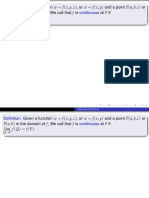
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Homework3 PDF
Homework3 PDF
Uploaded by
eouahiauCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A-Math - Sec 4 - Prelims Exam Paper - 2023 - Ngee Ann SecDocument94 pagesA-Math - Sec 4 - Prelims Exam Paper - 2023 - Ngee Ann SecAnh Thi PhanNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Complete Algebra Calculus Laplace Cheat SheetDocument14 pagesComplete Algebra Calculus Laplace Cheat SheetJeremy100% (3)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 2014 Homework 001 PDFDocument1 page2014 Homework 001 PDFeouahiauNo ratings yet
- Vector Fields Line Integrals Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path Conservative Fields and Potential Functions Green's TheoremDocument40 pagesVector Fields Line Integrals Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path Conservative Fields and Potential Functions Green's TheoremeouahiauNo ratings yet
- Line Integrals Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path Conservative Fields and Potential FunctionsDocument19 pagesLine Integrals Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path Conservative Fields and Potential FunctionseouahiauNo ratings yet
- 2014 Lecture 006Document32 pages2014 Lecture 006eouahiauNo ratings yet
- 2014 Lecture 005 PDFDocument48 pages2014 Lecture 005 PDFeouahiauNo ratings yet
- R Be Any Region On The Xy-Plane, A Function F X, Y Monratthepoint A, B Rif F X, Y M For All Points X, Y R, and M F A, BDocument25 pagesR Be Any Region On The Xy-Plane, A Function F X, Y Monratthepoint A, B Rif F X, Y M For All Points X, Y R, and M F A, BeouahiauNo ratings yet
- Matb 210/math200 in 2014-2015Document21 pagesMatb 210/math200 in 2014-2015eouahiauNo ratings yet
- Matb 200 in 2013-2014Document85 pagesMatb 200 in 2013-2014eouahiauNo ratings yet
- 2013 Lecture 002Document34 pages2013 Lecture 002eouahiauNo ratings yet
- PS L6 T8 Area - CircumferenceofCirclesDocument19 pagesPS L6 T8 Area - CircumferenceofCirclesChi Wei TanNo ratings yet
- Maths Diwali AssignmentDocument9 pagesMaths Diwali AssignmentdivyanshuvarmaNo ratings yet
- Y10 U2 Summative 2022 - ADVANCED PaperDocument8 pagesY10 U2 Summative 2022 - ADVANCED PaperMannat KHICHA [07R17M]No ratings yet
- LLL WikipediaDocument7 pagesLLL Wikipedia00carambolaNo ratings yet
- 1994 UsamoDocument2 pages1994 Usamoadeogun kehindeNo ratings yet
- Partial Differentiation of Z F (X, Y), U F (X, Y, Z) : DX Dy DyDocument12 pagesPartial Differentiation of Z F (X, Y), U F (X, Y, Z) : DX Dy DyWasik BillahNo ratings yet
- 30-C-2 - Maths (Standard)Document23 pages30-C-2 - Maths (Standard)Sagar TiwariNo ratings yet
- Mathematical ModellingDocument12 pagesMathematical ModellingAnirvan ShuklaNo ratings yet
- SRDP Am Ma Formelsammlung ENDocument24 pagesSRDP Am Ma Formelsammlung ENOmar AliNo ratings yet
- Similarity TestDocument7 pagesSimilarity TestMelchor BalolongNo ratings yet
- CurlDocument3 pagesCurlSubhasish ShitNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.2: Dihedral Groups: Matthew MacauleyDocument7 pagesLecture 2.2: Dihedral Groups: Matthew MacauleyjskaneiNo ratings yet
- Math Unit 9 Q&ADocument22 pagesMath Unit 9 Q&AmNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Symmetric LoadsDocument13 pagesAircraft Symmetric LoadsNavish KotwalNo ratings yet
- Matrix Multiplication: Simplify. Write "Undefined" For Expressions That Are UndefinedDocument4 pagesMatrix Multiplication: Simplify. Write "Undefined" For Expressions That Are UndefinedKuber PadiaNo ratings yet
- LAB 11: Implementation of Forward & Inverse Kinematics On 3 DOF Manipulator in MATLABDocument12 pagesLAB 11: Implementation of Forward & Inverse Kinematics On 3 DOF Manipulator in MATLABGHULAM ESSANo ratings yet
- Fabric GeometryDocument21 pagesFabric GeometryAnonymous Pt7NHkat9No ratings yet
- Basic Mathematical Tools For Imaging and Visualization: Dr. Tobias LasserDocument15 pagesBasic Mathematical Tools For Imaging and Visualization: Dr. Tobias LasserhisuinNo ratings yet
- 5 Harmonic ConjugatesDocument6 pages5 Harmonic ConjugatesUniverse gamerNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Level - 1 (Problems Based On Fundamentals)Document37 pagesExercises: Level - 1 (Problems Based On Fundamentals)QSQFNo ratings yet
- MATH (Reviewer) Midterm CalculusDocument1 pageMATH (Reviewer) Midterm CalculusAngge SarcenoNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Historic StructuresDocument3 pagesModelling of Historic Structureslcruz117No ratings yet
- Vidymandir TestDocument16 pagesVidymandir TestArshil Khan100% (1)
- Iit Jam 2018 QuestionDocument16 pagesIit Jam 2018 Questiondinesh rajputNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: 2 QUARTER Summative Test Grade 8 Carpentry Multiple Choice: Directions: Select The BestDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: 2 QUARTER Summative Test Grade 8 Carpentry Multiple Choice: Directions: Select The Bestlouie vertudazoNo ratings yet
- Standard Sample Paper XyzDocument7 pagesStandard Sample Paper XyzMaurya SachinNo ratings yet
- Perimeter of A Semicircle and Quarter CircleDocument18 pagesPerimeter of A Semicircle and Quarter Circlepurple crocNo ratings yet
- Quadric Surfaces - Reduction To Canonical Standard FormDocument43 pagesQuadric Surfaces - Reduction To Canonical Standard Formdbowden333No ratings yet
Homework3 PDF
Homework3 PDF
Uploaded by
eouahiauOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Homework3 PDF
Homework3 PDF
Uploaded by
eouahiauCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Student ID: Major: 28. (, ) = 2 ; is the circular disk 2 + 2 3.
Write your answer on extra sheet of paper, if necessary Remark.
One can parametrize the boundary the disk by using = 3 cos and
Homework 3 of Math 200 Mathematical Analysis III in 2009 Due Monday through = 3 sin , (0 2).
Thursday, 26th-29th September. Hand to the TA room on G/F of Block 1, if your
tutorial class is on holiday.
13.5 (Read example 6 on p.873 and example 3 on p. 881) Find all the points (, ) on
the given surface = (, ) at which the tangent plane is horizontal.
Remark. A normal vector n to the tangent plane of the graph of = (, )
is given by n = ( , , 1) = (, )i + (, )j k, so the tangent plane is
horizontal at the point (, , (, )) of if and only if the point (, ) satises the 13.6 Find the dierential of the following functions:
equations (, ) = (, ) = 0.
1. (, ) = 32 + 4 2 2 :
5. = 2 + 2 6 + 2 + 5
dierential = + = (6 + 4) + (4 4).
Remarks. (i) If = (, , ) is a function of 3 variables, then ( or if one
just want to indicate the function rather the dependent variable ), then
6. = 10 + 8 6 2 2
= + + .
(ii) one should think of the (component) dierentials , , is another symbol
the canonical basis vectors i, j and k.
13.5 (Read example 6 on p883) Find the highest and lowest points (if they exist) on 7. (, , ) = log(2 + 2 + 2 ), then by chain rule of one variable, one has
the graph = (, ) : 1 2 2
= 2 ( + 2 + 2 ) = 2 . So the dierential
+ 2 + 2 + 2 + 2
18. = 34 + 43 + 6 4 16 3 + 12 2 = 122 ( ), = 24( ). 2
Then ( , ) = (0, 0) if and only if (, ) = ( , ), or ( , ) or = + + = 2 + + .
+ 2 + 2
There is only the lowest point on the graph, because (, 0) = 34 + 43 =
32 2 + 43 32 when 1, and then (, 0) is not bounded from above, so 8. (, , ) = sin(), = + + .
there is not any highest point on the graph.
+ ( )( ) ( + )( )
14. (, ) = , = = ,
( )2 ( )2
( )( ) ( + )( )
= =
( )2
21. = exp(2 4 2 2 ). In fact, it follow that exp is an increasing function,
= 2
+ 2
= 2
.
so it suces to determine the highest and lowest points of the function (, ) = ( ) ( ) ( )
2 4 2 2 .
16. (, , ) = exp(2 2 2 ),
= exp(2 2 2 )( + + ).
13.7 Use the exact value ( ) and the dierential to approximate the value ().
13.5 (Read example 6 on p883) Find the maximum and minimum values attained by
the given function (, ) on the given region in -plane. 17. (, ) = 2 + 2 ; (3, 4), and (2.97, 4.04)
(, ) =
i + j = (
22 2 , 22 2 ), and ( ) = (3, 4) = ( 35 , 45 ).
2 + 2 +
25. (, ) = 2 + 2 2; is the triangular region with vertices at (0, 0), (2, 0),
() = (3 0.03, 4 + 0.04), (where h is a vector = (0.03, 0.04) )
and (0, 2).
= ( + h) = ( ) + ( ) h + higher order terms in h
( ) + ( ) h
= (3, 4) + (3, 4) (0.03, 0.04) = 5 + ( 35 , 45 ) (0.03, 0.04) = 5 + 0.07
5 .
18. (, ) = 2 2 ; (13, 5), and (13.2, 4.9) 8. = + + ; = 2 2 , = 2 + 2 , = 2 2
1
19. (, ) = 1++ ; (3, 6), and (3.02, 6.05)
13.7 Find , , :
10. = 2 2 2 , = + , = + , = +
13.6 Use dierentials to approximate the indicated number:
26. ( 26)( 3 28)( 4 17)
11. = sin(/), = 2 3 , = + 2 + 3
27. 0.4 = exp(1.12 0.92 )
13.7 Find and as functions of , and , assuming = (, ) satises the given
equation:
13.7 (Read theorem 1, examples 1 and 3 in 13.7) Find both by using the chain 19. 2/3 + 2/3 + 2/3 = 1
rule, and by expressing explicitly as a function of before dierentiating:
Plugging = (, ) into the equation, we have 2/3 + 2/3 + ((, ))2/3 = 1,
3. = sin(); = , = 2 , = 3 and dierentiate this identity with respect to and respectively, we have
1 ( 2/3 ) 2 2
0= = + 2/3 + ((, ))2/3 = 1/3 + ((, ))1/3 , so
3 3
2
= .
4. = log( + + ); 2
= cos , = sin , = 2
20. 3 + 3 + 3 =
13.7 (Read theorem 2, example 4 in 13.7) Find and :
6. = sin ; = 2 + , = , =
2 2 2
23. + + =1
2 2 2
7. = 2 + 2 + 2 ; = 3 sin , = 3 cos , = 4
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A-Math - Sec 4 - Prelims Exam Paper - 2023 - Ngee Ann SecDocument94 pagesA-Math - Sec 4 - Prelims Exam Paper - 2023 - Ngee Ann SecAnh Thi PhanNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Complete Algebra Calculus Laplace Cheat SheetDocument14 pagesComplete Algebra Calculus Laplace Cheat SheetJeremy100% (3)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 2014 Homework 001 PDFDocument1 page2014 Homework 001 PDFeouahiauNo ratings yet
- Vector Fields Line Integrals Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path Conservative Fields and Potential Functions Green's TheoremDocument40 pagesVector Fields Line Integrals Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path Conservative Fields and Potential Functions Green's TheoremeouahiauNo ratings yet
- Line Integrals Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path Conservative Fields and Potential FunctionsDocument19 pagesLine Integrals Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path Conservative Fields and Potential FunctionseouahiauNo ratings yet
- 2014 Lecture 006Document32 pages2014 Lecture 006eouahiauNo ratings yet
- 2014 Lecture 005 PDFDocument48 pages2014 Lecture 005 PDFeouahiauNo ratings yet
- R Be Any Region On The Xy-Plane, A Function F X, Y Monratthepoint A, B Rif F X, Y M For All Points X, Y R, and M F A, BDocument25 pagesR Be Any Region On The Xy-Plane, A Function F X, Y Monratthepoint A, B Rif F X, Y M For All Points X, Y R, and M F A, BeouahiauNo ratings yet
- Matb 210/math200 in 2014-2015Document21 pagesMatb 210/math200 in 2014-2015eouahiauNo ratings yet
- Matb 200 in 2013-2014Document85 pagesMatb 200 in 2013-2014eouahiauNo ratings yet
- 2013 Lecture 002Document34 pages2013 Lecture 002eouahiauNo ratings yet
- PS L6 T8 Area - CircumferenceofCirclesDocument19 pagesPS L6 T8 Area - CircumferenceofCirclesChi Wei TanNo ratings yet
- Maths Diwali AssignmentDocument9 pagesMaths Diwali AssignmentdivyanshuvarmaNo ratings yet
- Y10 U2 Summative 2022 - ADVANCED PaperDocument8 pagesY10 U2 Summative 2022 - ADVANCED PaperMannat KHICHA [07R17M]No ratings yet
- LLL WikipediaDocument7 pagesLLL Wikipedia00carambolaNo ratings yet
- 1994 UsamoDocument2 pages1994 Usamoadeogun kehindeNo ratings yet
- Partial Differentiation of Z F (X, Y), U F (X, Y, Z) : DX Dy DyDocument12 pagesPartial Differentiation of Z F (X, Y), U F (X, Y, Z) : DX Dy DyWasik BillahNo ratings yet
- 30-C-2 - Maths (Standard)Document23 pages30-C-2 - Maths (Standard)Sagar TiwariNo ratings yet
- Mathematical ModellingDocument12 pagesMathematical ModellingAnirvan ShuklaNo ratings yet
- SRDP Am Ma Formelsammlung ENDocument24 pagesSRDP Am Ma Formelsammlung ENOmar AliNo ratings yet
- Similarity TestDocument7 pagesSimilarity TestMelchor BalolongNo ratings yet
- CurlDocument3 pagesCurlSubhasish ShitNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.2: Dihedral Groups: Matthew MacauleyDocument7 pagesLecture 2.2: Dihedral Groups: Matthew MacauleyjskaneiNo ratings yet
- Math Unit 9 Q&ADocument22 pagesMath Unit 9 Q&AmNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Symmetric LoadsDocument13 pagesAircraft Symmetric LoadsNavish KotwalNo ratings yet
- Matrix Multiplication: Simplify. Write "Undefined" For Expressions That Are UndefinedDocument4 pagesMatrix Multiplication: Simplify. Write "Undefined" For Expressions That Are UndefinedKuber PadiaNo ratings yet
- LAB 11: Implementation of Forward & Inverse Kinematics On 3 DOF Manipulator in MATLABDocument12 pagesLAB 11: Implementation of Forward & Inverse Kinematics On 3 DOF Manipulator in MATLABGHULAM ESSANo ratings yet
- Fabric GeometryDocument21 pagesFabric GeometryAnonymous Pt7NHkat9No ratings yet
- Basic Mathematical Tools For Imaging and Visualization: Dr. Tobias LasserDocument15 pagesBasic Mathematical Tools For Imaging and Visualization: Dr. Tobias LasserhisuinNo ratings yet
- 5 Harmonic ConjugatesDocument6 pages5 Harmonic ConjugatesUniverse gamerNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Level - 1 (Problems Based On Fundamentals)Document37 pagesExercises: Level - 1 (Problems Based On Fundamentals)QSQFNo ratings yet
- MATH (Reviewer) Midterm CalculusDocument1 pageMATH (Reviewer) Midterm CalculusAngge SarcenoNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Historic StructuresDocument3 pagesModelling of Historic Structureslcruz117No ratings yet
- Vidymandir TestDocument16 pagesVidymandir TestArshil Khan100% (1)
- Iit Jam 2018 QuestionDocument16 pagesIit Jam 2018 Questiondinesh rajputNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: 2 QUARTER Summative Test Grade 8 Carpentry Multiple Choice: Directions: Select The BestDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: 2 QUARTER Summative Test Grade 8 Carpentry Multiple Choice: Directions: Select The Bestlouie vertudazoNo ratings yet
- Standard Sample Paper XyzDocument7 pagesStandard Sample Paper XyzMaurya SachinNo ratings yet
- Perimeter of A Semicircle and Quarter CircleDocument18 pagesPerimeter of A Semicircle and Quarter Circlepurple crocNo ratings yet
- Quadric Surfaces - Reduction To Canonical Standard FormDocument43 pagesQuadric Surfaces - Reduction To Canonical Standard Formdbowden333No ratings yet