Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsFault Tree Analysis
Fault Tree Analysis
Uploaded by
joyce ramirezFault Tree Analysis defined
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- ME 142L Gear Pump Test ExperimentmadeDocument8 pagesME 142L Gear Pump Test Experimentmadejoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Introduction CSPDocument7 pagesIntroduction CSPjoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- Ece132L - Instrumentation & Control Laboratory Laboratory Activity #1 DC AmmeterDocument4 pagesEce132L - Instrumentation & Control Laboratory Laboratory Activity #1 DC Ammeterjoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- EXP 1 DC AmmeterDocument4 pagesEXP 1 DC Ammeterjoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- Further Research CSPDocument2 pagesFurther Research CSPjoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- Activity #3Document5 pagesActivity #3joyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 Thyristor CircuitsDocument22 pagesExperiment 8 Thyristor Circuitsjoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- Activity #1Document7 pagesActivity #1joyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- Me 141l Experiment Pressure GagesmadeDocument5 pagesMe 141l Experiment Pressure Gagesmadejoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 - Diode Wave Shaping and Zener Diode Voltage RegulationDocument38 pagesExperiment 4 - Diode Wave Shaping and Zener Diode Voltage Regulationjoyce ramirez100% (1)
- Experiment 2 - Diode Test and FamiliarizationDocument15 pagesExperiment 2 - Diode Test and Familiarizationjoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Component and Equipment FamiliarizationDocument18 pagesExperiment 1 - Component and Equipment Familiarizationjoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- ECE104L 9thEXPDocument7 pagesECE104L 9thEXPjoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
Fault Tree Analysis
Fault Tree Analysis
Uploaded by
joyce ramirez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageFault Tree Analysis defined
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFault Tree Analysis defined
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageFault Tree Analysis
Fault Tree Analysis
Uploaded by
joyce ramirezFault Tree Analysis defined
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
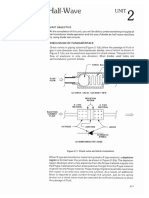
FAULT TREE ANALYSIS
Fault tree analysis (FTA) is a top-down, deductive
analytical method. In FTA,
initiating primary events such as component failures,
human errors, and external
events are traced through Boolean logic gates to an
undesired top event such as
boiler explosion or tower crane collapse. The intent is to
identify ways to make top
events less probable, and verify that safety goals have
been achieved.
FTA may be qualitative or quantitative. When failure and
event probabilities are
unknown, qualitative fault trees may be analyzed for
minimal cut sets. For
example, if any minimal cut set contains a single base
event, then the top event
may be caused by a single failure.
Some use both fault trees and event trees. An event tree
starts from an undesired
initiator (loss of critical supply, component failure etc.) and
follows possible further
system events through to a series of final consequences.
As each new event is
considered, a new node on the tree is added with a split of
probabilities of taking
either branch. The probabilities of a range of "top events"
arising from the initial
event can then be seen.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- ME 142L Gear Pump Test ExperimentmadeDocument8 pagesME 142L Gear Pump Test Experimentmadejoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Introduction CSPDocument7 pagesIntroduction CSPjoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- Ece132L - Instrumentation & Control Laboratory Laboratory Activity #1 DC AmmeterDocument4 pagesEce132L - Instrumentation & Control Laboratory Laboratory Activity #1 DC Ammeterjoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- EXP 1 DC AmmeterDocument4 pagesEXP 1 DC Ammeterjoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- Further Research CSPDocument2 pagesFurther Research CSPjoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- Activity #3Document5 pagesActivity #3joyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 Thyristor CircuitsDocument22 pagesExperiment 8 Thyristor Circuitsjoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- Activity #1Document7 pagesActivity #1joyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- Me 141l Experiment Pressure GagesmadeDocument5 pagesMe 141l Experiment Pressure Gagesmadejoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 - Diode Wave Shaping and Zener Diode Voltage RegulationDocument38 pagesExperiment 4 - Diode Wave Shaping and Zener Diode Voltage Regulationjoyce ramirez100% (1)
- Experiment 2 - Diode Test and FamiliarizationDocument15 pagesExperiment 2 - Diode Test and Familiarizationjoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Component and Equipment FamiliarizationDocument18 pagesExperiment 1 - Component and Equipment Familiarizationjoyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- ECE104L 9thEXPDocument7 pagesECE104L 9thEXPjoyce ramirezNo ratings yet