Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Use The Assessment Statements As Focal Points For Your Independent Study
Use The Assessment Statements As Focal Points For Your Independent Study
Uploaded by
jarnold90Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Iso 140 5 1998 en FR PDFDocument11 pagesIso 140 5 1998 en FR PDFKésia Cardoso SilvaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map - Shs GenbioDocument2 pagesCurriculum Map - Shs GenbioMary Luz Dolente Eder100% (3)
- IB Biology Syllabus Points With Mark SchemeDocument29 pagesIB Biology Syllabus Points With Mark Schemeemy4147100% (4)
- Cover FactorDocument5 pagesCover Factorselvapdm50% (2)
- Curriculum Map of Standards and Learning Competencies - Grade 11 Science (General Biology 1)Document2 pagesCurriculum Map of Standards and Learning Competencies - Grade 11 Science (General Biology 1)Camille Sison-AlmirolNo ratings yet
- 4 Gcse Edexcel BiologyDocument17 pages4 Gcse Edexcel BiologyRumana KhanNo ratings yet
- DP1 Biology Course Outline Semester One 2021-2022Document2 pagesDP1 Biology Course Outline Semester One 2021-2022Maaher AdmaniNo ratings yet
- 2 - CED Reading Alignment Biology in Focus 2nd Edition 2EDocument5 pages2 - CED Reading Alignment Biology in Focus 2nd Edition 2EDani HussainNo ratings yet
- CELLS 2.1: Outline: To Give A Brief Account or SummaryDocument10 pagesCELLS 2.1: Outline: To Give A Brief Account or SummaryHrithik SolaniNo ratings yet
- RPT SC Yr5 2011Document6 pagesRPT SC Yr5 2011gurlzmiuraNo ratings yet
- Specification Accredited A Level Gce Biology A h420Document73 pagesSpecification Accredited A Level Gce Biology A h420Kirsten AntonioNo ratings yet
- Annual Plant Reviews, Biology of the Plant CuticleFrom EverandAnnual Plant Reviews, Biology of the Plant CuticleMarkus RiedererNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure QPDocument22 pages2.1 Cell Structure QPFatima NissaNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Syllabus CurriculumDocument17 pagesIB Biology Syllabus Curriculumju5940No ratings yet
- Cell Structure: The Big PictureDocument77 pagesCell Structure: The Big PictureSoumiya SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Chem413-Fall 2021-2022-Part 1-Introduction To Biochemistry 1 of 2Document21 pagesChem413-Fall 2021-2022-Part 1-Introduction To Biochemistry 1 of 2Elif Deniz YeşilyaprakNo ratings yet
- Biology SL NotesDocument51 pagesBiology SL NotesBasma EnbehNo ratings yet
- General Biology Module 2Document11 pagesGeneral Biology Module 2Jee-Anne HerbularioNo ratings yet
- BioAct Chapter 2 - QuestionDocument44 pagesBioAct Chapter 2 - QuestionNOOR JANNAH FIRDOUSE BINTI ISMAIL KM-PensyarahNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Pages 51-62Document19 pagesModule 5 Pages 51-62Yuritzi Carrillo-JavanaNo ratings yet
- (ZS) Mitochondria Exam QDocument7 pages(ZS) Mitochondria Exam QrbptcprhzmNo ratings yet
- Life Science Grade 10 June Exam 2019Document15 pagesLife Science Grade 10 June Exam 2019shandamakanaka4No ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument19 pagesCell CycleLaureen BarbsNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Assignments Term 2 - 2022 120112Document10 pagesGrade 10 Assignments Term 2 - 2022 120112rsithole2006No ratings yet
- Ib Biology List of ObjectivesDocument6 pagesIb Biology List of Objectivespaulo05132No ratings yet
- Bio Review Tasksf23Document16 pagesBio Review Tasksf23Shayan UzzamanNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Year 5 Science 2008Document5 pagesYearly Plan Year 5 Science 2008marccw2000No ratings yet
- 1.2 NotesDocument16 pages1.2 Notesyara hazemNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument17 pagesModule 6 - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesKimberly CelisNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 Subject Overview 2023 2024Document5 pagesSCIENCE 9 Subject Overview 2023 2024Paulo MoralesNo ratings yet
- AS 2.1.1 Spec NotesDocument28 pagesAS 2.1.1 Spec Notesmilksheikh2004No ratings yet
- Biology Class 9 Revised Syllabus Break Up 2020-21-23Document7 pagesBiology Class 9 Revised Syllabus Break Up 2020-21-23MohammadNo ratings yet
- Edexcel International GCSE Biology Chapter 1 Learning PlanDocument3 pagesEdexcel International GCSE Biology Chapter 1 Learning PlanMaya HughesNo ratings yet
- National Senior Certificate: Grade 10Document9 pagesNational Senior Certificate: Grade 10kgodisojan2No ratings yet
- Cell Division, Cell Diversity & Cellular Organisation 1 QPDocument10 pagesCell Division, Cell Diversity & Cellular Organisation 1 QPMAHSHIDNo ratings yet
- Science-7 TOS DATDocument3 pagesScience-7 TOS DATryan anthony manubayNo ratings yet
- IB DP Bio - A 2.2 Cell Structure - Student NotesDocument26 pagesIB DP Bio - A 2.2 Cell Structure - Student NotesannaninaibNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Scheme of Wrok 2023Document11 pagesGrade 10 Scheme of Wrok 2023ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Module Generalbiology1 1-1-13Document13 pages1st Quarter Module Generalbiology1 1-1-13Hubilla, Krisha Loveah M.No ratings yet
- ACFrOgBbQCcqyr6FIJibqX4hE3FHdhVW3wVGHPyrUQnf2lv3cNvyfS umtiIGzkrLjok oiM25qC41GrFQ CfCShQ9dbW68-cw3VeoRKzbo2mzbTjxkXuaN-uQHgQiWAJW4R8Jijybt0N2i10lZseM1icCQqeUZoS2zt7M-DbADocument6 pagesACFrOgBbQCcqyr6FIJibqX4hE3FHdhVW3wVGHPyrUQnf2lv3cNvyfS umtiIGzkrLjok oiM25qC41GrFQ CfCShQ9dbW68-cw3VeoRKzbo2mzbTjxkXuaN-uQHgQiWAJW4R8Jijybt0N2i10lZseM1icCQqeUZoS2zt7M-DbAmalwandekubheka02No ratings yet
- 6-STAGE - Progression TestDocument17 pages6-STAGE - Progression TestSnikitha SiddavatamNo ratings yet
- Panitia Biologi: Yearly Plan Biology Form 4Document17 pagesPanitia Biologi: Yearly Plan Biology Form 4Wan RoziahNo ratings yet
- Understandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)Document10 pagesUnderstandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)beaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells - Docx 1Document6 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells - Docx 1SandraNo ratings yet
- G10 TOS DiagnosticDocument1 pageG10 TOS DiagnosticJr CapanangNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Applications: Human GeneticsDocument55 pagesConcepts and Applications: Human GeneticsJJ AlmagroNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.2 Skeleton NotesDocument14 pagesTopic 1.2 Skeleton NotesNicholasNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Biology Worksheet - Cell-The Unit of LifeDocument1 pageCBSE Class 9 Biology Worksheet - Cell-The Unit of Lifesaipranav chinthakunta100% (1)
- Biology SECSept 2022Document24 pagesBiology SECSept 2022Elena XuerebNo ratings yet
- Mine SylBioGr9Document6 pagesMine SylBioGr9Suzan.FilizNo ratings yet
- Senior High School Department Curriculum MapDocument5 pagesSenior High School Department Curriculum MapCamille Sison-AlmirolNo ratings yet
- Cells - 3 V2 (Division & Mitosis)Document21 pagesCells - 3 V2 (Division & Mitosis)mormerodNo ratings yet
- Future Ready Learning: Week 3-4: Exercise 2 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesFuture Ready Learning: Week 3-4: Exercise 2 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsLihza May Alliah GalangNo ratings yet
- Membranas Biologicas Lectura Obligatoria 2017Document24 pagesMembranas Biologicas Lectura Obligatoria 2017Midori OkaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division, Diversity, Differentiation MCQ and 6 MarkerDocument22 pagesCell Division, Diversity, Differentiation MCQ and 6 Markerangelicacamilla2005No ratings yet
- Null 47Document5 pagesNull 47TsheguhNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - CAPE BioDocument15 pagesSyllabus - CAPE BioTravis SatnarineNo ratings yet
- AP Daily Videos Ap Biology PDFDocument9 pagesAP Daily Videos Ap Biology PDFAnitaNo ratings yet
- Bioscheme of Work Class 9Document7 pagesBioscheme of Work Class 9Stella ElytraNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Cell Biology Exam Questions and Mark SchemesDocument19 pagesTopic 1 - Cell Biology Exam Questions and Mark SchemesHumna RazzaqNo ratings yet
- يساردلا ماعل 2023 / 2024 Biology Gr 10 LO's 2023-2024 For Test of Concepts (TOC) ExamDocument2 pagesيساردلا ماعل 2023 / 2024 Biology Gr 10 LO's 2023-2024 For Test of Concepts (TOC) ExamZyad MâğdyNo ratings yet
- Annual Plant Reviews, Flowering and its ManipulationFrom EverandAnnual Plant Reviews, Flowering and its ManipulationCharles AinsworthNo ratings yet
- Portable Gas Detector Protege ZM Datasheet ANZDocument5 pagesPortable Gas Detector Protege ZM Datasheet ANZCarlos PereaNo ratings yet
- Home Work Assignment - 1Document4 pagesHome Work Assignment - 1Agnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Strength of PlanetsDocument12 pagesLesson Strength of Planetsshunmugathason100% (1)
- Suprema PC SDK 3.1 (3.1.0.0) Reference ManualDocument300 pagesSuprema PC SDK 3.1 (3.1.0.0) Reference ManualRafael SperandioNo ratings yet
- Ir2112 (S) & (PBF) : High and Low Side DriverDocument17 pagesIr2112 (S) & (PBF) : High and Low Side DriverMugahed DammagNo ratings yet
- CT Job DesignDocument7 pagesCT Job DesignAKOMOLAFE ABAYOMINo ratings yet
- Materi 7b Mohr CircleDocument35 pagesMateri 7b Mohr Circle17 / Imada Millatul KNo ratings yet
- Sanyo ICs STKs PDFDocument117 pagesSanyo ICs STKs PDFFreddy Monge BarbaranNo ratings yet
- SPC Pulsar NS 200 BS IV - AS200 (2018 07 24)Document105 pagesSPC Pulsar NS 200 BS IV - AS200 (2018 07 24)Willy Mansilla ANo ratings yet
- Ac LGD User InstructionsDocument2 pagesAc LGD User InstructionsGaudencio Alberco vilcayauriNo ratings yet
- Ambardar Book ChaptersDocument809 pagesAmbardar Book ChaptersJeffrey Hufford100% (1)
- NA2XSYDocument5 pagesNA2XSYВладимир УсольцевNo ratings yet
- Skepticism About TruthDocument3 pagesSkepticism About TruthHoward MokNo ratings yet
- D4429, CBRDocument22 pagesD4429, CBRসামিউল হাসান শান্তNo ratings yet
- Ratio and ProportionDocument5 pagesRatio and Proportionsathyece9086No ratings yet
- M14Document28 pagesM14Vijay RajaindranNo ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument18 pagesAtmosphere현성JacobNo ratings yet
- Full Paper IMPACT OF TEAMWORK ON ORGANIZATIONAL PRODUCTIVITY IN SOME SELECTED BASIC SCHOOLSDocument13 pagesFull Paper IMPACT OF TEAMWORK ON ORGANIZATIONAL PRODUCTIVITY IN SOME SELECTED BASIC SCHOOLSPrasad SirsangiNo ratings yet
- Metrology For Smart Electrical GridsDocument34 pagesMetrology For Smart Electrical Gridsjsantodo_2No ratings yet
- Theoretical Course of English Grammar - Lecture 2Document5 pagesTheoretical Course of English Grammar - Lecture 2ქეთი გეგეშიძეNo ratings yet
- OilsDocument38 pagesOilsMohammed AdelNo ratings yet
- Structural Calc Analysis of in Patient BLDG Facade Rev003Document67 pagesStructural Calc Analysis of in Patient BLDG Facade Rev003عزة الإسلامNo ratings yet
- CIRP Annals - Manufacturing Technology: J. Kru Ger (2), T.K. Lien (2), A. VerlDocument19 pagesCIRP Annals - Manufacturing Technology: J. Kru Ger (2), T.K. Lien (2), A. VerlFrancesc HDNo ratings yet
- Exercise 02 - BKF1313 Chapter 2 Part 2Document2 pagesExercise 02 - BKF1313 Chapter 2 Part 2Cornelius PhilipNo ratings yet
- Structural Design Calculation of CCT at BhimavaramDocument61 pagesStructural Design Calculation of CCT at Bhimavaramepe civilNo ratings yet
- HemantDocument22 pagesHemantJatin JakadNo ratings yet
- Separation - Level 6 - QuestionsDocument5 pagesSeparation - Level 6 - QuestionsShahnaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2G Drive TestDocument73 pages2G Drive TestAhmad Ramadan0% (1)
Use The Assessment Statements As Focal Points For Your Independent Study
Use The Assessment Statements As Focal Points For Your Independent Study
Uploaded by
jarnold90Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Use The Assessment Statements As Focal Points For Your Independent Study
Use The Assessment Statements As Focal Points For Your Independent Study
Uploaded by
jarnold90Copyright:
Available Formats
Use the assessment statements as focal points for your
independent study.
2.1 CELL THEORY
Revised at I’m
Assessment statement Obj Done in class
home confident!
2.1.1 Outline the cell theory. 2
2.1.2 Discuss the evidence for the cell theory. 3
2.1.3 State that unicellular organisms carry out 1
all the functions of life.
2.1.4 Compare the relative sizes of molecules, 3
cell membrane thickness, viruses, bacteria,
organelles and cells, using the appropriate
SI unit.
2.1.5 Calculate the linear magnification of 2
drawings and the actual size of specimens
in images of known magnification.
2.1.6 Explain the importance of the surface area 3
to volume ratio as a factor limiting cell size.
2.1.7 State that multicellular organisms show 1
emergent properties.
2.1.8 Explain that cells in multicellular organisms 3
differentiate to carry out specialized
functions by expressing some of their
genes but not others.
2.1.9 State that stem cells retain the capacity to 1
divide and have the ability to differentiate
along different pathways.
2.1.10 Outline one therapeutic use of stem cells. 2
2.2 PROKARYOTIC CELLS
Revised at I’m
Assessment statement Obj Done in class
home confident!
2.2.1 Draw and label a diagram of the 1
ultrastructure of Escherichia coli (E. coli) as
an example of a prokaryote.
2.2.2 Annotate the diagram from 2.2.1 with the 2
functions of each named structure.
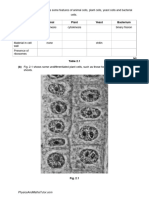
2.2.3 Identify structures from 2.2.1 in electron 2
micrographs of E. coli.
2.2.4 State that prokaryotic cells divide by binary 1
fission.
2.3 EUKARYOTIC CELLS
2.3.1 Draw and label a diagram of the 1
ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example
of an animal cell.
2.3.2 Annotate the diagram from 2.3.1 with the 2
functions of each named structure.
2.3.3 Identify structures from 2.3.1 in electron 2
micrographs of liver cells.
2.3.4 Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 3
2.3.5 State three differences between plant and 1
animal cells.
2.3.6 Outline two roles of extracellular 2
components.
2.4 MEMBRANES
Revised at I’m
Assessment statement Obj Done in class
home confident!
2.4.1 Draw and label a diagram to show the structure 1
of membranes.
2.4.2 Explain how the hydrophobic and hydrophilic 3
properties of phospholipids help to maintain
the structure of cell membranes.
2.4.3 List the functions of membrane proteins. 1
2.4.4 Define diffusion and osmosis. 1
2.4.5 Explain passive transport across membranes by 3
simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion.
2.4.6 Explain the role of protein pumps and ATP in 3
active transport across membranes.
2.4.7 Explain how vesicles are used to transport 3
materials within a cell between the rough
endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus and
plasma membrane.
2.4.8 Describe how the fluidity of the membrane 2
allows it to change shape, break and re-form
during endocytosis and exocytosis.
2.5 CELL DIVISION
2.5.1 Outline the stages in the cell cycle, including 2
interphase (G1, S, G2), mitosis and cytokinesis.
2.5.2 State that tumours (cancers) are the result of 1
uncontrolled cell division and that these can
occur in any organ or tissue.
2.5.3 State that interphase is an active period in the 1
life of a cell when many metabolic reactions
occur, including protein synthesis, DNA
replication and an increase in the number of
mitochondria and/or chloroplasts.
2.5.4 Describe the events that occur in the four 2
phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase,
anaphase and telophase).
2.5.5 Explain how mitosis produces two genetically 3
identical nuclei.
2.5.6 State that growth, embryonic development, 1
tissue repair and asexual reproduction involve
mitosis.
You might also like
- Iso 140 5 1998 en FR PDFDocument11 pagesIso 140 5 1998 en FR PDFKésia Cardoso SilvaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map - Shs GenbioDocument2 pagesCurriculum Map - Shs GenbioMary Luz Dolente Eder100% (3)
- IB Biology Syllabus Points With Mark SchemeDocument29 pagesIB Biology Syllabus Points With Mark Schemeemy4147100% (4)
- Cover FactorDocument5 pagesCover Factorselvapdm50% (2)
- Curriculum Map of Standards and Learning Competencies - Grade 11 Science (General Biology 1)Document2 pagesCurriculum Map of Standards and Learning Competencies - Grade 11 Science (General Biology 1)Camille Sison-AlmirolNo ratings yet
- 4 Gcse Edexcel BiologyDocument17 pages4 Gcse Edexcel BiologyRumana KhanNo ratings yet
- DP1 Biology Course Outline Semester One 2021-2022Document2 pagesDP1 Biology Course Outline Semester One 2021-2022Maaher AdmaniNo ratings yet
- 2 - CED Reading Alignment Biology in Focus 2nd Edition 2EDocument5 pages2 - CED Reading Alignment Biology in Focus 2nd Edition 2EDani HussainNo ratings yet
- CELLS 2.1: Outline: To Give A Brief Account or SummaryDocument10 pagesCELLS 2.1: Outline: To Give A Brief Account or SummaryHrithik SolaniNo ratings yet
- RPT SC Yr5 2011Document6 pagesRPT SC Yr5 2011gurlzmiuraNo ratings yet
- Specification Accredited A Level Gce Biology A h420Document73 pagesSpecification Accredited A Level Gce Biology A h420Kirsten AntonioNo ratings yet
- Annual Plant Reviews, Biology of the Plant CuticleFrom EverandAnnual Plant Reviews, Biology of the Plant CuticleMarkus RiedererNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure QPDocument22 pages2.1 Cell Structure QPFatima NissaNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Syllabus CurriculumDocument17 pagesIB Biology Syllabus Curriculumju5940No ratings yet
- Cell Structure: The Big PictureDocument77 pagesCell Structure: The Big PictureSoumiya SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Chem413-Fall 2021-2022-Part 1-Introduction To Biochemistry 1 of 2Document21 pagesChem413-Fall 2021-2022-Part 1-Introduction To Biochemistry 1 of 2Elif Deniz YeşilyaprakNo ratings yet
- Biology SL NotesDocument51 pagesBiology SL NotesBasma EnbehNo ratings yet
- General Biology Module 2Document11 pagesGeneral Biology Module 2Jee-Anne HerbularioNo ratings yet
- BioAct Chapter 2 - QuestionDocument44 pagesBioAct Chapter 2 - QuestionNOOR JANNAH FIRDOUSE BINTI ISMAIL KM-PensyarahNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Pages 51-62Document19 pagesModule 5 Pages 51-62Yuritzi Carrillo-JavanaNo ratings yet
- (ZS) Mitochondria Exam QDocument7 pages(ZS) Mitochondria Exam QrbptcprhzmNo ratings yet
- Life Science Grade 10 June Exam 2019Document15 pagesLife Science Grade 10 June Exam 2019shandamakanaka4No ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument19 pagesCell CycleLaureen BarbsNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Assignments Term 2 - 2022 120112Document10 pagesGrade 10 Assignments Term 2 - 2022 120112rsithole2006No ratings yet
- Ib Biology List of ObjectivesDocument6 pagesIb Biology List of Objectivespaulo05132No ratings yet
- Bio Review Tasksf23Document16 pagesBio Review Tasksf23Shayan UzzamanNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Year 5 Science 2008Document5 pagesYearly Plan Year 5 Science 2008marccw2000No ratings yet
- 1.2 NotesDocument16 pages1.2 Notesyara hazemNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument17 pagesModule 6 - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesKimberly CelisNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 Subject Overview 2023 2024Document5 pagesSCIENCE 9 Subject Overview 2023 2024Paulo MoralesNo ratings yet
- AS 2.1.1 Spec NotesDocument28 pagesAS 2.1.1 Spec Notesmilksheikh2004No ratings yet
- Biology Class 9 Revised Syllabus Break Up 2020-21-23Document7 pagesBiology Class 9 Revised Syllabus Break Up 2020-21-23MohammadNo ratings yet
- Edexcel International GCSE Biology Chapter 1 Learning PlanDocument3 pagesEdexcel International GCSE Biology Chapter 1 Learning PlanMaya HughesNo ratings yet
- National Senior Certificate: Grade 10Document9 pagesNational Senior Certificate: Grade 10kgodisojan2No ratings yet
- Cell Division, Cell Diversity & Cellular Organisation 1 QPDocument10 pagesCell Division, Cell Diversity & Cellular Organisation 1 QPMAHSHIDNo ratings yet
- Science-7 TOS DATDocument3 pagesScience-7 TOS DATryan anthony manubayNo ratings yet
- IB DP Bio - A 2.2 Cell Structure - Student NotesDocument26 pagesIB DP Bio - A 2.2 Cell Structure - Student NotesannaninaibNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Scheme of Wrok 2023Document11 pagesGrade 10 Scheme of Wrok 2023ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Module Generalbiology1 1-1-13Document13 pages1st Quarter Module Generalbiology1 1-1-13Hubilla, Krisha Loveah M.No ratings yet
- ACFrOgBbQCcqyr6FIJibqX4hE3FHdhVW3wVGHPyrUQnf2lv3cNvyfS umtiIGzkrLjok oiM25qC41GrFQ CfCShQ9dbW68-cw3VeoRKzbo2mzbTjxkXuaN-uQHgQiWAJW4R8Jijybt0N2i10lZseM1icCQqeUZoS2zt7M-DbADocument6 pagesACFrOgBbQCcqyr6FIJibqX4hE3FHdhVW3wVGHPyrUQnf2lv3cNvyfS umtiIGzkrLjok oiM25qC41GrFQ CfCShQ9dbW68-cw3VeoRKzbo2mzbTjxkXuaN-uQHgQiWAJW4R8Jijybt0N2i10lZseM1icCQqeUZoS2zt7M-DbAmalwandekubheka02No ratings yet
- 6-STAGE - Progression TestDocument17 pages6-STAGE - Progression TestSnikitha SiddavatamNo ratings yet
- Panitia Biologi: Yearly Plan Biology Form 4Document17 pagesPanitia Biologi: Yearly Plan Biology Form 4Wan RoziahNo ratings yet
- Understandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)Document10 pagesUnderstandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)beaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells - Docx 1Document6 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells - Docx 1SandraNo ratings yet
- G10 TOS DiagnosticDocument1 pageG10 TOS DiagnosticJr CapanangNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Applications: Human GeneticsDocument55 pagesConcepts and Applications: Human GeneticsJJ AlmagroNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.2 Skeleton NotesDocument14 pagesTopic 1.2 Skeleton NotesNicholasNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Biology Worksheet - Cell-The Unit of LifeDocument1 pageCBSE Class 9 Biology Worksheet - Cell-The Unit of Lifesaipranav chinthakunta100% (1)
- Biology SECSept 2022Document24 pagesBiology SECSept 2022Elena XuerebNo ratings yet
- Mine SylBioGr9Document6 pagesMine SylBioGr9Suzan.FilizNo ratings yet
- Senior High School Department Curriculum MapDocument5 pagesSenior High School Department Curriculum MapCamille Sison-AlmirolNo ratings yet
- Cells - 3 V2 (Division & Mitosis)Document21 pagesCells - 3 V2 (Division & Mitosis)mormerodNo ratings yet
- Future Ready Learning: Week 3-4: Exercise 2 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesFuture Ready Learning: Week 3-4: Exercise 2 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsLihza May Alliah GalangNo ratings yet
- Membranas Biologicas Lectura Obligatoria 2017Document24 pagesMembranas Biologicas Lectura Obligatoria 2017Midori OkaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division, Diversity, Differentiation MCQ and 6 MarkerDocument22 pagesCell Division, Diversity, Differentiation MCQ and 6 Markerangelicacamilla2005No ratings yet
- Null 47Document5 pagesNull 47TsheguhNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - CAPE BioDocument15 pagesSyllabus - CAPE BioTravis SatnarineNo ratings yet
- AP Daily Videos Ap Biology PDFDocument9 pagesAP Daily Videos Ap Biology PDFAnitaNo ratings yet
- Bioscheme of Work Class 9Document7 pagesBioscheme of Work Class 9Stella ElytraNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Cell Biology Exam Questions and Mark SchemesDocument19 pagesTopic 1 - Cell Biology Exam Questions and Mark SchemesHumna RazzaqNo ratings yet
- يساردلا ماعل 2023 / 2024 Biology Gr 10 LO's 2023-2024 For Test of Concepts (TOC) ExamDocument2 pagesيساردلا ماعل 2023 / 2024 Biology Gr 10 LO's 2023-2024 For Test of Concepts (TOC) ExamZyad MâğdyNo ratings yet
- Annual Plant Reviews, Flowering and its ManipulationFrom EverandAnnual Plant Reviews, Flowering and its ManipulationCharles AinsworthNo ratings yet
- Portable Gas Detector Protege ZM Datasheet ANZDocument5 pagesPortable Gas Detector Protege ZM Datasheet ANZCarlos PereaNo ratings yet
- Home Work Assignment - 1Document4 pagesHome Work Assignment - 1Agnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Strength of PlanetsDocument12 pagesLesson Strength of Planetsshunmugathason100% (1)
- Suprema PC SDK 3.1 (3.1.0.0) Reference ManualDocument300 pagesSuprema PC SDK 3.1 (3.1.0.0) Reference ManualRafael SperandioNo ratings yet
- Ir2112 (S) & (PBF) : High and Low Side DriverDocument17 pagesIr2112 (S) & (PBF) : High and Low Side DriverMugahed DammagNo ratings yet
- CT Job DesignDocument7 pagesCT Job DesignAKOMOLAFE ABAYOMINo ratings yet
- Materi 7b Mohr CircleDocument35 pagesMateri 7b Mohr Circle17 / Imada Millatul KNo ratings yet
- Sanyo ICs STKs PDFDocument117 pagesSanyo ICs STKs PDFFreddy Monge BarbaranNo ratings yet
- SPC Pulsar NS 200 BS IV - AS200 (2018 07 24)Document105 pagesSPC Pulsar NS 200 BS IV - AS200 (2018 07 24)Willy Mansilla ANo ratings yet
- Ac LGD User InstructionsDocument2 pagesAc LGD User InstructionsGaudencio Alberco vilcayauriNo ratings yet
- Ambardar Book ChaptersDocument809 pagesAmbardar Book ChaptersJeffrey Hufford100% (1)
- NA2XSYDocument5 pagesNA2XSYВладимир УсольцевNo ratings yet
- Skepticism About TruthDocument3 pagesSkepticism About TruthHoward MokNo ratings yet
- D4429, CBRDocument22 pagesD4429, CBRসামিউল হাসান শান্তNo ratings yet
- Ratio and ProportionDocument5 pagesRatio and Proportionsathyece9086No ratings yet
- M14Document28 pagesM14Vijay RajaindranNo ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument18 pagesAtmosphere현성JacobNo ratings yet
- Full Paper IMPACT OF TEAMWORK ON ORGANIZATIONAL PRODUCTIVITY IN SOME SELECTED BASIC SCHOOLSDocument13 pagesFull Paper IMPACT OF TEAMWORK ON ORGANIZATIONAL PRODUCTIVITY IN SOME SELECTED BASIC SCHOOLSPrasad SirsangiNo ratings yet
- Metrology For Smart Electrical GridsDocument34 pagesMetrology For Smart Electrical Gridsjsantodo_2No ratings yet
- Theoretical Course of English Grammar - Lecture 2Document5 pagesTheoretical Course of English Grammar - Lecture 2ქეთი გეგეშიძეNo ratings yet
- OilsDocument38 pagesOilsMohammed AdelNo ratings yet
- Structural Calc Analysis of in Patient BLDG Facade Rev003Document67 pagesStructural Calc Analysis of in Patient BLDG Facade Rev003عزة الإسلامNo ratings yet
- CIRP Annals - Manufacturing Technology: J. Kru Ger (2), T.K. Lien (2), A. VerlDocument19 pagesCIRP Annals - Manufacturing Technology: J. Kru Ger (2), T.K. Lien (2), A. VerlFrancesc HDNo ratings yet
- Exercise 02 - BKF1313 Chapter 2 Part 2Document2 pagesExercise 02 - BKF1313 Chapter 2 Part 2Cornelius PhilipNo ratings yet
- Structural Design Calculation of CCT at BhimavaramDocument61 pagesStructural Design Calculation of CCT at Bhimavaramepe civilNo ratings yet
- HemantDocument22 pagesHemantJatin JakadNo ratings yet
- Separation - Level 6 - QuestionsDocument5 pagesSeparation - Level 6 - QuestionsShahnaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2G Drive TestDocument73 pages2G Drive TestAhmad Ramadan0% (1)