Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M6u4 Arizonaex
M6u4 Arizonaex
Uploaded by
api-302577842Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Robert Potter - Tony Binns - Jennifer A. Elliott - Etienne Nel - David W. Smith - Geographies of Development - An Introduction To Development Studies-Routledge (2018)Document662 pagesRobert Potter - Tony Binns - Jennifer A. Elliott - Etienne Nel - David W. Smith - Geographies of Development - An Introduction To Development Studies-Routledge (2018)Andreas100% (1)
- MathDocument184 pagesMathZachary SchusterNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Learner's Activity Sheet Assessment ChecklistDocument16 pagesMathematics: Learner's Activity Sheet Assessment ChecklistDo HaNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Mathematics SyllabusDocument2 pages7th Grade Mathematics SyllabusDAizy AnnNo ratings yet
- WEEK 9.2. Lesson Plan Solution Graphing Linear InequalitiesDocument6 pagesWEEK 9.2. Lesson Plan Solution Graphing Linear InequalitiesEdelyn PaulinioNo ratings yet
- Sweet Algebra TaskDocument10 pagesSweet Algebra Taskapi-302577842No ratings yet
- BU1 Technical ManualDocument16 pagesBU1 Technical ManualkevinjonescomNo ratings yet
- M6u7 ArizonaexDocument8 pagesM6u7 Arizonaexapi-302577842No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Sorico Math Unit 1 1 2013-2014Document3 pagesGrade 8 Sorico Math Unit 1 1 2013-2014api-233707670100% (1)
- Articulated by Grade LevelDocument45 pagesArticulated by Grade LevelForrest FlenerNo ratings yet
- 6th UnpackingDocument33 pages6th UnpackingJESUS ANTONIO RAMOS MORONNo ratings yet
- Solving Equations With One Variable: Grade 8 Mathematics, Quarter, Unit 1.3Document5 pagesSolving Equations With One Variable: Grade 8 Mathematics, Quarter, Unit 1.3api-270891801No ratings yet
- Grade 6 Sorico Math Unit 3 1 2013-2014Document5 pagesGrade 6 Sorico Math Unit 3 1 2013-2014api-233707670No ratings yet
- Grade 6 Sorico Math Unit 2 3 2013-2014Document4 pagesGrade 6 Sorico Math Unit 2 3 2013-2014api-233707670No ratings yet
- Mathematics - Grade 6: X Y) To Describe Relationships BetweenDocument7 pagesMathematics - Grade 6: X Y) To Describe Relationships Betweenapi-365969613No ratings yet
- Grade 4 Unit 6 Scope and SequenceDocument8 pagesGrade 4 Unit 6 Scope and SequencereemaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan MathDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Mathapi-610287873No ratings yet
- New Jersey Student Learning Standards Mathematics - Grade 6Document18 pagesNew Jersey Student Learning Standards Mathematics - Grade 6Terrence AkinolaNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1 Lesson 20 LessonDocument6 pagesAlgebra 1 Lesson 20 Lessonapi-379755793No ratings yet
- Final Project of Record AssessmentDocument29 pagesFinal Project of Record Assessmentapi-208358319No ratings yet
- Assessment Project of RecordDocument19 pagesAssessment Project of Recordapi-208358319No ratings yet
- Mathematics Framework For California Public Schools: Kindergarten Through Grade TwelveDocument45 pagesMathematics Framework For California Public Schools: Kindergarten Through Grade TwelveBin BinNo ratings yet
- Math 6 Framework Standards For 2016 17Document13 pagesMath 6 Framework Standards For 2016 17api-302577842No ratings yet
- Module 4 MathDocument7 pagesModule 4 Mathgracesilvaespiritu1202No ratings yet
- Ccgps Math 6 6thgrade Unit4seDocument28 pagesCcgps Math 6 6thgrade Unit4seapi-239312188No ratings yet
- CC2 CH 6 TVDocument122 pagesCC2 CH 6 TVngyncloud100% (2)
- Week 2 Day 3Document6 pagesWeek 2 Day 3AJ ManialungNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Flip BookDocument100 pages7th Grade Flip BookChris DelawareNo ratings yet
- I-Day 32Document4 pagesI-Day 32Rainman InsanityNo ratings yet
- Math Year PlanDocument3 pagesMath Year Planapi-262109071No ratings yet
- Grade 7 Sorico Math Unit 3 3 2013-2014Document4 pagesGrade 7 Sorico Math Unit 3 3 2013-2014api-233707670No ratings yet
- Gse Math Unit 4Document79 pagesGse Math Unit 4api-256719324No ratings yet
- Test 1 PCK - EMTS71024 - MKT - 2023 - Memo - DiscussionDocument7 pagesTest 1 PCK - EMTS71024 - MKT - 2023 - Memo - DiscussionAbraham NghuleleNo ratings yet
- Math 6 Common Core Syllabus 2015-2016Document8 pagesMath 6 Common Core Syllabus 2015-2016api-262200380No ratings yet
- Grade 6 Sorico Math Unit 1 2 2013-2014Document5 pagesGrade 6 Sorico Math Unit 1 2 2013-2014api-233707670No ratings yet
- LP - MATH 9 Q1 m4Document6 pagesLP - MATH 9 Q1 m4Asmira CoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Day 3Document5 pagesWeek 2 Day 3Acire NonacNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Sorico Math Unit 2 1 2013-2014Document5 pagesGrade 8 Sorico Math Unit 2 1 2013-2014api-233707670No ratings yet
- Grade 2 Sorico Math Unit 1 1 2013-2014Document6 pagesGrade 2 Sorico Math Unit 1 1 2013-2014api-233707670No ratings yet
- Monday Prepared By: Samantha Krozek Grade: 5th Subject: Math Topic: Base Ten Division Common Core StandardDocument12 pagesMonday Prepared By: Samantha Krozek Grade: 5th Subject: Math Topic: Base Ten Division Common Core Standardapi-507217467No ratings yet
- 7 Grade Mathematics: What Is The Purpose of This Document?Document28 pages7 Grade Mathematics: What Is The Purpose of This Document?Johnny CoNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Mississippi College-And Career-Readiness Standards For Mathematics RCSD Quarter 1Document4 pagesGrade 7 Mississippi College-And Career-Readiness Standards For Mathematics RCSD Quarter 1Greg WalkerNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade UnpackedDocument45 pages7th Grade Unpackedapi-263084168No ratings yet
- FREEMATHCommonCoreStateStandards68Checklist 1 PDFDocument19 pagesFREEMATHCommonCoreStateStandards68Checklist 1 PDFKatt DuangmalaiNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Sorico Math Unit 1 1 2013-2014Document4 pagesGrade 3 Sorico Math Unit 1 1 2013-2014api-233707670100% (1)
- Exponential FunctionsDocument7 pagesExponential FunctionshneddoNo ratings yet
- I Can Standards 6ee5-9Document5 pagesI Can Standards 6ee5-9api-337275999No ratings yet
- Grade 7 Sorico Math Unit 2 1 2013-2014Document4 pagesGrade 7 Sorico Math Unit 2 1 2013-2014api-233707670100% (1)
- 6th Grade Common Core1Document2 pages6th Grade Common Core1api-292312023No ratings yet
- Alexa Iandolo - Ciee 3290 - Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesAlexa Iandolo - Ciee 3290 - Lesson Planapi-354589761No ratings yet
- Math Test 1 PDFDocument64 pagesMath Test 1 PDFAko Si JoannaNo ratings yet
- GR 8 Illustrated PracticesDocument3 pagesGR 8 Illustrated PracticesManas PatilNo ratings yet
- Grade-Six Chapter: Mathematics FrameworkDocument53 pagesGrade-Six Chapter: Mathematics Frameworkvenkatachalam.jNo ratings yet
- DLP 2023Document3 pagesDLP 2023Aiza MaltoNo ratings yet
- Whole Numbers Unit PlanDocument10 pagesWhole Numbers Unit Planapi-435456987No ratings yet
- A C O G 7: Ourse Utline FOR RadeDocument27 pagesA C O G 7: Ourse Utline FOR RadeKaela Sophia AndalisNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Sorico Math Unit 1 3 2013-2014Document4 pagesGrade 7 Sorico Math Unit 1 3 2013-2014api-233707670No ratings yet
- lp2 - Systems of Equations Their SolutionsDocument7 pageslp2 - Systems of Equations Their Solutionsapi-353551219No ratings yet
- Manhattan College Education Department Lesson Plan TemplateDocument9 pagesManhattan College Education Department Lesson Plan Templateapi-534924709No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 HandoutDocument5 pagesLecture 1 Handoutapi-450537250No ratings yet
- M6u7 ArizonaexDocument8 pagesM6u7 Arizonaexapi-302577842No ratings yet
- M6u4 Vocab CardsDocument12 pagesM6u4 Vocab Cardsapi-302577842No ratings yet
- Key Standards: Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Framework Student EditionDocument2 pagesKey Standards: Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Framework Student Editionapi-302577842No ratings yet
- Rational ExplorationsDocument2 pagesRational Explorationsapi-302577842No ratings yet
- M6u7 Outline Overview 2016Document20 pagesM6u7 Outline Overview 2016api-302577842No ratings yet
- 08 Math Homework-Taken From Students WorkbookDocument1 page08 Math Homework-Taken From Students Workbookapi-302577842No ratings yet
- M6u2 Conceptual Foundations 1Document5 pagesM6u2 Conceptual Foundations 1api-302577842No ratings yet
- M6u4 ConceptmapDocument1 pageM6u4 Conceptmapapi-302577842No ratings yet
- M6u1 Vocab CardsDocument24 pagesM6u1 Vocab Cardsapi-302577842No ratings yet
- Unit 9 Post Test ReviewDocument3 pagesUnit 9 Post Test Reviewapi-302577842No ratings yet
- Integer Addition Practice ADocument1 pageInteger Addition Practice Aapi-302577842No ratings yet
- Math Whiz Unit 3 MCDocument2 pagesMath Whiz Unit 3 MCapi-302577842No ratings yet
- CE441 Class Lecture 01Document9 pagesCE441 Class Lecture 01ASHJAEE MANSIB CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- Statistical Methods For Spatial Data AnalysisDocument3 pagesStatistical Methods For Spatial Data Analysissakali ali0% (1)
- Application of Irradiation For Food Preservation: Seminar ONDocument19 pagesApplication of Irradiation For Food Preservation: Seminar ONPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- Ag Test Package FormatDocument25 pagesAg Test Package FormatoparoystNo ratings yet
- Nepal National Building Code: Draft Final NBC 205: 2012Document52 pagesNepal National Building Code: Draft Final NBC 205: 2012Sudan ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Tacha's ReusmeDocument2 pagesTacha's ReusmeJames HamptonNo ratings yet
- The Dino GameDocument1 pageThe Dino Game296 004 Aditya ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Anullment CATHOLIC TRIBUNALDocument20 pagesAnullment CATHOLIC TRIBUNALMons Jr BaturianoNo ratings yet
- Jeanette Novakovich Formal ResumeDocument4 pagesJeanette Novakovich Formal ResumeJ'etté NovakovichNo ratings yet
- Bill of QuantityDocument6 pagesBill of QuantityKhairoden SangcopanNo ratings yet
- Earth Dams Foundation & Earth Material InvestigationDocument111 pagesEarth Dams Foundation & Earth Material Investigationmustafurade1No ratings yet
- List Product YellowDocument10 pagesList Product YellowfitriNo ratings yet
- Kansas Academy of Science: Info/about/policies/terms - JSPDocument6 pagesKansas Academy of Science: Info/about/policies/terms - JSPKeily VilcarromeroNo ratings yet
- Iso 7966 1993Document11 pagesIso 7966 1993Sci KelayNo ratings yet
- 42 Annual Conference of Linguistic Society of Nepal (42nd LSN)Document9 pages42 Annual Conference of Linguistic Society of Nepal (42nd LSN)Nani Babu GhimireNo ratings yet
- The Spirit of Jugaad / Bricolage For Enhanced Corporate EntrepreneurshipDocument20 pagesThe Spirit of Jugaad / Bricolage For Enhanced Corporate EntrepreneurshippanditpreachesNo ratings yet
- Is Codes ListDocument37 pagesIs Codes Listmoondonoo7No ratings yet
- Introduction To Management ScienceDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Management ScienceVenice Marie Arroyo100% (1)
- Product Description: Mark II Electric Fire Pump ControllersDocument2 pagesProduct Description: Mark II Electric Fire Pump ControllersBill Kerwin Nava JimenezNo ratings yet
- Model Course 1.07 PDFDocument75 pagesModel Course 1.07 PDFShiena CamineroNo ratings yet
- Allen Bradley 160 C SeriesDocument28 pagesAllen Bradley 160 C SeriesTihomir Matulić100% (1)
- Staff Data Format-AUCDocument1 pageStaff Data Format-AUCSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - PF and Parallel AC CircuitsDocument12 pagesLesson 4 - PF and Parallel AC CircuitsMichael SalvahanNo ratings yet
- Item Wise Rate TenderDocument5 pagesItem Wise Rate TenderB-05 ISHA PATELNo ratings yet
- Solution To Microwave Engineering Pozar Chapter 14 Exercise 17 With MATLABDocument3 pagesSolution To Microwave Engineering Pozar Chapter 14 Exercise 17 With MATLABJohn Bofarull GuixNo ratings yet
- D. Raghuram: Work ExperienceDocument3 pagesD. Raghuram: Work ExperienceNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Adam Izdebski & Michael Mulryan - Environment and Society in The Long LateDocument7 pagesAdam Izdebski & Michael Mulryan - Environment and Society in The Long Latecarlos murciaNo ratings yet
- Excavation TrainingDocument60 pagesExcavation TrainingFahad Abdul HaqNo ratings yet
M6u4 Arizonaex
M6u4 Arizonaex
Uploaded by
api-302577842Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
M6u4 Arizonaex
M6u4 Arizonaex
Uploaded by
api-302577842Copyright:
Available Formats
Arizona Mathematics Standards Articulated by Grade Level
Grade 6
Articulated by Grade Level
Approved by the Arizona State Board of Education
June 28, 2010
Explanations and Examples Grade 6
Arizona Department of Education: Standards and Assessment Division 1 Approved 6.28.10
Updated 5.20.11
Arizona Mathematics Standards Articulated by Grade Level
Grade 6
Grade 6 Overview
Ratios and Proportional Relationships (RP) Mathematical Practices (MP)
Understand ratio concepts and use ratio reasoning to solve 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them.
problems. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others.
The Number System (NS) 4. Model with mathematics.
Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and 5. Use appropriate tools strategically.
division to divide fractions by fractions. 6. Attend to precision.
Compute fluently with multi-digit numbers and find common 7. Look for and make use of structure.
factors and multiples. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning.
Apply and extend previous understandings of numbers to the
system of rational numbers.
Expressions and Equations (EE)
Apply and extend previous understandings of arithmetic to
algebraic expressions.
Reason about and solve one-variable equations and
inequalities.
Represent and analyze quantitative relationships between
dependent and independent variables.
Geometry (G)
Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area,
surface area, and volume.
Statistics and Probability (SP)
Develop understanding of statistical variability.
Summarize and describe distributions.
Explanations and Examples Grade 6
Arizona Department of Education: Standards and Assessment Division 2 Approved 6.28.10
Updated 5.20.11
Arizona Mathematics Standards Articulated by Grade Level
Expressions and Equations (EE)
Reason about and solve one-variable equations and inequalities.
Standards Mathematical Practices Explanations and Examples
Students are expected to:
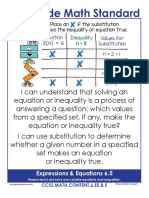
6.EE.5. Understand solving an equation or 6.MP.1. Make sense of Beginning experiences in solving equations should require students to
inequality as a process of answering a question: problems and persevere in understand the meaning of the equation as well as the question being asked.
which values from a specified set, if any, make solving them. Solving equations using reasoning and prior knowledge should be required of
the equation or inequality true? Use substitution students to allow them to develop effective strategies such as using reasoning,
to determine whether a given number in a 6.MP.2. Reason abstractly and fact families, and inverse operations. Students may use balance models in
specified set makes an equation or inequality quantitatively. representing and solving equations and inequalities.
true.
6.MP.4. Model with Consider the following situation: Joey had 26 papers in his desk. His teacher
Connection: 6-8.RST.7 mathematics. gave him some more and now he has 100. How many papers did his teacher
give him?
6.MP.7. Look for and make use This situation can be represented by the equation 26 + n = 100 where n is the
of structure. number of papers the teacher gives to Joey. This equation can be stated as
some number was added to 26 and the result was 100. Students ask
themselves What number was added to 26 to get 100? to help them determine
the value of the variable that makes the equation true. Students could use
several different strategies to find a solution to the problem.
o Reasoning: 26 + 70 is 96. 96 + 4 is 100, so the number added to 26
to get 100 is 74.
o Use knowledge of fact families to write related equations:
n + 26 = 100, 100 - n = 26, 100 - 26 = n. Select the equation that
helps you find n easily.
o Use knowledge of inverse operations: Since subtraction undoes
addition then subtract 26 from 100 to get the numerical value of n
o Scale model: There are 26 blocks on the left side of the scale and
100 blocks on the right side of the scale. All the blocks are the same
size. 74 blocks need to be added to the left side of the scale to
make the scale balance.
o Bar Model: Each bar represents one of the values. Students use this
visual representation to demonstrate that 26 and the unknown value
together make 100. 100
Continued on next page 26 n
Explanations and Examples Grade 6
Arizona Department of Education: Standards and Assessment Division 23 Approved 6.28.10
Updated 5.20.11
Arizona Mathematics Standards Articulated by Grade Level
Expressions and Equations (EE)
Reason about and solve one-variable equations and inequalities.
Standards Mathematical Practices Explanations and Examples
Students are expected to:
Examples:
The equation 0.44s 11 where s represents the number of stamps in a
booklet. The booklet of stamps costs 11 dollars and each stamp costs
44 cents. How many stamps are in the booklet? Explain the strategies
you used to determine your answer. Show that your solution is correct
using substitution.
Twelve is less than 3 times another number can be shown by the
inequality 12 3n . What numbers could possibly make this a true
statement?
6.EE.6. Use variables to represent numbers 6.MP.2. Reason abstractly and Connecting writing expressions with story problems and/or drawing pictures will
and write expressions when solving a real-world quantitatively. give students a context for this work. It is important for students to read algebraic
or mathematical problem; understand that a expressions in a manner that reinforces that the variable represents a number.
variable can represent an unknown number, or, 6.MP.4. Model with
Examples:
depending on the purpose at hand, any number mathematics.
Maria has three more than twice as many crayons as Elizabeth. Write
in a specified set.
an algebraic expression to represent the number of crayons that Maria
6.MP.7. Look for and make use has.
Connection: 6-8.RST.4 of structure. (Solution: 2c + 3 where c represents the number of crayons that
Elizabeth has.)
An amusement park charges $28 to enter and $0.35 per ticket. Write an
algebraic expression to represent the total amount spent.
(Solution: 28 + 0.35t where t represents the number of tickets
purchased)
Andrew has a summer job doing yard work. He is paid $15 per hour and
a $20 bonus when he completes the yard. He was paid $85 for
completing one yard. Write an equation to represent the amount of
money he earned.
(Solution: 15h + 20 = 85 where h is the number of hours worked)
Describe a problem situation that can be solved using the equation
2c + 3 = 15; where c represents the cost of an item
Bill earned $5.00 mowing the lawn on Saturday. He earned more money
on Sunday. Write an expression that shows the amount of money Bill
has earned. (Solution: $5.00 + n)
Explanations and Examples Grade 6
Arizona Department of Education: Standards and Assessment Division 24 Approved 6.28.10
Updated 5.20.11
Arizona Mathematics Standards Articulated by Grade Level
Expressions and Equations (EE)
Reason about and solve one-variable equations and inequalities.
Standards Mathematical Practices Explanations and Examples
Students are expected to:
6.EE.7. Solve real-world and mathematical 6.MP.1. Make sense of Students create and solve equations that are based on real world situations. It
problems by writing and solving equations of problems and persevere in may be beneficial for students to draw pictures that illustrate the equation in
the form x + p = q and px = q for cases in which solving them. problem situations. Solving equations using reasoning and prior knowledge
p, q and x are all nonnegative rational numbers should be required of students to allow them to develop effective strategies.
6.MP.2. Reason abstractly and
Connection: 6-8.RST.7 quantitatively. Example:
Meagan spent $56.58 on three pairs of jeans. If each pair of jeans costs
6.MP.3. Construct viable the same amount, write an algebraic equation that represents this
arguments and critique the situation and solve to determine how much one pair of jeans cost.
reasoning of others. $56.58
6.MP.4. Model with J J J
mathematics. Sample Solution: Students might say: I created the bar model to show
the cost of the three pairs of jeans. Each bar labeled J is the same size
6.MP.7. Look for and make use because each pair of jeans costs the same amount of money. The bar
of structure. model represents the equation 3J = $56.58. To solve the problem, I
need to divide the total cost of 56.58 between the three pairs of jeans. I
know that it will be more than $10 each because 10 x 3 is only 30 but
less than $20 each because 20 x 3 is 60. If I start with $15 each, I am up
to $45. I have $11.58 left. I then give each pair of jeans $3. Thats $9
more dollars. I only have $2.58 left. I continue until all the money is
divided. I ended up giving each pair of jeans another $0.86. Each pair of
jeans costs $18.86 (15+3+0.86). I double check that the jeans cost
$18.86 each because $18.86 x 3 is $56.58.
Julio gets paid $20 for babysitting. He spends $1.99 on a package of
trading cards and $6.50 on lunch. Write and solve an equation to show
how much money Julio has left.
(Solution: 20 = 1.99 + 6.50 + x, x = $11.51)
20
1.99 6.50 money left over (m)
Explanations and Examples Grade 6
Arizona Department of Education: Standards and Assessment Division 25 Approved 6.28.10
Updated 5.20.11
Arizona Mathematics Standards Articulated by Grade Level
Expressions and Equations (EE)
Reason about and solve one-variable equations and inequalities.
Standards Mathematical Practices Explanations and Examples
Students are expected to:
6.EE.8. Write an inequality of the form x > c or x 6.MP.1. Make sense of Examples:
< c to represent a constraint or condition in a problems and persevere in Graph x 4.
real-world or mathematical problem. Recognize solving them.
that inequalities of the form x > c or x < c have
infinitely many solutions; represent solutions of 6.MP.2. Reason abstractly and
such inequalities on number line diagrams. quantitatively.
Jonas spent more than $50 at an amusement park. Write an inequality
Connection: 6-8.RST.7 6.MP.3. Construct viable to represent the amount of money Jonas spent. What are some possible
arguments and critique the amounts of money Jonas could have spent? Represent the situation on
reasoning of others. a number line.
Less than $200.00 was spent by the Flores family on groceries last
6.MP.4. Model with
month. Write an inequality to represent this amount and graph this
mathematics.
inequality on a number line.
6.MP.7. Look for and make use Solution: 200 > x
of structure.
Explanations and Examples Grade 6
Arizona Department of Education: Standards and Assessment Division 26 Approved 6.28.10
Updated 5.20.11
Arizona Mathematics Standards Articulated by Grade Level
Expressions and Equations (EE)
Represent and analyze quantitative relationships between dependent and independent variables.
Standards Mathematical Practices Explanations and Examples
Students are expected to:
6.EE.9. Use variables to represent two 6.MP.1. Make sense of Students can use many forms to represent relationships between quantities.
quantities in a real-world problem that change in problems and persevere in Multiple representations include describing the relationship using language, a
relationship to one another; write an equation to solving them. table, an equation, or a graph. Translating between multiple representations
express one quantity, thought of as the helps students understand that each form represents the same relationship and
dependent variable, in terms of the other 6.MP.2. Reason abstractly and provides a different perspective on the function.
quantity, thought of as the independent quantitatively.
variable. Analyze the relationship between the Examples:
dependent and independent variables using 6.MP.3. Construct viable What is the relationship between the two variables? Write an expression
graphs and tables, and relate these to the arguments and critique the that illustrates the relationship.
equation. For example, in a problem involving reasoning of others.
motion at constant speed, list and graph x 1 2 3 4
ordered pairs of distances and times, and write y 2.5 5 7.5 10
the equation d = 65t to represent the 6.MP.4. Model with
relationship between distance and time. mathematics.
Use the graph below to describe the change in y as x increases by 1.
Connections: 6.RP.3; 6-8. RST.7; 6.MP.7. Look for and make use
ET06-S1C2-01; ET06-S1C2-02; of structure.
ET06-S1C2-03; ET06-S6C2-03; SC06-S2C2-03
6.MP.8. Look for and express
regularity in repeated
reasoning.
Continued on next page
Explanations and Examples Grade 6
Arizona Department of Education: Standards and Assessment Division 27 Approved 6.28.10
Updated 5.20.11
Arizona Mathematics Standards Articulated by Grade Level
Expressions and Equations (EE)
Represent and analyze quantitative relationships between dependent and independent variables.
Standards Mathematical Practices Explanations and Examples
Students are expected to:
Susan started with $1 in her savings. She plans to add $4 per week to
her savings. Use an equation, table and graph to demonstrate the
relationship between the number of weeks that pass and the amount in
her savings account.
o Language: Susan has $1 in her savings account. She is going to
save $4 each week.
o Equation: y = 4x + 1
o Table:
x y
0 1
1 5
2 9
o Graph:
Explanations and Examples Grade 6
Arizona Department of Education: Standards and Assessment Division 28 Approved 6.28.10
Updated 5.20.11
Arizona Mathematics Standards Articulated by Grade Level
Ratios and Proportional Relationships (RP)
Understand ratio concepts and use ratio reasoning to solve problems.
Standards Mathematical Practices Explanations and Examples
Students are expected to:
6.RP.3. Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve 6.MP.1. Make sense of Examples:
real-world and mathematical problems, e.g., by problems and persevere in Using the information in the table, find the number of yards in 24 feet.
reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape solving them.
diagrams, double number line diagrams, or Feet 3 6 9 15 24
equations. 6.MP.2. Reason abstractly and Yards 1 2 3 5 ?
a. Make tables of equivalent ratios relating quantitatively.
quantities with whole-number There are several strategies that students could use to determine the
measurements, find missing values in the 6.MP.4. Model with solution to this problem.
tables, and plot the pairs of values on the mathematics o Add quantities from the table to total 24 feet (9 feet and 15 feet);
coordinate plane. Use tables to compare therefore the number of yards must be 8 yards (3 yards and 5
ratios. 6.MP.5. Use appropriate tools yards).
b. Solve unit rate problems including those strategically. o Use multiplication to find 24 feet: 1) 3 feet x 8 = 24 feet; therefore 1
involving unit pricing and constant speed. yard x 8 = 8 yards, or 2) 6 feet x 4 = 24 feet; therefore 2 yards x 4 =
For example, if it took 7 hours to mow 4 8 yards.
6.MP.7. Look for and make use
lawns, then at that rate, how many lawns of structure. Compare the number of black to white circles. If the ratio remains the
could be mowed in 35 hours? At what rate
same, how many black circles will you have if you have 60 white circles?
were lawns being mowed?
c. Find a percent of a quantity as a rate per
100 (e.g., 30% of a quantity means 30/100
times the quantity); solve problems Black 4 40 20 60 ?
involving finding the whole, given a part and White 3 30 15 45 60
the percent.
d. Use ratio reasoning to convert If 6 is 30% of a value, what is that value? (Solution: 20)
measurement units; manipulate and
transform units appropriately when 0% 30% ? 100%
multiplying or dividing quantities.
Connections: 6.EE.9; 6-8.RST.7;
ET06-S6C2-03; SC06-S2C2-03
6
Continued on next page
Explanations and Examples Grade 6
Arizona Department of Education: Standards and Assessment Division 6 Approved 6.28.10
Updated 5.20.11
Arizona Mathematics Standards Articulated by Grade Level
Ratios and Proportional Relationships (RP)
Understand ratio concepts and use ratio reasoning to solve problems.
Standards Mathematical Practices Explanations and Examples
Students are expected to:
A credit card company charges 17% interest on any charges not paid at
the end of the month. Make a ratio table to show how much the interest
would be for several amounts. If your bill totals $450 for this month, how
much interest would you have to pay if you let the balance carry to the
next month? Show the relationship on a graph and use the graph to
predict the interest charges for a $300 balance.
Charges $1 $50 $100 $200 $450
Interest $0.17 $8.50 $17 $34 ?
Explanations and Examples Grade 6
Arizona Department of Education: Standards and Assessment Division 7 Approved 6.28.10
Updated 5.20.11
You might also like
- Robert Potter - Tony Binns - Jennifer A. Elliott - Etienne Nel - David W. Smith - Geographies of Development - An Introduction To Development Studies-Routledge (2018)Document662 pagesRobert Potter - Tony Binns - Jennifer A. Elliott - Etienne Nel - David W. Smith - Geographies of Development - An Introduction To Development Studies-Routledge (2018)Andreas100% (1)
- MathDocument184 pagesMathZachary SchusterNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Learner's Activity Sheet Assessment ChecklistDocument16 pagesMathematics: Learner's Activity Sheet Assessment ChecklistDo HaNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Mathematics SyllabusDocument2 pages7th Grade Mathematics SyllabusDAizy AnnNo ratings yet
- WEEK 9.2. Lesson Plan Solution Graphing Linear InequalitiesDocument6 pagesWEEK 9.2. Lesson Plan Solution Graphing Linear InequalitiesEdelyn PaulinioNo ratings yet
- Sweet Algebra TaskDocument10 pagesSweet Algebra Taskapi-302577842No ratings yet
- BU1 Technical ManualDocument16 pagesBU1 Technical ManualkevinjonescomNo ratings yet
- M6u7 ArizonaexDocument8 pagesM6u7 Arizonaexapi-302577842No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Sorico Math Unit 1 1 2013-2014Document3 pagesGrade 8 Sorico Math Unit 1 1 2013-2014api-233707670100% (1)
- Articulated by Grade LevelDocument45 pagesArticulated by Grade LevelForrest FlenerNo ratings yet
- 6th UnpackingDocument33 pages6th UnpackingJESUS ANTONIO RAMOS MORONNo ratings yet
- Solving Equations With One Variable: Grade 8 Mathematics, Quarter, Unit 1.3Document5 pagesSolving Equations With One Variable: Grade 8 Mathematics, Quarter, Unit 1.3api-270891801No ratings yet
- Grade 6 Sorico Math Unit 3 1 2013-2014Document5 pagesGrade 6 Sorico Math Unit 3 1 2013-2014api-233707670No ratings yet
- Grade 6 Sorico Math Unit 2 3 2013-2014Document4 pagesGrade 6 Sorico Math Unit 2 3 2013-2014api-233707670No ratings yet
- Mathematics - Grade 6: X Y) To Describe Relationships BetweenDocument7 pagesMathematics - Grade 6: X Y) To Describe Relationships Betweenapi-365969613No ratings yet
- Grade 4 Unit 6 Scope and SequenceDocument8 pagesGrade 4 Unit 6 Scope and SequencereemaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan MathDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Mathapi-610287873No ratings yet
- New Jersey Student Learning Standards Mathematics - Grade 6Document18 pagesNew Jersey Student Learning Standards Mathematics - Grade 6Terrence AkinolaNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1 Lesson 20 LessonDocument6 pagesAlgebra 1 Lesson 20 Lessonapi-379755793No ratings yet
- Final Project of Record AssessmentDocument29 pagesFinal Project of Record Assessmentapi-208358319No ratings yet
- Assessment Project of RecordDocument19 pagesAssessment Project of Recordapi-208358319No ratings yet
- Mathematics Framework For California Public Schools: Kindergarten Through Grade TwelveDocument45 pagesMathematics Framework For California Public Schools: Kindergarten Through Grade TwelveBin BinNo ratings yet
- Math 6 Framework Standards For 2016 17Document13 pagesMath 6 Framework Standards For 2016 17api-302577842No ratings yet
- Module 4 MathDocument7 pagesModule 4 Mathgracesilvaespiritu1202No ratings yet
- Ccgps Math 6 6thgrade Unit4seDocument28 pagesCcgps Math 6 6thgrade Unit4seapi-239312188No ratings yet
- CC2 CH 6 TVDocument122 pagesCC2 CH 6 TVngyncloud100% (2)
- Week 2 Day 3Document6 pagesWeek 2 Day 3AJ ManialungNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Flip BookDocument100 pages7th Grade Flip BookChris DelawareNo ratings yet
- I-Day 32Document4 pagesI-Day 32Rainman InsanityNo ratings yet
- Math Year PlanDocument3 pagesMath Year Planapi-262109071No ratings yet
- Grade 7 Sorico Math Unit 3 3 2013-2014Document4 pagesGrade 7 Sorico Math Unit 3 3 2013-2014api-233707670No ratings yet
- Gse Math Unit 4Document79 pagesGse Math Unit 4api-256719324No ratings yet
- Test 1 PCK - EMTS71024 - MKT - 2023 - Memo - DiscussionDocument7 pagesTest 1 PCK - EMTS71024 - MKT - 2023 - Memo - DiscussionAbraham NghuleleNo ratings yet
- Math 6 Common Core Syllabus 2015-2016Document8 pagesMath 6 Common Core Syllabus 2015-2016api-262200380No ratings yet
- Grade 6 Sorico Math Unit 1 2 2013-2014Document5 pagesGrade 6 Sorico Math Unit 1 2 2013-2014api-233707670No ratings yet
- LP - MATH 9 Q1 m4Document6 pagesLP - MATH 9 Q1 m4Asmira CoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Day 3Document5 pagesWeek 2 Day 3Acire NonacNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Sorico Math Unit 2 1 2013-2014Document5 pagesGrade 8 Sorico Math Unit 2 1 2013-2014api-233707670No ratings yet
- Grade 2 Sorico Math Unit 1 1 2013-2014Document6 pagesGrade 2 Sorico Math Unit 1 1 2013-2014api-233707670No ratings yet
- Monday Prepared By: Samantha Krozek Grade: 5th Subject: Math Topic: Base Ten Division Common Core StandardDocument12 pagesMonday Prepared By: Samantha Krozek Grade: 5th Subject: Math Topic: Base Ten Division Common Core Standardapi-507217467No ratings yet
- 7 Grade Mathematics: What Is The Purpose of This Document?Document28 pages7 Grade Mathematics: What Is The Purpose of This Document?Johnny CoNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Mississippi College-And Career-Readiness Standards For Mathematics RCSD Quarter 1Document4 pagesGrade 7 Mississippi College-And Career-Readiness Standards For Mathematics RCSD Quarter 1Greg WalkerNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade UnpackedDocument45 pages7th Grade Unpackedapi-263084168No ratings yet
- FREEMATHCommonCoreStateStandards68Checklist 1 PDFDocument19 pagesFREEMATHCommonCoreStateStandards68Checklist 1 PDFKatt DuangmalaiNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Sorico Math Unit 1 1 2013-2014Document4 pagesGrade 3 Sorico Math Unit 1 1 2013-2014api-233707670100% (1)
- Exponential FunctionsDocument7 pagesExponential FunctionshneddoNo ratings yet
- I Can Standards 6ee5-9Document5 pagesI Can Standards 6ee5-9api-337275999No ratings yet
- Grade 7 Sorico Math Unit 2 1 2013-2014Document4 pagesGrade 7 Sorico Math Unit 2 1 2013-2014api-233707670100% (1)
- 6th Grade Common Core1Document2 pages6th Grade Common Core1api-292312023No ratings yet
- Alexa Iandolo - Ciee 3290 - Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesAlexa Iandolo - Ciee 3290 - Lesson Planapi-354589761No ratings yet
- Math Test 1 PDFDocument64 pagesMath Test 1 PDFAko Si JoannaNo ratings yet
- GR 8 Illustrated PracticesDocument3 pagesGR 8 Illustrated PracticesManas PatilNo ratings yet
- Grade-Six Chapter: Mathematics FrameworkDocument53 pagesGrade-Six Chapter: Mathematics Frameworkvenkatachalam.jNo ratings yet
- DLP 2023Document3 pagesDLP 2023Aiza MaltoNo ratings yet
- Whole Numbers Unit PlanDocument10 pagesWhole Numbers Unit Planapi-435456987No ratings yet
- A C O G 7: Ourse Utline FOR RadeDocument27 pagesA C O G 7: Ourse Utline FOR RadeKaela Sophia AndalisNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Sorico Math Unit 1 3 2013-2014Document4 pagesGrade 7 Sorico Math Unit 1 3 2013-2014api-233707670No ratings yet
- lp2 - Systems of Equations Their SolutionsDocument7 pageslp2 - Systems of Equations Their Solutionsapi-353551219No ratings yet
- Manhattan College Education Department Lesson Plan TemplateDocument9 pagesManhattan College Education Department Lesson Plan Templateapi-534924709No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 HandoutDocument5 pagesLecture 1 Handoutapi-450537250No ratings yet
- M6u7 ArizonaexDocument8 pagesM6u7 Arizonaexapi-302577842No ratings yet
- M6u4 Vocab CardsDocument12 pagesM6u4 Vocab Cardsapi-302577842No ratings yet
- Key Standards: Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Framework Student EditionDocument2 pagesKey Standards: Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Framework Student Editionapi-302577842No ratings yet
- Rational ExplorationsDocument2 pagesRational Explorationsapi-302577842No ratings yet
- M6u7 Outline Overview 2016Document20 pagesM6u7 Outline Overview 2016api-302577842No ratings yet
- 08 Math Homework-Taken From Students WorkbookDocument1 page08 Math Homework-Taken From Students Workbookapi-302577842No ratings yet
- M6u2 Conceptual Foundations 1Document5 pagesM6u2 Conceptual Foundations 1api-302577842No ratings yet
- M6u4 ConceptmapDocument1 pageM6u4 Conceptmapapi-302577842No ratings yet
- M6u1 Vocab CardsDocument24 pagesM6u1 Vocab Cardsapi-302577842No ratings yet
- Unit 9 Post Test ReviewDocument3 pagesUnit 9 Post Test Reviewapi-302577842No ratings yet
- Integer Addition Practice ADocument1 pageInteger Addition Practice Aapi-302577842No ratings yet
- Math Whiz Unit 3 MCDocument2 pagesMath Whiz Unit 3 MCapi-302577842No ratings yet
- CE441 Class Lecture 01Document9 pagesCE441 Class Lecture 01ASHJAEE MANSIB CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- Statistical Methods For Spatial Data AnalysisDocument3 pagesStatistical Methods For Spatial Data Analysissakali ali0% (1)
- Application of Irradiation For Food Preservation: Seminar ONDocument19 pagesApplication of Irradiation For Food Preservation: Seminar ONPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- Ag Test Package FormatDocument25 pagesAg Test Package FormatoparoystNo ratings yet
- Nepal National Building Code: Draft Final NBC 205: 2012Document52 pagesNepal National Building Code: Draft Final NBC 205: 2012Sudan ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Tacha's ReusmeDocument2 pagesTacha's ReusmeJames HamptonNo ratings yet
- The Dino GameDocument1 pageThe Dino Game296 004 Aditya ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Anullment CATHOLIC TRIBUNALDocument20 pagesAnullment CATHOLIC TRIBUNALMons Jr BaturianoNo ratings yet
- Jeanette Novakovich Formal ResumeDocument4 pagesJeanette Novakovich Formal ResumeJ'etté NovakovichNo ratings yet
- Bill of QuantityDocument6 pagesBill of QuantityKhairoden SangcopanNo ratings yet
- Earth Dams Foundation & Earth Material InvestigationDocument111 pagesEarth Dams Foundation & Earth Material Investigationmustafurade1No ratings yet
- List Product YellowDocument10 pagesList Product YellowfitriNo ratings yet
- Kansas Academy of Science: Info/about/policies/terms - JSPDocument6 pagesKansas Academy of Science: Info/about/policies/terms - JSPKeily VilcarromeroNo ratings yet
- Iso 7966 1993Document11 pagesIso 7966 1993Sci KelayNo ratings yet
- 42 Annual Conference of Linguistic Society of Nepal (42nd LSN)Document9 pages42 Annual Conference of Linguistic Society of Nepal (42nd LSN)Nani Babu GhimireNo ratings yet
- The Spirit of Jugaad / Bricolage For Enhanced Corporate EntrepreneurshipDocument20 pagesThe Spirit of Jugaad / Bricolage For Enhanced Corporate EntrepreneurshippanditpreachesNo ratings yet
- Is Codes ListDocument37 pagesIs Codes Listmoondonoo7No ratings yet
- Introduction To Management ScienceDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Management ScienceVenice Marie Arroyo100% (1)
- Product Description: Mark II Electric Fire Pump ControllersDocument2 pagesProduct Description: Mark II Electric Fire Pump ControllersBill Kerwin Nava JimenezNo ratings yet
- Model Course 1.07 PDFDocument75 pagesModel Course 1.07 PDFShiena CamineroNo ratings yet
- Allen Bradley 160 C SeriesDocument28 pagesAllen Bradley 160 C SeriesTihomir Matulić100% (1)
- Staff Data Format-AUCDocument1 pageStaff Data Format-AUCSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - PF and Parallel AC CircuitsDocument12 pagesLesson 4 - PF and Parallel AC CircuitsMichael SalvahanNo ratings yet
- Item Wise Rate TenderDocument5 pagesItem Wise Rate TenderB-05 ISHA PATELNo ratings yet
- Solution To Microwave Engineering Pozar Chapter 14 Exercise 17 With MATLABDocument3 pagesSolution To Microwave Engineering Pozar Chapter 14 Exercise 17 With MATLABJohn Bofarull GuixNo ratings yet
- D. Raghuram: Work ExperienceDocument3 pagesD. Raghuram: Work ExperienceNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Adam Izdebski & Michael Mulryan - Environment and Society in The Long LateDocument7 pagesAdam Izdebski & Michael Mulryan - Environment and Society in The Long Latecarlos murciaNo ratings yet
- Excavation TrainingDocument60 pagesExcavation TrainingFahad Abdul HaqNo ratings yet