non-Sinusoidal Condition: Magnago Fernando, Reineri Claudio and Lovera SantiagoDocument26 pagesPower Quality Measurement Under Non-Sinusoidal Condition: Magnago Fernando, Reineri Claudio and Lovera SantiagoAman MalikNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power RequirementDocument3 pagesReactive Power RequirementPrasad GoreNo ratings yet
- Chap 11 AC Power Analysis - Rev PDFDocument65 pagesChap 11 AC Power Analysis - Rev PDFkokoamikNo ratings yet
- Unit-II Ac Circuits.Document65 pagesUnit-II Ac Circuits.sarwath sultanaNo ratings yet
- EE301 Lecture Handout AcDocument6 pagesEE301 Lecture Handout Acuama87No ratings yet
- Topic 6. AC Circuit AnalysisDocument93 pagesTopic 6. AC Circuit Analysiskeinhuat79100% (1)
- Phasor Diagrams For Transformer On LoadDocument3 pagesPhasor Diagrams For Transformer On LoadAdnan KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Basics of Power System Part 1 42 PDFDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Basics of Power System Part 1 42 PDFshaik jaheerNo ratings yet
- Analytical GMD Calculation For Inductions of Rectangular Conductors - C. W. Su - 2016Document10 pagesAnalytical GMD Calculation For Inductions of Rectangular Conductors - C. W. Su - 2016Antoine JaroszNo ratings yet
- Full Paper Nashik ConferenceDocument5 pagesFull Paper Nashik ConferenceBhaumik BankerNo ratings yet
- The Way Electricity Flows Through A CircuitDocument4 pagesThe Way Electricity Flows Through A CircuitSouparna NathNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Ug Table 2017Document2 pagesUg Table 2017ragupaNo ratings yet
- Negative Sequence Transformation: W1 W2 W3 W4 W5 W6Document1 pageNegative Sequence Transformation: W1 W2 W3 W4 W5 W6ragupaNo ratings yet
- 14.12 Protection of Transformers: Protective RelaysDocument1 page14.12 Protection of Transformers: Protective RelaysragupaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 12Document1 pageElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 12ragupaNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From Electrical - UG Core Course SyllabiDocument1 pageExtracted Pages From Electrical - UG Core Course SyllabiragupaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Bathroom Light With Back-Up Lamp - Full Project AvailableDocument2 pagesAutomatic Bathroom Light With Back-Up Lamp - Full Project AvailableragupaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 3Document1 pageElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 3ragupaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 16Document1 pageElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 16ragupaNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2ragupaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 13Document1 pageElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 13ragupaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 6Document1 pageElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 6ragupaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 15Document1 pageElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 15ragupaNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2ragupaNo ratings yet
- F HG I KJ: Performance of LinesDocument1 pageF HG I KJ: Performance of LinesragupaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 9Document1 pageElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 9ragupaNo ratings yet
- Performance of Lines: Definition: by Performance of Lines Is Meant The Determination of Efficiency and Regulation ofDocument1 pagePerformance of Lines: Definition: by Performance of Lines Is Meant The Determination of Efficiency and Regulation ofragupaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 6Document1 pageElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 6ragupaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 8Document1 pageElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 8ragupaNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1ragupaNo ratings yet