Professional Documents
Culture Documents
322 Catalepsia
322 Catalepsia
Uploaded by
Rommel Barbosa MonteiroCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 23 - Conditions Occurring After DeliveryDocument6 pagesChapter 23 - Conditions Occurring After DeliveryEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- 3 - 4 Surgical Treatment of Cherry EyeDocument7 pages3 - 4 Surgical Treatment of Cherry EyeAman RustagiNo ratings yet
- Department of Genetics: Covid-19 RT PCRDocument1 pageDepartment of Genetics: Covid-19 RT PCRAjo Jose100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Traumatic Brain Injury: Melissa J. Mcginn,, John T. PovlishockDocument11 pagesPathophysiology of Traumatic Brain Injury: Melissa J. Mcginn,, John T. Povlishocksiska misaliNo ratings yet
- Wagner2007 Ocular Pathology Rabbit EyeDocument10 pagesWagner2007 Ocular Pathology Rabbit EyeHugo OrtegaNo ratings yet
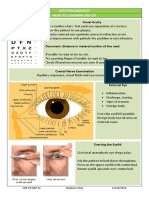
- Current Examination Methods of The Canine Eye: J. Beránek, P.J. VítDocument6 pagesCurrent Examination Methods of The Canine Eye: J. Beránek, P.J. VítOktavia firnandaNo ratings yet
- Examination of AnimalDocument5 pagesExamination of Animaldharmachakra ComNo ratings yet
- Surgery B PracticalDocument12 pagesSurgery B PracticalMohamed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Visual and Auditory DisturbancesDocument53 pagesVisual and Auditory DisturbancesJASTINE JOY PEREZNo ratings yet
- ProP Ophthalmic Examination Made EasyDocument5 pagesProP Ophthalmic Examination Made EasyRosario AyalaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination EyeDocument2 pagesClinical Examination EyeKirti JamwalNo ratings yet
- Eyelid DisordersDocument6 pagesEyelid DisordersCamilo PerezNo ratings yet
- Giansanti Rabbit and Cell Culture 2010Document8 pagesGiansanti Rabbit and Cell Culture 2010Igor VainerNo ratings yet
- Oftalmologia Del ConejoDocument4 pagesOftalmologia Del ConejoRueca HelenciyaNo ratings yet
- DR Bert Et Al Replies.j.acra.2006.10.021Document2 pagesDR Bert Et Al Replies.j.acra.2006.10.021NukuBtayaNo ratings yet
- PractNeurol 2011 Ahmad 332 40Document10 pagesPractNeurol 2011 Ahmad 332 40Yulyani PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Eyes Diseases RabbitDocument12 pagesEyes Diseases RabbitcarlesNo ratings yet
- Practicum of Autonomic Drugs2Document10 pagesPracticum of Autonomic Drugs2Andre PrawiradinataNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmic Emergency Tips/GuidelinesDocument23 pagesOphthalmic Emergency Tips/GuidelinesSibhi ThranNo ratings yet
- From The Laboratory of Pharmacology of The University of TorontoDocument3 pagesFrom The Laboratory of Pharmacology of The University of TorontoAlexNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Hvpotonic and Isotonic Solutions Containing Sodium Hvaluronate On The Svmptomatic Treatment of DRV Eve PatientsDocument5 pagesComparison of Hvpotonic and Isotonic Solutions Containing Sodium Hvaluronate On The Svmptomatic Treatment of DRV Eve PatientsGraciela CarlosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Disorders of The Eye and Vision - 2018 - Equine Internal MedicineDocument20 pagesChapter 17 - Disorders of The Eye and Vision - 2018 - Equine Internal Medicinemontselee99No ratings yet
- MC Day 2Document12 pagesMC Day 2vfomicevs59No ratings yet
- Berger 1986Document3 pagesBerger 1986kameliasitorusNo ratings yet
- Transpalbebral Exenteration in CattleDocument4 pagesTranspalbebral Exenteration in Cattleಮನೋಜ್ ಭಾರದ್ವಾಜ್No ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4 Effect of Mydriatic Drug On Rabbits EyeDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 4 Effect of Mydriatic Drug On Rabbits EyeShafakat100% (1)
- Vop 12566Document11 pagesVop 12566Blanca A SerranoNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis ReferatDocument26 pagesMyasthenia Gravis ReferatUlfa TitiswariNo ratings yet
- Entropion Correction in Dogs and Cats Using A Combination Hotz-Celsus and Lateral Eyelid Wedge Resection: Results in 311 EyesDocument6 pagesEntropion Correction in Dogs and Cats Using A Combination Hotz-Celsus and Lateral Eyelid Wedge Resection: Results in 311 EyesAndres Luna MendezNo ratings yet
- Como Realizar Una Biopsia en Penfigoide OcularDocument5 pagesComo Realizar Una Biopsia en Penfigoide OcularMiguel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Scedosporium Apiospermum Keratomycosis in A DogDocument4 pagesScedosporium Apiospermum Keratomycosis in A DogDavid Argüelles AndradeNo ratings yet
- Ophthal One LinersDocument6 pagesOphthal One LinersRv DeanNo ratings yet
- Edelhauser 1979Document11 pagesEdelhauser 1979KreAch3RNo ratings yet
- 263 FullDocument7 pages263 FullPrisky DianNo ratings yet
- TMP 195 DDocument4 pagesTMP 195 DFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Effect of Hinge Location On Corneal Sensation And.29Document7 pagesEffect of Hinge Location On Corneal Sensation And.29leoNo ratings yet
- Surgical Treatment of Parasitic Cysts Authorȍocument2 pagesSurgical Treatment of Parasitic Cysts Author Анагаахын ОрчуулгаNo ratings yet
- Standing EnukleasiiDocument3 pagesStanding Enukleasiig_meilisaNo ratings yet
- Giansanti IOVS 2008Document6 pagesGiansanti IOVS 2008Igor VainerNo ratings yet
- Rabbit Eye Expt.Document3 pagesRabbit Eye Expt.Padmanabha Gowda100% (1)
- Snakebite Management Guide For Healthcare Providers in Malaysia 2011Document8 pagesSnakebite Management Guide For Healthcare Providers in Malaysia 2011fifa_0304535100% (1)
- Cherry Eye: Prolapse of Third Eyelid Gland in Dog-A Case ReportDocument4 pagesCherry Eye: Prolapse of Third Eyelid Gland in Dog-A Case ReportRocioNo ratings yet
- AMMVEPEColirioenPerrosVe164 03oDocument6 pagesAMMVEPEColirioenPerrosVe164 03oNicolas Arias CardonaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Blepharoplastic Repair of Conformational Eyelid DefectsDocument11 pagesDiagnosis and Blepharoplastic Repair of Conformational Eyelid Defectstaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Strabismus, Amblyopia & LeukocoriaDocument14 pagesStrabismus, Amblyopia & LeukocoriaMuhammad Naufal WidyatmakaNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of EyeDocument74 pagesAbnormalities of EyeHikmat UllahNo ratings yet
- Study of Jones Procedure For Senile Entropion: Medical ScienceDocument3 pagesStudy of Jones Procedure For Senile Entropion: Medical SciencedhitadwynNo ratings yet
- Corneal Laceration Caused by River Crab: Clinical Ophthalmology DoveDocument4 pagesCorneal Laceration Caused by River Crab: Clinical Ophthalmology Dovesiti rumaisaNo ratings yet
- Lip-To-Lid Transposition and Husbandry Management For Severe Bilateral Eyelid Coloboma in Three Snow Leopards (Panthera Uncia)Document9 pagesLip-To-Lid Transposition and Husbandry Management For Severe Bilateral Eyelid Coloboma in Three Snow Leopards (Panthera Uncia)kradoNo ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument9 pagesGlaucomaREGINE YEO ZHI SHUENNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology How To Examine An Eye: Visual AcuityDocument2 pagesOphthalmology How To Examine An Eye: Visual AcuityOlalekan OgundareNo ratings yet
- Nerve Growth Factor-Induced Ocular Dominance Plasticity in Adult CatvisualcortexDocument5 pagesNerve Growth Factor-Induced Ocular Dominance Plasticity in Adult Catvisualcortextonylee24No ratings yet
- Javma-Javma 20 12 0706Document11 pagesJavma-Javma 20 12 0706Bright DerlacuzENo ratings yet
- December 2017 Ophthalmic PearlsDocument2 pagesDecember 2017 Ophthalmic PearlsMEDIWAY CLINICNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma TextDocument6 pagesGlaucoma TextZorka SzélesNo ratings yet
- Corneal Sensitivity and Ocular Surface Changes Following Preserved Amniotic Membrane Transplantation For Nonhealing Corneal UlcersDocument10 pagesCorneal Sensitivity and Ocular Surface Changes Following Preserved Amniotic Membrane Transplantation For Nonhealing Corneal UlcersDitha FadhilaNo ratings yet
- Role of Fasciotomy in Snake BiteDocument20 pagesRole of Fasciotomy in Snake BiteAmeliaCinantyaNo ratings yet
- Exame Do OlhoDocument11 pagesExame Do OlhoMirella Lopes da RochaNo ratings yet
- W2 - MEDSURG Guidelines For Nursing Interventions On Coma PatientsDocument6 pagesW2 - MEDSURG Guidelines For Nursing Interventions On Coma PatientsKyla L. Madjad100% (1)
- Effects of Genipin Corneal Crosslinking in Rabbit CorneasDocument5 pagesEffects of Genipin Corneal Crosslinking in Rabbit CorneasMauricio NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Male With Involutional Entropion of Inferior Eyelid: Laporan KasusDocument5 pagesMale With Involutional Entropion of Inferior Eyelid: Laporan KasusdhitadwynNo ratings yet
- Effects of A Topically Applied 2 - Delta-9 - Tetrahydrocannabinol Ophthalmic Solution On Intraocular Pressure and Aqueous Humor Flow Rate in Clinically Normal Dogs 2Document6 pagesEffects of A Topically Applied 2 - Delta-9 - Tetrahydrocannabinol Ophthalmic Solution On Intraocular Pressure and Aqueous Humor Flow Rate in Clinically Normal Dogs 2Róbson BatistaNo ratings yet
- OCULOPATHY - Disproves the orthodox and theoretical bases upon which glasses are so freely prescribed, and puts forward natural remedial methods of treatment for what are sometimes termed incurable visual defectsFrom EverandOCULOPATHY - Disproves the orthodox and theoretical bases upon which glasses are so freely prescribed, and puts forward natural remedial methods of treatment for what are sometimes termed incurable visual defectsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plans: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationRheeanne Mae Amilasan100% (1)
- Congenital Hip DysplasiaDocument5 pagesCongenital Hip DysplasiaMay Ann BoongalingNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube (NGT)Document31 pagesNasogastric Tube (NGT)annyeong_123No ratings yet
- Postmenopausal OsteoporosisDocument13 pagesPostmenopausal OsteoporosisAhmad YassirNo ratings yet
- Transcripts of Dr. William Barnhart Van Valin II (MJ DR.) Katherine Jackson V AEG Live September 6th 2013Document57 pagesTranscripts of Dr. William Barnhart Van Valin II (MJ DR.) Katherine Jackson V AEG Live September 6th 2013TeamMichaelNo ratings yet
- ES V 0281 001 FinalSPCDocument4 pagesES V 0281 001 FinalSPCPankaj BeniwalNo ratings yet
- 2019 ALS 1 Manual V4 FinalDocument53 pages2019 ALS 1 Manual V4 FinalyusupNo ratings yet
- FTPDocument13 pagesFTPbenitiyaNo ratings yet
- Grading of Hydronephrosis: An Ongoing Challenge: Abdurrahman OnenDocument13 pagesGrading of Hydronephrosis: An Ongoing Challenge: Abdurrahman OnensavitageraNo ratings yet
- Aar Insurance Kenya Aar Individual and Family Medical Plan Final 5 7 22Document12 pagesAar Insurance Kenya Aar Individual and Family Medical Plan Final 5 7 22tichips mobileNo ratings yet
- Case Report NystagmusDocument6 pagesCase Report Nystagmusghitza80No ratings yet
- Acog Practice Bulletin PDFDocument12 pagesAcog Practice Bulletin PDFVìctorQuesquen100% (1)
- Elevate Pitch Deck - Version 5 PDFDocument28 pagesElevate Pitch Deck - Version 5 PDFAnabiya AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Best Practices in Alternative Assessment of PerformanceDocument51 pagesBest Practices in Alternative Assessment of PerformanceRafat ElshemiNo ratings yet
- Essay 3 Charity - ST Jude Research Childrens HospitalDocument4 pagesEssay 3 Charity - ST Jude Research Childrens Hospitalapi-312759042No ratings yet
- Right Sided Heart FailureDocument18 pagesRight Sided Heart FailureShaf AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Heart Rate TrainingDocument3 pagesHeart Rate TrainingNetravathi EllurNo ratings yet
- Patient Information Guide: AH-QF-FO-07Document35 pagesPatient Information Guide: AH-QF-FO-07jose rajanNo ratings yet
- Iv Administration of Cancer Chemotherapy/Cytotoxic Drugs Via Intermittent Piggyback Infusion in A Peripheral Vein MaterialsDocument3 pagesIv Administration of Cancer Chemotherapy/Cytotoxic Drugs Via Intermittent Piggyback Infusion in A Peripheral Vein MaterialsJhe VictorianoNo ratings yet
- Cushing's DiseaseDocument1 pageCushing's DiseaseRiza Angela BarazanNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Date of CompletionDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Date of CompletionNicole AngelNo ratings yet
- Final Online Exam Guideline CBTDocument105 pagesFinal Online Exam Guideline CBTfaisalaminwani121No ratings yet
- Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission Required For ReproductionDocument33 pagesCopyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission Required For ReproductionKvaleramNo ratings yet
- How To Talk About Illness and Medicine in EnglishDocument5 pagesHow To Talk About Illness and Medicine in EnglishIsmaNo ratings yet
- 11-The PharynxDocument73 pages11-The PharynxM.IBRAHIM ALHAMECHNo ratings yet
- Definition and Description of Schizprenia in The DSM-5Document8 pagesDefinition and Description of Schizprenia in The DSM-5Danekka TanNo ratings yet
- THR-morbid ObesityDocument5 pagesTHR-morbid ObesityMohan DesaiNo ratings yet
322 Catalepsia
322 Catalepsia
Uploaded by
Rommel Barbosa MonteiroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
322 Catalepsia
322 Catalepsia
Uploaded by
Rommel Barbosa MonteiroCopyright:
Available Formats
Applanation tonometry and ophthalmoscopy of
the vervet monkey (Cercopithecus ethiops)
in phencyclidine catalepsia
Ernst Bdrdny
Phencyclidine, 1 to 1.2 mg. per kilogram body weight, is recommended for examination of
the eyes in untamed monkeys. Applanation tonometry with the Mackay-Marg machine was
performed in 109 vervets (Cercopithecus ethiops), mainly old males, contributing a total of
208 eyes without signs of present or past inflammation or trauma. A mean pressure of 17.7
mm. Hg was found. The detailed distribution of pressures is given in Table I. The highest,
pressure recorded was 30 mm. Hg, the lowest 12 mm. Hg. In 152 of the eyes not suspected
of glaucoma, the facility of outflow in vivo was subsequently measured with a perfusion
technique. There was no correlation between facility values and tonometric pressure.
DL 'uring work involving the screening of
large numbers of monkeys for glaucoma,
intraocular pressure, probably through an
action on aqueous secretion.1 Moreover, the
it was necessary to examine the untamed pupil is small in this anesthesia. Light
animals with the slit lamp, ophthalmo- ether anesthesia does not depress intra-
scope, and tonometer. Some form of tran- ocular pressure, but in order for a steady
quilization or anesthesia evidently was state to develop, the anesthesia should be
necessary; it had to be convenient, safe, reasonably even for about 15 minutes and
and without much effect on those auto- this is difficult to attain without consider-
nomic functions which determine eye pres- able individual attention.
sure. Light barbiturate anesthesia was not Recent reports indicate that phencycli-
suitable, for it produced nystagmus and dine has remarkable calming properties
turning of the eyes inward and upward. in several monkey species.2'3 Since it has
Large doses of barbiturate markedly lower very little action on visceral functions, in-
cluding the circulation,4 it was tried for
the present purpose and proved to be ex-
From the Department of Physiology, School of cellent. It produces a cataleptoid state in
Medicine, Makerere College, Kampala, Uganda, which the monkey not only is nonaggressive,
and the Department of Pharmacology, Uni- but also can be placed in various positions
versity of Uppsala, Sweden (permanent address without making attempts to right itself.
of author).
This study was supported by Research Grants
The vervets (Cercopithecus ethiops) were
B-3060 and NB-03637 from the Institute of mainly big males and very fierce. They
Neurological Diseases and Blindness, United were either injected while wrapped in a
States Public Health Service, Bethesda, Md. net or transferred to squeeze cages for in-
322
Downloaded From: http://iovs.arvojournals.org/pdfaccess.ashx?url=/data/journals/iovs/933143/ on 10/15/2017
Volume Applanation tonometry and ophthalmoscopy of vervet monkey 323
Numbe
jection. Phencyclidine hydrochloride was finished. If necessary, another series was
made up as 2 mg. per milliliter solution made after a rest of about a minute. The
in saline and given intramuscularly at a lowest of at least 3 valid readings was
dose of 1 to 1.2 mg. per kilogram. It is not used. Tonometry was done on 109 monkeys,
necessary to weigh the animals very ac- 10 of them contributing only one eye. Only
curately; the dose does not appear to be eyes with unilateral cataract, aqueous flare,
critical. or other evidence of present or past inflam-
Five to ten minutes after the injection, mation or trauma were discarded. The
the monkey can be safely handled without average pressure was 17.7 mm. Hg, and
gloves and its whiskers and eyebrows can the distribution of pressures recorded on
be clipped (very necessary if ophthalmos- one occasion in each eye is seen in Table
copy at short range is intended and the I. The readings were taken during the
observer is ticklish!). He can now be put interval from 8:30 A.M. to about 10 P.M.,
on the table in various positions without so that diurnal variations of pressure were
restraint and examined at ease. The included in the variability. The distribution
cataleptoid state lasts for about 45 minutes of differences between the two eyes is seen
at the dose indicated. After some hours, in Table II.
the animals seem to be completely normal. Only in a very few cases do the tabulated
There was no death among more than 100 values derive from anything but the first
successive monkeys, several of them very occasion of tonometry in the animal. Re-
old and decrepit. tonometry after a day or so was done if
At the height of drug action, the eyes the first occasion gave technically unac-
are directed straight ahead. There is no ceptable curves for any one of the two
nystagmus but frequent small bursts of eyes. In these cases the retonometry values
tremor of the eyes. The pupil is wide but
reacts to light. Sometimes a hippus can be
seen. Ophthalmoscopy is very easy, and Table I. Distribution of tonometric eye
fine detail can be studied since the eye is pressures in 208 vervet eyes under
quite steady between the bursts of tremor. phencyclidine
For tonometry, topical anesthesia is
necessary because the corneal reflex is quite No. of eyes
under suspicion
active. In the present study, one drop of (opposite eye ex-
2 per cent lidocaine (Xylocaine) was used. cluded because
The eyes of these monkeys are deep set and of evidence of
Pressure No. of trauma or
the lid reflex is active. It is, therefore, often (mm. Hg) eyes inflammation)
necessary to use some force to retract the 12 4 1
lids. The eyelids in monkeys are often some- 13 7
what greasy and slippery, and it was found 14 13
15 28
to be a great help in increasing friction to 16 24 1
wind die distal phalanx of the thumb and 17 25 1
forefinger used for parting the lids with 18 40 2
adhesive plaster. 19 14 2
20 24
Mackay-Marg tonometry was done with 21 9
the monkeys lying on their sides, with the 22 8 1
23 4 1
hand carrying the tonometer probe being 24 4
steadied on the table. Following a sugges- 25 1
tion by Dr. Robert Moses, a series of 10 to 26 2
27 0
20 applications of the probe was made in 28 0
very quick succession, without inspection 29 0
of the paper strip, until the series was 30 1 1
Downloaded From: http://iovs.arvojournals.org/pdfaccess.ashx?url=/data/journals/iovs/933143/ on 10/15/2017
324 Bdrdny In vestigatiDe Ophthalmology
August. 1963
Table II. Distribution of tonometric difference in facility. A similar lack of cor-
pressure differences between the two relation in normal eyes is evident in
eyes of 99 vervets Grant's" tonographic data for nonglaucoma-
tous humans.
Pressure difference
(mm. Hg) No. of animals Whether the pressures recorded under
0 23
phencyclidine are the physiologic ones is
1 27 an open question. The calibration of the
2 27 Mackay-Marg tonometer was checked in
3 12
4 6
the prescribed manner for each animal,
5 1 and, at the end of the investigation, the
6 1 instrument was tested on a thin rubber
7 2 balloon filled with water under known
pressure. It gave a correct pressure read-
ing. Thus, a systematic instrumental error
are the ones listed. A second and third is improbable. A pharmacologic one is not
tonometry was also done in several cases excluded.
of exceptionally high eye pressure. Some- I wish to thank Dr. John Lock of the Depart-
times the repeat tonometry gave lower ment of Pharmacology at Makerere for drawing
values. In all these cases, the first value my attention to phencyclidine. The sample used
obtained is tabulated. was a gift to Dr. Lock from Parke, Davis & Co.,
England.
In at least 5 of the animals, a suspicion
of simple glaucoma was present. In 3 of REFERENCES
them, the highest tonometry values were
1. Barany, E. H., and Rohen, J. W.: Glaucoma
26, 26, and 24 mm. Hg, respectively. In 2, in monkeys, A. M. A. Arch. Ophth, 69: 630,
the highest pressure was 22, but the discs 1963.
looked suspiciously excavated. These mon- 2. Chen, C. M., and Weston, J. K.: The analgesic
keys were not perfused but kept for further and anesthetic effect of l-( 1-phenylcyclohexyl)
study. piperidine-HCl on the monkey, Anesth. &
Analg. 39: 132, 1960.
Of the remaining tonometrized eyes, 152 3. Spalding, V. T., and Heymann, C. S.: The
were subjected to determination of facility value of phencyclidine in the anaesthesia of
in the untreated state by the two-pressure monkeys, Vet. Rec. 74: 158, 1962.
infusion technique described elsewhere.5 4. Chen, G., Ensor, C. R., Russell, D., and Boh-
This was done in deep pentobarbital anes- ner, B.: The pharmacology of 1-1-phenyl-
cyclohexyl) piperidine-HCl, J. Pharmacol. &
thesia, one to several days after the tonom- Exper. Therap. 127: 241, 1959.
etry experiment. There was no discernible 5. Barany, E. H.: The mode of action of pilo-
correlation between tonometric pressure carpine on outflow resistance in the eye of a t
under phencyclidine and facility of out- primate (Cercopithecus ethiops), INVEST.
flow under barbiturate anesthesia. Even in OPHTH. 1: 712, 1962.
6. Grant, W. M.: Tonography, in Newell, F. W.,
the three animals in which tonometric pres- editor: Glaucoma, Tr. of the Third Confer-
sure differed by 6 to 7 mm. Hg between ence, New York, 1959, Josiah Macy, Jr.
the two eyes, there was no corresponding Foundation, p. 21.
Downloaded From: http://iovs.arvojournals.org/pdfaccess.ashx?url=/data/journals/iovs/933143/ on 10/15/2017
You might also like
- Chapter 23 - Conditions Occurring After DeliveryDocument6 pagesChapter 23 - Conditions Occurring After DeliveryEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- 3 - 4 Surgical Treatment of Cherry EyeDocument7 pages3 - 4 Surgical Treatment of Cherry EyeAman RustagiNo ratings yet
- Department of Genetics: Covid-19 RT PCRDocument1 pageDepartment of Genetics: Covid-19 RT PCRAjo Jose100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Traumatic Brain Injury: Melissa J. Mcginn,, John T. PovlishockDocument11 pagesPathophysiology of Traumatic Brain Injury: Melissa J. Mcginn,, John T. Povlishocksiska misaliNo ratings yet
- Wagner2007 Ocular Pathology Rabbit EyeDocument10 pagesWagner2007 Ocular Pathology Rabbit EyeHugo OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Current Examination Methods of The Canine Eye: J. Beránek, P.J. VítDocument6 pagesCurrent Examination Methods of The Canine Eye: J. Beránek, P.J. VítOktavia firnandaNo ratings yet
- Examination of AnimalDocument5 pagesExamination of Animaldharmachakra ComNo ratings yet
- Surgery B PracticalDocument12 pagesSurgery B PracticalMohamed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Visual and Auditory DisturbancesDocument53 pagesVisual and Auditory DisturbancesJASTINE JOY PEREZNo ratings yet
- ProP Ophthalmic Examination Made EasyDocument5 pagesProP Ophthalmic Examination Made EasyRosario AyalaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination EyeDocument2 pagesClinical Examination EyeKirti JamwalNo ratings yet
- Eyelid DisordersDocument6 pagesEyelid DisordersCamilo PerezNo ratings yet
- Giansanti Rabbit and Cell Culture 2010Document8 pagesGiansanti Rabbit and Cell Culture 2010Igor VainerNo ratings yet
- Oftalmologia Del ConejoDocument4 pagesOftalmologia Del ConejoRueca HelenciyaNo ratings yet
- DR Bert Et Al Replies.j.acra.2006.10.021Document2 pagesDR Bert Et Al Replies.j.acra.2006.10.021NukuBtayaNo ratings yet
- PractNeurol 2011 Ahmad 332 40Document10 pagesPractNeurol 2011 Ahmad 332 40Yulyani PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Eyes Diseases RabbitDocument12 pagesEyes Diseases RabbitcarlesNo ratings yet
- Practicum of Autonomic Drugs2Document10 pagesPracticum of Autonomic Drugs2Andre PrawiradinataNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmic Emergency Tips/GuidelinesDocument23 pagesOphthalmic Emergency Tips/GuidelinesSibhi ThranNo ratings yet
- From The Laboratory of Pharmacology of The University of TorontoDocument3 pagesFrom The Laboratory of Pharmacology of The University of TorontoAlexNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Hvpotonic and Isotonic Solutions Containing Sodium Hvaluronate On The Svmptomatic Treatment of DRV Eve PatientsDocument5 pagesComparison of Hvpotonic and Isotonic Solutions Containing Sodium Hvaluronate On The Svmptomatic Treatment of DRV Eve PatientsGraciela CarlosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Disorders of The Eye and Vision - 2018 - Equine Internal MedicineDocument20 pagesChapter 17 - Disorders of The Eye and Vision - 2018 - Equine Internal Medicinemontselee99No ratings yet
- MC Day 2Document12 pagesMC Day 2vfomicevs59No ratings yet
- Berger 1986Document3 pagesBerger 1986kameliasitorusNo ratings yet
- Transpalbebral Exenteration in CattleDocument4 pagesTranspalbebral Exenteration in Cattleಮನೋಜ್ ಭಾರದ್ವಾಜ್No ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4 Effect of Mydriatic Drug On Rabbits EyeDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 4 Effect of Mydriatic Drug On Rabbits EyeShafakat100% (1)
- Vop 12566Document11 pagesVop 12566Blanca A SerranoNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis ReferatDocument26 pagesMyasthenia Gravis ReferatUlfa TitiswariNo ratings yet
- Entropion Correction in Dogs and Cats Using A Combination Hotz-Celsus and Lateral Eyelid Wedge Resection: Results in 311 EyesDocument6 pagesEntropion Correction in Dogs and Cats Using A Combination Hotz-Celsus and Lateral Eyelid Wedge Resection: Results in 311 EyesAndres Luna MendezNo ratings yet
- Como Realizar Una Biopsia en Penfigoide OcularDocument5 pagesComo Realizar Una Biopsia en Penfigoide OcularMiguel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Scedosporium Apiospermum Keratomycosis in A DogDocument4 pagesScedosporium Apiospermum Keratomycosis in A DogDavid Argüelles AndradeNo ratings yet
- Ophthal One LinersDocument6 pagesOphthal One LinersRv DeanNo ratings yet
- Edelhauser 1979Document11 pagesEdelhauser 1979KreAch3RNo ratings yet
- 263 FullDocument7 pages263 FullPrisky DianNo ratings yet
- TMP 195 DDocument4 pagesTMP 195 DFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Effect of Hinge Location On Corneal Sensation And.29Document7 pagesEffect of Hinge Location On Corneal Sensation And.29leoNo ratings yet
- Surgical Treatment of Parasitic Cysts Authorȍocument2 pagesSurgical Treatment of Parasitic Cysts Author Анагаахын ОрчуулгаNo ratings yet
- Standing EnukleasiiDocument3 pagesStanding Enukleasiig_meilisaNo ratings yet
- Giansanti IOVS 2008Document6 pagesGiansanti IOVS 2008Igor VainerNo ratings yet
- Rabbit Eye Expt.Document3 pagesRabbit Eye Expt.Padmanabha Gowda100% (1)
- Snakebite Management Guide For Healthcare Providers in Malaysia 2011Document8 pagesSnakebite Management Guide For Healthcare Providers in Malaysia 2011fifa_0304535100% (1)
- Cherry Eye: Prolapse of Third Eyelid Gland in Dog-A Case ReportDocument4 pagesCherry Eye: Prolapse of Third Eyelid Gland in Dog-A Case ReportRocioNo ratings yet
- AMMVEPEColirioenPerrosVe164 03oDocument6 pagesAMMVEPEColirioenPerrosVe164 03oNicolas Arias CardonaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Blepharoplastic Repair of Conformational Eyelid DefectsDocument11 pagesDiagnosis and Blepharoplastic Repair of Conformational Eyelid Defectstaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Strabismus, Amblyopia & LeukocoriaDocument14 pagesStrabismus, Amblyopia & LeukocoriaMuhammad Naufal WidyatmakaNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of EyeDocument74 pagesAbnormalities of EyeHikmat UllahNo ratings yet
- Study of Jones Procedure For Senile Entropion: Medical ScienceDocument3 pagesStudy of Jones Procedure For Senile Entropion: Medical SciencedhitadwynNo ratings yet
- Corneal Laceration Caused by River Crab: Clinical Ophthalmology DoveDocument4 pagesCorneal Laceration Caused by River Crab: Clinical Ophthalmology Dovesiti rumaisaNo ratings yet
- Lip-To-Lid Transposition and Husbandry Management For Severe Bilateral Eyelid Coloboma in Three Snow Leopards (Panthera Uncia)Document9 pagesLip-To-Lid Transposition and Husbandry Management For Severe Bilateral Eyelid Coloboma in Three Snow Leopards (Panthera Uncia)kradoNo ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument9 pagesGlaucomaREGINE YEO ZHI SHUENNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology How To Examine An Eye: Visual AcuityDocument2 pagesOphthalmology How To Examine An Eye: Visual AcuityOlalekan OgundareNo ratings yet
- Nerve Growth Factor-Induced Ocular Dominance Plasticity in Adult CatvisualcortexDocument5 pagesNerve Growth Factor-Induced Ocular Dominance Plasticity in Adult Catvisualcortextonylee24No ratings yet
- Javma-Javma 20 12 0706Document11 pagesJavma-Javma 20 12 0706Bright DerlacuzENo ratings yet
- December 2017 Ophthalmic PearlsDocument2 pagesDecember 2017 Ophthalmic PearlsMEDIWAY CLINICNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma TextDocument6 pagesGlaucoma TextZorka SzélesNo ratings yet
- Corneal Sensitivity and Ocular Surface Changes Following Preserved Amniotic Membrane Transplantation For Nonhealing Corneal UlcersDocument10 pagesCorneal Sensitivity and Ocular Surface Changes Following Preserved Amniotic Membrane Transplantation For Nonhealing Corneal UlcersDitha FadhilaNo ratings yet
- Role of Fasciotomy in Snake BiteDocument20 pagesRole of Fasciotomy in Snake BiteAmeliaCinantyaNo ratings yet
- Exame Do OlhoDocument11 pagesExame Do OlhoMirella Lopes da RochaNo ratings yet
- W2 - MEDSURG Guidelines For Nursing Interventions On Coma PatientsDocument6 pagesW2 - MEDSURG Guidelines For Nursing Interventions On Coma PatientsKyla L. Madjad100% (1)
- Effects of Genipin Corneal Crosslinking in Rabbit CorneasDocument5 pagesEffects of Genipin Corneal Crosslinking in Rabbit CorneasMauricio NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Male With Involutional Entropion of Inferior Eyelid: Laporan KasusDocument5 pagesMale With Involutional Entropion of Inferior Eyelid: Laporan KasusdhitadwynNo ratings yet
- Effects of A Topically Applied 2 - Delta-9 - Tetrahydrocannabinol Ophthalmic Solution On Intraocular Pressure and Aqueous Humor Flow Rate in Clinically Normal Dogs 2Document6 pagesEffects of A Topically Applied 2 - Delta-9 - Tetrahydrocannabinol Ophthalmic Solution On Intraocular Pressure and Aqueous Humor Flow Rate in Clinically Normal Dogs 2Róbson BatistaNo ratings yet
- OCULOPATHY - Disproves the orthodox and theoretical bases upon which glasses are so freely prescribed, and puts forward natural remedial methods of treatment for what are sometimes termed incurable visual defectsFrom EverandOCULOPATHY - Disproves the orthodox and theoretical bases upon which glasses are so freely prescribed, and puts forward natural remedial methods of treatment for what are sometimes termed incurable visual defectsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plans: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationRheeanne Mae Amilasan100% (1)
- Congenital Hip DysplasiaDocument5 pagesCongenital Hip DysplasiaMay Ann BoongalingNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube (NGT)Document31 pagesNasogastric Tube (NGT)annyeong_123No ratings yet
- Postmenopausal OsteoporosisDocument13 pagesPostmenopausal OsteoporosisAhmad YassirNo ratings yet
- Transcripts of Dr. William Barnhart Van Valin II (MJ DR.) Katherine Jackson V AEG Live September 6th 2013Document57 pagesTranscripts of Dr. William Barnhart Van Valin II (MJ DR.) Katherine Jackson V AEG Live September 6th 2013TeamMichaelNo ratings yet
- ES V 0281 001 FinalSPCDocument4 pagesES V 0281 001 FinalSPCPankaj BeniwalNo ratings yet
- 2019 ALS 1 Manual V4 FinalDocument53 pages2019 ALS 1 Manual V4 FinalyusupNo ratings yet
- FTPDocument13 pagesFTPbenitiyaNo ratings yet
- Grading of Hydronephrosis: An Ongoing Challenge: Abdurrahman OnenDocument13 pagesGrading of Hydronephrosis: An Ongoing Challenge: Abdurrahman OnensavitageraNo ratings yet
- Aar Insurance Kenya Aar Individual and Family Medical Plan Final 5 7 22Document12 pagesAar Insurance Kenya Aar Individual and Family Medical Plan Final 5 7 22tichips mobileNo ratings yet
- Case Report NystagmusDocument6 pagesCase Report Nystagmusghitza80No ratings yet
- Acog Practice Bulletin PDFDocument12 pagesAcog Practice Bulletin PDFVìctorQuesquen100% (1)
- Elevate Pitch Deck - Version 5 PDFDocument28 pagesElevate Pitch Deck - Version 5 PDFAnabiya AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Best Practices in Alternative Assessment of PerformanceDocument51 pagesBest Practices in Alternative Assessment of PerformanceRafat ElshemiNo ratings yet
- Essay 3 Charity - ST Jude Research Childrens HospitalDocument4 pagesEssay 3 Charity - ST Jude Research Childrens Hospitalapi-312759042No ratings yet
- Right Sided Heart FailureDocument18 pagesRight Sided Heart FailureShaf AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Heart Rate TrainingDocument3 pagesHeart Rate TrainingNetravathi EllurNo ratings yet
- Patient Information Guide: AH-QF-FO-07Document35 pagesPatient Information Guide: AH-QF-FO-07jose rajanNo ratings yet
- Iv Administration of Cancer Chemotherapy/Cytotoxic Drugs Via Intermittent Piggyback Infusion in A Peripheral Vein MaterialsDocument3 pagesIv Administration of Cancer Chemotherapy/Cytotoxic Drugs Via Intermittent Piggyback Infusion in A Peripheral Vein MaterialsJhe VictorianoNo ratings yet
- Cushing's DiseaseDocument1 pageCushing's DiseaseRiza Angela BarazanNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Date of CompletionDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Date of CompletionNicole AngelNo ratings yet
- Final Online Exam Guideline CBTDocument105 pagesFinal Online Exam Guideline CBTfaisalaminwani121No ratings yet
- Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission Required For ReproductionDocument33 pagesCopyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission Required For ReproductionKvaleramNo ratings yet
- How To Talk About Illness and Medicine in EnglishDocument5 pagesHow To Talk About Illness and Medicine in EnglishIsmaNo ratings yet
- 11-The PharynxDocument73 pages11-The PharynxM.IBRAHIM ALHAMECHNo ratings yet
- Definition and Description of Schizprenia in The DSM-5Document8 pagesDefinition and Description of Schizprenia in The DSM-5Danekka TanNo ratings yet
- THR-morbid ObesityDocument5 pagesTHR-morbid ObesityMohan DesaiNo ratings yet