Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Terbutaline Sulfate
Terbutaline Sulfate
Uploaded by
Jay ArCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Contract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Document3 pagesContract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Ivanne Hisoler71% (7)
- 11111a - CarbetocinDocument3 pages11111a - Carbetocinhahahahaaaaaaa0% (2)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyKrissy Java79% (14)
- HydrocortisoneDocument2 pagesHydrocortisoneIvanne Hisoler100% (15)
- LisinoprilDocument1 pageLisinoprilKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- OfloxacinDocument2 pagesOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Daily Assignment PlanDocument2 pagesDaily Assignment PlanIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- HydralazineDocument1 pageHydralazineIvanne Hisoler75% (8)
- Promethazine HCLDocument2 pagesPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- TerbutalineDocument1 pageTerbutalineRyan Paul Balot0% (1)
- Terbutaline BricanylDocument1 pageTerbutaline BricanylB PNo ratings yet
- BetamethasoneDocument3 pagesBetamethasoneMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Terbutaline SulfateDocument2 pagesTerbutaline SulfateRhoellet VenzonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 pagesDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic: Systemic Administration AssessmentDocument3 pagesPharmacologic: Systemic Administration Assessmentitsmeaya100% (1)
- ChlorphenamineDocument1 pageChlorphenaminereinaNo ratings yet
- Phenergan (Promethazine)Document1 pagePhenergan (Promethazine)E100% (1)
- Ceftriaxone, Misoprostol, OxytocinDocument4 pagesCeftriaxone, Misoprostol, OxytocinKrizia Bonilla100% (1)
- Drug Study of Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesDrug Study of Magnesium SulfateEm Hernandez Arana83% (6)
- CaptoprilDocument2 pagesCaptoprilJohn Louie EscardaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: College of NursingDocument3 pagesDrug Study: College of NursingJulie MayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument23 pagesDrug StudyEdward Baes33% (3)
- DORMICUMDocument1 pageDORMICUMArian Rose100% (1)
- Drug Study - Cimetidine (Tagamet)Document3 pagesDrug Study - Cimetidine (Tagamet)mikErlh100% (3)
- BuscopanDocument3 pagesBuscopanJulie May100% (1)
- AMINOPHYLLINEDocument2 pagesAMINOPHYLLINEmusiclover017100% (1)
- Generic Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument6 pagesGeneric NameKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- HydralazineDocument2 pagesHydralazineShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Drug Mode of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument3 pagesDrug Mode of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameJinky Nacar DomingoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MgSO4Document1 pageDrug Study MgSO4Brigette Quirante100% (1)
- Ampicillin PDFDocument3 pagesAmpicillin PDFandriNo ratings yet
- Beclomethasone Dipropionate (Drug Study)Document2 pagesBeclomethasone Dipropionate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- AminophyllineDocument9 pagesAminophyllineZaira BataloNo ratings yet
- Betamethasone (Drug Study)Document4 pagesBetamethasone (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- MethergineDocument2 pagesMethergineRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PethidineDocument2 pagesDrug Study Pethidinerica sebabillonesNo ratings yet
- Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesLabetalol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Study of FurosemideDocument5 pagesDrug Study of FurosemideAntonette Lei100% (1)
- Drug Study Delivery RoomDocument7 pagesDrug Study Delivery RoomkhleeoNo ratings yet
- Clomid Drug StudyDocument3 pagesClomid Drug StudySheen Ivashkov-BelikovNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SulfasalazineDocument2 pagesDrug Study SulfasalazineBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Calcium GluconateDocument2 pagesCalcium GluconateMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (1)
- RitodrineDocument4 pagesRitodrineMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Diltiazem CardizemDocument2 pagesDiltiazem CardizemLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Drug STudyDocument2 pagesAtropine Sulfate Drug STudyLiway100% (1)
- Dexamethasone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDexamethasone Drug StudyVIDMENTON PHNo ratings yet
- Drug Indication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument1 pageDrug Indication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationSheng Gosep100% (3)
- Drugs StudyDocument6 pagesDrugs StudyAllan MacacapagalNo ratings yet
- Delivery Room Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDelivery Room Drug StudyChinimansiNo ratings yet
- Availability: Dinoprostone (Pge, Prostaglandin E)Document3 pagesAvailability: Dinoprostone (Pge, Prostaglandin E)steffy sojan100% (1)
- Drug Study - Atropine Sulfate (Atropair)Document2 pagesDrug Study - Atropine Sulfate (Atropair)mikErlh100% (1)
- Drug Study AminophyllineDocument1 pageDrug Study Aminophyllinejunie100% (3)
- XylocaineDocument1 pageXylocaineRozanne BanzaliNo ratings yet
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULARDocument2 pagesCARDIOVASCULARAERONH JOHN PURIFICANDONo ratings yet
- Salbutamol - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSalbutamol - Drug Studygervisrael.gonzales.twphosiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SalbutamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study Salbutamolliza sian100% (2)
- Albuterol (Ventolin, Salbutamol)Document1 pageAlbuterol (Ventolin, Salbutamol)Jocelyn Rivera100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyApril Sarol67% (3)
- Ms Task Gomez Ellyza Syrelle CDocument19 pagesMs Task Gomez Ellyza Syrelle CSyrelle GomezNo ratings yet
- Pharm Drugs ChartsDocument21 pagesPharm Drugs ChartsTris100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument27 pagesDrug StudyChan SorianoNo ratings yet
- Land Titles Cases (6.21.14)Document31 pagesLand Titles Cases (6.21.14)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Lumantas MD v. CalapizDocument2 pagesLumantas MD v. CalapizIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- Eminent Domain Case DigestsDocument18 pagesEminent Domain Case DigestsIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Case Digest (QC v. Ericta)Document1 pageCase Digest (QC v. Ericta)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Republic vs. Castellvi DigestDocument1 pageRepublic vs. Castellvi DigestIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Promethazine HCLDocument2 pagesPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- Persons - Midterms NotesDocument23 pagesPersons - Midterms NotesEvina Michaela LupangoNo ratings yet
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- MethotrexateDocument2 pagesMethotrexateIvanne Hisoler83% (6)
- DroperidolDocument1 pageDroperidolIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument1 pageMagnesium SulfateIvanne Hisoler67% (3)
- Penicillin G BenzathineDocument1 pagePenicillin G BenzathineIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- MetoclopramideDocument1 pageMetoclopramideIvanne Hisoler89% (28)
- MethadoneDocument2 pagesMethadoneIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- DactinomycinDocument1 pageDactinomycinIvanne Hisoler0% (2)
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemideIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- DigoxinDocument1 pageDigoxinIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- Dopamine HCLDocument1 pageDopamine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamIvanne Hisoler71% (7)
- DisulfiramDocument1 pageDisulfiramIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- AmpicillinDocument1 pageAmpicillinIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- Sistemi Nervor VegjetativDocument38 pagesSistemi Nervor VegjetativelisaNo ratings yet
- PropranololDocument6 pagesPropranololanon_678895677No ratings yet
- Terbutaline SulfateDocument1 pageTerbutaline SulfateIvanne Hisoler100% (2)
- BricanylDocument4 pagesBricanylianecunarNo ratings yet
Terbutaline Sulfate
Terbutaline Sulfate
Uploaded by
Jay ArOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Terbutaline Sulfate
Terbutaline Sulfate
Uploaded by
Jay ArCopyright:
Available Formats
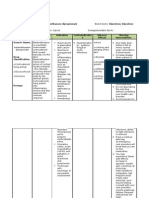
Generic Name Pharmacologic General Indications Concentrations CNS: Restlessness, apprehension, Before
Terbutaline sulfate Class In low doses, acts relatively - Prophylaxis and - Hypersensitivity to anxiety, fear, CNS stimulation, - Observe 15 rights of drug
Beta2-selective selectively at beta2-adrenergic treatment of bronchial terbutaline hyperkinesia, insomnia, tremor, administration.
Trade Name adrenergic receptors to cause bronchodilation asthma and reversible - Tachyarrhythmias, drowsiness, irritability, weakness, - Reduce dosage with hepatic or
Brethine antagonist and relax the pregnant uterus; bronchospasm that may tachycardia caused by vertigo, headache, seizures renal failure.
At higher doses, beta2 selectively is occur with bronchitis and digitalis intoxication - Assess for hypersensitivity to drug
Minimum Dose Therapeutic Class lost and the drug acts at beta1 emphysema, in patients - General anesthesia CV: Cardiac arrhythmias, - Assess for any contraindications t
5 mg at 6-hr Antasthmatic, 12 yr and older with halogenated palpitations, angina pain, changes in the drug.
receptors to cause typical
intervals tid Bronchodilator, sympathomimetic cardiac effects. - Unlabeled use: Tocolytic hydrocarbons or BP and ECG - Educate about side effects of drug
Sympathomimetic, to prevent preterm labor cyclopropane
Maximum Dose Tocolytic drug Pharmacokinetics - Unstable vasomotor GI: Nausea, vomiting, heartburn, During
15 mg/day system disorders unusual or bad taste in mouth - Use minimal doses for minimal
D: May cross placenta; enters - Labor and delivery periods of time, drug tolerance can
Pregnancy Risk
Contents - Lactation Respiratory: Respiratory occur with prolonged use.
Factor breast milk
Terbutaline sulfate M: Tissue difficulties, pulmonary edema, - Keep a beta-blocker, such as
B Precaution
coughing, bronchospasm atenolol, readily available in case
E: Urine - Diabetes, Coronary cardiac dysrhythmias occur.
Availability and
insufficiency, CAD, - For oral forms, administer with
color Route Onset Peak Duration Other: Sweating, pallor, flushing,
History of CVA, COPD water to facilitate swallowing.
- Tablets: 2.5, 5 muscle cramps, elevated LFTs
Oral 30 min 2-3 hr 4-8 hr patient, - For parenteral forms, avoid contac
mg Hyperthyroidism, with the needle.
- Injection: 1 SubQ 5-15 30-60 1.5-4 hr
History of seizure - Stay with patient throughout
min min
mg/mL disorder, whole duration of administration.
Drug Half Life Psychoneurotic
Routes of individuals,
2-4 hr After
administration Hypertension - Monitor client for at least 30
Oral
minutes.
Subcutaneous Drug interaction - Arrange for regular follow-up,
> Drug to drug including blood tests, to evaluate
- Increased likelihood of effects.
cardiac arrhythmias - Instruct to report chest pain,
with halogenated dizziness, insomnia, weakness,
hydrocarbon anesthetics tremor or irregular heartbeat, failur
- Risk of bronchospasms to respond to usual dosage.
if combined with - Instruct to take medication as
diuretics directed for the full course of
- Increased risk of therapy, even if feeling better.
hypokalemia and ECG - Do not double dose.
changes with MAOIs - Do proper documentation.
and TCAs
> Drug to food
- none reported
Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source:
Karch, Amy: 2009 Karch, Amy: 2009 Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincotts Nursing Drug Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincotts Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincotts Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincotts Nursing Drug Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincotts Nursing Drug
Lippincotts Nursing Drug Lippincotts Nursing Drug Guide, pp. 1125-1126 Nursing Drug Guide, pp. 1126 Nursing Drug Guide, pp. 1126 Guide, pp. 1126 Guide, pp. 1127
Guide, pp. 1125-1126 Guide, pp. 1125
You might also like
- Contract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Document3 pagesContract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Ivanne Hisoler71% (7)
- 11111a - CarbetocinDocument3 pages11111a - Carbetocinhahahahaaaaaaa0% (2)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyKrissy Java79% (14)
- HydrocortisoneDocument2 pagesHydrocortisoneIvanne Hisoler100% (15)
- LisinoprilDocument1 pageLisinoprilKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- OfloxacinDocument2 pagesOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Daily Assignment PlanDocument2 pagesDaily Assignment PlanIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- HydralazineDocument1 pageHydralazineIvanne Hisoler75% (8)
- Promethazine HCLDocument2 pagesPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- TerbutalineDocument1 pageTerbutalineRyan Paul Balot0% (1)
- Terbutaline BricanylDocument1 pageTerbutaline BricanylB PNo ratings yet
- BetamethasoneDocument3 pagesBetamethasoneMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Terbutaline SulfateDocument2 pagesTerbutaline SulfateRhoellet VenzonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 pagesDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic: Systemic Administration AssessmentDocument3 pagesPharmacologic: Systemic Administration Assessmentitsmeaya100% (1)
- ChlorphenamineDocument1 pageChlorphenaminereinaNo ratings yet
- Phenergan (Promethazine)Document1 pagePhenergan (Promethazine)E100% (1)
- Ceftriaxone, Misoprostol, OxytocinDocument4 pagesCeftriaxone, Misoprostol, OxytocinKrizia Bonilla100% (1)
- Drug Study of Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesDrug Study of Magnesium SulfateEm Hernandez Arana83% (6)
- CaptoprilDocument2 pagesCaptoprilJohn Louie EscardaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: College of NursingDocument3 pagesDrug Study: College of NursingJulie MayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument23 pagesDrug StudyEdward Baes33% (3)
- DORMICUMDocument1 pageDORMICUMArian Rose100% (1)
- Drug Study - Cimetidine (Tagamet)Document3 pagesDrug Study - Cimetidine (Tagamet)mikErlh100% (3)
- BuscopanDocument3 pagesBuscopanJulie May100% (1)
- AMINOPHYLLINEDocument2 pagesAMINOPHYLLINEmusiclover017100% (1)
- Generic Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument6 pagesGeneric NameKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- HydralazineDocument2 pagesHydralazineShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Drug Mode of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument3 pagesDrug Mode of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameJinky Nacar DomingoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MgSO4Document1 pageDrug Study MgSO4Brigette Quirante100% (1)
- Ampicillin PDFDocument3 pagesAmpicillin PDFandriNo ratings yet
- Beclomethasone Dipropionate (Drug Study)Document2 pagesBeclomethasone Dipropionate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- AminophyllineDocument9 pagesAminophyllineZaira BataloNo ratings yet
- Betamethasone (Drug Study)Document4 pagesBetamethasone (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- MethergineDocument2 pagesMethergineRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PethidineDocument2 pagesDrug Study Pethidinerica sebabillonesNo ratings yet
- Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesLabetalol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Study of FurosemideDocument5 pagesDrug Study of FurosemideAntonette Lei100% (1)
- Drug Study Delivery RoomDocument7 pagesDrug Study Delivery RoomkhleeoNo ratings yet
- Clomid Drug StudyDocument3 pagesClomid Drug StudySheen Ivashkov-BelikovNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SulfasalazineDocument2 pagesDrug Study SulfasalazineBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Calcium GluconateDocument2 pagesCalcium GluconateMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (1)
- RitodrineDocument4 pagesRitodrineMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Diltiazem CardizemDocument2 pagesDiltiazem CardizemLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Drug STudyDocument2 pagesAtropine Sulfate Drug STudyLiway100% (1)
- Dexamethasone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDexamethasone Drug StudyVIDMENTON PHNo ratings yet
- Drug Indication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument1 pageDrug Indication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationSheng Gosep100% (3)
- Drugs StudyDocument6 pagesDrugs StudyAllan MacacapagalNo ratings yet
- Delivery Room Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDelivery Room Drug StudyChinimansiNo ratings yet
- Availability: Dinoprostone (Pge, Prostaglandin E)Document3 pagesAvailability: Dinoprostone (Pge, Prostaglandin E)steffy sojan100% (1)
- Drug Study - Atropine Sulfate (Atropair)Document2 pagesDrug Study - Atropine Sulfate (Atropair)mikErlh100% (1)
- Drug Study AminophyllineDocument1 pageDrug Study Aminophyllinejunie100% (3)
- XylocaineDocument1 pageXylocaineRozanne BanzaliNo ratings yet
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULARDocument2 pagesCARDIOVASCULARAERONH JOHN PURIFICANDONo ratings yet
- Salbutamol - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSalbutamol - Drug Studygervisrael.gonzales.twphosiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SalbutamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study Salbutamolliza sian100% (2)
- Albuterol (Ventolin, Salbutamol)Document1 pageAlbuterol (Ventolin, Salbutamol)Jocelyn Rivera100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyApril Sarol67% (3)
- Ms Task Gomez Ellyza Syrelle CDocument19 pagesMs Task Gomez Ellyza Syrelle CSyrelle GomezNo ratings yet
- Pharm Drugs ChartsDocument21 pagesPharm Drugs ChartsTris100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument27 pagesDrug StudyChan SorianoNo ratings yet
- Land Titles Cases (6.21.14)Document31 pagesLand Titles Cases (6.21.14)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Lumantas MD v. CalapizDocument2 pagesLumantas MD v. CalapizIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- Eminent Domain Case DigestsDocument18 pagesEminent Domain Case DigestsIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Case Digest (QC v. Ericta)Document1 pageCase Digest (QC v. Ericta)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Republic vs. Castellvi DigestDocument1 pageRepublic vs. Castellvi DigestIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Promethazine HCLDocument2 pagesPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- Persons - Midterms NotesDocument23 pagesPersons - Midterms NotesEvina Michaela LupangoNo ratings yet
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- MethotrexateDocument2 pagesMethotrexateIvanne Hisoler83% (6)
- DroperidolDocument1 pageDroperidolIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument1 pageMagnesium SulfateIvanne Hisoler67% (3)
- Penicillin G BenzathineDocument1 pagePenicillin G BenzathineIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- MetoclopramideDocument1 pageMetoclopramideIvanne Hisoler89% (28)
- MethadoneDocument2 pagesMethadoneIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- DactinomycinDocument1 pageDactinomycinIvanne Hisoler0% (2)
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemideIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- DigoxinDocument1 pageDigoxinIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- Dopamine HCLDocument1 pageDopamine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamIvanne Hisoler71% (7)
- DisulfiramDocument1 pageDisulfiramIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- AmpicillinDocument1 pageAmpicillinIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- Sistemi Nervor VegjetativDocument38 pagesSistemi Nervor VegjetativelisaNo ratings yet
- PropranololDocument6 pagesPropranololanon_678895677No ratings yet
- Terbutaline SulfateDocument1 pageTerbutaline SulfateIvanne Hisoler100% (2)
- BricanylDocument4 pagesBricanylianecunarNo ratings yet