Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ritemed Losartan: Manufacturer Info
Ritemed Losartan: Manufacturer Info
Uploaded by
Angie MandeoyaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Nursing Care Plan and Diagnosis For MastectomyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan and Diagnosis For MastectomyAngie Mandeoya100% (2)
- Mechanical VentilationDocument26 pagesMechanical VentilationNirupama Ks91% (11)
- Drugs AnalysisDocument6 pagesDrugs AnalysisPauline CarenNo ratings yet
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDocument5 pagesSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Adult: PO HTN Initial: 50-100 Mg/day in Single or Divided Doses Increase SlowlyDocument3 pagesAdult: PO HTN Initial: 50-100 Mg/day in Single or Divided Doses Increase SlowlyJoanna Marie Lumbre BalbiranNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - SpironolactoneDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY - SpironolactoneMarianne Claire P. Bartolome50% (2)
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Enalapril: Indications and DosageDocument18 pagesEnalapril: Indications and Dosageshahera rosdiNo ratings yet
- Obat ObgynDocument8 pagesObat ObgynMuhammad Naqiuddin JalaluddinNo ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument9 pagesFINAL Drug StudyKristen Leigh MarianoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudyCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Lovastatin PDFDocument3 pagesLovastatin PDFHannaNo ratings yet
- LOSARTANDocument19 pagesLOSARTANRani SujithNo ratings yet
- Dulcolax® (Adult Supp) : ConstipationDocument8 pagesDulcolax® (Adult Supp) : ConstipationStephany Rae MamauagNo ratings yet
- Dulcolax® (Adult Supp) : ConstipationDocument8 pagesDulcolax® (Adult Supp) : ConstipationStephany Rae MamauagNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Drug Name Classifications Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing Responsibility CnsDocument4 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Classifications Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing Responsibility CnsMarielle SorianoNo ratings yet
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFranco ObedozaNo ratings yet
- Combizar Drug StudyDocument6 pagesCombizar Drug StudymrnmrsllNo ratings yet
- Lisinopril, TAB: Generic Name of Medication: Brand/trade Name of MedicationDocument6 pagesLisinopril, TAB: Generic Name of Medication: Brand/trade Name of MedicationCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- Hemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Document4 pagesHemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Stacy MC PelitoNo ratings yet
- 13 Drug StudyDocument6 pages13 Drug StudyRachel Yvonne Cabacungan100% (1)
- LisinoprilDocument3 pagesLisinoprilLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Drug Study For ITPDocument25 pagesDrug Study For ITPMary Ann QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyQueenie Gail Duarte RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ko ToDocument4 pagesDrug Study Ko ToGian Carlo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Document13 pagesEmergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Marichu BajadoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyRai D. MacapantonNo ratings yet
- See Full Prescribing Information For Complete Boxed WarningDocument39 pagesSee Full Prescribing Information For Complete Boxed WarningsadafNo ratings yet
- Casas - Mood StabilizersDocument16 pagesCasas - Mood StabilizersKarl Kuis SantanderNo ratings yet
- MM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM MDocument9 pagesMM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM M배기숭No ratings yet
- RamiprilDocument3 pagesRamiprilNovi YulianaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyjazmine_caritos100% (2)
- Banocide and Banocide ForteDocument10 pagesBanocide and Banocide ForteJosephNo ratings yet
- RiteMED MetoprololDocument7 pagesRiteMED MetoprololAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKaguraNo ratings yet
- Lisinopril PDFDocument3 pagesLisinopril PDFHannaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudySharwen_R_Rome_5572No ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument3 pagesDrug StudiesSteve PerezNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument4 pagesAcetazolamideAnkit RuhilNo ratings yet
- General: Genetic Implications: Pronunciation: Maz Trade Name(s)Document7 pagesGeneral: Genetic Implications: Pronunciation: Maz Trade Name(s)jenm1228No ratings yet
- CHN Drug StudyDocument10 pagesCHN Drug StudyJoshua Cyryll ComiaNo ratings yet
- Pedia Ward Drug Study...Document12 pagesPedia Ward Drug Study...Sheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- METFORMINDocument4 pagesMETFORMINkhesler BacallaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY SpironolactoneDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY SpironolactoneJerremy LuqueNo ratings yet
- Generic: Acetazolamide Brand: DiamoxDocument33 pagesGeneric: Acetazolamide Brand: DiamoxAshley Topp100% (1)
- Furosemide Mims EngDocument17 pagesFurosemide Mims EngNur Ilmi SofiahNo ratings yet
- Levofloxacin-1Document31 pagesLevofloxacin-1Fallen AngelNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For End Stage Renal DiseaseDocument16 pagesDrug Study For End Stage Renal DiseaselenecarglbnNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Description Classificat Ion Indication Contraindica Tion Side Effects Nursing Responsibilit IesDocument8 pagesName of Drug Description Classificat Ion Indication Contraindica Tion Side Effects Nursing Responsibilit IesJimmy Merez Jr.No ratings yet
- LalalalaaaaDocument6 pagesLalalalaaaaRobert LeblancNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyCharm LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPedia Drug StudyPeetah PanNo ratings yet
- Drug OrderDocument4 pagesDrug OrderVic MagtotoNo ratings yet
- Fluvastatin - Drug StudyDocument1 pageFluvastatin - Drug StudyKevin H. MilanesNo ratings yet
- Assignment: ON AntilipidemicsDocument15 pagesAssignment: ON AntilipidemicsMansi DabolaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyTeanu Jose Gabrillo TamayoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument15 pagesDrug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesitsmechachaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Prioritization: Speaker: Vicki RobertsonDocument2 pagesConcepts in Prioritization: Speaker: Vicki RobertsonAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Harri AnnaDocument57 pagesHarri AnnaAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Risk For Aspiration: Risk For Aspiration: at Risk For Entry of Gastrointestinal Secretions, Oropharyngeal SecretionDocument6 pagesRisk For Aspiration: Risk For Aspiration: at Risk For Entry of Gastrointestinal Secretions, Oropharyngeal SecretionAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- 50 Motivational Nursing Quotes PDFDocument6 pages50 Motivational Nursing Quotes PDFAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- NCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyDocument3 pagesNCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- NCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsDocument9 pagesNCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsAngie Mandeoya100% (1)
- Day 2 QuizDocument2 pagesDay 2 QuizAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Respondeat Superior PDFDocument1 pageRespondeat Superior PDFAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- I. Calculating IV Flow Rates: Day 2 AnswerDocument2 pagesI. Calculating IV Flow Rates: Day 2 AnswerAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- 000print or NCPDocument6 pages000print or NCPAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Pharm 1.31 SOCK Method For Learning Pharm 1Document1 pagePharm 1.31 SOCK Method For Learning Pharm 1Angie Mandeoya100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Acute Head InjuryDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Acute Head InjuryAngie Mandeoya67% (3)
- GastritisDocument16 pagesGastritisAngie Mandeoya50% (2)
- Drug Study: 75 Yrs. OldDocument3 pagesDrug Study: 75 Yrs. OldAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- FINAL - References & AppendicesDocument23 pagesFINAL - References & AppendicesAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Guide: St. Anthony's College Nursing DepartmentDocument10 pagesNursing Process Guide: St. Anthony's College Nursing DepartmentAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Different Disasters: Erica G. Mandeoya Grade 7-JadeDocument3 pagesCompilation of Different Disasters: Erica G. Mandeoya Grade 7-JadeAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Exam SmpleDocument18 pagesPsychiatric Exam SmpleAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- 50 Motivational Nursing QuotesDocument6 pages50 Motivational Nursing QuotesAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Theories of Human Nature Key Issues Mikael Stenmark 2012Document16 pagesTheories of Human Nature Key Issues Mikael Stenmark 2012Angie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument7 pages1 PBAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Explore LapDocument5 pagesExplore LapAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Labor: About Privacy and Cookie Policy Disclaimer ContactDocument11 pagesLabor: About Privacy and Cookie Policy Disclaimer ContactAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- InfectionDocument4 pagesInfectionAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Erica G. Mandeoya Erica G. Mandeoya Erica G. Mandeoya: Grade 7-Jade Grade 7 - Jade Grade 7 - JadeDocument1 pageErica G. Mandeoya Erica G. Mandeoya Erica G. Mandeoya: Grade 7-Jade Grade 7 - Jade Grade 7 - JadeAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Men's Knowledge of Labor and ChildbirthDocument6 pagesMen's Knowledge of Labor and ChildbirthAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- TheoriesDocument2 pagesTheoriesAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Leong Et Al-2004-BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyDocument2 pagesLeong Et Al-2004-BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Toxic Multinodular Goiter Physical ExaminationDocument2 pagesToxic Multinodular Goiter Physical ExaminationAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Jalan Nafas Pada Pasien Dengan Tumor Mandibula: Laporan KasusDocument27 pagesManajemen Jalan Nafas Pada Pasien Dengan Tumor Mandibula: Laporan KasusMulia AndaraNo ratings yet
- Affimed Presentation-Mar2020 Final-1 PDFDocument22 pagesAffimed Presentation-Mar2020 Final-1 PDFElio GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Healthy Sleep FsDocument4 pagesHealthy Sleep Fsvivek_sharma13No ratings yet
- Neurological Disorders Practice Test QuestionsDocument6 pagesNeurological Disorders Practice Test QuestionsBenedict AlvarezNo ratings yet
- National Guidelines For HIV Care and Treatment 2021Document556 pagesNational Guidelines For HIV Care and Treatment 2021Moin PandithNo ratings yet
- Ivan Report Legal MedicineDocument41 pagesIvan Report Legal MedicineJohn Ivan GabisNo ratings yet
- Documentation Dissection: New Patient Visit OafDocument3 pagesDocumentation Dissection: New Patient Visit OaftestNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic HepatitisDocument72 pagesAcute and Chronic HepatitisArun George100% (3)
- Lane 2003Document324 pagesLane 2003GheryNo ratings yet
- Guidline of Management of Porta CathDocument8 pagesGuidline of Management of Porta CathroncekeyNo ratings yet
- Care HospitalDocument2 pagesCare Hospitalaryan.agarwal1586No ratings yet
- Client Intake Form - NailsDocument2 pagesClient Intake Form - NailsGGenZ ConsultingNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2006-2007 FullDocument56 pagesAnnual Report 2006-2007 FullSt George's Healthcare NHS TrustNo ratings yet
- Mentor: DR - CHETHANA Pediatric Nephrologist Indira Gandhi Institute of Child HealthDocument41 pagesMentor: DR - CHETHANA Pediatric Nephrologist Indira Gandhi Institute of Child HealthVishalSapateNo ratings yet
- Propofol Infusion Syndrome PDFDocument3 pagesPropofol Infusion Syndrome PDFPGI AnaesthesiaNo ratings yet
- Fibromyalgia and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome - Seven Proven Steps To Less Pain and More EnergyDocument196 pagesFibromyalgia and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome - Seven Proven Steps To Less Pain and More EnergyLyssa Jada-Marie CarterNo ratings yet
- Law and Ethics in Medical PracticeDocument5 pagesLaw and Ethics in Medical Practiceandersonmack047No ratings yet
- CARMS Timeline 2023-2024Document3 pagesCARMS Timeline 2023-2024haykalkNo ratings yet
- 2004, Vol.6, No.4, Pediatric Surgery PDFDocument95 pages2004, Vol.6, No.4, Pediatric Surgery PDFAnty Dewi Sarty RanyabarNo ratings yet
- Cronic Heart Failure - EscDocument55 pagesCronic Heart Failure - EscRisti Graharti100% (1)
- Colon CancerDocument14 pagesColon CancerCherrymae BenzonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management of Patients With Anemia - 01Document38 pagesNursing Care Management of Patients With Anemia - 01Sionur 00No ratings yet
- DissolutionDocument14 pagesDissolutionLePetitCeriseNo ratings yet
- WWW Dermiqque Co Uk Profhilo TreatmentDocument5 pagesWWW Dermiqque Co Uk Profhilo TreatmentDer miqqueNo ratings yet
- Statins and DiabetesDocument9 pagesStatins and DiabetesJonathan TorresNo ratings yet
- Ne 35 4 2010 04 16 Smith 200117 SDC1Document28 pagesNe 35 4 2010 04 16 Smith 200117 SDC1Gunawan SusantoNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument28 pagesMeningitisMarcelo Fabian Lopez Santa CruzNo ratings yet
- Do Not Resuscitate Confirmation Form: To Direct The Practice of Paramedics and Firefighters After February 1, 2008Document2 pagesDo Not Resuscitate Confirmation Form: To Direct The Practice of Paramedics and Firefighters After February 1, 2008eschiuNo ratings yet
- Guna - Lumbar: Clinical IndicationsDocument5 pagesGuna - Lumbar: Clinical Indicationsheywally07No ratings yet
Ritemed Losartan: Manufacturer Info
Ritemed Losartan: Manufacturer Info
Uploaded by
Angie MandeoyaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ritemed Losartan: Manufacturer Info
Ritemed Losartan: Manufacturer Info
Uploaded by
Angie MandeoyaCopyright:
Available Formats
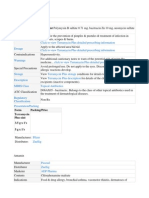
RiteMED Losartan
Concise Prescribing Info Manufacturer Info
Concise Prescribing Info
Manufacturer
RiteMED
Distributor
United Lab
Contents
Losartan K
Indications / Uses
Monotherapy or in combination w/ other antihypertensive agents for the treatment of HTN.
Dosage / Direction for Use
HTN Adult Initial & maintenance dose: 50 mg once daily, may be increased to 100 mg once
daily. Patients w/ intravascular vol-depletion eg, those treated w/ high-dose diuretics, history
of liver disease & moderate to severe renal disease 25 mg once daily. Total daily dose: 25-100
mg once or bid. Childn 6 yr Recommended starting dose: 0.7 mg/kg once daily up to a total of
50 mg, 50 kg 50 mg up to a max of 100 mg daily, 20-<50 kg 25 mg up to a max of 50 mg
daily. Hypertensive patients w/ left ventricular hypertrophy Initially 50 mg once daily, add
hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) 12.5 mg daily &/or increased losartan to 100 mg once daily
followed by an increase in HCTZ 25 mg once daily based on BP response.
Administration
May be taken with or without food.
Contraindications
Pregnancy.
Special Precautions
Correct intravascular vol-depletion eg, those treated w/ high-dose diuretics prior to therapy.
Monitor serum K levels in diabetic patients w/ nephropathy. Electrolyte/fluid imbalance.
Reversible changes in renal function, severe CHF, uni- or bilateral renal artery stenosis; history
of liver impairment. Concurrent use w/ K-sparing diuretics, K supplements or salt substitutes
containing K & drugs affecting renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Ischemic cardiopathy or
cerebrovascular disease. Lactation. Neonates, childn w/ GFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 & liver
impairment. Infants w/ history of in utero exposure to losartan.
Side Effects / Adverse Reactions
CV, endocrine, GI, hematologic, liver/biliary; metabolic, musculoskeletal, nervous
system/psychiatric, resp, skin, special senses & urogenital adverse effects. Asthenia, chest pain,
edema, facial edema, fatigue, fever, infection, flu-like disease, orthostatic effects, syncope,
trauma.
Interactions
Lithium; K-sparing diuretics (eg, spirinolactone, triamterene, amiloride), K supplements or K-
containing salt substitutes; NSAIDs including selective COX-2 inhibitors; rifampicin;
fluconazole.
Preg Safety (US)
Category D: There is positive evidence of human foetal risk, but the benefits from use in
pregnant women may be acceptable despite the risk (e.g., if the drug is needed in a life-
threatening situation or for a serious disease for which safer drugs cannot be used or are
ineffective).
MIMS Class
Angiotensin II Antagonists
ATC Classification
C09CA01 - losartan ; Belongs to the class of angiotensin II antagonists. Used in the treatment of
cardiovascular disease.
Regulatory Classification
Rx
Concise Info
Losartan
> Indications
> Dosage Available Brands
> Dosage Details Actimed Lo...
> Hepatic Impairment Aesartan
> Administration Anzar
> Contraindications Arbloc
> Special Precaution Artal
> Adverse Drug Reactions Besartan
> Pregnancy Category (US FDA) Cardizar
> Monitoring Parameters Cozaar
> Overdosage Doxar
> Drug Interactions Dylaran/Dy...
> Mechanism of Action
> Storage
See more brands
> MIMS Class
Other Known Brands
A.R.A.
Actizar
Amozar
Angioten
Angisartan
Blozar
Boie Losar...
Cotenace
Eseflah
Ezartan 50
See more brands
Listed in Dosage.
Indications
Adult : PO HTN 50 mg once daily, may increase to 100 mg/day as single dose or
Dosage in 2 divided doses if needed. Patients w/ intravascular volume depletion: Initial:
25 mg once daily. Heart failure Initial: 12.5 mg once daily, may be doubled at
wkly intervals. Maintenance: 50 mg once daily. Max: 150 mg once daily.
Diabetic nephropathy in Type 2 DM Initial: 50 mg once daily, may increase to
100 mg once daily depending on BP response.
Oral
Dosage Details Hypertension
Adult: 50 mg once daily, may increase to 100 mg/day as single dose or in 2
divided doses if needed. Patients w/ intravascular volume depletion: Initially,
25 mg once daily.
Child: 6 yr 20-50 kg: Initially, 0.7 mg/kg. Max: 50 mg/day; >50 kg: Initially, 1.4
mg/kg. Max: 100 mg/day.
Elderly: >75 yr Initially, 25 mg/day.
Oral
Diabetic nephropathy in Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Adult: Initially, 50 mg once daily, may increase to 100 mg once daily depending
on BP response.
Elderly: >75 yr Initially, 25 mg/day.
Oral
Heart failure
Adult: Initially, 12.5 mg once daily, may be doubled at wkly intervals.
Maintenance: 50 mg once daily. Max: 150 mg once daily if tolerated.
Hepatic Hypertension; Diabetic nephropathy in Type 2 diabetes mellitus: Mild or
moderate: Initially, 25 mg once daily. Severe: Contraindicated.
Impairment
May be taken with or without food.
Administration
Concomitant use w/ aliskiren in patients w/ diabetes and renal impairment
Contraindications (GFR <60 mL/min). Severe hepatic impairment. Pregnancy.
Volume-depleted patients including patients on high-dose diuretics. Patients
Special w/ bilateral renal artery stenosis, aortic or mitral stenosis. Renal and mild to
Precautions moderate hepatic impairment. Lactation.
Upper resp infection, nasal congestion, sinusitis, headache, dizziness, back
Adverse Drug pain, leg pain, muscle cramps, asthenia or fatigue, neutropenia, chest pain,
Reactions cough, bronchitis, UTI, diarrhoea, gastritis, anaemia, hypoglycaemia, diabetic
vascular disease, cataracts, cellulitis, hyperkalaemia, myalgia, arthralgia,
hypotension, muscular weakness, hypoaesthesia, infection, knee pain. Rarely,
pruritus, rash, urticaria, angioedema, elevated liver enzyme values,
rhabdomyolysis.
ROUTE(S) : PO
Pregnancy
Category (US
FDA) Category D: There is positive evidence of human foetal risk, but the benefits
from use in pregnant women may be acceptable despite the risk (e.g., if the
drug is needed in a life-threatening situation or for a serious disease for which
safer drugs cannot be used or are ineffective).
Monitoring Monitor BP, electrolytes and renal function.
Parameters
Symptoms: Hypotension, tachycardia, bradycardia (could occur from
Overdosage parasympathetic stimulation). Management: Supportive and symptomatic
treatment. May include immediate admin of activated charcoal after oral
intake.
May decrease plasma levels w/ fluconazole and rifampicin. May increase serum
Drug Interactions lithium levels and toxicity. May antagonise hypotensive effect and increase risk
of renal impairment w/ NSAIDs. Increased risk of hyperkalaemia w/ K-sparing
diuretics (e.g. amiloride, triamterene, spironolactone), K supplements or K-
containing salt substitutes.
Potentially Fatal: May increase nephrotoxic, hyperkalaemic and hypotensive
effect w/ aliskiren in patients w/ diabetes and renal impairment (GFR <60
mL/min).
Description: Losartan is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist. It selectively and
Mechanism of competitively blocks the vasoconstricting and aldosterone-secreting effects of
Action angiotensin II by selectively antagonising its binding to AT1 receptors.
Onset: 6 hr.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption: Readily absorbed from the GI tract. Bioavailability: 25-33%. Time
to peak plasma concentration: Approx 1 hr (losartan); approx 3-4 hr (active
metabolite).
Distribution: Volume of distribution: 34 L (losartan); 12 L (active metabolite).
Plasma protein binding: >98%.
Metabolism: Metabolised primarily by CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 isoenzymes to
active carboxylic acid metabolite (E-3174).
Excretion: Via urine (approx 4% as unchanged drug; approx 6% as active
metabolite); faeces (as unchanged drug and metabolites). Terminal elimination
half-life: Approx 1.5-2.5 hr (losartan); approx 3-9 hr (E-3174).
Store between 15-30C. Protect from light.
Storage
Angiotensin II Antagonists
MIMS Class
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Nursing Care Plan and Diagnosis For MastectomyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan and Diagnosis For MastectomyAngie Mandeoya100% (2)
- Mechanical VentilationDocument26 pagesMechanical VentilationNirupama Ks91% (11)
- Drugs AnalysisDocument6 pagesDrugs AnalysisPauline CarenNo ratings yet
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDocument5 pagesSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Adult: PO HTN Initial: 50-100 Mg/day in Single or Divided Doses Increase SlowlyDocument3 pagesAdult: PO HTN Initial: 50-100 Mg/day in Single or Divided Doses Increase SlowlyJoanna Marie Lumbre BalbiranNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - SpironolactoneDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY - SpironolactoneMarianne Claire P. Bartolome50% (2)
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Enalapril: Indications and DosageDocument18 pagesEnalapril: Indications and Dosageshahera rosdiNo ratings yet
- Obat ObgynDocument8 pagesObat ObgynMuhammad Naqiuddin JalaluddinNo ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument9 pagesFINAL Drug StudyKristen Leigh MarianoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudyCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Lovastatin PDFDocument3 pagesLovastatin PDFHannaNo ratings yet
- LOSARTANDocument19 pagesLOSARTANRani SujithNo ratings yet
- Dulcolax® (Adult Supp) : ConstipationDocument8 pagesDulcolax® (Adult Supp) : ConstipationStephany Rae MamauagNo ratings yet
- Dulcolax® (Adult Supp) : ConstipationDocument8 pagesDulcolax® (Adult Supp) : ConstipationStephany Rae MamauagNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Drug Name Classifications Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing Responsibility CnsDocument4 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Classifications Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing Responsibility CnsMarielle SorianoNo ratings yet
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFranco ObedozaNo ratings yet
- Combizar Drug StudyDocument6 pagesCombizar Drug StudymrnmrsllNo ratings yet
- Lisinopril, TAB: Generic Name of Medication: Brand/trade Name of MedicationDocument6 pagesLisinopril, TAB: Generic Name of Medication: Brand/trade Name of MedicationCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- Hemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Document4 pagesHemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Stacy MC PelitoNo ratings yet
- 13 Drug StudyDocument6 pages13 Drug StudyRachel Yvonne Cabacungan100% (1)
- LisinoprilDocument3 pagesLisinoprilLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Drug Study For ITPDocument25 pagesDrug Study For ITPMary Ann QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyQueenie Gail Duarte RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ko ToDocument4 pagesDrug Study Ko ToGian Carlo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Document13 pagesEmergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Marichu BajadoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyRai D. MacapantonNo ratings yet
- See Full Prescribing Information For Complete Boxed WarningDocument39 pagesSee Full Prescribing Information For Complete Boxed WarningsadafNo ratings yet
- Casas - Mood StabilizersDocument16 pagesCasas - Mood StabilizersKarl Kuis SantanderNo ratings yet
- MM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM MDocument9 pagesMM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM M배기숭No ratings yet
- RamiprilDocument3 pagesRamiprilNovi YulianaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyjazmine_caritos100% (2)
- Banocide and Banocide ForteDocument10 pagesBanocide and Banocide ForteJosephNo ratings yet
- RiteMED MetoprololDocument7 pagesRiteMED MetoprololAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKaguraNo ratings yet
- Lisinopril PDFDocument3 pagesLisinopril PDFHannaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudySharwen_R_Rome_5572No ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument3 pagesDrug StudiesSteve PerezNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument4 pagesAcetazolamideAnkit RuhilNo ratings yet
- General: Genetic Implications: Pronunciation: Maz Trade Name(s)Document7 pagesGeneral: Genetic Implications: Pronunciation: Maz Trade Name(s)jenm1228No ratings yet
- CHN Drug StudyDocument10 pagesCHN Drug StudyJoshua Cyryll ComiaNo ratings yet
- Pedia Ward Drug Study...Document12 pagesPedia Ward Drug Study...Sheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- METFORMINDocument4 pagesMETFORMINkhesler BacallaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY SpironolactoneDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY SpironolactoneJerremy LuqueNo ratings yet
- Generic: Acetazolamide Brand: DiamoxDocument33 pagesGeneric: Acetazolamide Brand: DiamoxAshley Topp100% (1)
- Furosemide Mims EngDocument17 pagesFurosemide Mims EngNur Ilmi SofiahNo ratings yet
- Levofloxacin-1Document31 pagesLevofloxacin-1Fallen AngelNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For End Stage Renal DiseaseDocument16 pagesDrug Study For End Stage Renal DiseaselenecarglbnNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Description Classificat Ion Indication Contraindica Tion Side Effects Nursing Responsibilit IesDocument8 pagesName of Drug Description Classificat Ion Indication Contraindica Tion Side Effects Nursing Responsibilit IesJimmy Merez Jr.No ratings yet
- LalalalaaaaDocument6 pagesLalalalaaaaRobert LeblancNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyCharm LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPedia Drug StudyPeetah PanNo ratings yet
- Drug OrderDocument4 pagesDrug OrderVic MagtotoNo ratings yet
- Fluvastatin - Drug StudyDocument1 pageFluvastatin - Drug StudyKevin H. MilanesNo ratings yet
- Assignment: ON AntilipidemicsDocument15 pagesAssignment: ON AntilipidemicsMansi DabolaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyTeanu Jose Gabrillo TamayoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument15 pagesDrug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesitsmechachaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Prioritization: Speaker: Vicki RobertsonDocument2 pagesConcepts in Prioritization: Speaker: Vicki RobertsonAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Harri AnnaDocument57 pagesHarri AnnaAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Risk For Aspiration: Risk For Aspiration: at Risk For Entry of Gastrointestinal Secretions, Oropharyngeal SecretionDocument6 pagesRisk For Aspiration: Risk For Aspiration: at Risk For Entry of Gastrointestinal Secretions, Oropharyngeal SecretionAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- 50 Motivational Nursing Quotes PDFDocument6 pages50 Motivational Nursing Quotes PDFAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- NCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyDocument3 pagesNCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- NCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsDocument9 pagesNCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsAngie Mandeoya100% (1)
- Day 2 QuizDocument2 pagesDay 2 QuizAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Respondeat Superior PDFDocument1 pageRespondeat Superior PDFAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- I. Calculating IV Flow Rates: Day 2 AnswerDocument2 pagesI. Calculating IV Flow Rates: Day 2 AnswerAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- 000print or NCPDocument6 pages000print or NCPAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Pharm 1.31 SOCK Method For Learning Pharm 1Document1 pagePharm 1.31 SOCK Method For Learning Pharm 1Angie Mandeoya100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Acute Head InjuryDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Acute Head InjuryAngie Mandeoya67% (3)
- GastritisDocument16 pagesGastritisAngie Mandeoya50% (2)
- Drug Study: 75 Yrs. OldDocument3 pagesDrug Study: 75 Yrs. OldAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- FINAL - References & AppendicesDocument23 pagesFINAL - References & AppendicesAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Guide: St. Anthony's College Nursing DepartmentDocument10 pagesNursing Process Guide: St. Anthony's College Nursing DepartmentAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Different Disasters: Erica G. Mandeoya Grade 7-JadeDocument3 pagesCompilation of Different Disasters: Erica G. Mandeoya Grade 7-JadeAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Exam SmpleDocument18 pagesPsychiatric Exam SmpleAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- 50 Motivational Nursing QuotesDocument6 pages50 Motivational Nursing QuotesAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Theories of Human Nature Key Issues Mikael Stenmark 2012Document16 pagesTheories of Human Nature Key Issues Mikael Stenmark 2012Angie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument7 pages1 PBAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Explore LapDocument5 pagesExplore LapAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Labor: About Privacy and Cookie Policy Disclaimer ContactDocument11 pagesLabor: About Privacy and Cookie Policy Disclaimer ContactAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- InfectionDocument4 pagesInfectionAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Erica G. Mandeoya Erica G. Mandeoya Erica G. Mandeoya: Grade 7-Jade Grade 7 - Jade Grade 7 - JadeDocument1 pageErica G. Mandeoya Erica G. Mandeoya Erica G. Mandeoya: Grade 7-Jade Grade 7 - Jade Grade 7 - JadeAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Men's Knowledge of Labor and ChildbirthDocument6 pagesMen's Knowledge of Labor and ChildbirthAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- TheoriesDocument2 pagesTheoriesAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Leong Et Al-2004-BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyDocument2 pagesLeong Et Al-2004-BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Toxic Multinodular Goiter Physical ExaminationDocument2 pagesToxic Multinodular Goiter Physical ExaminationAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Jalan Nafas Pada Pasien Dengan Tumor Mandibula: Laporan KasusDocument27 pagesManajemen Jalan Nafas Pada Pasien Dengan Tumor Mandibula: Laporan KasusMulia AndaraNo ratings yet
- Affimed Presentation-Mar2020 Final-1 PDFDocument22 pagesAffimed Presentation-Mar2020 Final-1 PDFElio GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Healthy Sleep FsDocument4 pagesHealthy Sleep Fsvivek_sharma13No ratings yet
- Neurological Disorders Practice Test QuestionsDocument6 pagesNeurological Disorders Practice Test QuestionsBenedict AlvarezNo ratings yet
- National Guidelines For HIV Care and Treatment 2021Document556 pagesNational Guidelines For HIV Care and Treatment 2021Moin PandithNo ratings yet
- Ivan Report Legal MedicineDocument41 pagesIvan Report Legal MedicineJohn Ivan GabisNo ratings yet
- Documentation Dissection: New Patient Visit OafDocument3 pagesDocumentation Dissection: New Patient Visit OaftestNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic HepatitisDocument72 pagesAcute and Chronic HepatitisArun George100% (3)
- Lane 2003Document324 pagesLane 2003GheryNo ratings yet
- Guidline of Management of Porta CathDocument8 pagesGuidline of Management of Porta CathroncekeyNo ratings yet
- Care HospitalDocument2 pagesCare Hospitalaryan.agarwal1586No ratings yet
- Client Intake Form - NailsDocument2 pagesClient Intake Form - NailsGGenZ ConsultingNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2006-2007 FullDocument56 pagesAnnual Report 2006-2007 FullSt George's Healthcare NHS TrustNo ratings yet
- Mentor: DR - CHETHANA Pediatric Nephrologist Indira Gandhi Institute of Child HealthDocument41 pagesMentor: DR - CHETHANA Pediatric Nephrologist Indira Gandhi Institute of Child HealthVishalSapateNo ratings yet
- Propofol Infusion Syndrome PDFDocument3 pagesPropofol Infusion Syndrome PDFPGI AnaesthesiaNo ratings yet
- Fibromyalgia and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome - Seven Proven Steps To Less Pain and More EnergyDocument196 pagesFibromyalgia and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome - Seven Proven Steps To Less Pain and More EnergyLyssa Jada-Marie CarterNo ratings yet
- Law and Ethics in Medical PracticeDocument5 pagesLaw and Ethics in Medical Practiceandersonmack047No ratings yet
- CARMS Timeline 2023-2024Document3 pagesCARMS Timeline 2023-2024haykalkNo ratings yet
- 2004, Vol.6, No.4, Pediatric Surgery PDFDocument95 pages2004, Vol.6, No.4, Pediatric Surgery PDFAnty Dewi Sarty RanyabarNo ratings yet
- Cronic Heart Failure - EscDocument55 pagesCronic Heart Failure - EscRisti Graharti100% (1)
- Colon CancerDocument14 pagesColon CancerCherrymae BenzonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management of Patients With Anemia - 01Document38 pagesNursing Care Management of Patients With Anemia - 01Sionur 00No ratings yet
- DissolutionDocument14 pagesDissolutionLePetitCeriseNo ratings yet
- WWW Dermiqque Co Uk Profhilo TreatmentDocument5 pagesWWW Dermiqque Co Uk Profhilo TreatmentDer miqqueNo ratings yet
- Statins and DiabetesDocument9 pagesStatins and DiabetesJonathan TorresNo ratings yet
- Ne 35 4 2010 04 16 Smith 200117 SDC1Document28 pagesNe 35 4 2010 04 16 Smith 200117 SDC1Gunawan SusantoNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument28 pagesMeningitisMarcelo Fabian Lopez Santa CruzNo ratings yet
- Do Not Resuscitate Confirmation Form: To Direct The Practice of Paramedics and Firefighters After February 1, 2008Document2 pagesDo Not Resuscitate Confirmation Form: To Direct The Practice of Paramedics and Firefighters After February 1, 2008eschiuNo ratings yet
- Guna - Lumbar: Clinical IndicationsDocument5 pagesGuna - Lumbar: Clinical Indicationsheywally07No ratings yet