Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Admission Control
Admission Control
Uploaded by
Faiz Salih MaebedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Admission Control
Admission Control
Uploaded by
Faiz Salih MaebedCopyright:
Available Formats
Admission Control
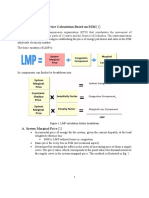
If the connections of new subscribers are not limited, the air interfaces will be overloaded, the actual
coverage of a cell will diminish significantly, and the quality of connected services cannot be guaranteed.
As a result, we need to check whether the addition of a new subscriber will impair ( )the network
performance before admitting the connection request. The module that performs that function is the
.
In WCDMA admission control, there are two algorithms: admission control based on power, and
admission control based on throughput
Uplink admission control based on power can be denoted in the following formula:
I Total_old +I >I Threshold
(I: Node B receiving power)
Uplink:
PTotal_old +P >P Threshold
(P: Node B transmission power)
Uplink admission control based on throughput can be denoted in the following formula:
UL+L > UL_Threshold
Uplink:
DL+L > DL_Threshold
DL and DL are respectively the load factors of uplink and downlink before the admission. L
is the load factor of new subscribers.
In ZTEs WCDMA system, the admission control falls into two categories: new subscriber
admission and handoff admission. Handoff admission is prior to new subscriber admission.
During testing, the admitted subscribers in 12.2 kb/s could reach as high as 123, approximately
the theoretical limit.
You might also like
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Admission Control and Load Control in Umts NetworkDocument4 pagesAdmission Control and Load Control in Umts Networkantony_claret100% (2)
- Turn Your Power Supply's Power Limit Into Current LimitDocument6 pagesTurn Your Power Supply's Power Limit Into Current LimitgubiliNo ratings yet
- Huawei TCP LimitationsDocument2 pagesHuawei TCP LimitationsFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet
- Admission ControlDocument1 pageAdmission ControlFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet
- ZTE Admission ControlDocument6 pagesZTE Admission Controltongai_mutengwa51940% (1)
- D Channel AnalysisDocument5 pagesD Channel AnalysisAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- 14-WCDMA Load ControlDocument48 pages14-WCDMA Load ControlShafiyyah100% (1)
- Zwf25!04!008 Rseps Based Hsupa RRMDocument23 pagesZwf25!04!008 Rseps Based Hsupa RRMlikameleNo ratings yet
- +++ 01040615 PDFDocument5 pages+++ 01040615 PDFHumberto Jose Arias BarrosNo ratings yet
- Increasing Power Transferability Research Paper 10.1109@TDC.2003.1335079Document6 pagesIncreasing Power Transferability Research Paper 10.1109@TDC.2003.1335079globaldata94No ratings yet
- Pes 2006Document8 pagesPes 2006David NurkovičNo ratings yet
- 08-WCDMA Power ControlDocument46 pages08-WCDMA Power ControlMalik Pervaiz IqbalNo ratings yet
- BCTC Feasiblity HVDC Lower MainDocument78 pagesBCTC Feasiblity HVDC Lower MainTrevor Cline100% (1)
- WO - NAST3036 - E01 - 1 Load Balance - 46Document46 pagesWO - NAST3036 - E01 - 1 Load Balance - 46noumizredhaNo ratings yet
- GW 1000Document2 pagesGW 1000soxos_incNo ratings yet
- Siomina-Yuan2005 Chapter OptimizationOfPilotPowerForSer PDFDocument12 pagesSiomina-Yuan2005 Chapter OptimizationOfPilotPowerForSer PDFLira del RosarioNo ratings yet
- 2 WCDMA Power ControlDocument77 pages2 WCDMA Power ControlrogertehNo ratings yet
- HUAWEI WCDMA Power Control & ParametersDocument76 pagesHUAWEI WCDMA Power Control & Parametersমোহাম্মাদ নাবিল নূর88% (8)
- 4 WCDMA Load Control Algorithm and Parameters RAN10Document166 pages4 WCDMA Load Control Algorithm and Parameters RAN10MkathuriNo ratings yet
- Diversity FacotorDocument3 pagesDiversity FacotorKhaled MegahedNo ratings yet
- A Discussion of Anti-Islanding Protection Schemes Incorporated inDocument6 pagesA Discussion of Anti-Islanding Protection Schemes Incorporated injpvaleoNo ratings yet
- Analysis On Distributed Generation Integration Into Low Voltage System NetworkDocument12 pagesAnalysis On Distributed Generation Integration Into Low Voltage System Networksana ullahNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Pilot Power For Service Coverage and Smooth Handover in Wcdma NetworksDocument12 pagesOptimization of Pilot Power For Service Coverage and Smooth Handover in Wcdma NetworkskamalNo ratings yet
- 10 WCDMA Power ControlDocument35 pages10 WCDMA Power Controltelecom_ashok257No ratings yet
- WCDMA Power Calculation GuideDocument14 pagesWCDMA Power Calculation Guidesyed79% (14)
- Ece 542 PDFDocument77 pagesEce 542 PDFpassed2No ratings yet
- Impact of DG Interface Control On Islanding Detection and Nondetection ZonesDocument9 pagesImpact of DG Interface Control On Islanding Detection and Nondetection ZonesahmedrizwanchampNo ratings yet
- What Is Power Congestion and Code CongestionDocument15 pagesWhat Is Power Congestion and Code CongestionAgus Andriyas100% (3)
- Mobile and Broadband Access Networks Lab Session OPNET: UMTS - Part 2 Background InformationDocument6 pagesMobile and Broadband Access Networks Lab Session OPNET: UMTS - Part 2 Background InformationMarvin Nicolas Rivera QuispeNo ratings yet
- QOS Capacity EnhancementDocument10 pagesQOS Capacity EnhancementJulius AmadeNo ratings yet
- WCDMA Power Control Principle: Huawei Confidential. All Rights ReservedDocument46 pagesWCDMA Power Control Principle: Huawei Confidential. All Rights ReservedFachrudinSudomoNo ratings yet
- Uplink Power Based Admission Control in Multi-Cell Wcdma Networks With Heterogeneous TrafficDocument20 pagesUplink Power Based Admission Control in Multi-Cell Wcdma Networks With Heterogeneous TrafficRicha BudhirajaNo ratings yet
- Load Tap Changing Control - BeckwithDocument9 pagesLoad Tap Changing Control - BeckwithTarcisio FlávioNo ratings yet
- R.Seshadri Larsen & Toubro Limited Mysore WorksDocument6 pagesR.Seshadri Larsen & Toubro Limited Mysore WorksbgraoNo ratings yet
- WCDMA Downlink Load Sharing With Dynamic Control of Soft Handover ParametersDocument5 pagesWCDMA Downlink Load Sharing With Dynamic Control of Soft Handover ParametersmaregbesolaNo ratings yet
- 2 - WCDMA Power ControlDocument50 pages2 - WCDMA Power ControlSabrine Chahbi100% (1)
- Code Congestion in 3g ReduceDocument4 pagesCode Congestion in 3g ReduceFanoZalfanoNo ratings yet
- Study of Z-Source Inverter Using Different Control TechniquesDocument6 pagesStudy of Z-Source Inverter Using Different Control TechniquesAnonymous lPvvgiQjRNo ratings yet
- 10 RAN Feature Description (Power Control)Document8 pages10 RAN Feature Description (Power Control)Elmoukhtar BidihNo ratings yet
- Locational Marginal Price Calculation Based On PJMDocument7 pagesLocational Marginal Price Calculation Based On PJMReymark EmbateNo ratings yet
- ZerothDocument12 pagesZerothRonak TalesaraNo ratings yet
- WCDMA Power ControlDocument44 pagesWCDMA Power ControlMohammed AdilNo ratings yet
- ZTE DRBC (ZTE Dynamic Radio Bearer Control Algorithm)Document45 pagesZTE DRBC (ZTE Dynamic Radio Bearer Control Algorithm)Faise Jan100% (3)
- Power Theft Prevention PDFDocument5 pagesPower Theft Prevention PDFRohanNo ratings yet
- Power Control - UMTSDocument36 pagesPower Control - UMTSGiotbuonkhongtenToiNo ratings yet
- State Estimation and Total Transfer Capability Calculation in Deregulated Power SystemDocument5 pagesState Estimation and Total Transfer Capability Calculation in Deregulated Power SystemawolNo ratings yet
- Eee20. Wireless C Based Power Theft Identifier.Document3 pagesEee20. Wireless C Based Power Theft Identifier.Cris AngelesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 FuzzyDocument1 pageChapter 15 FuzzyAnubhav PandeyNo ratings yet
- LST UcellcacDocument8 pagesLST UcellcacAriefSuryoWidodoNo ratings yet
- AGC (Chapter 9 of W&W)Document94 pagesAGC (Chapter 9 of W&W)G Venkata Nagesh Kumar100% (1)
- 2a Payment For Investment enDocument5 pages2a Payment For Investment enadamoussaikaNo ratings yet
- 7TLA2 18sadehDocument6 pages7TLA2 18sadehdragomir_marian9856No ratings yet
- Embedded System Timing Analysis Basics: Part 2 - Fan-Out & Loading AnalysisDocument6 pagesEmbedded System Timing Analysis Basics: Part 2 - Fan-Out & Loading AnalysisMuni TheBossNo ratings yet
- HVDC - Lecture 1Document17 pagesHVDC - Lecture 1yesmuraliNo ratings yet
- An3166 PDFDocument10 pagesAn3166 PDFJonathan JaegerNo ratings yet
- CC613 D00381 D XxenDocument6 pagesCC613 D00381 D XxenMaximiliano PerezNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Sleep CycleDocument4 pagesSleep CycleFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet
- Next Action We Should Monitor and Adjust The ParametersDocument8 pagesNext Action We Should Monitor and Adjust The ParametersFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet
- LTE ENodeB Transmission Bandwidth RequirementDocument2 pagesLTE ENodeB Transmission Bandwidth RequirementFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet
- Radio Network Engineering Process PDFDocument12 pagesRadio Network Engineering Process PDFFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet
- Radio Network Engineering Process PDFDocument12 pagesRadio Network Engineering Process PDFFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet
- UMTS 1carriersDocument21 pagesUMTS 1carriersFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet
- UMTS Cell Selection and ReselectionDocument5 pagesUMTS Cell Selection and ReselectionFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet
- UMTTS Cell Selection and Reselection LMPDocument3 pagesUMTTS Cell Selection and Reselection LMPFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet
- Libyana Bands Investigations and Expansion For 4G: Prepared by:NPO TEAMDocument11 pagesLibyana Bands Investigations and Expansion For 4G: Prepared by:NPO TEAMFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet
- 3G Resellection RulesDocument2 pages3G Resellection RulesFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet
- Huawei RNC-Parameter-ReferenceDocument2,133 pagesHuawei RNC-Parameter-ReferenceFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet
- TRI 229 Issue Needs To Check ZTE Report: TH STDocument7 pagesTRI 229 Issue Needs To Check ZTE Report: TH STFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet
- Admission ControlDocument1 pageAdmission ControlFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet
- Immediate Assignment RejectDocument5 pagesImmediate Assignment RejectFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet
- BSSGP LayerDocument18 pagesBSSGP LayerFaiz Salih MaebedNo ratings yet