Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views15 Oct (Recovered)
15 Oct (Recovered)
Uploaded by
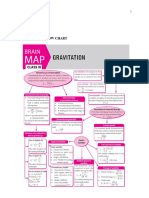
Ashok PradhanThis document contains a physics test with multiple choice and short answer questions. The multiple choice section has 5 questions about gravitational forces and properties of planets and satellites. The short answer section asks students to define key physics concepts like gravitational potential, write the dimensional formula for Newton's gravitational constant G, calculate time periods and velocities related to orbital motion, and explain variations in gravitational acceleration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Enrichment From Conceptual PhysicsDocument16 pagesEnrichment From Conceptual PhysicsJavison GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Gravitation TESTDocument3 pagesGravitation TESTUJJVAL GAHOINo ratings yet
- Gravitation DPPDocument4 pagesGravitation DPPJishan AnsariNo ratings yet
- G R R R: Iii. The Depth at Which The Effective Value of Acceleration Due To Gravity IsDocument2 pagesG R R R: Iii. The Depth at Which The Effective Value of Acceleration Due To Gravity IsAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- 10 Physics Laws of MotionDocument3 pages10 Physics Laws of MotionHasan shaikhNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument1 pageGravitationgaya8404No ratings yet
- Gravitation 1 PDFDocument5 pagesGravitation 1 PDFAbhishek BordoloiNo ratings yet
- P G L 1 O P: Hysics Ravitation Evel Bjective RoblemsDocument8 pagesP G L 1 O P: Hysics Ravitation Evel Bjective RoblemsGrag MeNo ratings yet
- 7 - GravitationDocument5 pages7 - GravitationAvik DasNo ratings yet
- Gravitation-04-Objective UnSolvedDocument6 pagesGravitation-04-Objective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 11th Physics NEET 1 Mark Vol-2 EMDocument53 pages11th Physics NEET 1 Mark Vol-2 EMjohnsonNo ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument20 pagesExerciseabcdefgNo ratings yet
- Gravitation (QB) WA 12thDocument16 pagesGravitation (QB) WA 12thRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- R M KM: GravitationDocument3 pagesR M KM: GravitationpaulaNo ratings yet
- Questions For Short AnswerDocument15 pagesQuestions For Short Answermayank singhNo ratings yet
- Physics Gravitation MCQDocument5 pagesPhysics Gravitation MCQShorya KumarNo ratings yet
- CH-8 GravitationDocument16 pagesCH-8 Gravitationnm.ananya2008No ratings yet
- Fiitjee Coimbatore Centre: 10 - Physics - PCMDocument3 pagesFiitjee Coimbatore Centre: 10 - Physics - PCMC.M.M GAMINGNo ratings yet
- MCQ Type QuestionDocument6 pagesMCQ Type Questionmishra.raj1212006No ratings yet
- Bansalclasses: PhysicsDocument16 pagesBansalclasses: Physicsmayank singhNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Mains AssignmentDocument15 pagesGravitation Mains AssignmentEdInstitute SitesNo ratings yet
- 07 GravitationDocument3 pages07 GravitationMUHAMMED ANAS KNo ratings yet
- Unit 6112Document4 pagesUnit 6112ASTHA THAKURNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Pace Booklet - Part-2Document7 pagesGravitation Pace Booklet - Part-2pratikprahladkaNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument6 pagesGravitationSuresh ShahNo ratings yet
- Gravitation 2Document2 pagesGravitation 2malhar366No ratings yet
- Work Energy Power and GravitationDocument5 pagesWork Energy Power and Gravitationaryan aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Due To GravityDocument3 pagesAcceleration Due To GravityOrbit MBBS Preparation0% (1)
- Gravitation Questions On Gravitation, Paper 2Document2 pagesGravitation Questions On Gravitation, Paper 2Trilok AkhaniNo ratings yet
- Gravitation: Newton's Law of GravitationDocument22 pagesGravitation: Newton's Law of GravitationvenkyNo ratings yet
- MCQ Questions With Answers Class 9 Chapter 10 GravitationDocument6 pagesMCQ Questions With Answers Class 9 Chapter 10 GravitationvishiNo ratings yet
- 7 GravitationDocument7 pages7 GravitationLalitNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Ex. Module-2Document21 pagesGravitation Ex. Module-2Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- 11 Gravitation (JEE) On 29-10-2023 With AnsDocument9 pages11 Gravitation (JEE) On 29-10-2023 With AnsLakshya BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Gravitation ExpertDocument3 pagesGravitation ExpertUJJVAL GAHOINo ratings yet
- Gravitation: Single Answer Type QuestionsDocument22 pagesGravitation: Single Answer Type QuestionsRamesh BadamNo ratings yet
- Physics: Greenfingers Global School, KhargharDocument7 pagesPhysics: Greenfingers Global School, KhargharAnupma SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Xi Neet WT - 25 PhysicsDocument6 pagesXi Neet WT - 25 PhysicsspvsathyabamaNo ratings yet
- Physics: Worksheet - 11 (Lecture-1)Document2 pagesPhysics: Worksheet - 11 (Lecture-1)Akshay KoradiyaNo ratings yet
- 07 GravitationDocument32 pages07 GravitationHaltz t00nNo ratings yet
- Important Gravitation Questions - Free PDF DownloadDocument18 pagesImportant Gravitation Questions - Free PDF Downloadafranazeer16No ratings yet
- 11th GRAVITATION AssignmentDocument4 pages11th GRAVITATION AssignmentYogita GNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Questions On Gravitation, Paper 1: G 3 GR 4 G 3 GR 4Document2 pagesGravitation Questions On Gravitation, Paper 1: G 3 GR 4 G 3 GR 4chitra_shresthaNo ratings yet
- Gra 15 02 2024Document14 pagesGra 15 02 2024aquib.aquil40036No ratings yet
- Gravitation QDocument12 pagesGravitation QRamchandra MurthyNo ratings yet
- Prov Ak - Jmn25-Cat-7Document26 pagesProv Ak - Jmn25-Cat-7Raj AmbolikarNo ratings yet
- 07 - GravitationDocument5 pages07 - GravitationMohit YadavNo ratings yet
- Physics: Question Bank-4Document41 pagesPhysics: Question Bank-4Ara AhmedNo ratings yet
- CBSE PMT GravitationDocument6 pagesCBSE PMT GravitationSavgun KaurNo ratings yet
- 100 Questions For JEE Main Physics by Eduniti Knowledge HuntDocument9 pages100 Questions For JEE Main Physics by Eduniti Knowledge HuntOmkar VanjariNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Practice SheetDocument9 pagesGravitation Practice Sheetbasavarajbadiger247No ratings yet
- Gravitation: M M R M M K FDocument4 pagesGravitation: M M R M M K FZahidNo ratings yet
- Gravitation MCQ TestDocument2 pagesGravitation MCQ TestrhythmNo ratings yet
- 01 09gravitation 144-162Document8 pages01 09gravitation 144-162eamcetmaterialsNo ratings yet
- Test 21 - Gravitation - Bottom of PyramidDocument5 pagesTest 21 - Gravitation - Bottom of PyramidMUZAMMIlNo ratings yet
- V V V VV VV VV VV VV VV VVV: Class 11 - JEE Main Test - 05 / (Dt. 04-09-2021) PhysicsDocument3 pagesV V V VV VV VV VV VV VV VVV: Class 11 - JEE Main Test - 05 / (Dt. 04-09-2021) PhysicsManvi MakkarNo ratings yet
- Physics Group - I (Question & Answer)Document40 pagesPhysics Group - I (Question & Answer)Praveen GsNo ratings yet
- Gravitation PDFDocument5 pagesGravitation PDFQSQF100% (1)
- Question 1142815Document8 pagesQuestion 1142815phantomghost6413No ratings yet
- AIPMST SECONDARY Sample Questions PapersDocument19 pagesAIPMST SECONDARY Sample Questions PapersAIPMST Secondary0% (1)
- Examples On Mathematical Induction: Trigonometry: Sin Sin 1 SinDocument11 pagesExamples On Mathematical Induction: Trigonometry: Sin Sin 1 SinAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- COLUMMNDocument2 pagesCOLUMMNAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Moving Coil GalvanometerDocument5 pagesMoving Coil GalvanometerAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- State Biot Servat Law and Hence Obtain An Expression For The Magnetic Induction Produced by Infinite Long Current Carrying Conductor at Any Point Near ItDocument5 pagesState Biot Servat Law and Hence Obtain An Expression For The Magnetic Induction Produced by Infinite Long Current Carrying Conductor at Any Point Near ItAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Curret 2Document2 pagesCurret 2Ashok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument1 pageCurrent ElectricityAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument6 pagesOpticsAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Edge and Screw DislocationDocument5 pagesComparison Between Edge and Screw DislocationAshok Pradhan0% (1)
- Comparison Between Edge and Screw DislocationDocument5 pagesComparison Between Edge and Screw DislocationAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Weekly Test PhysicsDocument2 pagesWeekly Test PhysicsAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Math 29juneDocument2 pagesMath 29juneAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Ifa 2i 8kandb 3j 4k, Then The Magnitude of A (A) 13 (B) (C) (D) 2Document1 pageIfa 2i 8kandb 3j 4k, Then The Magnitude of A (A) 13 (B) (C) (D) 2Ashok PradhanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper 03 Chapter 5 Laws of MotionDocument9 pagesCBSE Test Paper 03 Chapter 5 Laws of MotionTHANIGAINATHAN.G.D 10A3No ratings yet
- PHYSICS - Experiment 4Document8 pagesPHYSICS - Experiment 4Nikka ReyesNo ratings yet
- Workbook Answers Chapter 5 Asal PhysicsDocument2 pagesWorkbook Answers Chapter 5 Asal PhysicsSaw Lip Xuan JeffNo ratings yet
- SPH 4U - Work-Energy TheoremDocument3 pagesSPH 4U - Work-Energy TheoremyashmkNo ratings yet
- Free Fall - Austria, Joyce NicoleDocument3 pagesFree Fall - Austria, Joyce NicoleJoyce AustriaNo ratings yet
- Rigid Body DynamicsDocument44 pagesRigid Body DynamicsTrickkrickNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 - Describe The Motion of An ObjectDocument27 pagesWEEK 1 - Describe The Motion of An ObjectRicMartin80% (15)
- Study Package On Newtons Law of MotionDocument59 pagesStudy Package On Newtons Law of MotionApex Institute67% (3)
- Dynamics: Kinematics of Rigid BodiesDocument12 pagesDynamics: Kinematics of Rigid BodiesAizuddinNo ratings yet
- Online ReviewDocument7 pagesOnline ReviewCanjiNo ratings yet
- Mastering PHDocument12 pagesMastering PHDaniela PresiadoNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 1 Introduction To Mechanical VibrationDocument2 pagesLecture # 1 Introduction To Mechanical VibrationIjazzzAliNo ratings yet
- RM Sol ProbDocument26 pagesRM Sol ProbSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Dynamics For Racing GamesDocument18 pagesVehicle Dynamics For Racing GameskrishnasrikanthNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Double Star SystemDocument10 pagesProblem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Double Star SystemVongNo ratings yet
- Physics - 1st Semester Study GuideDocument2 pagesPhysics - 1st Semester Study GuideAaryan Singh100% (1)
- EUREKADocument42 pagesEUREKADante'dcCastilloNo ratings yet
- Physics Challenge For Teachers and Students: Solution To October 2008 ChallengeDocument3 pagesPhysics Challenge For Teachers and Students: Solution To October 2008 ChallengeRagini SharmaNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Pacejka's AnalyticalDocument42 pagesImplementation of Pacejka's AnalyticalRenan AlvesNo ratings yet
- Gravity, Air Resistance, Terminal Velocity, and Projectile MotionDocument23 pagesGravity, Air Resistance, Terminal Velocity, and Projectile MotionlidahtakbertulangNo ratings yet
- AE3212 I 2 Static Stab 1 AcDocument23 pagesAE3212 I 2 Static Stab 1 AcRadj90No ratings yet
- Review Notes in Physics 1Document13 pagesReview Notes in Physics 1Anonymous cuVSFiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 29 - Rolling MotionDocument15 pagesLecture 29 - Rolling MotionpvsunilNo ratings yet
- Physics F4C3 Gravitation BI (Student's Copy) 3.1-3.3Document30 pagesPhysics F4C3 Gravitation BI (Student's Copy) 3.1-3.3Nurul alya Qistina sulaimanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 103 Moment of Inertia: PhysicsDocument4 pagesExperiment 103 Moment of Inertia: PhysicsJag MasterNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion by Ken ChanDocument17 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion by Ken ChanMimi LuiNo ratings yet
- Conclusion 204Document1 pageConclusion 204Jamie ToriagaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Newton IDocument2 pagesDynamic Newton IIrvan HasanNo ratings yet
- ES 12 Probset 3 1Document3 pagesES 12 Probset 3 1Christian GalopeNo ratings yet
15 Oct (Recovered)
15 Oct (Recovered)
Uploaded by
Ashok Pradhan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesThis document contains a physics test with multiple choice and short answer questions. The multiple choice section has 5 questions about gravitational forces and properties of planets and satellites. The short answer section asks students to define key physics concepts like gravitational potential, write the dimensional formula for Newton's gravitational constant G, calculate time periods and velocities related to orbital motion, and explain variations in gravitational acceleration.
Original Description:
jkj
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a physics test with multiple choice and short answer questions. The multiple choice section has 5 questions about gravitational forces and properties of planets and satellites. The short answer section asks students to define key physics concepts like gravitational potential, write the dimensional formula for Newton's gravitational constant G, calculate time periods and velocities related to orbital motion, and explain variations in gravitational acceleration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pages15 Oct (Recovered)
15 Oct (Recovered)
Uploaded by
Ashok PradhanThis document contains a physics test with multiple choice and short answer questions. The multiple choice section has 5 questions about gravitational forces and properties of planets and satellites. The short answer section asks students to define key physics concepts like gravitational potential, write the dimensional formula for Newton's gravitational constant G, calculate time periods and velocities related to orbital motion, and explain variations in gravitational acceleration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
SUCCESS STUDY CIRCLE (WEEKLY TEST )
SUB-Physics F.M-25 Time-45min
Q1 answer all [15=5]
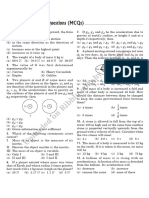
i. Weight of a body of mass m decreases by 1% when it is raised to height h above the earth's surface. If the body is
taken to a depth h in a mine, change in its weight is
(a) 2% decrease (b) 0.5% decrease (c) 1% increase (d) 0.5% increase
ii. The acceleration of a body due to the attraction of the earth (radius R) at a distance 2R from the surface of the earth is
(g = acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth)
g g g
(a) (b) (c) (d) g
9 3 4
iii. A planet has mass 1/10 of that of earth, while radius is 1/3 that of earth. If a person can throw a stone on earth
surface to a height of 90m, then he will be able to throw the stone on that planet to a height
(a) 90m (b) 40m (c) 100m (d) 45m
iv. Acceleration due to gravity on moon is 1/6 of the acceleration due to gravity on earth. If the ratio of densities of earth
5
(m ) and moon ( e ) is e then radius of moon Rm in terms of R e will be
m 3
5 1 3 1
a) Re (b) Re (c) Re (d) Re
18 6 18 2 3
v. The moon's radius is 1/4 that of the earth and its mass is 1/80 times that of the earth. If g represents the acceleration
due to gravity on the surface of the earth, that on the surface of the moon is
g g g g
(a) (b) (c) (d)
4 5 6 8
SUCCESS STUDY CIRCLE (WEEKLY TEST )
SUB-Physics F.M-25 Time-45min
Q1 answer all [15=5]
i. Weight of a body of mass m decreases by 1% when it is raised to height h above the earth's surface. If the body is
taken to a depth h in a mine, change in its weight is
(a) 2% decrease (b) 0.5% decrease (c) 1% increase (d) 0.5% increase
ii. The acceleration of a body due to the attraction of the earth (radius R) at a distance 2R from the surface of the earth is
(g = acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth)
g g g
(a) (b) (c) (d) g
9 3 4
iii. A planet has mass 1/10 of that of earth, while radius is 1/3 that of earth. If a person can throw a stone on earth
surface to a height of 90m, then he will be able to throw the stone on that planet to a height
(a) 90m (b) 40m (c) 100m (d) 45m
iv. Acceleration due to gravity on moon is 1/6 of the acceleration due to gravity on earth. If the ratio of densities of earth
5
(m ) and moon ( e ) is e then radius of moon Rm in terms of R e will be
m 3
5 1 3 1
a) Re (b) Re (c) Re (d) Re
18 6 18 2 3
v. The moon's radius is 1/4 that of the earth and its mass is 1/80 times that of the earth. If g represents the acceleration
due to gravity on the surface of the earth, that on the surface of the moon is
g g g g
(a) (b) (c) (d)
4 5 6 8
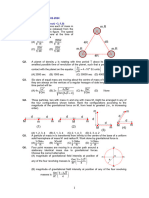
Q2 Answer any five [25=10]
i. Differentiate between gravitational potential and potential energy
ii. Write the dimensional formula of G
iii. Define gravitational intensity.
iv. Calculate the time period of satellite at height g from surface of earth
v. Calculate the variation of g with height
vi. Four particles of masses m, 2m, 3m and 4m are kept in sequence at the corners of a square of side a. The
magnitude of gravitational force acting on a particle of mass m placed at the centre of the square will be
how much?
Q3 Answer all [2.54=10]
i. Variation in g Due to Rotation of Earth.
ii. Calculate the relation between orbital velocity and escape velocity
iii. Define Keplers law of planetary motion
iv. Calculate the acceleration due to gravity due latitude of earth
Q2 Answer any five [25=10]
vii. Differentiate between gravitational potential and potential energy
viii. Write the dimensional formula of G
ix. Define gravitational intensity.
x. Calculate the time period of satellite at height g from surface of earth
xi. Calculate the variation of g with height
xii. Four particles of masses m, 2m, 3m and 4m are kept in sequence at the corners of a square of side a. The
magnitude of gravitational force acting on a particle of mass m placed at the centre of the square will be
how much?
Q3 Answer all [2.54=10]
v. Variation in g Due to Rotation of Earth.
vi. Calculate the relation between orbital velocity and escape velocity
vii. Define Keplers law of planetary motion
viii. Calculate the acceleration due to gravity due latitude of earth
You might also like
- Enrichment From Conceptual PhysicsDocument16 pagesEnrichment From Conceptual PhysicsJavison GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Gravitation TESTDocument3 pagesGravitation TESTUJJVAL GAHOINo ratings yet
- Gravitation DPPDocument4 pagesGravitation DPPJishan AnsariNo ratings yet
- G R R R: Iii. The Depth at Which The Effective Value of Acceleration Due To Gravity IsDocument2 pagesG R R R: Iii. The Depth at Which The Effective Value of Acceleration Due To Gravity IsAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- 10 Physics Laws of MotionDocument3 pages10 Physics Laws of MotionHasan shaikhNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument1 pageGravitationgaya8404No ratings yet
- Gravitation 1 PDFDocument5 pagesGravitation 1 PDFAbhishek BordoloiNo ratings yet
- P G L 1 O P: Hysics Ravitation Evel Bjective RoblemsDocument8 pagesP G L 1 O P: Hysics Ravitation Evel Bjective RoblemsGrag MeNo ratings yet
- 7 - GravitationDocument5 pages7 - GravitationAvik DasNo ratings yet
- Gravitation-04-Objective UnSolvedDocument6 pagesGravitation-04-Objective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 11th Physics NEET 1 Mark Vol-2 EMDocument53 pages11th Physics NEET 1 Mark Vol-2 EMjohnsonNo ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument20 pagesExerciseabcdefgNo ratings yet
- Gravitation (QB) WA 12thDocument16 pagesGravitation (QB) WA 12thRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- R M KM: GravitationDocument3 pagesR M KM: GravitationpaulaNo ratings yet
- Questions For Short AnswerDocument15 pagesQuestions For Short Answermayank singhNo ratings yet
- Physics Gravitation MCQDocument5 pagesPhysics Gravitation MCQShorya KumarNo ratings yet
- CH-8 GravitationDocument16 pagesCH-8 Gravitationnm.ananya2008No ratings yet
- Fiitjee Coimbatore Centre: 10 - Physics - PCMDocument3 pagesFiitjee Coimbatore Centre: 10 - Physics - PCMC.M.M GAMINGNo ratings yet
- MCQ Type QuestionDocument6 pagesMCQ Type Questionmishra.raj1212006No ratings yet
- Bansalclasses: PhysicsDocument16 pagesBansalclasses: Physicsmayank singhNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Mains AssignmentDocument15 pagesGravitation Mains AssignmentEdInstitute SitesNo ratings yet
- 07 GravitationDocument3 pages07 GravitationMUHAMMED ANAS KNo ratings yet
- Unit 6112Document4 pagesUnit 6112ASTHA THAKURNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Pace Booklet - Part-2Document7 pagesGravitation Pace Booklet - Part-2pratikprahladkaNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument6 pagesGravitationSuresh ShahNo ratings yet
- Gravitation 2Document2 pagesGravitation 2malhar366No ratings yet
- Work Energy Power and GravitationDocument5 pagesWork Energy Power and Gravitationaryan aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Due To GravityDocument3 pagesAcceleration Due To GravityOrbit MBBS Preparation0% (1)
- Gravitation Questions On Gravitation, Paper 2Document2 pagesGravitation Questions On Gravitation, Paper 2Trilok AkhaniNo ratings yet
- Gravitation: Newton's Law of GravitationDocument22 pagesGravitation: Newton's Law of GravitationvenkyNo ratings yet
- MCQ Questions With Answers Class 9 Chapter 10 GravitationDocument6 pagesMCQ Questions With Answers Class 9 Chapter 10 GravitationvishiNo ratings yet
- 7 GravitationDocument7 pages7 GravitationLalitNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Ex. Module-2Document21 pagesGravitation Ex. Module-2Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- 11 Gravitation (JEE) On 29-10-2023 With AnsDocument9 pages11 Gravitation (JEE) On 29-10-2023 With AnsLakshya BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Gravitation ExpertDocument3 pagesGravitation ExpertUJJVAL GAHOINo ratings yet
- Gravitation: Single Answer Type QuestionsDocument22 pagesGravitation: Single Answer Type QuestionsRamesh BadamNo ratings yet
- Physics: Greenfingers Global School, KhargharDocument7 pagesPhysics: Greenfingers Global School, KhargharAnupma SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Xi Neet WT - 25 PhysicsDocument6 pagesXi Neet WT - 25 PhysicsspvsathyabamaNo ratings yet
- Physics: Worksheet - 11 (Lecture-1)Document2 pagesPhysics: Worksheet - 11 (Lecture-1)Akshay KoradiyaNo ratings yet
- 07 GravitationDocument32 pages07 GravitationHaltz t00nNo ratings yet
- Important Gravitation Questions - Free PDF DownloadDocument18 pagesImportant Gravitation Questions - Free PDF Downloadafranazeer16No ratings yet
- 11th GRAVITATION AssignmentDocument4 pages11th GRAVITATION AssignmentYogita GNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Questions On Gravitation, Paper 1: G 3 GR 4 G 3 GR 4Document2 pagesGravitation Questions On Gravitation, Paper 1: G 3 GR 4 G 3 GR 4chitra_shresthaNo ratings yet
- Gra 15 02 2024Document14 pagesGra 15 02 2024aquib.aquil40036No ratings yet
- Gravitation QDocument12 pagesGravitation QRamchandra MurthyNo ratings yet
- Prov Ak - Jmn25-Cat-7Document26 pagesProv Ak - Jmn25-Cat-7Raj AmbolikarNo ratings yet
- 07 - GravitationDocument5 pages07 - GravitationMohit YadavNo ratings yet
- Physics: Question Bank-4Document41 pagesPhysics: Question Bank-4Ara AhmedNo ratings yet
- CBSE PMT GravitationDocument6 pagesCBSE PMT GravitationSavgun KaurNo ratings yet
- 100 Questions For JEE Main Physics by Eduniti Knowledge HuntDocument9 pages100 Questions For JEE Main Physics by Eduniti Knowledge HuntOmkar VanjariNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Practice SheetDocument9 pagesGravitation Practice Sheetbasavarajbadiger247No ratings yet
- Gravitation: M M R M M K FDocument4 pagesGravitation: M M R M M K FZahidNo ratings yet
- Gravitation MCQ TestDocument2 pagesGravitation MCQ TestrhythmNo ratings yet
- 01 09gravitation 144-162Document8 pages01 09gravitation 144-162eamcetmaterialsNo ratings yet
- Test 21 - Gravitation - Bottom of PyramidDocument5 pagesTest 21 - Gravitation - Bottom of PyramidMUZAMMIlNo ratings yet
- V V V VV VV VV VV VV VV VVV: Class 11 - JEE Main Test - 05 / (Dt. 04-09-2021) PhysicsDocument3 pagesV V V VV VV VV VV VV VV VVV: Class 11 - JEE Main Test - 05 / (Dt. 04-09-2021) PhysicsManvi MakkarNo ratings yet
- Physics Group - I (Question & Answer)Document40 pagesPhysics Group - I (Question & Answer)Praveen GsNo ratings yet
- Gravitation PDFDocument5 pagesGravitation PDFQSQF100% (1)
- Question 1142815Document8 pagesQuestion 1142815phantomghost6413No ratings yet
- AIPMST SECONDARY Sample Questions PapersDocument19 pagesAIPMST SECONDARY Sample Questions PapersAIPMST Secondary0% (1)
- Examples On Mathematical Induction: Trigonometry: Sin Sin 1 SinDocument11 pagesExamples On Mathematical Induction: Trigonometry: Sin Sin 1 SinAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- COLUMMNDocument2 pagesCOLUMMNAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Moving Coil GalvanometerDocument5 pagesMoving Coil GalvanometerAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- State Biot Servat Law and Hence Obtain An Expression For The Magnetic Induction Produced by Infinite Long Current Carrying Conductor at Any Point Near ItDocument5 pagesState Biot Servat Law and Hence Obtain An Expression For The Magnetic Induction Produced by Infinite Long Current Carrying Conductor at Any Point Near ItAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Curret 2Document2 pagesCurret 2Ashok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument1 pageCurrent ElectricityAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument6 pagesOpticsAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Edge and Screw DislocationDocument5 pagesComparison Between Edge and Screw DislocationAshok Pradhan0% (1)
- Comparison Between Edge and Screw DislocationDocument5 pagesComparison Between Edge and Screw DislocationAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Weekly Test PhysicsDocument2 pagesWeekly Test PhysicsAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Math 29juneDocument2 pagesMath 29juneAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Ifa 2i 8kandb 3j 4k, Then The Magnitude of A (A) 13 (B) (C) (D) 2Document1 pageIfa 2i 8kandb 3j 4k, Then The Magnitude of A (A) 13 (B) (C) (D) 2Ashok PradhanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper 03 Chapter 5 Laws of MotionDocument9 pagesCBSE Test Paper 03 Chapter 5 Laws of MotionTHANIGAINATHAN.G.D 10A3No ratings yet
- PHYSICS - Experiment 4Document8 pagesPHYSICS - Experiment 4Nikka ReyesNo ratings yet
- Workbook Answers Chapter 5 Asal PhysicsDocument2 pagesWorkbook Answers Chapter 5 Asal PhysicsSaw Lip Xuan JeffNo ratings yet
- SPH 4U - Work-Energy TheoremDocument3 pagesSPH 4U - Work-Energy TheoremyashmkNo ratings yet
- Free Fall - Austria, Joyce NicoleDocument3 pagesFree Fall - Austria, Joyce NicoleJoyce AustriaNo ratings yet
- Rigid Body DynamicsDocument44 pagesRigid Body DynamicsTrickkrickNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 - Describe The Motion of An ObjectDocument27 pagesWEEK 1 - Describe The Motion of An ObjectRicMartin80% (15)
- Study Package On Newtons Law of MotionDocument59 pagesStudy Package On Newtons Law of MotionApex Institute67% (3)
- Dynamics: Kinematics of Rigid BodiesDocument12 pagesDynamics: Kinematics of Rigid BodiesAizuddinNo ratings yet
- Online ReviewDocument7 pagesOnline ReviewCanjiNo ratings yet
- Mastering PHDocument12 pagesMastering PHDaniela PresiadoNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 1 Introduction To Mechanical VibrationDocument2 pagesLecture # 1 Introduction To Mechanical VibrationIjazzzAliNo ratings yet
- RM Sol ProbDocument26 pagesRM Sol ProbSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Dynamics For Racing GamesDocument18 pagesVehicle Dynamics For Racing GameskrishnasrikanthNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Double Star SystemDocument10 pagesProblem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Double Star SystemVongNo ratings yet
- Physics - 1st Semester Study GuideDocument2 pagesPhysics - 1st Semester Study GuideAaryan Singh100% (1)
- EUREKADocument42 pagesEUREKADante'dcCastilloNo ratings yet
- Physics Challenge For Teachers and Students: Solution To October 2008 ChallengeDocument3 pagesPhysics Challenge For Teachers and Students: Solution To October 2008 ChallengeRagini SharmaNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Pacejka's AnalyticalDocument42 pagesImplementation of Pacejka's AnalyticalRenan AlvesNo ratings yet
- Gravity, Air Resistance, Terminal Velocity, and Projectile MotionDocument23 pagesGravity, Air Resistance, Terminal Velocity, and Projectile MotionlidahtakbertulangNo ratings yet
- AE3212 I 2 Static Stab 1 AcDocument23 pagesAE3212 I 2 Static Stab 1 AcRadj90No ratings yet
- Review Notes in Physics 1Document13 pagesReview Notes in Physics 1Anonymous cuVSFiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 29 - Rolling MotionDocument15 pagesLecture 29 - Rolling MotionpvsunilNo ratings yet
- Physics F4C3 Gravitation BI (Student's Copy) 3.1-3.3Document30 pagesPhysics F4C3 Gravitation BI (Student's Copy) 3.1-3.3Nurul alya Qistina sulaimanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 103 Moment of Inertia: PhysicsDocument4 pagesExperiment 103 Moment of Inertia: PhysicsJag MasterNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion by Ken ChanDocument17 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion by Ken ChanMimi LuiNo ratings yet
- Conclusion 204Document1 pageConclusion 204Jamie ToriagaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Newton IDocument2 pagesDynamic Newton IIrvan HasanNo ratings yet
- ES 12 Probset 3 1Document3 pagesES 12 Probset 3 1Christian GalopeNo ratings yet