Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PLANT CELL: Parts and Functions
PLANT CELL: Parts and Functions
Uploaded by
nniChaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetEderlyn Zate100% (1)
- Raven Biology of Plants 8th Edition Evert Test BankDocument13 pagesRaven Biology of Plants 8th Edition Evert Test Bankbridgetmercersftzmojgre100% (13)
- Animal Cell PDFDocument5 pagesAnimal Cell PDFPerry Sin67% (3)
- Animal Cell StructureDocument2 pagesAnimal Cell StructureShaik HamedNo ratings yet
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 pagesParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- What Are Cell OrganellesDocument19 pagesWhat Are Cell OrganellesMaraon CharitaNo ratings yet
- DR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Document14 pagesDR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Cole- Min Khant KyawNo ratings yet
- Cell Vocabulary: NameDocument3 pagesCell Vocabulary: NameStephanie BannickNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure & Fxns FOR OBSERVATIONDocument48 pagesThe Cell Structure & Fxns FOR OBSERVATIONAlyssaNo ratings yet
- Cell VocabularyDocument3 pagesCell Vocabularyapi-537617514No ratings yet
- Animal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyDocument28 pagesAnimal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyPixie DurstNo ratings yet
- Cells: by - NatalieDocument24 pagesCells: by - NatalieNatalie Jaiswal100% (1)
- Foundation - 1 RecapDocument15 pagesFoundation - 1 RecapSonakshi ChavanNo ratings yet
- Act 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportDocument8 pagesAct 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportRicky SalazarNo ratings yet
- Biology 1: Cell Theory Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument4 pagesBiology 1: Cell Theory Cell Structure and FunctionsEmilio Villafria IVNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellElmer Tunggolh, Jr.No ratings yet
- Animal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalDocument6 pagesAnimal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalJohnson Macayan FernándezNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerJes NapiñasNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypesDocument6 pagesLESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypessandraNo ratings yet
- PRPM110L Module 3 & 4Document10 pagesPRPM110L Module 3 & 4CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Parts of A Cell BIOLOGYDocument43 pagesParts of A Cell BIOLOGYSam Ferbyn LomotanNo ratings yet
- Assign 2 BioA 3201Document6 pagesAssign 2 BioA 3201Princess CabardoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument18 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsAleia Trixie100% (1)
- Assignment II: Macaranas, Mar SDocument7 pagesAssignment II: Macaranas, Mar SMar MacaranasNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument22 pagesBiologyKent TediosNo ratings yet
- 2 - Cell+WSDocument3 pages2 - Cell+WSRohan SoniNo ratings yet
- Peroxisomes CytoplasmDocument2 pagesPeroxisomes CytoplasmCorrine MatiasNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument6 pagesCELLSFenny May SebonNo ratings yet
- Cell Oragnelle CompleteDocument2 pagesCell Oragnelle Completeafzal0026No ratings yet
- The CellDocument24 pagesThe CellCaren AdongoNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Plant CellDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 2 Plant CellAiman Haikal100% (1)
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument16 pagesReviewer in BiologyAngel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane: Apparatus Proteins Lipids Vesicles Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Nucleus Cells PlantDocument3 pagesCell Membrane: Apparatus Proteins Lipids Vesicles Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Nucleus Cells PlantPauline Grace MontifalconNo ratings yet
- Sample AssignmentDocument4 pagesSample Assignmentmuhammad saeedNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- Advance Biology NotesDocument15 pagesAdvance Biology Notesvince luigi tamundongNo ratings yet
- Cellular Organization Part2Document4 pagesCellular Organization Part2Vince CedricNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument31 pagesAnimal CellAlyssa Sofia AlihNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: Differences Between Light and Electron MicroscopeDocument14 pagesCell Structure: Differences Between Light and Electron Microscopeshen doweNo ratings yet
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapDocument17 pagesCELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapSonakshi Chavan100% (1)
- 660a7ab160d0bf0018eb0ea0 - ## - Cell The Unit of Life Short NotesDocument2 pages660a7ab160d0bf0018eb0ea0 - ## - Cell The Unit of Life Short Notespradhananita848No ratings yet
- General Biology: System Consists of TheDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology: System Consists of ThePhilipp MendozaNo ratings yet
- 01 Cell and Tissue PDFDocument11 pages01 Cell and Tissue PDFAnand ClassesNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure-Group #4Document17 pagesCell Structure-Group #4Andrea MorochoNo ratings yet
- Cell 2 Grading in Science ViiDocument6 pagesCell 2 Grading in Science ViiJerez De PaduaNo ratings yet
- Biology Prelim NotesDocument47 pagesBiology Prelim NotesAmanie SidawiNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesDocument43 pagesHDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesMariam Qais100% (1)
- Gen Bio 1 Prelim HandoutsDocument7 pagesGen Bio 1 Prelim HandoutsWinter ShiruzuNo ratings yet
- A Cell Is The Smallest Unit of A Living ThingDocument4 pagesA Cell Is The Smallest Unit of A Living ThingJONAVIE DEMALATANo ratings yet
- Session 2: Cells - The Basic Units of Life: WWW - Learnxtra.co - ZaDocument5 pagesSession 2: Cells - The Basic Units of Life: WWW - Learnxtra.co - ZaKaylaNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellDocument23 pagesPlant and Animal CellAnnisa Aulia100% (1)
- Name: Course: Registration Number: Assignment One: Describe The Structure Function and Adaptation of Animal CellsDocument5 pagesName: Course: Registration Number: Assignment One: Describe The Structure Function and Adaptation of Animal CellsDerrick kinyaNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Activity No.1 Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument4 pagesActivity No.1 Cell and Molecular Biologyjocelynmillano115100% (1)
- The CellDocument18 pagesThe Cellaviralgupta15092009No ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Hemeaglobin Short NotesDocument5 pagesHemeaglobin Short NotesrajusirivastavNo ratings yet
- 1998 Structure-Function Relationships of Antimicrobial PeptidesDocument12 pages1998 Structure-Function Relationships of Antimicrobial PeptidesNupur TyagiNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Genetic ControlDocument57 pagesCell Structure and Genetic ControlMOHANNAD ALNEMAHNo ratings yet
- ) "PDF PDFDocument18 pages) "PDF PDFRyan LiNo ratings yet
- The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and CancerDocument3 pagesThe Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and CancerKaren SinorNo ratings yet
- Ex 3 Anaphysio PDFDocument6 pagesEx 3 Anaphysio PDFJayren Ramos TanghalNo ratings yet
- Plasmid Curing of Escherichia Coli Cells With Ethidium BromideDocument4 pagesPlasmid Curing of Escherichia Coli Cells With Ethidium BromideLucasJ.LenziNo ratings yet
- Exercises Genetics USTH2022Document15 pagesExercises Genetics USTH2022yungiang157No ratings yet
- A Conceptual Approach: GeneticsDocument12 pagesA Conceptual Approach: GeneticsSamina QadirNo ratings yet
- Biology 12 00189 v3Document20 pagesBiology 12 00189 v3Albert FengNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Technology Exam Questions and Mark Scheme ILDocument6 pagesRecombinant DNA Technology Exam Questions and Mark Scheme ILRutba SafdarNo ratings yet
- Practical Report - BiotechnologyDocument23 pagesPractical Report - Biotechnologylightning proNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of The Cell The Importance of Carbon Water and Membranes Best Ch022005f 090428000448 Phpapp02Document15 pagesThe Chemistry of The Cell The Importance of Carbon Water and Membranes Best Ch022005f 090428000448 Phpapp02AC QueuNo ratings yet
- Utility of The Housekeeping Genes 18S rRNA, B-Actin-04Document8 pagesUtility of The Housekeeping Genes 18S rRNA, B-Actin-04u77No ratings yet
- CHAPTER III-3. The Cellular Basis of Life: Self TestDocument8 pagesCHAPTER III-3. The Cellular Basis of Life: Self TestLyka Abdullah TayuanNo ratings yet
- 4 Molecular MachinesDocument15 pages4 Molecular Machinesharshit khareNo ratings yet
- Telomere-Related Markers For Cancer: Xiaotian Yuan, Mingkai Dai and Dawei XuDocument23 pagesTelomere-Related Markers For Cancer: Xiaotian Yuan, Mingkai Dai and Dawei XuathayafebNo ratings yet
- (B) Enzymes Are Biological Catalysts. (I) Explain What Is Meant by The Term CatalystDocument5 pages(B) Enzymes Are Biological Catalysts. (I) Explain What Is Meant by The Term CatalystSugeng Riyanto0% (1)
- Membrane Transport Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesMembrane Transport Practice QuestionsLogan ParkisonNo ratings yet
- Passive Facilitated DiffusionDocument2 pagesPassive Facilitated DiffusionIbrahim DharmawanNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Molecular BiologyDocument7 pagesLiterature Review Molecular Biologyafdtsebxc100% (1)
- ResultDocument1 pageResultNandini Pritesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument24 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular BiologyLaras Bani WasesoNo ratings yet
- Rna SplicingDocument2 pagesRna SplicingChintya AurelyaaNo ratings yet
- Supplement For Development and Validation of A Novel RNA, Mei Wang, 2018Document26 pagesSupplement For Development and Validation of A Novel RNA, Mei Wang, 2018mrkhprojectNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Hemostasis - Contributions of Platelets, Coagulation Factors, and The Vessel WallDocument25 pagesMechanisms of Hemostasis - Contributions of Platelets, Coagulation Factors, and The Vessel WallelhierofanteNo ratings yet
- Coagulation Cascade 3 - Halflives of The Coagulation FactorsDocument1 pageCoagulation Cascade 3 - Halflives of The Coagulation FactorsAbdur rehmanNo ratings yet
- Analytik Jena Biometra Agarose Gel Electrophoresis BrochureDocument16 pagesAnalytik Jena Biometra Agarose Gel Electrophoresis BrochureDean RwankoteNo ratings yet
PLANT CELL: Parts and Functions
PLANT CELL: Parts and Functions
Uploaded by
nniChaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PLANT CELL: Parts and Functions
PLANT CELL: Parts and Functions
Uploaded by
nniChaCopyright:
Available Formats
PLANT CELL
PLANT CELL: Parts and Functions
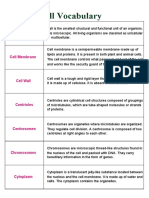
Cell wall: The cell wall is a rigid layer that surrounds the
plant cells. It is made up of cellulose.
Cell membrane: It is the outer boundary of the cell, it
encloses the cytoplasm and the organelles of the cells.
Chloroplasts: It is an elongated or disc-shaped organelle
containing chlorophyll. They have two membranes and have
structures that look like stack of coins. They are flattened
structures which contain chemical chlorophyll.
Cytoskeleton: It is a network of fibers made up of micro-
tubule and micro-filament. They maintain the shape and gives
support to the cell.
Microtubules: They are hollow cylinder like structures found
in the cytoplasm of the cells. Its function is transport and
structural support.
Microfilaments: Microfilaments are solid rod like structures
whose primary function is structural support.
Plasmodesmata: They are microscopic channels which
traverse the cell walls of plant cells and enables transport and
communication between them.
Vacuole: Vacuoles are known as cells storage center. Plant
cells have large membrane bound chamber called vacuole. Its
main function is storage.
Tonoplast: A vacuole that is surrounded by a membrane is called tonoplast.
Plastids: Plastids are storage organelles. They store products like starch for synthesis of fatty acids and terpenes.
Leucoplast: They are a type of plastid which are non-pigmented.
Chromoplast: They are plastids responsible for pigment synthesis and storage. They are found in photosynthetic eukaryotic
species. They are found in colored organs of plants like fruits and flowers.
Golgi complex: The Golgi bodies look like the endoplasmic reticulum and are situated near the nucleus. They are found in
almost all eukaryotic cells. Their main function is to process and package macromolecules synthesized from other parts of
the cell. The Golgi apparatus is referred to as the cell's packaging center.
Ribosomes: Ribosomes are smallest and the most abundant cell organelle. It comprises of RNA and protein. Ribosomes
are sites for protein synthesis.
Endoplasmic reticulum: They are responsible for protein translation, and protein transport to be used in the cell
membrane. They also aid in sequestration of calcium, and production and storage of glycogen and other macromolecules.
Mitochondria: Mitochondria are surrounded by two membranes. They are described as the 'power plants' of the cell as
they convert glucose to energy molecules (ATP).
Lysosome: Lysosome contain digestive enzymes. They digest excess or worn out organelles, food particles and any
foreign bodies.
Micro body: It is a single membrane bound organelle that comprises of degradative enzymes
Cytoplasm: It is a gel-like matrix inside enclosed by the cell membrane. The cytoplasm supports cell organelles and also
prevents the cell from bursting or shrinking.
Nucleus: It is the control center of the cell.
ANIMAL CELL
ANIMAL CELL: Parts and Functions
Cell membrane:It is a semi-permeable barrier, allowing only a few
molecules to move across it.
Cytoplasm:The fluid matrix that fills the cell is the cytoplasm.
Nucleus : Nucleus is the house for most of the cells genetic
material- the DNA and RNA.
Ribosomes:Ribosomes is the site for protein synthesis where the
translation of the RNA takes place.
Endoplasmic reticulum:ER is the transport system of the cell. It
transports molecules that need certain changes and also
molecules to their destination.
Lysosomes:It is the digestive system of the cell.
Centrosomes:It is located near the nucleus of the cell and is
known as the 'microtubule organizing center' of the cell.
Vacuoles :In many organisms vacuoles are storage organelles.
Golgi bodies:Golgi bodies are the packaging center of the cell.
Mitochondria:Mitochondria is the main energy source of the cell.
Peroxisomes:They help in digesting long chains of fatty acids and
amino acids and help in synthesis of cholesterol.
Cytoskeleton:They give structural support and maintain the
shape of the cell.
Cilia and Flagella:Cilia are short and are in large number per cell
while flagella are longer and are fewer in number.The flagellar
motion is undulating and wave-like whereas the ciliary movement
is power stroke and recovery stroke.
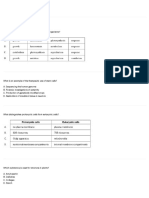
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PLANT AND ANIMAL CELL
1 A plant cell is usually larger in size. An animal cell is comparatively smaller in size.
It is enclosed by a rigid cellulose cell It is enclosed by a thin, flexible plasma
wall in addition to plasma membrane. membrane only.
3 It cannot change its shape. An animal cell can often change its shape.
4 Plastids are present. Plant cells Plastids are usually absent.
exposed to sunlight contain chloroplast.
A mature plant cell contains a large An animal cell often possesses many small
5 central vacuole. vacuoles.
Nucleus lies on one side in the Nucleus usually lies in the centre.
6 peripheral cytoplasm.
Centrioles are usually absent except in Centrioles are practically present in animal
7 motile cells of lower plants. cells
Lysosomes are rare. Lysosomes are always present in animal
8 cells.
Glyoxysomes may be present. They are absent.
9
Tight junctions and desmosomes are Tight junctions and desmosomesare present
10 lacking. between cells.
Plasmodesmata is present. Plasmodesmata are usually absent.
11 Reserve food is generally in the form of Reserve food is usually glycogen.
starch.
12 Plant cell synthesise all amino acids , Animal cell cannot synthesise all the amino
coenzymes and vitamins required by acids, co enzymes and vitamins required by
them. them.
13 Spindles formed during cell divisions in Spindle formed during cell division is
anastral i.e. without asters at opposite amphiastral i.e. has an ester at each pole.
poles.
14 Cytokinesis occurs by cell plate Cytokinesis occurs by construction or
method. furrowing.
15 Plant cell does not burst if placed in Animal cell lacking contractile vacuoles usually
hypotonic solution due to the presence burst, if placed in hypertonic solution.
of the cell wall.
You might also like
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetEderlyn Zate100% (1)
- Raven Biology of Plants 8th Edition Evert Test BankDocument13 pagesRaven Biology of Plants 8th Edition Evert Test Bankbridgetmercersftzmojgre100% (13)
- Animal Cell PDFDocument5 pagesAnimal Cell PDFPerry Sin67% (3)
- Animal Cell StructureDocument2 pagesAnimal Cell StructureShaik HamedNo ratings yet
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 pagesParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- What Are Cell OrganellesDocument19 pagesWhat Are Cell OrganellesMaraon CharitaNo ratings yet
- DR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Document14 pagesDR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Cole- Min Khant KyawNo ratings yet
- Cell Vocabulary: NameDocument3 pagesCell Vocabulary: NameStephanie BannickNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure & Fxns FOR OBSERVATIONDocument48 pagesThe Cell Structure & Fxns FOR OBSERVATIONAlyssaNo ratings yet
- Cell VocabularyDocument3 pagesCell Vocabularyapi-537617514No ratings yet
- Animal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyDocument28 pagesAnimal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyPixie DurstNo ratings yet
- Cells: by - NatalieDocument24 pagesCells: by - NatalieNatalie Jaiswal100% (1)
- Foundation - 1 RecapDocument15 pagesFoundation - 1 RecapSonakshi ChavanNo ratings yet
- Act 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportDocument8 pagesAct 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportRicky SalazarNo ratings yet
- Biology 1: Cell Theory Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument4 pagesBiology 1: Cell Theory Cell Structure and FunctionsEmilio Villafria IVNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellElmer Tunggolh, Jr.No ratings yet
- Animal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalDocument6 pagesAnimal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalJohnson Macayan FernándezNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerJes NapiñasNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypesDocument6 pagesLESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypessandraNo ratings yet
- PRPM110L Module 3 & 4Document10 pagesPRPM110L Module 3 & 4CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Parts of A Cell BIOLOGYDocument43 pagesParts of A Cell BIOLOGYSam Ferbyn LomotanNo ratings yet
- Assign 2 BioA 3201Document6 pagesAssign 2 BioA 3201Princess CabardoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument18 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsAleia Trixie100% (1)
- Assignment II: Macaranas, Mar SDocument7 pagesAssignment II: Macaranas, Mar SMar MacaranasNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument22 pagesBiologyKent TediosNo ratings yet
- 2 - Cell+WSDocument3 pages2 - Cell+WSRohan SoniNo ratings yet
- Peroxisomes CytoplasmDocument2 pagesPeroxisomes CytoplasmCorrine MatiasNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument6 pagesCELLSFenny May SebonNo ratings yet
- Cell Oragnelle CompleteDocument2 pagesCell Oragnelle Completeafzal0026No ratings yet
- The CellDocument24 pagesThe CellCaren AdongoNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Plant CellDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 2 Plant CellAiman Haikal100% (1)
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument16 pagesReviewer in BiologyAngel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane: Apparatus Proteins Lipids Vesicles Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Nucleus Cells PlantDocument3 pagesCell Membrane: Apparatus Proteins Lipids Vesicles Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Nucleus Cells PlantPauline Grace MontifalconNo ratings yet
- Sample AssignmentDocument4 pagesSample Assignmentmuhammad saeedNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- Advance Biology NotesDocument15 pagesAdvance Biology Notesvince luigi tamundongNo ratings yet
- Cellular Organization Part2Document4 pagesCellular Organization Part2Vince CedricNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument31 pagesAnimal CellAlyssa Sofia AlihNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: Differences Between Light and Electron MicroscopeDocument14 pagesCell Structure: Differences Between Light and Electron Microscopeshen doweNo ratings yet
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapDocument17 pagesCELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapSonakshi Chavan100% (1)
- 660a7ab160d0bf0018eb0ea0 - ## - Cell The Unit of Life Short NotesDocument2 pages660a7ab160d0bf0018eb0ea0 - ## - Cell The Unit of Life Short Notespradhananita848No ratings yet
- General Biology: System Consists of TheDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology: System Consists of ThePhilipp MendozaNo ratings yet
- 01 Cell and Tissue PDFDocument11 pages01 Cell and Tissue PDFAnand ClassesNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure-Group #4Document17 pagesCell Structure-Group #4Andrea MorochoNo ratings yet
- Cell 2 Grading in Science ViiDocument6 pagesCell 2 Grading in Science ViiJerez De PaduaNo ratings yet
- Biology Prelim NotesDocument47 pagesBiology Prelim NotesAmanie SidawiNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesDocument43 pagesHDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesMariam Qais100% (1)
- Gen Bio 1 Prelim HandoutsDocument7 pagesGen Bio 1 Prelim HandoutsWinter ShiruzuNo ratings yet
- A Cell Is The Smallest Unit of A Living ThingDocument4 pagesA Cell Is The Smallest Unit of A Living ThingJONAVIE DEMALATANo ratings yet
- Session 2: Cells - The Basic Units of Life: WWW - Learnxtra.co - ZaDocument5 pagesSession 2: Cells - The Basic Units of Life: WWW - Learnxtra.co - ZaKaylaNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellDocument23 pagesPlant and Animal CellAnnisa Aulia100% (1)
- Name: Course: Registration Number: Assignment One: Describe The Structure Function and Adaptation of Animal CellsDocument5 pagesName: Course: Registration Number: Assignment One: Describe The Structure Function and Adaptation of Animal CellsDerrick kinyaNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Activity No.1 Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument4 pagesActivity No.1 Cell and Molecular Biologyjocelynmillano115100% (1)
- The CellDocument18 pagesThe Cellaviralgupta15092009No ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Hemeaglobin Short NotesDocument5 pagesHemeaglobin Short NotesrajusirivastavNo ratings yet
- 1998 Structure-Function Relationships of Antimicrobial PeptidesDocument12 pages1998 Structure-Function Relationships of Antimicrobial PeptidesNupur TyagiNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Genetic ControlDocument57 pagesCell Structure and Genetic ControlMOHANNAD ALNEMAHNo ratings yet
- ) "PDF PDFDocument18 pages) "PDF PDFRyan LiNo ratings yet
- The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and CancerDocument3 pagesThe Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and CancerKaren SinorNo ratings yet
- Ex 3 Anaphysio PDFDocument6 pagesEx 3 Anaphysio PDFJayren Ramos TanghalNo ratings yet
- Plasmid Curing of Escherichia Coli Cells With Ethidium BromideDocument4 pagesPlasmid Curing of Escherichia Coli Cells With Ethidium BromideLucasJ.LenziNo ratings yet
- Exercises Genetics USTH2022Document15 pagesExercises Genetics USTH2022yungiang157No ratings yet
- A Conceptual Approach: GeneticsDocument12 pagesA Conceptual Approach: GeneticsSamina QadirNo ratings yet
- Biology 12 00189 v3Document20 pagesBiology 12 00189 v3Albert FengNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Technology Exam Questions and Mark Scheme ILDocument6 pagesRecombinant DNA Technology Exam Questions and Mark Scheme ILRutba SafdarNo ratings yet
- Practical Report - BiotechnologyDocument23 pagesPractical Report - Biotechnologylightning proNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of The Cell The Importance of Carbon Water and Membranes Best Ch022005f 090428000448 Phpapp02Document15 pagesThe Chemistry of The Cell The Importance of Carbon Water and Membranes Best Ch022005f 090428000448 Phpapp02AC QueuNo ratings yet
- Utility of The Housekeeping Genes 18S rRNA, B-Actin-04Document8 pagesUtility of The Housekeeping Genes 18S rRNA, B-Actin-04u77No ratings yet
- CHAPTER III-3. The Cellular Basis of Life: Self TestDocument8 pagesCHAPTER III-3. The Cellular Basis of Life: Self TestLyka Abdullah TayuanNo ratings yet
- 4 Molecular MachinesDocument15 pages4 Molecular Machinesharshit khareNo ratings yet
- Telomere-Related Markers For Cancer: Xiaotian Yuan, Mingkai Dai and Dawei XuDocument23 pagesTelomere-Related Markers For Cancer: Xiaotian Yuan, Mingkai Dai and Dawei XuathayafebNo ratings yet
- (B) Enzymes Are Biological Catalysts. (I) Explain What Is Meant by The Term CatalystDocument5 pages(B) Enzymes Are Biological Catalysts. (I) Explain What Is Meant by The Term CatalystSugeng Riyanto0% (1)
- Membrane Transport Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesMembrane Transport Practice QuestionsLogan ParkisonNo ratings yet
- Passive Facilitated DiffusionDocument2 pagesPassive Facilitated DiffusionIbrahim DharmawanNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Molecular BiologyDocument7 pagesLiterature Review Molecular Biologyafdtsebxc100% (1)
- ResultDocument1 pageResultNandini Pritesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument24 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular BiologyLaras Bani WasesoNo ratings yet
- Rna SplicingDocument2 pagesRna SplicingChintya AurelyaaNo ratings yet
- Supplement For Development and Validation of A Novel RNA, Mei Wang, 2018Document26 pagesSupplement For Development and Validation of A Novel RNA, Mei Wang, 2018mrkhprojectNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Hemostasis - Contributions of Platelets, Coagulation Factors, and The Vessel WallDocument25 pagesMechanisms of Hemostasis - Contributions of Platelets, Coagulation Factors, and The Vessel WallelhierofanteNo ratings yet
- Coagulation Cascade 3 - Halflives of The Coagulation FactorsDocument1 pageCoagulation Cascade 3 - Halflives of The Coagulation FactorsAbdur rehmanNo ratings yet
- Analytik Jena Biometra Agarose Gel Electrophoresis BrochureDocument16 pagesAnalytik Jena Biometra Agarose Gel Electrophoresis BrochureDean RwankoteNo ratings yet